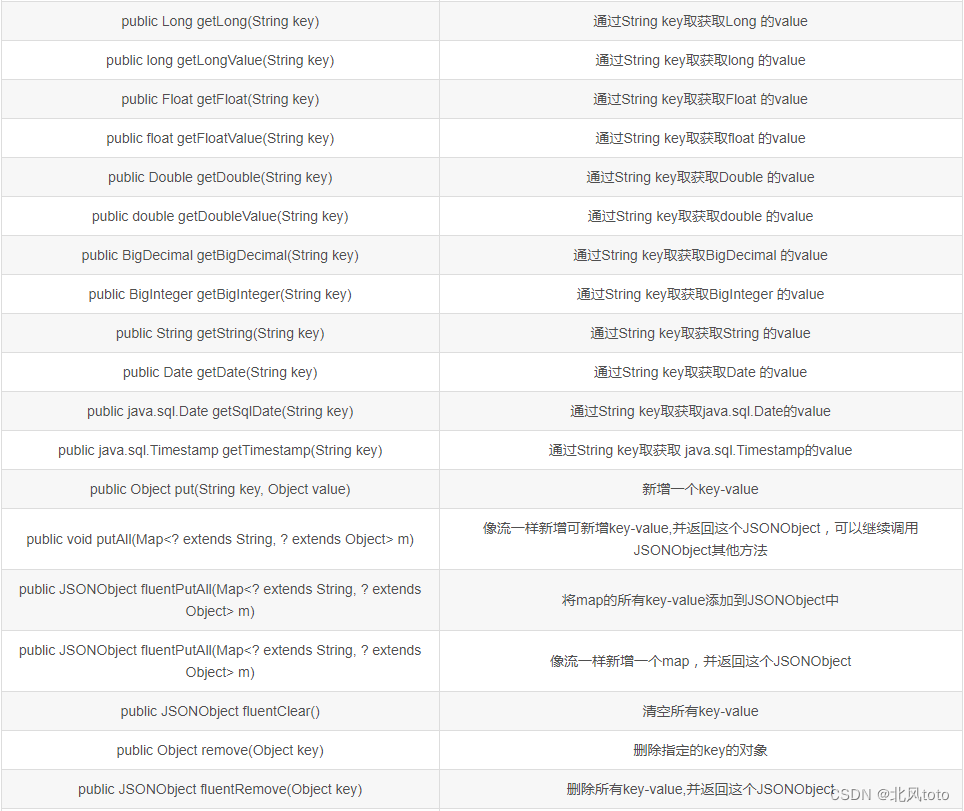
前言
上篇文章我们讲解了IOC比较重要的后置处理器注册方法,本篇文章讲解实例化前的准备工作,包括国际化、多播器创建、监听器注册等节点。
正文
进入refresh方法中,可以看到在正式实例化初始化方法前,还有4个方法:
1、initMessageSource();
这个方法主要作用就是使用国际化,定制不同的消息文本,比如定义了一个Person的Bean,它有name属性,我们需要在不同的国家展示对应国家所在语言名称,这时候就可以使用国际化了。
2、initApplicationEventMulticaster();
初始化应用事件广播器。这是观察者模式得典型应用。我们知道观察者模式由主题Subject和Observer组成。广播器相当于主题Subject,其包含多个监听器。当主题发生变化时会通知所有的监听器。
3、onRefresh();
onRefresh 是一个为使用者进行扩展的方法,如:springboot。
4、registerListeners();
将内部的、以及我们自定义的监听器添加到缓存中,以及添加事件源到缓存中,为后续逻辑处理做准备。
方法1:initMessageSource
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
//判断工厂中是否存在MessageSource类型的定义信息
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
//实例化
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// 设置父类消息解析对象
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
// 实例化一个空的DelegatingMessageSource 对象
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
//设置父类消息解析对象
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
//注册添加到一级缓存中
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
方法2:initApplicationEventMulticaster
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
//获取工厂对象
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
//判断工厂中是否有ApplicationEventMulticaster的定义信息
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
//实例化,为后续实例化环节做准备
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
//创建一个多播器
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
//添加到一级缓存中
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
方法3:onRefresh
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
}
该方法为拓展接口,供子类实现。
方法4:registerListeners
protected void registerListeners() {
// 将上下文中的监听器集合注册到多播器集合中
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
自定义监听器以及事件源:
事件源:
package service.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2611556444074013268L;
/**
* Create a new {@code ApplicationEvent}.
*
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred or with
* which the event is associated (never {@code null})
*/
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
监听器:
package service.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
public class MyListener1 implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
System.out.println("MyListener"+event.toString());
}
}
package service.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
public class MyListener2 implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
System.out.println("MyListener"+event.toString());
}
}
xml文件配置监听器:
<bean class="service.event.MyListener1" name="myListener1"></bean>
<bean class="service.event.MyListener2" name="myListener2"></bean>
入口编写:
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClassPathApplicationContext applicationContext=new MyClassPathApplicationContext("application-scan.xml");
applicationContext.publishEvent(new MyEvent("猪大肠事件"));
}
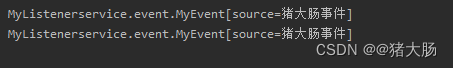
运行结果:
总结
这篇文章内容比较简单,主要是实例化前的准备工作。国际化定制消息类型,初始化多播器,注册监听器,提交发布早期事件。