一、Spring启示录
阅读以下代码:

dao
package org.example1.dao;
/**
* 持久层
* @className UserDao
* @since 1.0
**/
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 根据id删除用户信息
*/
void deleteById();
}package org.example1.dao.impl;
import org.example1.dao.UserDao;
/**
* @className UserDaoImplForMySQL
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserDaoImplForMySQL implements UserDao {
@Override
public void deleteById() {
System.out.println("MySQL数据库正在删除用户信息......");
}
}service
package org.example1.service;
/**
* 业务层
* @className UserService
* @since 1.0
**/
public interface UserService {
/**
* 删除用户信息
*/
void deleteUser();
}
package org.example1.service.impl;
import org.example1.dao.UserDao;
import org.example1.dao.impl.UserDaoImplForMySQL;
import org.example1.service.UserService;
/**
* @className UserServiceImpl
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImplForMySQL();
@Override
public void deleteUser() {
userDao.deleteById();
}
}
web
package org.example1.web;
import org.example1.service.UserService;
import org.example1.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
/**
* 表示层
* @className UserAction
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserAction {
private UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
/**
* 删除用户信息的请求
*/
public void deleteRequest(){
userService.deleteUser();
}
}
client-test
package org.example1.client;
import org.example1.web.UserAction;
/**
* @className Test
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserAction userAction = new UserAction();
userAction.deleteRequest();
}
}运行结果:

可以看出,UserDaoImplForMySQL中主要是连接MySQL数据库进行操作。如果更换到Oracle数据库上,则需要再提供一个UserDaoImplForOracle,如下:

package org.example1.dao.impl;
import org.example1.dao.UserDao;
/**
* @className UserDaoImplForOracle
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserDaoImplForOracle implements UserDao {
@Override
public void deleteById() {
System.out.println("Oracle数据库正在删除用户数据....");
}
}很明显,以上的操作正在进行功能的扩展,添加了一个新的类UserDaoImplForOracle来应付数据库的变化,这里的变化会引起连锁反应吗?当然会,如果想要切换到Oracle数据库上,UserServiceImpl类代码就需要修改,如下:

1.OCP开闭原则
这样一来就违背了开闭原则OCP。开闭原则是这样说的:在软件开发过程中应当对扩展开放,对修改关闭。
也就是说,如果在进行功能扩展的时候,添加额外的类是没问题的,但因为功能扩展而修改之前运行正常的程序,这是忌讳的,不被允许的。
因为一旦修改之前运行正常的程序,就会导致项目整体要进行全方位的重新测试。这是相当麻烦的过程。
导致以上问题的主要原因是:代码和代码之间的耦合度太高。如下图所示:

可以很明显的看出,上层是依赖下层的。UserController依赖UserServiceImpl,而UserServiceImpl依赖UserDaoImplForMySQL,这样就会导致下面只要改动,上面必然会受牵连(跟着也会改),所谓牵一发而动全身。这样也就同时违背了另一个开发原则:依赖倒置原则。
2.依赖倒置原则DIP
依赖倒置原则(Dependence Inversion Principle),简称DIP,主要倡导面向抽象编程,面向接口编程,不要面向具体编程,让上层不再依赖下层,下面改动了,上面的代码不会受到牵连。
这样可以大大降低程序的耦合度,耦合度低了,扩展力就强了,同时代码复用性也会增强。(软件七大开发原则都是在为解耦合服务) 你可能会说,上面的代码已经面向接口编程了呀:

确实已经面向接口编程了,但对象的创建是:new UserDaoImplForOracle()显然并没有完全面向接口编程,还是使用到了具体的接口实现类。什么叫做完全面向接口编程?什么叫做完全符合依赖倒置原则呢?请看以下代码:

如果代码是这样编写的,才算是完全面向接口编程,才符合依赖倒置原则。那你可能会问,这样userDao是null,在执行的时候就会出现空指针异常呀。你说的有道理,确实是这样的,所以我们要解决这个问题。解决空指针异常的问题,其实就是解决两个核心的问题:
-
第一个问题:谁来负责对象的创建。【也就是说谁来:new UserDaoImplForOracle()/new UserDaoImplForMySQL()】
-
第二个问题:谁来负责把创建的对象赋到这个属性上。【也就是说谁来把上面创建的对象赋给userDao属性】
如果我们把以上两个核心问题解决了,就可以做到既符合OCP开闭原则,又符合依赖倒置原则。 很荣幸的通知你:Spring框架可以做到。
在Spring框架中,它可以帮助我们new对象,并且它还可以将new出来的对象赋到属性上。换句话说,Spring框架可以帮助我们创建对象,并且可以帮助我们维护对象和对象之间的关系。比如:

Spring可以new出来UserDaoImplForMySQL对象,也可以new出来UserDaoImplForOracle对象,并且还可以让new出来的dao对象和service对象产生关系(产生关系其实本质上就是给属性赋值)。
很显然,这种方式是将对象的创建权/管理权交出去了,不再使用硬编码的方式了。同时也把对象关系的管理权交出去了,也不再使用硬编码的方式了。像这种把对象的创建权交出去,把对象关系的管理权交出去,被称为控制反转。
3.控制反转IoC
控制反转(Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC),是面向对象编程中的一种设计思想,可以用来降低代码之间的耦合度,符合依赖倒置原则。 控制反转的核心是:将对象的创建权交出去,将对象和对象之间关系的管理权交出去,由第三方容器来负责创建与维护。 控制反转常见的实现方式:依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI) 通常,依赖注入的实现又包括两种方式:
-
set方法注入
-
构造方法注入
而Spring框架就是一个实现了IoC思想的框架。 IoC可以认为是一种全新的设计模式,但是理论和时间成熟相对较晚,并没有包含在GoF中。(GoF指的是23种设计模式)
反转是什么呢?
反转的是两件事:
第一件事:我不在程序中采用硬编码的方式来new对象了。(new对象我不管了,new对象的权利交出去了。)
第二件事:我不在程序中采用硬编码的方式来维护对象的关系了。(对象之间关系的维护权,我也不管了,交出去了。)
控制反转:是一种编程思想。或者叫做一种新型的设计模式。由于出现的比较新,没有被纳入GoF23种设计模式范围内。
注意术语:
OCP:开闭原则(开发原则)
DIP:依赖倒置原则(开发原则)
IoC:控制反转(一种思想,一种新型的设计模式)
DI:依赖注入(控制反转思想的具体实现方式)
二、Spring概述
1.Spring简介

2.来自百度百科
Spring是一个开源框架,它由Rod Johnson创建。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。
从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。
Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
Spring最初的出现是为了解决EJB臃肿的设计,以及难以测试等问题。
Spring为简化开发而生,让程序员只需关注核心业务的实现,尽可能的不再关注非业务逻辑代码(事务控制,安全日志等)。
2.Spring8大模块
注意:Spring5版本之后是8个模块。在Spring5中新增了WebFlux模块。

⑴.Spring Core模块
这是Spring框架最基础的部分,它提供了依赖注入(DependencyInjection)特征来实现容器对Bean的管理。核心容器的主要组件是 BeanFactory,BeanFactory是工厂模式的一个实现,是任何Spring应用的核心。它使用IoC将应用配置和依赖从实际的应用代码中分离出来。
⑵.Spring Context模块
如果说核心模块中的BeanFactory使Spring成为容器的话,那么上下文模块就是Spring成为框架的原因。 这个模块扩展了BeanFactory,增加了对国际化(I18N)消息、事件传播、验证的支持。另外提供了许多企业服务,例如电子邮件、JNDI访问、EJB集成、远程以及时序调度(scheduling)服务。也包括了对模版框架例如Velocity和FreeMarker集成的支持
⑶.Spring AOP模块
Spring在它的AOP模块中提供了对面向切面编程的丰富支持,Spring AOP 模块为基于 Spring 的应用程序中的对象提供了事务管理服务。通过使用 Spring AOP,不用依赖组件,就可以将声明性事务管理集成到应用程序中,可以自定义拦截器、切点、日志等操作。
⑷.Spring DAO模块
提供了一个JDBC的抽象层和异常层次结构,消除了烦琐的JDBC编码和数据库厂商特有的错误代码解析,用于简化JDBC。
⑸.Spring ORM模块
Spring提供了ORM模块。Spring并不试图实现它自己的ORM解决方案,而是为几种流行的ORM框架提供了集成方案,包括Hibernate、JDO和iBATIS SQL映射,这些都遵从 Spring 的通用事务和 DAO 异常层次结构。
⑹.Spring Web MVC模块
Spring为构建Web应用提供了一个功能全面的MVC框架。虽然Spring可以很容易地与其它MVC框架集成,例如Struts,但Spring的MVC框架使用IoC对控制逻辑和业务对象提供了完全的分离。
⑺.Spring WebFlux模块
Spring Framework 中包含的原始 Web 框架 Spring Web MVC 是专门为 Servlet API 和 Servlet 容器构建的。反应式堆栈 Web 框架 Spring WebFlux 是在 5.0 版的后期添加的。它是完全非阻塞的,支持反应式流(Reactive Stream)背压,并在Netty,Undertow和Servlet 3.1+容器等服务器上运行。

⑻.Spring Web模块
Web 上下文模块建立在应用程序上下文模块之上,为基于 Web 的应用程序提供了上下文,提供了Spring和其它Web框架的集成,比如Struts、WebWork。还提供了一些面向服务支持,例如:实现文件上传的multipart请求。
3.Spring特点
⑴.轻量
从大小与开销两方面而言Spring都是轻量的。完整的Spring框架可以在一个大小只有1MB多的JAR文件里发布。并且Spring所需的处理开销也是微不足道的。
Spring是非侵入式(不依赖其他框架)的:Spring应用中的对象不依赖于Spring的特定类。
⑵.控制反转
Spring通过一种称作控制反转(IoC)的技术促进了松耦合。当应用了IoC,一个对象依赖的其它对象会通过被动的方式传递进来,而不是这个对象自己创建或者查找依赖对象。你可以认为IoC与JNDI相反——不是对象从容器中查找依赖,而是容器在对象初始化时不等对象请求就主动将依赖传递给它。
⑶.面向切面
Spring提供了面向切面编程的丰富支持,允许通过分离应用的业务逻辑与系统级服务(例如审计(auditing)和事务(transaction)管理)进行内聚性的开发。应用对象只实现它们应该做的——完成业务逻辑——仅此而已。它们并不负责(甚至是意识)其它的系统级关注点,例如日志或事务支持。
⑷.容器
Spring包含并管理应用对象的配置和生命周期,在这个意义上它是一种容器,你可以配置你的每个bean如何被创建——基于一个可配置原型(prototype),你的bean可以创建一个单独的实例或者每次需要时都生成一个新的实例——以及它们是如何相互关联的。然而,Spring不应该被混同于传统的重量级的EJB容器,它们经常是庞大与笨重的,难以使用。
⑸.框架
Spring可以将简单的组件配置、组合成为复杂的应用。在Spring中,应用对象被声明式地组合,典型地是在一个XML文件里。Spring也提供了很多基础功能(事务管理、持久化框架集成等等),将应用逻辑的开发留给了你。 所有Spring的这些特征使你能够编写更干净、更可管理、并且更易于测试的代码。它们也为Spring中的各种模块提供了基础支持。
4.本教程软件版本
-
IDEA工具:2022.1.4
-
JDK:Java17(Spring6要求JDK最低版本是Java17)
-
Maven:3.8.6
-
Spring:6.0.0-M2
-
JUnit:4.13.2
三、Spring的入门程序
1.Spring的下载
官网地址:Spring | Home

官网地址(中文):Spring 中文网 官网

打开Spring官网后,可以看到Spring Framework,以及通过Spring Framework衍生的其它框架:

我们即将要学习的就是Spring Framework。 怎么下载呢?
-
第一步:进入github

-
第二步:找到下图位置,点击超链接

-
第三步:找到下图位置,点击超链接

-
第四步:按照下图步骤操作

-
第五步:继续在springframework目录下找下图的spring,点开之后你会看到很多不同的版本

-
第六步:选择对应的版本

-
第七步:点击上图的url

点击spring-5.3.9-dist.zip下载spring框架。 将下载的zip包解压:

docs:spring框架的API帮助文档
libs:spring框架的jar文件(用spring框架就是用这些jar包)
schema:spring框架的XML配置文件相关的约束文件
2.Spring的jar文件
打开libs目录,会看到很多jar包:

spring-core-5.3.9.jar:字节码(这个是支撑程序运行的jar包) spring-core-5.3.9-javadoc.jar:代码中的注释 spring-core-5.3.9-sources.jar:源码 我们来看一下spring框架都有哪些jar包:

| JAR文件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| spring-aop-5.3.9.jar | 这个jar 文件包含在应用中使用Spring 的AOP 特性时所需的类 |
| spring-aspects-5.3.9.jar | 提供对AspectJ的支持,以便可以方便的将面向切面的功能集成进IDE中 |
| spring-beans-5.3.9.jar | 这个jar 文件是所有应用都要用到的,它包含访问配置文件、创建和管理bean 以及进行Inversion ofControl / Dependency Injection(IoC/DI)操作相关的所有类。如果应用只需基本的IoC/DI 支持,引入spring-core.jar 及spring-beans.jar 文件就可以了。 |
| spring-context-5.3.9.jar | 这个jar 文件为Spring 核心提供了大量扩展。可以找到使用Spring ApplicationContext特性时所需的全部类,JDNI 所需的全部类,instrumentation组件以及校验Validation 方面的相关类。 |
| spring-context-indexer-5.3.9.jar | 虽然类路径扫描非常快,但是Spring内部存在大量的类,添加此依赖,可以通过在编译时创建候选对象的静态列表来提高大型应用程序的启动性能。 |
| spring-context-support-5.3.9.jar | 用来提供Spring上下文的一些扩展模块,例如实现邮件服务、视图解析、缓存、定时任务调度等 |
| spring-core-5.3.9.jar | Spring 框架基本的核心工具类。Spring 其它组件要都要使用到这个包里的类,是其它组件的基本核心,当然你也可以在自己的应用系统中使用这些工具类。 |
| spring-expression-5.3.9.jar | Spring表达式语言。 |
| spring-instrument-5.3.9.jar | Spring3.0对服务器的代理接口。 |
| spring-jcl-5.3.9.jar | Spring的日志模块。JCL,全称为"Jakarta Commons Logging",也可称为"Apache Commons Logging"。 |
| spring-jdbc-5.3.9.jar | Spring对JDBC的支持。 |
| spring-jms-5.3.9.jar | 这个jar包提供了对JMS 1.0.2/1.1的支持类。JMS是Java消息服务。属于JavaEE规范之一。 |
| spring-messaging-5.3.9.jar | 为集成messaging api和消息协议提供支持 |
| spring-orm-5.3.9.jar | Spring集成ORM框架的支持,比如集成hibernate,mybatis等。 |
| spring-oxm-5.3.9.jar | 为主流O/X Mapping组件提供了统一层抽象和封装,OXM是Object Xml Mapping。对象和XML之间的相互转换。 |
| spring-r2dbc-5.3.9.jar | Reactive Relational Database Connectivity (关系型数据库的响应式连接) 的缩写。这个jar文件是Spring对r2dbc的支持。 |
| spring-test-5.3.9.jar | 对Junit等测试框架的简单封装。 |
| spring-tx-5.3.9.jar | 为JDBC、Hibernate、JDO、JPA、Beans等提供的一致的声明式和编程式事务管理支持。 |
| spring-web-5.3.9.jar | Spring集成MVC框架的支持,比如集成Struts等。 |
| spring-webflux-5.3.9.jar | WebFlux是 Spring5 添加的新模块,用于 web 的开发,功能和 SpringMVC 类似的,Webflux 使用当前一种比较流程响应式编程出现的框架。 |
| spring-webmvc-5.3.9.jar | SpringMVC框架的类库 |
| spring-websocket-5.3.9.jar | Spring集成WebSocket框架时使用 |
注意: 如果你只是想用Spring的IoC功能,仅需要引入:spring-context即可。将这个jar包添加到classpath当中。 如果采用maven只需要引入context的依赖即可。
<!--Spring6的正式版发布之前,这个仓库地址是需要的-->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>repository.spring.milestone</id>
<name>Spring Milestone Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖:使用的是6.0.0-M2里程碑版-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>3.第一个Spring程序
前期准备:
-
打开IDEA创建Empty Project:spring6
第一步:添加spring context的依赖,pom.xml配置如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example1</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-002-first</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>注意:打包方式jar。
当加入spring context的依赖之后,会关联引入其他依赖:
spring aop:面向切面编程
spring beans:IoC核心
spring core:spring的核心工具包
spring jcl:spring的日志包
spring expression:spring表达式

第二步:添加junit依赖
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>第三步:定义bean:User

第四步:编写spring的配置文件:beans.xml。该文件放在类的根路径下。
resources就是根路径

上图是使用IDEA工具自带的spring配置文件的模板进行创建。
配置文件中进行bean的配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--这就是Spring的配置文件-->
<!--IDEA工具为我们提供了这个文件的模板,一定要使用这个模板来创建。-->
<!--这个文件名不一定叫做spring.xml,可以是其它名字。-->
<!--这个文件最好是放在类路径当中,方便后期的移植。-->
<!--放在resources根目录下,就相当于是放到了类的根路径下。-->
<!--配置bean,这样spring才可以帮助我们管理这个对象。-->
<!--
bean标签的两个重要属性:
id:是这个bean的身份证号,不能重复,是唯一的标识。
class:必须填写类的全路径,全限定类名。(带包名的类名)
-->
<bean id="userBean" class="org.example1.bean.User"/>
</beans>bean的id和class属性:
-
id属性:代表对象的唯一标识。可以看做一个人的身份证号。
-
class属性:用来指定要创建的java对象的类名,这个类名必须是全限定类名(带包名)。
第五步:编写测试程序
@Test
public void testFistSpringCode(){
// 第一步:获取Spring容器对象。
// ApplicationContext 翻译为:应用上下文。其实就是Spring容器。
// ApplicationContext 是一个接口。
// ApplicationContext 接口下有很多实现类。其中有一个实现类叫做:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 专门从类路径当中加载spring配置文件的一个Spring上下文对象。
// 这行代码只要执行:就相当于启动了Spring容器,解析spring.xml文件,并且实例化所有的bean对象,放到spring容器当中。
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 第二步:根据bean的id从Spring容器中获取这个对象。
Object userBean = applicationContext.getBean("userBean");
System.out.println(userBean);
}第六步:运行测试程序

4.第一个Spring程序详细剖析

⑴.bean标签的id属性可以重复吗?


运行测试程序:

通过测试得出:在spring的配置文件中id是不能重名。
⑵. 底层是怎么创建对象的,是通过反射机制调用无参数构造方法吗?

在User类中添加无参数构造方法,如上。
运行测试程序:

通过测试得知:创建对象时确实调用了无参数构造方法。
如果提供一个有参数构造方法,不提供无参数构造方法会怎样呢?

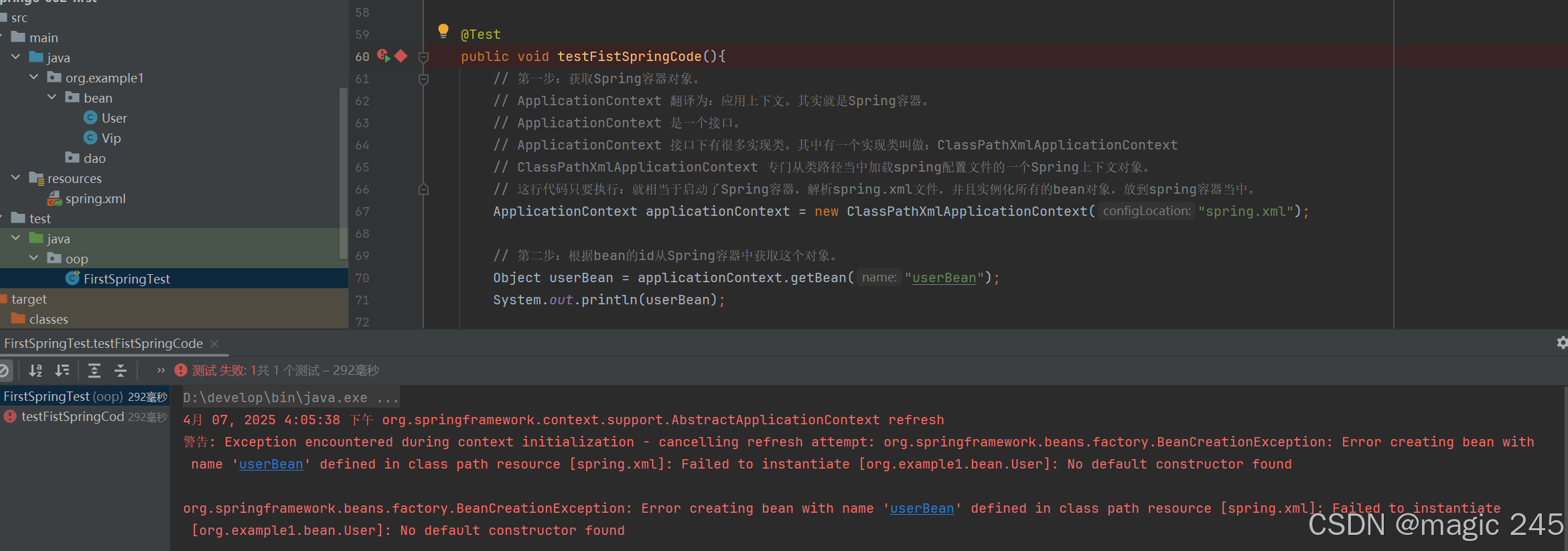
通过测试得知:spring是通过调用类的无参数构造方法来创建对象的,所以要想让spring给你创建对象,必须保证无参数构造方法是存在的。
Spring是如何创建对象的呢?原理是什么?
// dom4j解析beans.xml文件,从中获取class的全限定类名
// 通过反射机制调用无参数构造方法创建对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("org.example1.bean.User");
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();⑶把创建好的对象存储到一个什么样的数据结构当中了呢?

⑷.spring配置文件的名字必须叫做beans.xml吗?

起名随意
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");通过以上的java代码可以看出,这个spring配置文件名字是我们负责提供的,显然spring配置文件的名字是随意的。
⑸.像这样的beans.xml文件可以有多个吗?

再创建一个spring配置文件,起名:beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="vipBean" class="org.example1.bean.Vip"/>
</beans> @Test
public void testFistSpringCode(){
// 第一步:获取Spring容器对象。
// ApplicationContext 翻译为:应用上下文。其实就是Spring容器。
// ApplicationContext 是一个接口。
// ApplicationContext 接口下有很多实现类。其中有一个实现类叫做:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 专门从类路径当中加载spring配置文件的一个Spring上下文对象。
// 这行代码只要执行:就相当于启动了Spring容器,解析spring.xml文件,并且实例化所有的bean对象,放到spring容器当中。
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml","beans.xml");
// 第二步:根据bean的id从Spring容器中获取这个对象。
Object userBean = applicationContext.getBean("userBean");
System.out.println(userBean);
Object vipBean = applicationContext.getBean("vipBean");
System.out.println(vipBean);
}运行测试程序:

还可以专门创建一个文件夹



通过测试得知,spring的配置文件可以有多个,在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造方法的参数上传递文件路径即可。这是为什么呢?通过源码可以看到:

⑹.在配置文件中配置的类必须是自定义的吗,可以使用JDK中的类吗,例如:java.util.Date?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置java.util.Date Bean-->
<bean id="nowTime" class="java.util.Date"/>
</beans> @Test
public void testFistSpringCode(){
// 第一步:获取Spring容器对象。
// ApplicationContext 翻译为:应用上下文。其实就是Spring容器。
// ApplicationContext 是一个接口。
// ApplicationContext 接口下有很多实现类。其中有一个实现类叫做:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 专门从类路径当中加载spring配置文件的一个Spring上下文对象。
// 这行代码只要执行:就相当于启动了Spring容器,解析spring.xml文件,并且实例化所有的bean对象,放到spring容器当中。
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 第二步:根据bean的id从Spring容器中获取这个对象。
Object nowTime = applicationContext.getBean("nowTime");
System.out.println(nowTime);
}运行测试程序:

通过测试得知,在spring配置文件中配置的bean可以任意类,只要这个类不是抽象的,并且提供了无参数构造方法。
⑺.getBean()方法调用时,如果指定的id不存在会怎样?

运行测试程序:

通过测试得知,当id不存在的时候,会出现异常
⑻.getBean()方法返回的类型是Object,如果访问子类的特有属性和方法时,还需要向下转型,有其它办法可以解决这个问题吗?

⑼.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是从类路径中加载配置文件,如果没有在类路径当中,又应该如何加载配置文件呢?

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="vipBean2" class="org.example1.bean.Vip"/>
</beans>ApplicationContext applicationContext2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("d:/spring6.xml");
Vip vip = applicationContext2.getBean("vipBean2", Vip.class);
System.out.println(vip);没有在类路径中的话,需要使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类进行加载配置文件。
这种方式较少用。一般都是将配置文件放到类路径当中,这样可移植性更强。
⑽.ApplicationContext的超级父接口BeanFactory。
BeanFactory beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Object vipBean = beanFactory.getBean("vipBean");
System.out.println(vipBean);BeanFactory是Spring容器的超级接口。ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口。
//ApplicationContext接口的超级父接口是:BeanFactory(翻译为Bean工厂,就是能够生产Bean对象的一个工厂对象。) //BeanFactory是IoC容器的顶级接口。 //Spring的IoC容器底层实际上使用了:工厂模式。 //Spring底层的IoC是怎么实现的?XML解析 + 工厂模式 + 反射机制

注意:
@Test
public void testBeginInitBean(){
// 注意:不是在调用getBean()方法的时候创建对象,执行以下代码的时候,就会实例化对象。
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");}
容器一旦创建就会有对象
5.Spring6启用Log4j2日志框架
从Spring5之后,Spring框架支持集成的日志框架是Log4j2.如何启用日志框架:
第一步:引入Log4j2的依赖
<!--log4j2的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>第二步:在类的根路径下提供log4j2.xml配置文件(文件名固定为:log4j2.xml,文件必须放到类根路径下。)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<loggers>
<!--
level指定日志级别,从低到高的优先级:
ALL < TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL < OFF
-->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="spring6log"/>
</root>
</loggers>
<appenders>
<!--输出日志信息到控制台-->
<console name="spring6log" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<!--控制日志输出的格式-->
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS} [%t] %-3level %logger{1024} - %msg%n"/>
</console>
</appenders>
</configuration>第三步:使用日志框架
@Test
public void testBeginInitBean(){
// 注意:不是在调用getBean()方法的时候创建对象,执行以下代码的时候,就会实例化对象。
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 你自己怎么去使用log4j2记录日志信息呢?
// 第一步:创建日志记录器对象
// 获取FirstSpringTest类的日志记录器对象,也就是说只要是FirstSpringTest类中的代码执行记录日志的话,就输出相关的日志信息。
Logger logger = (Logger) LoggerFactory.getLogger(FirstSpringTest.class);
// 第二步:记录日志,根据不同的级别来输出日志
logger.info("我是一条消息");
logger.debug("我是一条调试信息");
logger.error("我是一条错误信息");
}
四、Spring对IoC的实现
1.IoC 控制反转
-
控制反转是一种思想。
-
控制反转是为了降低程序耦合度,提高程序扩展力,达到OCP原则,达到DIP原则。
-
控制反转,反转的是什么?
-
将对象的创建权利交出去,交给第三方容器负责。
-
将对象和对象之间关系的维护权交出去,交给第三方容器负责。
-
-
控制反转这种思想如何实现呢?
-
DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入
-
2.依赖注入
依赖注入实现了控制反转的思想。 Spring通过依赖注入的方式来完成Bean管理的。 Bean管理说的是:Bean对象的创建,以及Bean对象中属性的赋值(或者叫做Bean对象之间关系的维护)。 依赖注入:
-
依赖指的是对象和对象之间的关联关系。
-
注入指的是一种数据传递行为,通过注入行为来让对象和对象产生关系。
依赖注入常见的实现方式包括两种:
-
第一种:set注入
-
第二种:构造注入
新建模块:spring6-002-dependency-injection
⑴.set注入
set注入,基于set方法实现的,底层会通过反射机制调用属性对应的set方法然后给属性赋值。这种方式要求属性必须对外提供set方法。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example1</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-002-first</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--log4j2的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
dao
package org.example1.dao;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class UserDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserDao.class);
public void insert(){
//System.out.println("数据库正在保存用户信息。");
// 使用一下log4j2日志框架
logger.info("数据库正在保存用户信息。");
}
}service
package org.example1.service;
import org.example1.dao.UserDao;
/**
* Bean
* @className UserService
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
/* // 这个set方法是IDEA工具生成的,符合javabean规范。
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}*/
public void saveUser(){
// 保存用户信息到数据库
userDao.insert();
}
}
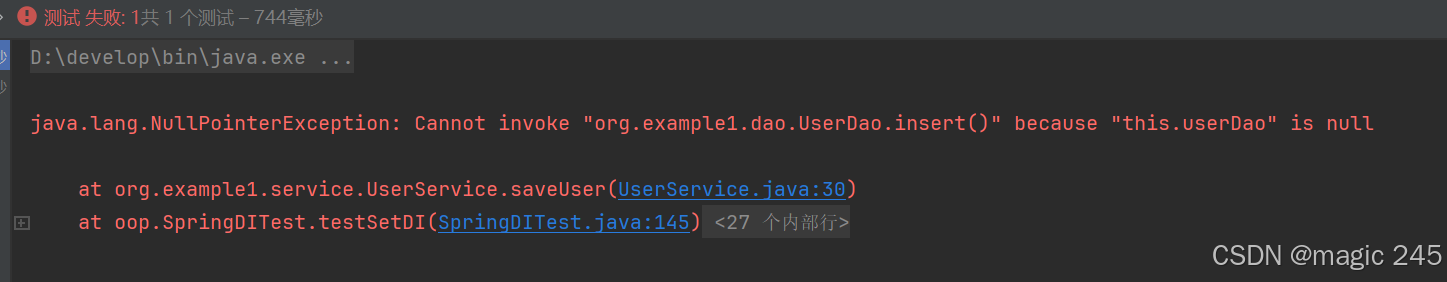
@Test
public void testSetDI(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceBean", UserService.class);
userService.saveUser();
}
加入set方法

依旧报错:
<!-- 想让Spring调用对应的set方法,需要配置property标签 --> <!-- name属性怎么指定值:set方法的方法名,去掉set,然后把剩下的单词首字母变小写,写到这里。--> <!-- ref翻译为引用。英语单词:references。ref后面指定的是要注入的bean的id。-->


实现原理: 通过property标签获取到属性名:userDao
通过属性名推断出set方法名:setUserDao
通过反射机制调用setUserDao()方法给属性赋值
property标签的name是属性名。
property标签的ref是要注入的bean对象的id。(通过ref属性来完成bean的装配,这是bean最简单的一种装配方式。装配指的是:创建系统组件之间关联的动作)
另外,对于property标签来说,ref属性也可以采用标签的方式,但使用ref属性是多数的:
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao">
<ref bean="userDaoBean"/>
</property>
</bean>总结:set注入的核心实现原理:通过反射机制调用set方法来给属性赋值,让两个对象之间产生关系。
⑵.构造注入
核心原理:通过调用构造方法来给属性赋值。
①使用参数
dao
public class UserDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserDao.class);
public void insert(){
//System.out.println("数据库正在保存用户信息。");
// 使用一下log4j2日志框架
logger.info("数据库正在保存用户信息。");
}
}public class VipDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(VipDao.class);
public void insert(){
logger.info("正在保存Vip信息!!!!");
}
}service
public class CustomerService {
private UserDao userDao;
private VipDao vipDao;
public CustomerService(UserDao userDao, VipDao vipDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
this.vipDao = vipDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
vipDao.insert();
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="org.example1.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="vipDaoBean" class="org.example1.dao.VipDao"/>
<bean id="csBean" class="org.example1.service.CustomerService">
<!--构造注入-->
<!--
index属性指定参数下标,第一个参数是0,第二个参数是1,第三个参数是2,以此类推。
ref属性用来指定注入的bean的id
-->
<!--指定构造方法的第一个参数,下标是0-->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="userDaoBean"/>
<!--指定构造方法的第二个参数,下标是1-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="vipDaoBean"/>
</bean>
</beans>执行测试程序:

②不使用参数下标,使用参数的名字
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="org.example1.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="vipDaoBean" class="org.example1.dao.VipDao"/>
<bean id="csBean2" class="org.example1.service.CustomerService">
<constructor-arg name="vipDao" ref="userDaoBean"/>
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="vipDaoBean"/>
</bean>
<bean id="csBean" class="org.example1.service.CustomerService">
<!--构造注入-->
<!--
index属性指定参数下标,第一个参数是0,第二个参数是1,第三个参数是2,以此类推。
ref属性用来指定注入的bean的id
-->
<!--指定构造方法的第一个参数,下标是0-->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="userDaoBean"/>
<!--指定构造方法的第二个参数,下标是1-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="vipDaoBean"/>
</bean>
</beans> @Test
public void testConstructorDI(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
CustomerService customerService = applicationContext.getBean("csBean", CustomerService.class);
customerService.save();
CustomerService csBean2 = applicationContext.getBean("csBean2", CustomerService.class);
csBean2.save();
}
③还可以不指定参数下标,不指定参数名字
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="yyyy" class="org.example1.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="xxxx" class="org.example1.dao.VipDao"/>
<bean id="csBean3" class="org.example1.service.CustomerService">
<!--不指定下标,也不指定参数名,让spring自己做类型匹配吧。-->
<!--这种方式实际上是根据类型进行注入的。spring会自动根据类型来判断把ref注入给哪个参数。-->
<constructor-arg ref="yyyy"/>
<constructor-arg ref="xxxx"/>
</bean>
<bean id="csBean2" class="org.example1.service.CustomerService">
<constructor-arg name="vipDao" ref="yyyy"/>
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="xxxx"/>
</bean>
<bean id="csBean" class="org.example1.service.CustomerService">
<!--构造注入-->
<!--
index属性指定参数下标,第一个参数是0,第二个参数是1,第三个参数是2,以此类推。
ref属性用来指定注入的bean的id
-->
<!--指定构造方法的第一个参数,下标是0-->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="yyyy"/>
<!--指定构造方法的第二个参数,下标是1-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="xxxx"/>
</bean>
</beans> @Test
public void testConstructorDI(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
CustomerService customerService = applicationContext.getBean("csBean", CustomerService.class);
customerService.save();
CustomerService csBean2 = applicationContext.getBean("csBean2", CustomerService.class);
csBean2.save();
CustomerService csBean3 = applicationContext.getBean("csBean3", CustomerService.class);
csBean3.save();
}
3.set注入专题
⑴.注入外部Bean
在之前四、2.⑴中使用的案例就是注入外部Bean的方式。
dao
/**
* @className OrderDao
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderDao.class);
public void insert(){
logger.info("订单正在生成....");
}
}service
public class OrderService {
private OrderDao orderDao;
// 通过set方法给属性赋值。
public void setOrderDao(OrderDao orderDao) {
this.orderDao = orderDao;
}
/**
* 生成订单的业务方法。。。
*/
public void generate(){
orderDao.insert();
}
}
@Test
public void testSetDI2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderServiceBean", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
外部Bean的特点:bean定义到外面,在property标签中使用ref属性进行注入。通常这种方式是常用。
⑵.注入内部Bean
内部Bean的方式:在bean标签中嵌套bean标签。

@Test
public void testSetDI2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
OrderService orderService2 = applicationContext.getBean("orderServiceBean2", OrderService.class);
orderService2.generate();
}⑶.注入简单类型
我们之前在进行注入的时候,对象的属性是另一个对象。
public class UserService{
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao){
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}那如果对象的属性是int类型呢?
public class User{
private int age;
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
}可以通过set注入的方式给该属性赋值吗?
-
当然可以。因为只要能够调用set方法就可以给属性赋值。
编写程序给一个User对象的属性赋值
第一步:定义User类
package org.example1.bean;
/**
* @className User
* @since 1.0
**/
public class User {
private String username; // String是简单类型
private String password;
private int age; // int是简单类型
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
第二步:编写spring配置文件

第三步:编写测试程序
@Test
public void testSimpleTypeSet(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
User user = applicationContext.getBean("userBean", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
需要特别注意:如果给简单类型赋值,使用value属性或value标签。而不是ref。 简单类型包括哪些呢?可以通过Spring的源码来分析一下:BeanUtils类
public class BeanUtils{
//.......
/**
* Check if the given type represents a "simple" property: a simple value
* type or an array of simple value types.
* <p>See {@link #isSimpleValueType(Class)} for the definition of <em>simple
* value type</em>.
* <p>Used to determine properties to check for a "simple" dependency-check.
* @param type the type to check
* @return whether the given type represents a "simple" property
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#checkDependencies
* @see #isSimpleValueType(Class)
*/
public static boolean isSimpleProperty(Class<?> type) {
Assert.notNull(type, "'type' must not be null");
return isSimpleValueType(type) || (type.isArray() && isSimpleValueType(type.getComponentType()));
}
/**
* Check if the given type represents a "simple" value type: a primitive or
* primitive wrapper, an enum, a String or other CharSequence, a Number, a
* Date, a Temporal, a URI, a URL, a Locale, or a Class.
* <p>{@code Void} and {@code void} are not considered simple value types.
* @param type the type to check
* @return whether the given type represents a "simple" value type
* @see #isSimpleProperty(Class)
*/
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type ||
Class.class == type));
}
//........
}通过源码分析得知,简单类型包括:
-
基本数据类型
-
基本数据类型对应的包装类
-
String或其他的CharSequence子类
-
Number子类
-
Date子类
-
Enum子类
-
URI
-
URL
-
Temporal子类
-
Locale
-
Class
-
另外还包括以上简单值类型对应的数组类型。
经典案例:给数据源的属性注入值: 假设我们现在要自己手写一个数据源,我们都知道所有的数据源都要实现javax.sql.DataSource接口,并且数据源中应该有连接数据库的信息,例如:driver、url、username、password等。
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @className MyDataSource
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
我们给driver、url、username、password四个属性分别提供了setter方法,我们可以使用spring的依赖注入完成数据源对象的创建和属性的赋值吗?看配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
</beans>测试程序:
@Test
public void testDataSource(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-datasource.xml");
MyDataSource dataSource = applicationContext.getBean("dataSource", MyDataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource);
}执行测试程序:

你学会了吗?
接下来,我们编写一个程序,把所有的简单类型全部测试一遍:
编写一个类A:
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URL;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
* @className A
* @since 1.0
**/
public class A {
private byte b;
private short s;
private int i;
private long l;
private float f;
private double d;
private boolean flag;
private char c;
private Byte b1;
private Short s1;
private Integer i1;
private Long l1;
private Float f1;
private Double d1;
private Boolean flag1;
private Character c1;
private String str;
private Date date;
private Season season;
private URI uri;
private URL url;
private LocalDate localDate;
private Locale locale;
private Class clazz;
// 生成setter方法
// 生成toString方法
}
enum Season {
SPRING, SUMMER, AUTUMN, WINTER
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="a" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.A">
<property name="b" value="1"/>
<property name="s" value="1"/>
<property name="i" value="1"/>
<property name="l" value="1"/>
<property name="f" value="1"/>
<property name="d" value="1"/>
<property name="flag" value="false"/>
<property name="c" value="a"/>
<property name="b1" value="2"/>
<property name="s1" value="2"/>
<property name="i1" value="2"/>
<property name="l1" value="2"/>
<property name="f1" value="2"/>
<property name="d1" value="2"/>
<property name="flag1" value="true"/>
<property name="c1" value="a"/>
<property name="str" value="zhangsan"/>
<!--注意:value后面的日期字符串格式不能随便写,必须是Date对象toString()方法执行的结果。-->
<!--如果想使用其他格式的日期字符串,就需要进行特殊处理了。具体怎么处理,可以看后面的课程!!!!-->
<property name="date" value="Fri Sep 30 15:26:38 CST 2022"/>
<property name="season" value="WINTER"/>
<property name="uri" value="/save.do"/>
<!--spring6之后,会自动检查url是否有效,如果无效会报错。-->
<property name="url" value="http://www.baidu.com"/>
<property name="localDate" value="EPOCH"/>
<!--java.util.Locale 主要在软件的本地化时使用。它本身没有什么功能,更多的是作为一个参数辅助其他方法完成输出的本地化。-->
<property name="locale" value="CHINESE"/>
<property name="clazz" value="java.lang.String"/>
</bean>
</beans>编写测试程序:
@Test
public void testAllSimpleType(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-all-simple-type.xml");
A a = applicationContext.getBean("a", A.class);
System.out.println(a);
}执行结果如下:

需要注意的是:
-
如果把Date当做简单类型的话,日期字符串格式不能随便写。格式必须符合Date的toString()方法格式。显然这就比较鸡肋了。如果我们提供一个这样的日期字符串:2010-10-11,在这里是无法赋值给Date类型的属性的。
-
spring6之后,当注入的是URL,那么这个url字符串是会进行有效性检测的。如果是一个存在的url,那就没问题。如果不存在则报错。
⑷级联属性赋值(了解)
package org.example1.bean;
/**
* 表示班级
* @className Clazz
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Clazz {
// 班级名称
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Clazz{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}package org.example1.bean;
/**
* 表示学生
* @className Student
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Student {
private String name;
// 学生属于哪个班级
private Clazz clazz;
public void setClazz(Clazz clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
// 使用级联属性赋值,这个需要这个get方法。
public Clazz getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", clazz=" + clazz +
'}';
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--使用级联属性赋值需要注意两点:
1. 配置的顺序不能颠倒,必须如下顺序。
2. clazz属性必须提供getter方法。
-->
<bean id="studentBean" class="org.example1.bean.Student">
<!--简单类型,使用value-->
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<!--这不是简单类型,使用ref-->
<property name="clazz" ref="clazzBean"/>
<!--级联属性赋值-->
<property name="clazz.name" value="高三二班"/>
</bean>
<bean id="clazzBean" class="org.example1.bean.Clazz"></bean>
</beans> @Test
public void testCascade(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cascade.xml");
Student studentBean = applicationContext.getBean("studentBean", Student.class);
System.out.println(studentBean);
Clazz clazzBean = applicationContext.getBean("clazzBean", Clazz.class);
System.out.println(clazzBean);
}
要点:
-
在spring配置文件中,如上,注意顺序。
-
在spring配置文件中,clazz属性必须提供getter方法。
⑸注入数组
当数组中的元素是简单类型:aiHaos
当数组中的元素是非简单类型:womens
package org.example1.bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @className QianDaYe
* @since 1.0
**/
public class QianDaYe {
private String[] aiHaos;
// 多个女性朋友
private Woman[] womens;
public void setWomens(Woman[] womens) {
this.womens = womens;
}
public void setAiHaos(String[] aiHaos) {
this.aiHaos = aiHaos;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "QianDaYe{" +
"aiHaos=" + Arrays.toString(aiHaos) +
", womens=" + Arrays.toString(womens) +
'}';
}
}package org.example1.bean;
/**
* @className Woman
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Woman {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Woman{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
test
@Test
public void testArray(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-array.xml");
QianDaYe yuQian = applicationContext.getBean("yuQian", QianDaYe.class);
System.out.println(yuQian);
}
⑹注入List集合、注入Set集合、注入Map集合、注入Properties
java.util.Properties继承java.util.Hashtable,所以Properties也是一个Map集合。
Set集合:无序不可重复
List集合:有序可重复
注意:注入List集合的时候使用list标签,如果List集合中是简单类型使用value标签,反之使用ref标签。
要点:
使用<set>标签
set集合中元素是简单类型的使用value标签,反之使用ref标签。
要点:
使用<map>标签
如果key是简单类型,使用 key 属性,反之使用 key-ref 属性。
如果value是简单类型,使用 value 属性,反之使用 value-ref 属性。
要点:
使用<props>标签嵌套<prop>标签完成。
package org.example1.bean;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @className Person
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Person {
// 注入List集合
private List<String> names;
// 注入Set集合
private Set<String> addrs;
// 注入Map集合
// 多个电话
private Map<Integer, String> phones;
// 注入属性类对象
// Properties本质上也是一个Map集合。
// Properties的父类Hashtable,Hashtable实现了Map接口。
// 虽然这个也是一个Map集合,但是和Map的注入方式有点像,但是不同。
// Properties的key和value只能是String类型。
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public void setPhones(Map<Integer, String> phones) {
this.phones = phones;
}
public void setNames(List<String> names) {
this.names = names;
}
public void setAddrs(Set<String> addrs) {
this.addrs = addrs;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"names=" + names +
", addrs=" + addrs +
", phones=" + phones +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="personBean" class="org.example1.bean.Person">
<property name="properties">
<!--注入Properties属性类对象-->
<props>
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="phones">
<!--注入Map集合-->
<map>
<!--如果key和value不是简单类型就用这个配置。-->
<!--<entry key-ref="" value-ref=""/>-->
<!--如果是简单类型就是key和value-->
<entry key="1" value="110"/>
<entry key="2" value="120"/>
<entry key="3" value="119"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="names">
<!--list集合有序可重复-->
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="addrs">
<!--set集合无序不可重复-->
<set>
<value>北京大兴区</value>
<value>北京大兴区</value>
<value>北京海淀区</value>
<value>北京海淀区</value>
<value>北京大兴区</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>test
@Test
public void testCollection(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-collection.xml");
Person personBean = applicationContext.getBean("personBean", Person.class);
System.out.println(personBean);
}
⑺注入null和空字符串
注入空字符串使用:<value/> 或者 value="" 注入null使用:<null/> 或者 不为该属性赋值
-
我们先来看一下,怎么注入空字符串。
package org.example1.bean;
/**
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Cat {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="org.example1.bean.Cat">
<!--不给属性注入,属性的默认值就是null-->
<!--<property name="name" value="tom"></property>-->
<!-- 这不是注入null,这只是注入了一个"null"字符串-->
<property name="name" value="null"/>
<!--这种方式是手动注入null-->
<!--<property name="name">
<null/>
</property>-->
<!--注入空字符串第一种方式-->
<!--<property name="name" value=""/>-->
<!--注入空字符串第二种方式-->
<!-- <property name="name">
<value/>
</property>-->
<property name="age" value="3"></property>
</bean>
</beans>test
@Test
public void testNull(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
Cat catBean = applicationContext.getBean("catBean", Cat.class);
System.out.println(catBean.getName().toUpperCase());
}


⑻注入的值中含有特殊符号
XML中有5个特殊字符,分别是:<、>、'、"、&
以上5个特殊符号在XML中会被特殊对待,会被当做XML语法的一部分进行解析,如果这些特殊符号直接出现在注入的字符串当中,会报错。

解决方案包括两种:
-
第一种:特殊符号使用转义字符代替。
-
第二种:将含有特殊符号的字符串放到:<![CDATA[]]> 当中。因为放在CDATA区中的数据不会被XML文件解析器解析。
5个特殊字符对应的转义字符分别是:
| 特殊字符 | 转义字符 |
|---|---|
< | < |
> | > |
& | & |
' | ' |
" | " |
先使用转义字符来代替:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="mathBean" class="org.example1.bean.MathBean">
<!--第一种方案:使用实体符号代替特殊符号-->
<property name="result" value="2 < 3" />
<!--第二种方案:使用<![CDATA[]]>-->
<!-- <property name="result">
<!–只能使用value标签–>
<value><![CDATA[2 < 3]]></value>
</property>-->
</bean>
</beans>test
@Test
public void testSpecial(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
MathBean mathBean = applicationContext.getBean("mathBean", MathBean.class);
System.out.println(mathBean);
}
我们再来使用CDATA方式:


4.p命名空间注入
目的:简化配置。 使用p命名空间注入的前提条件包括两个:
-
第一:在XML头部信息中添加p命名空间的配置信息:
-
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
-
第二:p命名空间注入是基于setter方法的,所以需要对应的属性提供setter方法。
p命名空间注入底层还是set注入,只不过p命名空间注入可以让spring配置变的更加简单。
package org.example1.bean;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @className Dog
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Dog {
// 简单类型
private String name;
private int age;
// 非简单类型
private Date birth;
// p命名空间注入底层还是set注入,只不过p命名空间注入可以让spring配置变的更加简单。
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birth=" + birth +
'}';
}
}

test
@Test
public void testP(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-p.xml");
Dog dogBean = applicationContext.getBean("dogBean", Dog.class);
System.out.println(dogBean);
}
把setter方法去掉:

所以p命名空间实际上是对set注入的简化。
5.c命名空间注入
c命名空间是简化构造方法注入的。
使用c命名空间的两个前提条件:
第一:需要在xml配置文件头部添加信息:xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
第二:需要提供构造方法。
// c命名空间是简化构造注入的。 // c命名空间注入办法是基于构造方法的。

package org.example1.bean;
/**
* @className People
* @since 1.0
**/
public class People {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean sex;
// c命名空间是简化构造注入的。
// c命名空间注入办法是基于构造方法的。
public People(String name, int age, boolean sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
'}';
}
}
test
@Test
public void testC(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-c.xml");
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}


注意:不管是p命名空间还是c命名空间,注入的时候都可以注入简单类型以及非简单类型。
6.util命名空间
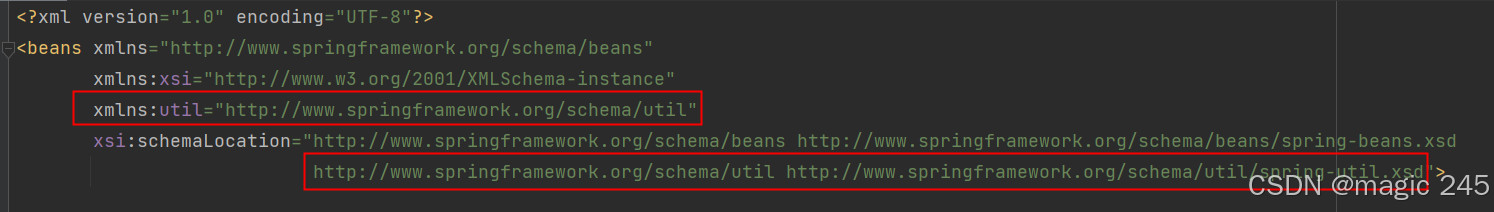
使用util命名空间可以让配置复用。 使用util命名空间的前提是:在spring配置文件头部添加配置信息。
如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!--引入util命名空间
在spring的配置文件头部添加:
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
-->
<util:properties id="prop">
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123</prop>
</util:properties>
<!--数据源1-->
<bean id="ds1" class="org.example1.jdbc.MyDataSource1">
<property name="properties" ref="prop"/>
</bean>
<!--数据源2-->
<bean id="ds2" class="org.example1.jdbc.MyDataSource2">
<property name="properties" ref="prop"/>
</bean>
</beans>
package org.example1.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @className MyDataSource1
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource1 implements DataSource {
// 连接数据库的信息
/*private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;*/
// Properties属性类对象,这是一个Map集合,key和value都是String类型。
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource1{" +
"properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
package org.example1.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @className MyDataSource2
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource2 implements DataSource {
// Properties属性类对象,这是一个Map集合,key和value都是String类型。
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource1{" +
"properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
test
@Test
public void testUtil(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-util.xml");
MyDataSource1 ds1 = applicationContext.getBean("ds1", MyDataSource1.class);
MyDataSource2 ds2 = applicationContext.getBean("ds2", MyDataSource2.class);
System.out.println(ds1);
System.out.println(ds2);
}
7.基于XML的自动装配
Spring还可以完成自动化的注入,自动化注入又被称为自动装配。它可以根据名字进行自动装配,也可以根据类型进行自动装配。
⑴根据名称自动装配
public class OrderDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderDao.class);
public void insert(){
logger.info("订单正在生成....");
}
}
public class OrderService {
private OrderDao orderDao;
// 通过set方法给属性赋值。
public void setOrderDao(OrderDao orderDao) {
this.orderDao = orderDao;
}
/**
* 生成订单的业务方法。。。
*/
public void generate(){
orderDao.insert();
}
}Spring的配置文件这样配置:
<!--根据名字进行自动装配-->
<!--注意:自动装配也是基于set方式实现的。-->
<bean id="orderService" class="org.example1.service.OrderService" autowire="byName"></bean>
<!--id一般也叫作bean的名称。-->
<!--根据名字进行自动装配的时候,被注入的对象的bean的id不能随便写,怎么写?set方法的方法名去掉set,剩下单词首字母小写。-->
<bean id="orderDao" class="org.example1.dao.OrderDao"/>test
@Test
public void testAutowire(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-autowire.xml");
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
⑵根据类型自动装配
/**
* @className AccountDao
* @since 1.0
**/
public class AccountDao {
public void insert(){
System.out.println("正在保存账户信息");
}
}
/**
* @className AccountService
* @since 1.0
**/
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void save(){
accountDao.insert();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--byType表示根据类型自动装配-->
<bean id="accountService" class="org.example1.service.AccountService" autowire="byType"/>
<bean class="org.example1.dao.AccountDao"/>
</beans>@Test
public void testAutowireByType(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-autowire.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
accountService.save();
}执行结果:

我们把UserService中的set方法注释掉,再执行:

可以看到无论是byName还是byType,在装配的时候都是基于set方法的。所以set方法是必须要提供的。提供构造方法是不行的,大家可以测试一下。这里就不再赘述。
如果byType,根据类型装配时,如果配置文件中有两个类型一样的bean会出现什么问题呢?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.AccountService" autowire="byType"/>
<bean id="x" class="org.example1.dao.AccountDao"/>
<bean id="y" class="org.example1.dao.AccountDao"/>
</beans>执行测试程序:

测试结果说明了,当byType进行自动装配的时候,配置文件中某种类型的Bean必须是唯一的,不能出现多个。
8.Spring引入外部属性配置文件
我们都知道编写数据源的时候是需要连接数据库的信息的,例如:driver url username password等信息。这些信息可以单独写到一个属性配置文件中吗,这样用户修改起来会更加的方便。当然可以。
第一步:写一个数据源类,提供相关属性。
package org.example1.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* 所有的数据源都要实现java规范:javax.sql.DataSource
* 什么是数据源:能够给你提供Connection对象的,都是数据源。
*
* @className MyDataSource
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource { // 可以把数据源交给Spring容器来管理。
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 获取数据库连接对象的时候需要4个信息:driver url username password
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
第二步:在类路径下新建jdbc.properties文件,并配置信息。
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=abc123第三步:在spring配置文件中引入context命名空间。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>
第四步:在spring中配置使用jdbc.properties文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 加载类路径下的 jdbc.properties -->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置 DataSource Bean -->
<bean id="ds" class="org.example1.jdbc.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
</beans>测试程序:
@Test
public void testProperties(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-properties.xml");
MyDataSource ds = applicationContext.getBean("ds", MyDataSource.class);
System.out.println(ds);
}



















