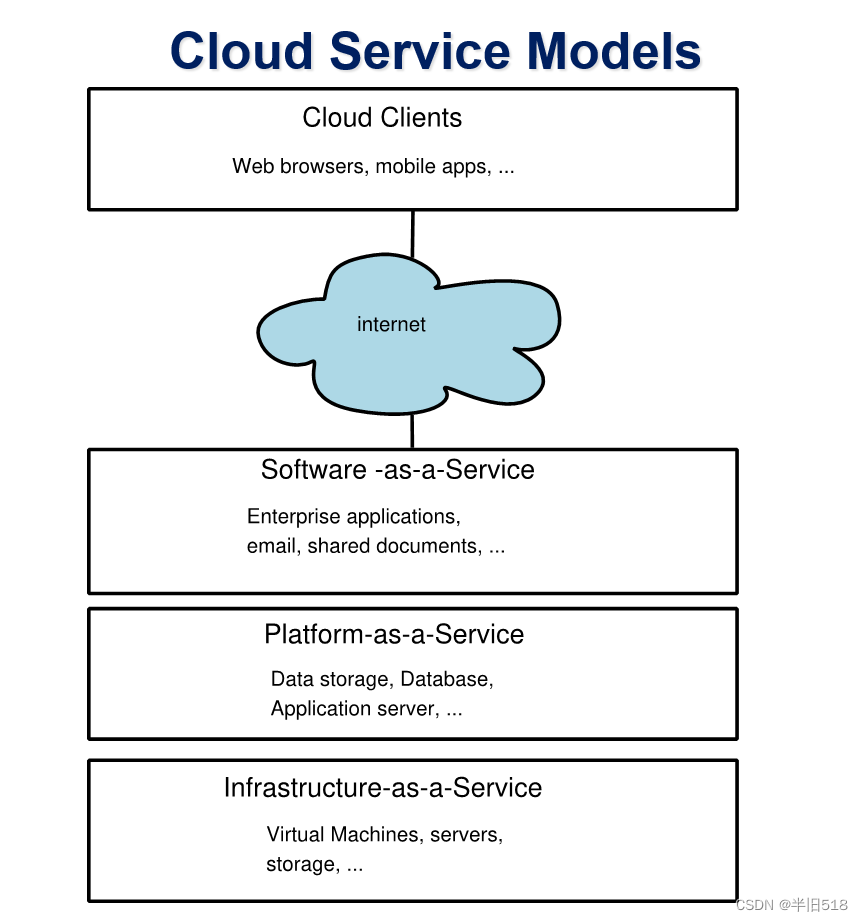
昨晚的problem e 一直wa。因为答案,不唯一,调起来只能肉眼debug。被干emo了qwq。好在赛后看到 ugly2333的 思路和我差不多,最后还是要选取度数较小的最优,
好像从度数的角度出发,不容易wa。
题意:
给你一个图,用矩阵表示。
问是否可以翻转一些行的状态,使得图连通。
思路:
- 我们先利用并查集,求出所有连通块
- 发现所有连通块之间都没有边。
case 1
连通块数为1,直接输出0即可(因为已经连通
case 2
假如有一个连通块不是完全图,那么我们可以对这个连通块中的一个点操作,之后就可以使得连通。
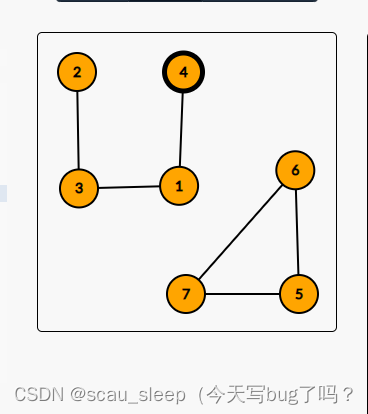
图1
我们发现有一些性质,
- 原本 { 5 , 6 , 7 } \{5,6,7\} {5,6,7}是一个3完全图,只要对节点4操作,那么就可以和这个连通块 { 5 , 6 , 7 } \{5,6,7\} {5,6,7}连通
- 因为原图 ( 4 , 3 ) , ( 4 , 2 ) (4,3),(4,2) (4,3),(4,2)没有边,所以我们断开 ( 4 , 1 ) (4,1) (4,1),不会影响 { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } \{1,2,3,4\} {1,2,3,4}的连通性
我们对第一个连通块的4号节点操作,那么图变为

图2
是不是对
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
}
\{1,2,3,4\}
{1,2,3,4}中的任何一个点操作都可以?
不是!!!!!对于图1中的1号节点操作
那么图变为
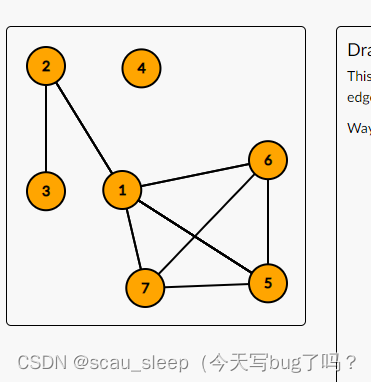
发现图1中度数最小的4号节点变的不连通!!!!!!
结论:如果存在不是完全图,的连通块,那么我们选择度数最小的点
case3
所有连通块都是完全图,
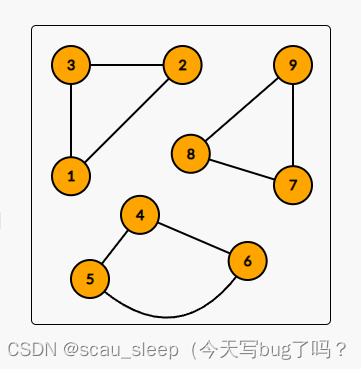
假如只有两个连通块。
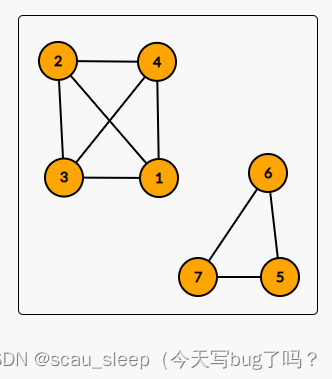
图4
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
}
\{1,2,3,4\}
{1,2,3,4} 和
{
5
,
6
,
7
}
\{5,6,7\}
{5,6,7}怎么连通?
对于节点4操作,告诉了我们一个性质:
- 4会和 { 5 , 6 , 7 } \{5,6,7\} {5,6,7}构成一个 4完全图
- 4会和 { 1 , 3 , 2 } \{1,3,2\} {1,3,2}失去连通性,
- 那么问题就转换为了新的
{
1
,
2
,
3
}
\{1,2,3\}
{1,2,3} 和
{
5
,
6
,
7
,
4
}
\{5,6,7,4\}
{5,6,7,4}怎么连通。
结论:如果存在两个完全图,的连通块,那么我们贪心选择点数最少的连通块
case4
所有连通块都是完全图,
假如有超过两个连通块。
我们还是对4号节点操作
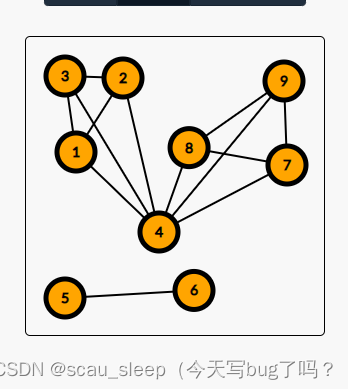
这里和case3的时候有点不同。
- { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } \{1,2,3,4\} {1,2,3,4}是4完全图, { 4 , 7 , 8 , 9 } \{4,7,8,9\} {4,7,8,9}是4完全图
- { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 7 , 8 , 9 } \{1,2,3,4,7,8,9\} {1,2,3,4,7,8,9}不是7完全图
- 这个问题就变成了case2
总结:
- case1 连通块数为1,直接输出0
- case2 所有连通块中,有不是完全图的,那么我们操作连通块中最小度数的节点输出。
- case3 所有连通块都是完全图,且只有两个连通块,我们操作较小的那个连通块内的所有节点。
- case4 所有连通块都是完全图,且有2个以上的连通块,我们先操作任意一个连通块的一个点,转换为case2
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#define For(i,x,y) for(int i = (x); i <= (y); i ++ )
#define fori(i,x,y) for(int i = (x); i < (y); i ++ )
#define sz(a) (int)a.size()
#define ALL(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define mst(x,a) memset(x,a,sizeof(x))
#define pb push_back
#define eb emplace_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define debug(a) cout << #a << ": " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pa;
typedef pair<ll,ll>pai;
typedef pair<db,db> pdd;
const db eps = 1e-6;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
template<typename T1, typename T2> void ckmin(T1 &a, T2 b) { if (a > b) a = b; }
template<typename T1, typename T2> void ckmax(T1 &a, T2 b) { if (a < b) a = b; }
int read() {
int x = 0, f = 0; char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) f |= ch == '-', ch = getchar();
while (isdigit(ch)) x = 10 * x + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return f ? -x : x;
}
template<typename T> void print(T x) {
if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;
if (x >= 10) print(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
template<typename T> void print(T x, char let) {
print(x), putchar(let);
}
template<class T> bool uin(T &a, T b) { return a > b ? (a = b, true) : false; }
template<class T> bool uax(T &a, T b) { return a < b ? (a = b, true) : false; }
const int maxn = 4000 + 5;
int g[maxn][maxn];
int p[maxn];
int find(int x){
if(x == p[x]) return x;
return p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
int n;
void merge(int a, int b){
int fa = find(a), fb = find(b);
if(fa == fb) return ;
p[fa] = fb;
}
vector<int> color[maxn];
void init(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
string s; cin>>s;
s = " " + s;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) {
if(s[j] == '1'){
g[i][j] = 1;
int a = i, b = j;
merge(a,b);
}else g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) color[i].clear();
}
void sol(){
init();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) color[find(i)].pb(i);
//check all graph
vector<pair<int,int>> allG;
int ansp = -1;
for(int col = 1; col <= n; col ++ ) {
if(col != find(col)) continue;
//col == find(col)
auto& v = color[col];
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i ++ ) {
for(int j = 0; j < v.size(); j ++ ) {
if(i == j) continue;
cnt += (g[v[i]][v[j]]);
if(g[v[i]][v[j]] == 0) ansp = v[i];
}
}
int tot = v.size();
//connect
if(tot == n){
cout << 0 << endl;
return ;
}
// if(cnt == tot*(tot-1)/2)
if(cnt == tot*(tot-1)){
allG.pb({tot,col});
// debug(tot);
// debug(col);
}
}
int ans;
if(ansp == -1){
//mi > 2
//all is graph
sort(ALL(allG));
int col = allG.front().second;
auto& v = color[col];
if(allG.size() == 2 || v.size() == 1){
ans = allG.front().first;
cout << ans << endl;
int begin = 0;
for(int x: v) {
if(begin) cout << ' ';
cout << x;
begin = 1;
}
cout << endl;
}else {
cout << 2 << endl;
cout << v.front() << ' ' << color[allG[1].second].front()<<endl;
}
}else {
//wa on this
/* cout << 1 << endl;
cout <<ansp<<endl; */
cout << 1 << endl;
//init
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) {
if(i == ansp || j == ansp) continue;
if(g[i][j])p[find(i)] = find(j);
}
//reverse
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) if(g[ansp][j] == 0) p[find(ansp)] = find(j);
int occ = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) occ += (find(i) == i);
if(occ == 1){
cout <<ansp<<endl;
return ;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) if(find(i) != find(ansp)){
ansp = i;
break;
}
cout << ansp<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int tt; cin>>tt;
while(tt--)
sol();
return 0;
}