Caffeine+Redis两级缓存架构
在高性能的服务项目中,我们一般会将一些热点数据存储到 Redis这类缓存中间件中,只有当缓存的访问没有命中时再查询数据库。在提升访问速度的同时,也能降低数据库的压力。
但是在一些场景下单纯使用 Redis 的分布式缓存不能满足高性能的要求,所以还需要加入使用本地缓存Caffeine,从而再次提升程序的响应速度与服务性能。于是,就产生了使用本地缓存(Caffeine)作为一级缓存,再加上分布式缓存(Redis)作为二级缓存的两级缓存架构。
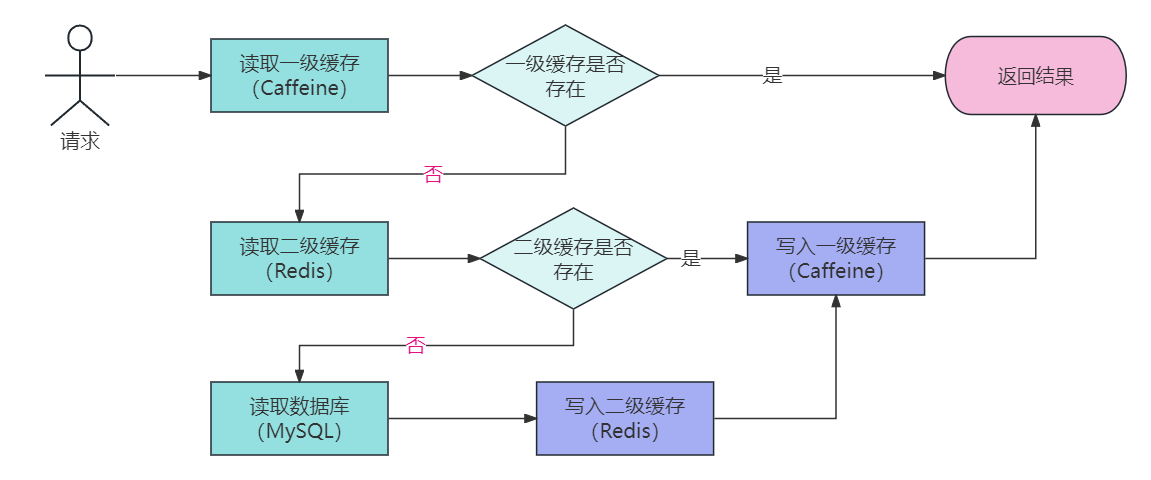
两级缓存架构优缺点
优点:
- 一级缓存基于应用的内存,访问速度非常快,对于一些变更频率低、实时性要求低的数据,可以放在本地缓存中,提升访问速度;
- 使用一级缓存能够减少和 Redis 的二级缓存的远程数据交互,减少网络 I/O 开销,降低这一过程中在网络通信上的耗时。
缺点:
- 数据一致性问题:两级缓存与数据库的数据要保持一致,一旦数据发生了修改,在修改数据库的同时,一级缓存、二级缓存应该同步更新。
- 分布式多应用情况下:一级缓存之间也会存在一致性问题,当一个节点下的本地缓存修改后,需要通知其他节点也刷新本地一级缓存中的数据,否则会出现读取到过期数据的情况。
- 缓存的过期时间、过期策略以及多线程的问题
Caffeine+Redis两级缓存架构实战
1、准备表结构和数据
准备如下的表结构和相关数据
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
插入对应的相关数据
DELETE FROM user;
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
2、创建项目
创建一个SpringBoot项目,然后引入相关的依赖,首先是父依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
具体的其他的依赖
<!-- spring-boot-starter-web 的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入MyBatisPlus的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库使用MySQL数据库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库连接池 Druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.14</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
3、配置信息
然后我们需要在application.properties中配置数据源的相关信息
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
然后我们需要在SpringBoot项目的启动类上配置Mapper接口的扫描路径

4、添加User实体
添加user的实体类
@ToString
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
5、创建Mapper接口
在MyBatisPlus中的Mapper接口需要继承BaseMapper.
/**
* MyBatisPlus中的Mapper接口继承自BaseMapper
*/
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
6、测试操作
然后来完成对User表中数据的查询操作
@SpringBootTest
class MpDemo01ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void queryUser() {
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
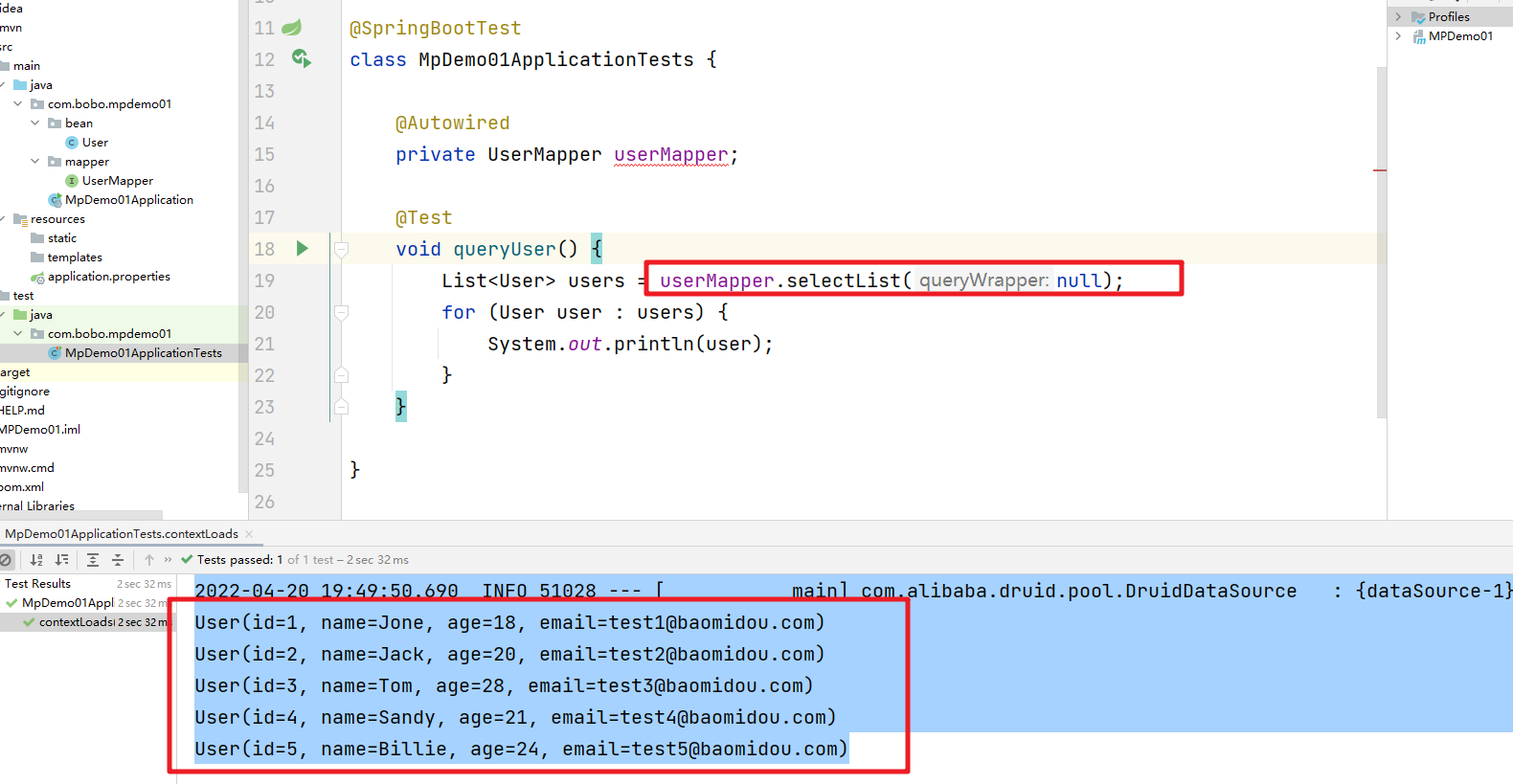
7、日志输出
为了便于学习我们可以指定日志的实现StdOutImpl来处理
# 指定日志输出
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl

然后操作数据库的时候就可以看到对应的日志信息了:
手动两级缓存架构实战
@Configuration
public class CaffeineConfig {
@Bean
public Cache<String,Object> caffeineCache(){
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(128)//初始大小
.maximumSize(1024)//最大数量
.expireAfterWrite(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//过期时间 15S
.build();
}
}
//Caffeine+Redis两级缓存查询
public User query1_2(long userId){
String key = "user-"+userId;
User user = (User) cache.get(key,
k -> {
//先查询 Redis (2级缓存)
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (Objects.nonNull(obj)) {
log.info("get data from redis:"+key);
return obj;
}
// Redis没有则查询 DB(MySQL)
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(userId);
log.info("get data from database:"+userId);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, user2, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return user2;
});
return user;
}
在 Cache 的 get 方法中,会先从Caffeine缓存中进行查找,如果找到缓存的值那么直接返回。没有的话查找 Redis,Redis 再不命中则查询数据库,最后都同步到Caffeine的缓存中。
通过案例演示也可以达到对应的效果。
另外修改、删除的代码可以看代码案例!
注解方式两级缓存架构实战
在 spring中,提供了 CacheManager 接口和对应的注解
- @Cacheable:根据键从缓存中取值,如果缓存存在,那么获取缓存成功之后,直接返回这个缓存的结果。如果缓存不存在,那么执行方法,并将结果放入缓存中。
- @CachePut:不管之前的键对应的缓存是否存在,都执行方法,并将结果强制放入缓存。
- @CacheEvict:执行完方法后,会移除掉缓存中的数据。
使用注解,就需要配置 spring 中的 CacheManager ,在这个CaffeineConfig类中
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(){
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager=new CaffeineCacheManager();
cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(128)
.maximumSize(1024)
.expireAfterWrite(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
return cacheManager;
}
EnableCaching
在启动类上再添加上 @EnableCaching 注解
在UserService类对应的方法上添加 @Cacheable 注解
//Caffeine+Redis两级缓存查询-- 使用注解
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#userId")
public User query2_2(long userId){
String key = "user-"+userId;
//先查询 Redis (2级缓存)
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (Objects.nonNull(obj)) {
log.info("get data from redis:"+key);
return (User)obj;
}
// Redis没有则查询 DB(MySQL)
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId);
log.info("get data from database:"+userId);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, user, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return user;
}
然后就可以达到类似的效果。
@Cacheable 注解的属性:
| 参数 | 解释 | col3 |
|---|---|---|
| key | 缓存的key,可以为空,如果指定要按照SpEL表达式编写,如不指定,则按照方法所有参数组合 | @Cacheable(value=”testcache”, key=”#userName”) |
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如:@Cacheable(value=”mycache”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | @Cacheable(value=”testcache”, condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
| methodName | 当前方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | 当前方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | 当前被调用的对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | 当前被调用的对象的class | #root.targetClass |
| args | 当前方法参数组成的数组 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | 当前被调用的方法使用的Cache | #root.caches[0].name |
这里有一个condition属性指定发生的条件
示例表示只有当userId为偶数时才会进行缓存
//只有当userId为偶数时才会进行缓存
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#userId", condition="#userId%2==0")
public User query2_3(long userId){
String key = "user-"+userId;
//先查询 Redis (2级缓存)
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (Objects.nonNull(obj)) {
log.info("get data from redis:"+key);
return (User)obj;
}
// Redis没有则查询 DB(MySQL)
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId);
log.info("get data from database:"+userId);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, user, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return user;
}
CacheEvict
@CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。
当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作。
@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。即value表示清除操作是发生在哪些Cache上的(对应Cache的名称);key表示需要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会使用默认策略生成的key;condition表示清除操作发生的条件。下面我们来介绍一下新出现的两个属性allEntries和beforeInvocation。
//清除缓存(所有的元素)
@CacheEvict(value="user", key = "#userId",allEntries=true)
public void deleteAll(long userId) {
System.out.println(userId);
}
//beforeInvocation=true:在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素
@CacheEvict(value="user", key = "#userId",beforeInvocation=true)
public void delete(long userId) {
System.out.println(userId);
}
自定义注解实现两级缓存架构实战
首先定义一个注解,用于添加在需要操作缓存的方法上:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DoubleCache {
String cacheName();
String key(); //支持springEl表达式
long l2TimeOut() default 120;
CacheType type() default CacheType.FULL;
}
l2TimeOut 为可以设置的二级缓存 Redis 的过期时间
CacheType 是一个枚举类型的变量,表示操作缓存的类型
public enum CacheType {
FULL, //存取
PUT, //只存
DELETE //删除
}
从前面我们知道,key要支持 springEl 表达式,写一个ElParser的方法,使用表达式解析器解析参数:
public class ElParser {
public static String parse(String elString, TreeMap<String,Object> map){
elString=String.format("#{%s}",elString);
//创建表达式解析器
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
//通过evaluationContext.setVariable可以在上下文中设定变量。
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
map.entrySet().forEach(entry->
context.setVariable(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue())
);
//解析表达式
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(elString, new TemplateParserContext());
//使用Expression.getValue()获取表达式的值,这里传入了Evaluation上下文
String value = expression.getValue(context, String.class);
return value;
}
}
package com.msb.caffeine.cache;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CacheAspect {
private final Cache cache;
private final RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.msb.caffeine.cache.DoubleCache)")
public void cacheAspect() {
}
@Around("cacheAspect()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//拼接解析springEl表达式的map
String[] paramNames = signature.getParameterNames();
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
TreeMap<String, Object> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) {
treeMap.put(paramNames[i],args[i]);
}
DoubleCache annotation = method.getAnnotation(DoubleCache.class);
String elResult = ElParser.parse(annotation.key(), treeMap);
String realKey = annotation.cacheName() + ":" + elResult;
//强制更新
if (annotation.type()== CacheType.PUT){
Object object = point.proceed();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(realKey, object,annotation.l2TimeOut(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
cache.put(realKey, object);
return object;
}
//删除
else if (annotation.type()== CacheType.DELETE){
redisTemplate.delete(realKey);
cache.invalidate(realKey);
return point.proceed();
}
//读写,查询Caffeine
Object caffeineCache = cache.getIfPresent(realKey);
if (Objects.nonNull(caffeineCache)) {
log.info("get data from caffeine");
return caffeineCache;
}
//查询Redis
Object redisCache = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(realKey);
if (Objects.nonNull(redisCache)) {
log.info("get data from redis");
cache.put(realKey, redisCache);
return redisCache;
}
log.info("get data from database");
Object object = point.proceed();
if (Objects.nonNull(object)){
//写入Redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(realKey, object,annotation.l2TimeOut(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//写入Caffeine
cache.put(realKey, object);
}
return object;
}
}
切面中主要做了下面几件工作:
- 通过方法的参数,解析注解中 key 的 springEl 表达式,组装真正缓存的 key。
- 根据操作缓存的类型,分别处理存取、只存、删除缓存操作。
- 删除和强制更新缓存的操作,都需要执行原方法,并进行相应的缓存删除或更新操作。
- 存取操作前,先检查缓存中是否有数据,如果有则直接返回,没有则执行原方法,并将结果存入缓存。
然后使用的话就非常方便了,代码中只保留原有业务代码,再添加上我们自定义的注解就可以了:
@DoubleCache(cacheName = "user", key = "#userId",
type = CacheType.FULL)
public User query3(Long userId) {
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId);
return user;
}
@DoubleCache(cacheName = "user",key = "#user.userId",
type = CacheType.PUT)
public int update3(User user) {
return userMapper.updateById(user);
}
@DoubleCache(cacheName = "user",key = "#user.userId",
type = CacheType.DELETE)
public void deleteOrder(User user) {
userMapper.deleteById(user);
}
两级缓存架构的缓存一致性问题
就是如果一个应用修改了缓存,另外一个应用的caffeine缓存是没有办法感知的,所以这里就会有缓存的一致性问题

解决方案也很简单,就是在Redis中做一个发布和订阅。
遇到修改缓存的处理,需要向对应的频道发布一条消息,然后应用同步监听这条消息,有消息则需要删除本地的Caffeine缓存。
核心代码如下: