一:下载libusb文件
下载最新的库的下载网站:https://libusb.info/
下载:


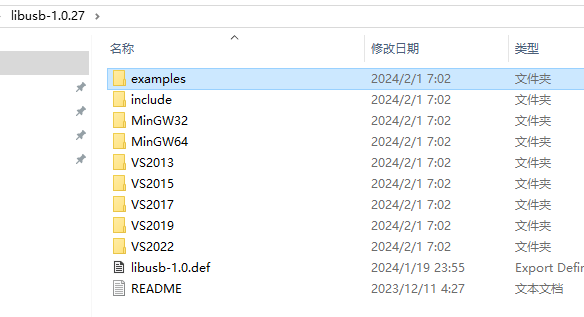
解压后目录如下:
二:库文件添加QT中
根据自己的编译器选择库:
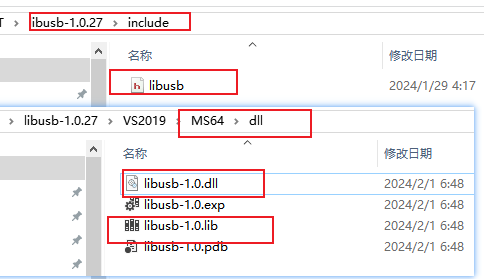
①将头文件中添加libusb.h
②源文件中添加libusb-1.0.lib

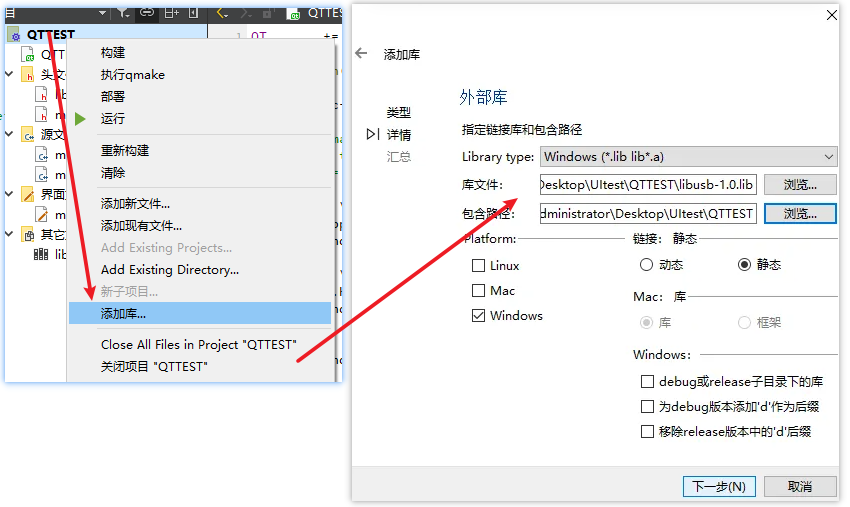
③添加库文件:
三:编译工程
添加库后直接编译,不报错即为成功:
四:example
参考例程中的调用方法:
/*
* Test suite program based of libusb-0.1-compat testlibusb
* Copyright (c) 2013 Nathan Hjelm <hjelmn@mac.ccom>
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "libusb.h"
int verbose = 0;
static void print_endpoint_comp(const struct libusb_ss_endpoint_companion_descriptor *ep_comp)
{
printf(" USB 3.0 Endpoint Companion:\n");
printf(" bMaxBurst: %u\n", ep_comp->bMaxBurst);
printf(" bmAttributes: %02xh\n", ep_comp->bmAttributes);
printf(" wBytesPerInterval: %u\n", ep_comp->wBytesPerInterval);
}
static void print_endpoint(const struct libusb_endpoint_descriptor *endpoint)
{
int i, ret;
printf(" Endpoint:\n");
printf(" bEndpointAddress: %02xh\n", endpoint->bEndpointAddress);
printf(" bmAttributes: %02xh\n", endpoint->bmAttributes);
printf(" wMaxPacketSize: %u\n", endpoint->wMaxPacketSize);
printf(" bInterval: %u\n", endpoint->bInterval);
printf(" bRefresh: %u\n", endpoint->bRefresh);
printf(" bSynchAddress: %u\n", endpoint->bSynchAddress);
for (i = 0; i < endpoint->extra_length;) {
if (LIBUSB_DT_SS_ENDPOINT_COMPANION == endpoint->extra[i + 1]) {
struct libusb_ss_endpoint_companion_descriptor *ep_comp;
ret = libusb_get_ss_endpoint_companion_descriptor(NULL, endpoint, &ep_comp);
if (LIBUSB_SUCCESS != ret)
continue;
print_endpoint_comp(ep_comp);
libusb_free_ss_endpoint_companion_descriptor(ep_comp);
}
i += endpoint->extra[i];
}
}
static void print_altsetting(const struct libusb_interface_descriptor *interface)
{
uint8_t i;
printf(" Interface:\n");
printf(" bInterfaceNumber: %u\n", interface->bInterfaceNumber);
printf(" bAlternateSetting: %u\n", interface->bAlternateSetting);
printf(" bNumEndpoints: %u\n", interface->bNumEndpoints);
printf(" bInterfaceClass: %u\n", interface->bInterfaceClass);
printf(" bInterfaceSubClass: %u\n", interface->bInterfaceSubClass);
printf(" bInterfaceProtocol: %u\n", interface->bInterfaceProtocol);
printf(" iInterface: %u\n", interface->iInterface);
for (i = 0; i < interface->bNumEndpoints; i++)
print_endpoint(&interface->endpoint[i]);
}
static void print_2_0_ext_cap(struct libusb_usb_2_0_extension_descriptor *usb_2_0_ext_cap)
{
printf(" USB 2.0 Extension Capabilities:\n");
printf(" bDevCapabilityType: %u\n", usb_2_0_ext_cap->bDevCapabilityType);
printf(" bmAttributes: %08xh\n", usb_2_0_ext_cap->bmAttributes);
}
static void print_ss_usb_cap(struct libusb_ss_usb_device_capability_descriptor *ss_usb_cap)
{
printf(" USB 3.0 Capabilities:\n");
printf(" bDevCapabilityType: %u\n", ss_usb_cap->bDevCapabilityType);
printf(" bmAttributes: %02xh\n", ss_usb_cap->bmAttributes);
printf(" wSpeedSupported: %u\n", ss_usb_cap->wSpeedSupported);
printf(" bFunctionalitySupport: %u\n", ss_usb_cap->bFunctionalitySupport);
printf(" bU1devExitLat: %u\n", ss_usb_cap->bU1DevExitLat);
printf(" bU2devExitLat: %u\n", ss_usb_cap->bU2DevExitLat);
}
static void print_bos(libusb_device_handle *handle)
{
struct libusb_bos_descriptor *bos;
uint8_t i;
int ret;
ret = libusb_get_bos_descriptor(handle, &bos);
if (ret < 0)
return;
printf(" Binary Object Store (BOS):\n");
printf(" wTotalLength: %u\n", bos->wTotalLength);
printf(" bNumDeviceCaps: %u\n", bos->bNumDeviceCaps);
for (i = 0; i < bos->bNumDeviceCaps; i++) {
struct libusb_bos_dev_capability_descriptor *dev_cap = bos->dev_capability[i];
if (dev_cap->bDevCapabilityType == LIBUSB_BT_USB_2_0_EXTENSION) {
struct libusb_usb_2_0_extension_descriptor *usb_2_0_extension;
ret = libusb_get_usb_2_0_extension_descriptor(NULL, dev_cap, &usb_2_0_extension);
if (ret < 0)
return;
print_2_0_ext_cap(usb_2_0_extension);
libusb_free_usb_2_0_extension_descriptor(usb_2_0_extension);
} else if (dev_cap->bDevCapabilityType == LIBUSB_BT_SS_USB_DEVICE_CAPABILITY) {
struct libusb_ss_usb_device_capability_descriptor *ss_dev_cap;
ret = libusb_get_ss_usb_device_capability_descriptor(NULL, dev_cap, &ss_dev_cap);
if (ret < 0)
return;
print_ss_usb_cap(ss_dev_cap);
libusb_free_ss_usb_device_capability_descriptor(ss_dev_cap);
}
}
libusb_free_bos_descriptor(bos);
}
static void print_interface(const struct libusb_interface *interface)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < interface->num_altsetting; i++)
print_altsetting(&interface->altsetting[i]);
}
static void print_configuration(struct libusb_config_descriptor *config)
{
uint8_t i;
printf(" Configuration:\n");
printf(" wTotalLength: %u\n", config->wTotalLength);
printf(" bNumInterfaces: %u\n", config->bNumInterfaces);
printf(" bConfigurationValue: %u\n", config->bConfigurationValue);
printf(" iConfiguration: %u\n", config->iConfiguration);
printf(" bmAttributes: %02xh\n", config->bmAttributes);
printf(" MaxPower: %u\n", config->MaxPower);
for (i = 0; i < config->bNumInterfaces; i++)
print_interface(&config->interface[i]);
}
static void print_device(libusb_device *dev, libusb_device_handle *handle)
{
struct libusb_device_descriptor desc;
unsigned char string[256];
const char *speed;
int ret;
uint8_t i;
switch (libusb_get_device_speed(dev)) {
case LIBUSB_SPEED_LOW: speed = "1.5M"; break;
case LIBUSB_SPEED_FULL: speed = "12M"; break;
case LIBUSB_SPEED_HIGH: speed = "480M"; break;
case LIBUSB_SPEED_SUPER: speed = "5G"; break;
case LIBUSB_SPEED_SUPER_PLUS: speed = "10G"; break;
default: speed = "Unknown";
}
ret = libusb_get_device_descriptor(dev, &desc);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to get device descriptor");
return;
}
printf("Dev (bus %u, device %u): %04X - %04X speed: %s\n",
libusb_get_bus_number(dev), libusb_get_device_address(dev),
desc.idVendor, desc.idProduct, speed);
if (!handle)
libusb_open(dev, &handle);
if (handle) {
if (desc.iManufacturer) {
ret = libusb_get_string_descriptor_ascii(handle, desc.iManufacturer, string, sizeof(string));
if (ret > 0)
printf(" Manufacturer: %s\n", (char *)string);
}
if (desc.iProduct) {
ret = libusb_get_string_descriptor_ascii(handle, desc.iProduct, string, sizeof(string));
if (ret > 0)
printf(" Product: %s\n", (char *)string);
}
if (desc.iSerialNumber && verbose) {
ret = libusb_get_string_descriptor_ascii(handle, desc.iSerialNumber, string, sizeof(string));
if (ret > 0)
printf(" Serial Number: %s\n", (char *)string);
}
}
if (verbose) {
for (i = 0; i < desc.bNumConfigurations; i++) {
struct libusb_config_descriptor *config;
ret = libusb_get_config_descriptor(dev, i, &config);
if (LIBUSB_SUCCESS != ret) {
printf(" Couldn't retrieve descriptors\n");
continue;
}
print_configuration(config);
libusb_free_config_descriptor(config);
}
if (handle && desc.bcdUSB >= 0x0201)
print_bos(handle);
}
if (handle)
libusb_close(handle);
}
#ifdef __linux__
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static int test_wrapped_device(const char *device_name)
{
libusb_device_handle *handle;
int r, fd;
fd = open(device_name, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("Error could not open %s: %s\n", device_name, strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
r = libusb_wrap_sys_device(NULL, fd, &handle);
if (r) {
printf("Error wrapping device: %s: %s\n", device_name, libusb_strerror(r));
close(fd);
return 1;
}
print_device(libusb_get_device(handle), handle);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
#else
static int test_wrapped_device(const char *device_name)
{
(void)device_name;
printf("Testing wrapped devices is not supported on your platform\n");
return 1;
}
#endif
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const char *device_name = NULL;
libusb_device **devs;
ssize_t cnt;
int r, i;
for (i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
if (!strcmp(argv[i], "-v")) {
verbose = 1;
} else if (!strcmp(argv[i], "-d") && (i + 1) < argc) {
i++;
device_name = argv[i];
} else {
printf("Usage %s [-v] [-d </dev/bus/usb/...>]\n", argv[0]);
printf("Note use -d to test libusb_wrap_sys_device()\n");
return 1;
}
}
r = libusb_init_context(/*ctx=*/NULL, /*options=*/NULL, /*num_options=*/0);
if (r < 0)
return r;
if (device_name) {
r = test_wrapped_device(device_name);
} else {
cnt = libusb_get_device_list(NULL, &devs);
if (cnt < 0) {
libusb_exit(NULL);
return 1;
}
for (i = 0; devs[i]; i++)
print_device(devs[i], NULL);
libusb_free_device_list(devs, 1);
}
libusb_exit(NULL);
return r;
}