目录
Map接口
Map接口的常用方法
删除方法
判断方法
查找方法
增加方法
Map常用方法&遍历操作
HashTable
字典-Dictionary,v>
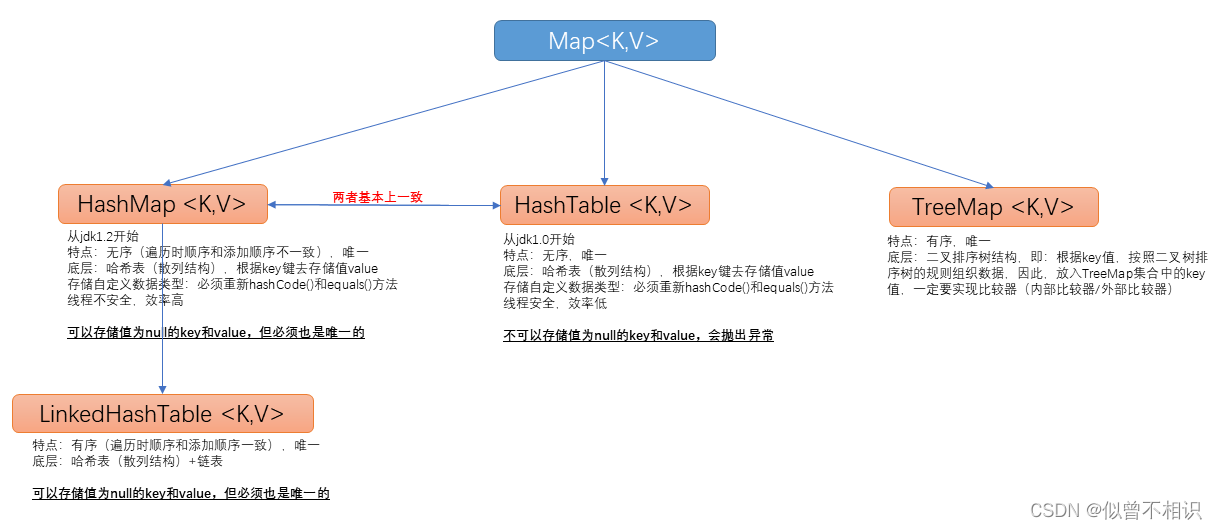
HashMap、HashTable和LinkedHashMap
TreeMap
【2】TreeMap-存储自定义数据类型-【内部比较器】
HashMap底层源码
jdk8-源码片段
TreeMap底层源码
Collection接口-底层源码
HashSet底层源码
TreeSet底层源码
Collections工具类
Map接口
Map接口中存储的是键值对,每一个元素都是由key和value组成。
Map接口中的元素key键是唯一的、不重复的,
Map接口的常用方法
删除方法
void clear():清空Map
V remove(Object key):根据key值删除Map集合中的元素
default boolean remove(Object key,Object value):当Map中存在的指定的key和value时,则删除对应的元素
判断方法
boolean containsKey(Object key):判断Map集合中是否包含指定的key
boolean containsValue(Object value):判断Map集合中是否包含指定的value
boolean equals(Object obj):比较是否相等(比较两个Map中的元素是否相等)
boolean isEmpty():判断Map是否为空
查找方法
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():可用于遍历Map集合的元素
V get(Object key):根据key键获取对应的value值
Set<K> keySet():获取所有的key键组成的Set集合——key是唯一的,使用Set集合存储
Collection<V> values():获取所有的value值组成的Collection集合对象——value可能是重复的,使用Collection存储
int size():获取Map中存储的键值对元素数量
增加方法
V put(K key, V value):向Map中存放key-value键值对元素;如果key已经存在,那么就会返回对应元素的value值
default V replace(K key, V value):只有当目标映射到某个值时,才能替换指定键的条目
Map常用方法&遍历操作
示例代码如下,
//methods
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//添加元素
map.put("k1",955631);
map.put("k2",526331);
map.put("k3",101313);
map.put("k4",16526323);
map.put("k3",46261);//k3已经存在,此时46261会覆盖掉原有的值101313
//移除操作
map.remove("k1");
//清空
// map.clear();
//获取长度
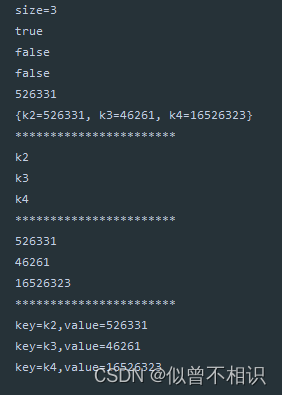
System.out.println("size="+map.size());
//判断操作
System.out.println(map.containsKey("k3"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue("46261"));
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//查找方法
System.out.println(map.get("k2"));
//打印结果
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("***********************");
//keySet()方法——获取集合中所有的键key
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (Iterator<String> iterator = keySet.iterator();iterator.hasNext();) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("***********************");
//values方法——获取集合中所有的值value
Collection<Object> values = map.values();
for(Iterator<Object> iterator = values.iterator();iterator.hasNext();)
System.out.println(iterator.next());
System.out.println("***********************");
//entrySet方法-获取集合中所有的key-value键值对
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Object>> iterator = entries.iterator();iterator.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Object> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key="+next.getKey()+",value="+next.getValue());
}
}
HashTable

字典-Dictionary<K,V>
Dictionary类是HashTable类的抽象父类,它将键映射到值。 每个键和每个值都是一个对象。 在任何一个Dictionary对象中,每个键最多与一个值相关联。 给定一个Dictionary和一个键,可以查找关联的元素。 任何非null对象都可以用作键和值。
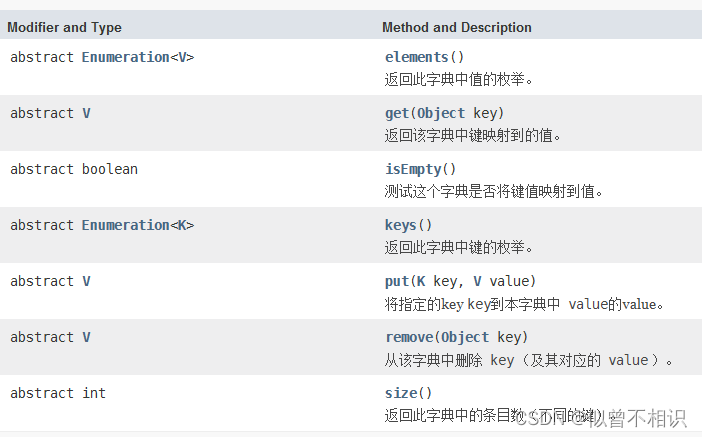
Dictionary类的成员方法如下,
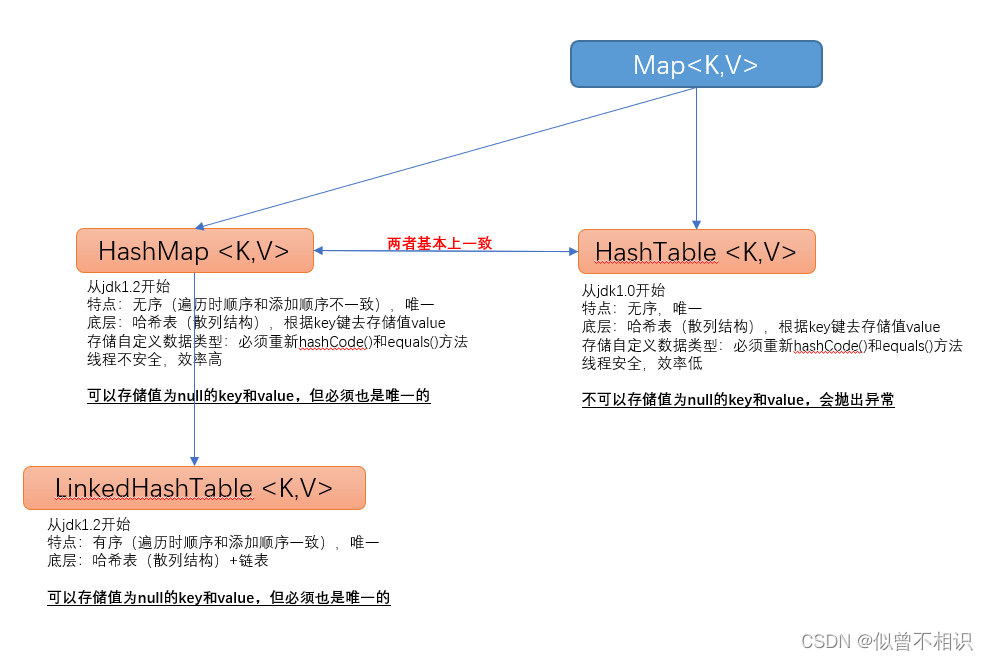
HashMap、HashTable和LinkedHashMap

总结如下,
TreeMap
TreeMap集合中的元素是唯一的、不可重复,有序的(升序/降序),底层是对二叉树数据结构的实现。在遍历TreeMap时,根据key值,按照中序遍历的方式,得到一个升序的元素序列。

【1】TreeMap-存储基本数据类型
示例代码如下,
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("k4",65953);
map.put("k3",195626);
map.put("k1",12365);
map.put("k2",6212365);
map.put("k3",195626);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();iterator.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key="+next.getKey()+",value="+next.getValue());
}
}【2】TreeMap-存储自定义数据类型-【内部比较器】
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
//properties
private Integer age;
private String name;
//methods
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return Objects.equals(age, student.age) &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(age, name);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//按照姓名比较
return this.getName().compareTo(o.getName());
}
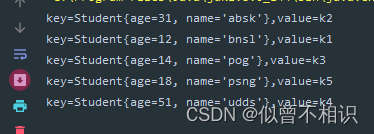
}示例代码如下,按照学生姓名排序,以二叉排序树规则存放数据,
private static void test_Student_1(){
Map<Student,String> map = new TreeMap<>();//传入比较器参数
map.put(new Student(51,"udds"),"k4");
map.put(new Student(18,"psng"),"k5");
map.put(new Student(12,"bnsl"),"k1");
map.put(new Student(31,"absk"),"k2");
map.put(new Student(14,"pog"),"k3");
//遍历操作
Set<Map.Entry<Student,String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<Student,String>> iterator = entries.iterator();iterator.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<Student,String> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key="+next.getKey()+",value="+next.getValue());
}
}
【3】TreeMap-存储自定义数据类型-【外部比较器】
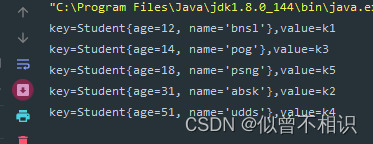
自定义外部比较器,指定:按照年龄顺序进行元素的存储和遍历操作,
private static void test_Student_2(){
Comparator<Student> comparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge().compareTo(o2.getAge());
}
};
Map<Student,String> map = new TreeMap<>(comparator);//传入比较器参数
map.put(new Student(51,"udds"),"k4");
map.put(new Student(18,"psng"),"k5");
map.put(new Student(12,"bnsl"),"k1");
map.put(new Student(31,"absk"),"k2");
map.put(new Student(14,"pog"),"k3");
//遍历操作
Set<Map.Entry<Student,String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<Student,String>> iterator = entries.iterator();iterator.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<Student,String> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key="+next.getKey()+",value="+next.getValue());
}
}
HashMap底层源码
HashMap底层是通过“数组+链表”的结构实现的,简要图示如下,
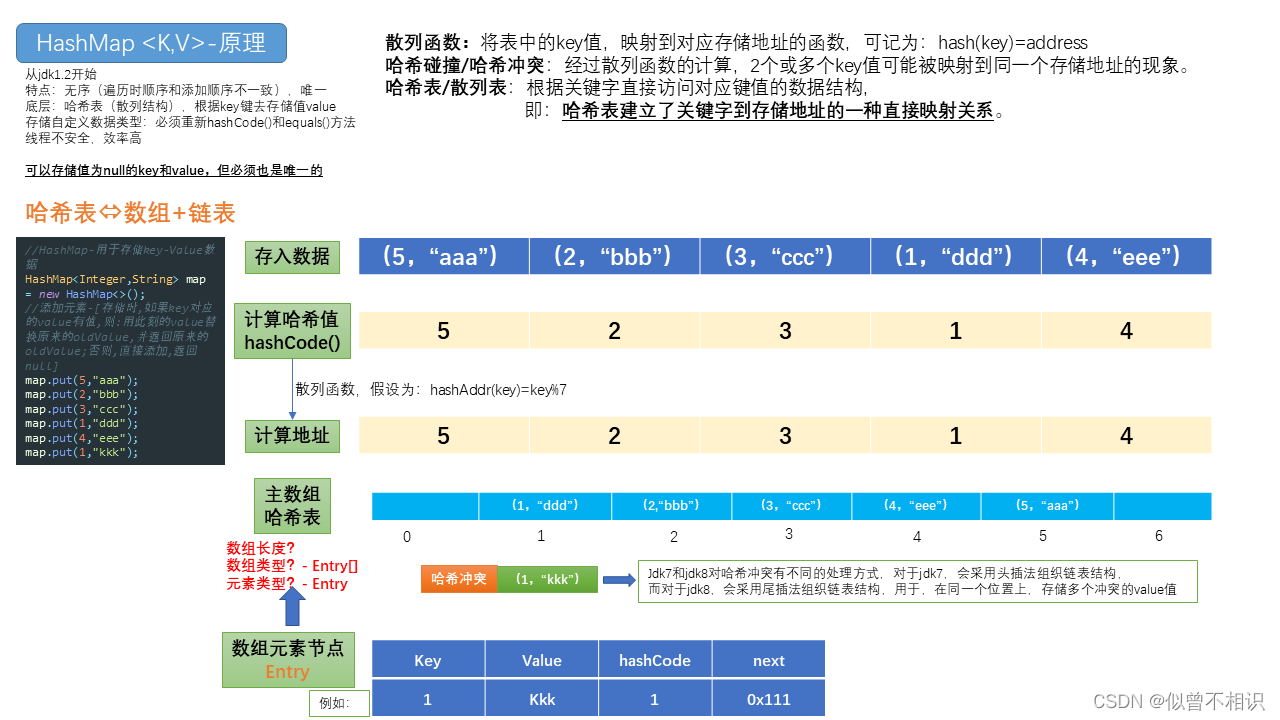
jdk8-源码片段
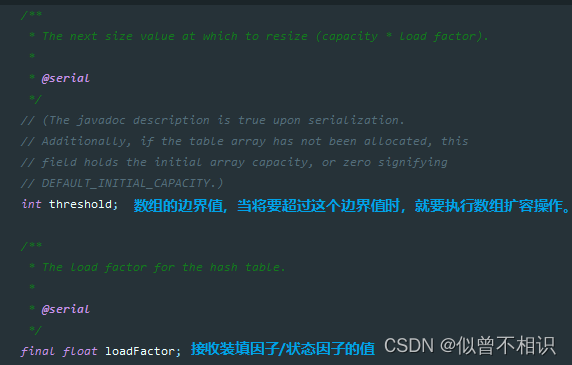
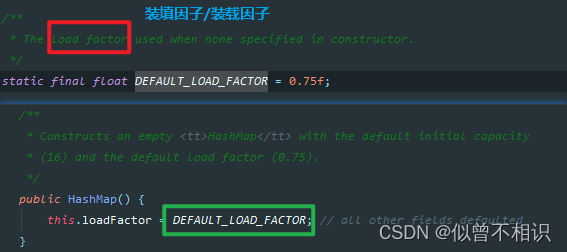
【1】装填因子/装载因子(α):HashMap表中元素数量与表的实际长度的比值,用于表示该哈希表的装满程度,即:α=表中记录数/表的实际长度。
【2】取余运算小技巧:当被除数为2的倍数时,可通过&运算符做取余运算,效率更高,如下所示,
Random random = new Random();
int h = Math.abs(random.nextInt()%100),
length = 8;
System.out.println("h="+h+",length="+length);
//h对length取余运算
System.out.println(h%length);
//通过&运算符取余运算
System.out.println((length-1)&h);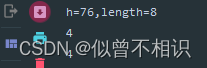
继承结构
重要属性


构造器
默认的,jdk8中在创建HashMap对象时,并未直接为底层数组table分配存储空间。
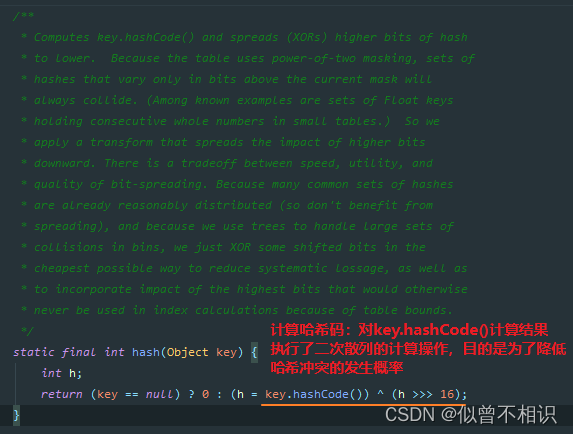
计算哈希码
创建新元素Node方法
添加元素-put()方法
jdk8使用无参构造函数创建HashMap对象,在存储<key,value>键值对时,首先会判断底层数组table是否已经被初始化;然后再执行键值对的添加操作。

以下为putVal()方法的源码,
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key key键对应的哈希值
* @param key the key key键
* @param value the value to put 将要存放的value值
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value 是否修改已存在的value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none 返回值
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {//变量声明
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;//步骤1:判断数组是否已经初始化,未初始化,则去执行初始化方法resize()
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;//记录当前哈希表长度// (n - 1) & hash运算:哈希表长度和hash码按位与运算,等价于:hash%n的取余运算
//步骤2:根据hash值,判断是否存在哈希冲突if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)//当前位置处的元素为空,不存在哈希冲突
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//直接创建新的结点,并放入元素即可
else {//出现哈希冲突,处理冲突
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;//afterNodeAccess在HashMap中为一个空方法,是为子类LinkedHashMap预留的方法
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}//修改次数自增
++modCount;//步骤3:长度size加1,并根据threshold边界值判断是否需要调用resize()方法扩充底层数组
if (++size > threshold)
resize();//afterNodeInsertion在HashMap中为一个空方法,是为子类LinkedHashMap预留的方法
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
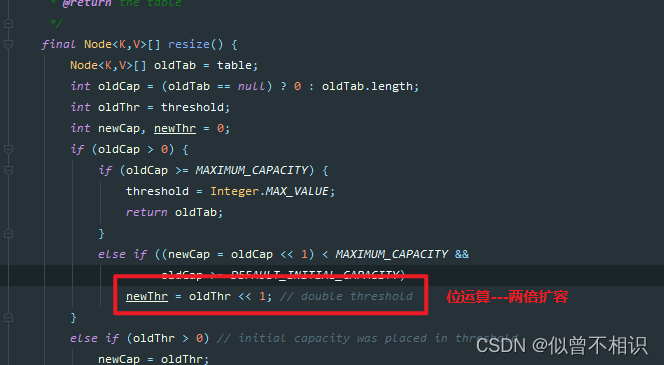
数组初始化/扩容方法-resize()

面试题:填充因子为什么为0.75?
HashMap源码中的注释解释:0.75的填充因子,可以充分考虑到时间和空间的复杂度,保证HashMap在添加和查询操作时的效率。
As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of the operations of the <tt>HashMap</tt> class, including <tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>). The expected number of entries in the map and its load factor should be taken into account when setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of rehash operations. If the initial capacity is greater than the maximum number of entries divided by the load factor, no rehash operations will ever occur.
面试题:主数组的长度为什么为2的n次方
①提升效率,在添加元素的putVal()方法中,有一个通过&按位与运算来提升运算效率的代码段(如下所示),这种运算方式要求:length的值,必须为2的次方;
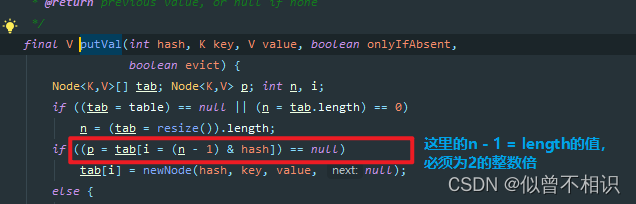
②防止哈希冲突/位置冲突。当length为2的次方时,可以降低哈希冲突/位置冲突的概率。
当length是2的整数倍时,例如length=8,当hash值分别为2和3,计算出来的数组下标分别为3和2,未出现哈希冲突/位置冲突,

当length不是2的整数倍,例如length=9,当hash值分别为2和3,计算出来的数组下标也是相同的,就很容易出现哈希冲突/位置冲突,

TreeMap底层源码
TreeMap的底层对红黑树的实现。

继承结构
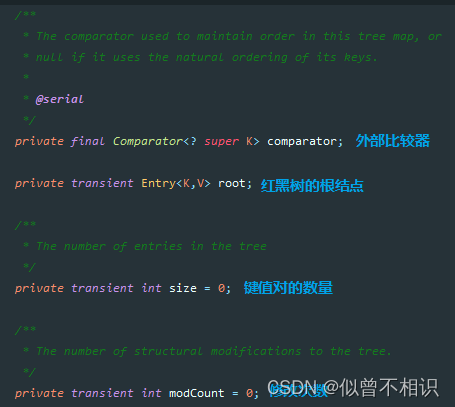
重要属性
其中,Entry结点的定义如下,
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
/**
* Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with
* {@code null} child links, and BLACK color.
*/
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
/**
* Returns the key.
*
* @return the key
*/
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
/**
* Returns the value associated with the key.
*
* @return the value associated with the key
*/
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
/**
* Replaces the value currently associated with the key with the given
* value.
*
* @return the value associated with the key before this method was
* called
*/
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return keyHash ^ valueHash;
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
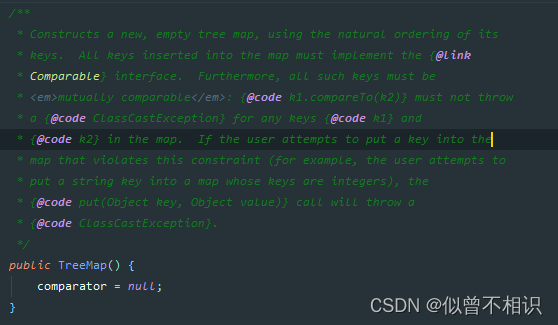
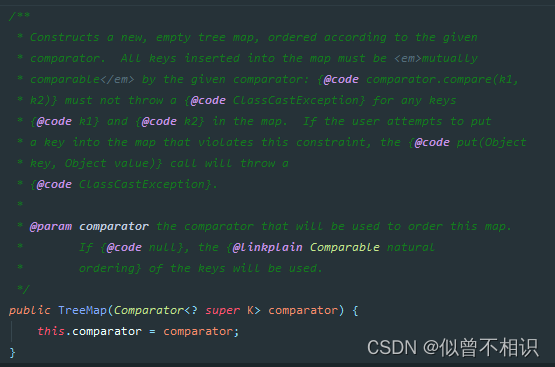
}空参构造器
空参构造器的外部比较器为null,默认会使用元素本身的内部比较器,
有参构造器
使用有参构造器,可以指定要使用的外部比较器对象,
添加元素-put方法
put方法用于存储一个<key,value>键值对结构的元素,jdk8的源码如下,
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
*
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//判断根结点root是否为空
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
//初始化根结点-[将新的结点作为根结点存储]
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths-获取内部维护的外部比较器对象
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//以下两种比较器的执行流程,其实是一致的-实质上都是对二叉树的遍历操作
//判断外部比较器是否为空
if (cpr != null) {
//外部比较器不为空,就使用外部比较器
do {
//遍历左右子树,找到当前key值要存储的位置
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);//调用外部比较器
if (cmp < 0)
//key的值小于当前结点-向下遍历左子树
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
//key的值大于当前结点-向下遍历右子树
t = t.right;
else
//key的值相同-执行value的替换操作-并返回旧的oldValue结点值
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//外部比较器为空,则默认使用内部比较器
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
//遍历左右子树,找到当前key值要存储的位置
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);//调用内部比较器
if (cmp < 0)
//key的值小于当前结点-向下遍历左子树
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
//key的值大于当前结点-向下遍历右子树
t = t.right;
else
//key的值相同-执行value的替换操作-并返回旧的oldValue结点值
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//根据key和value创建新的树节点
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
//将新节点作为树的左节点存放
parent.left = e;
else
//将新节点作为树的右节点存放
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;//<key,value>元素的数量自增
modCount++;//修改次数自增
return null;//返回null值
}
Collection接口-底层源码
以下HashSet、TreeSet集合属于Collection接口的子类,但是底层分别是通过Map接口子类HashMap、TreeMap实现的。为了在继承结构上做出区分,将其做为新的章节叙述。
HashSet底层源码
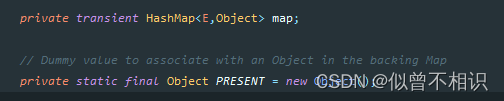
HashSet底层就是通过HashMap实现的,
重要属性
构造器
HashSet的若干个构造器,内部执行的操作就是在创建HashMap的实例,
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified
* collection. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with default load factor
* (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to contain the elements in
* the specified collection.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* the specified initial capacity and the specified load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* the specified initial capacity and default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty linked hash set. (This package private
* constructor is only used by LinkedHashSet.) The backing
* HashMap instance is a LinkedHashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and the specified load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map
* @param dummy ignored (distinguishes this
* constructor from other int, float constructor.)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive
*/
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
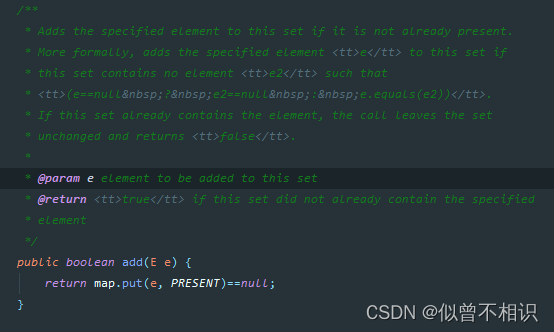
}添加方法-add()
HashSet集合的add()存储元素时,会将元素e存放到内部维护的HashMap集合的key键的位置上,而对应的Value值的位置,则是用一个统一的Object类型的PRESENT成员属性来进行填充。
TreeSet底层源码
TreeSet集合,底层是借助TreeMap实现。
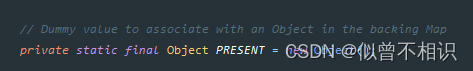
重要属性
/**
* The backing map.
*/
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();空参构造器
空参构造器内部创建了一个TreeMap对象,
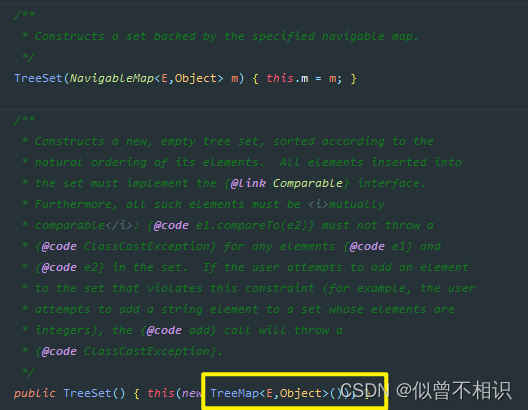
PS:此处,源码中的NavigableMap是TreeMap的父接口,

有参构造器
有参构造器中,同样创建了一个TreeMap对象,
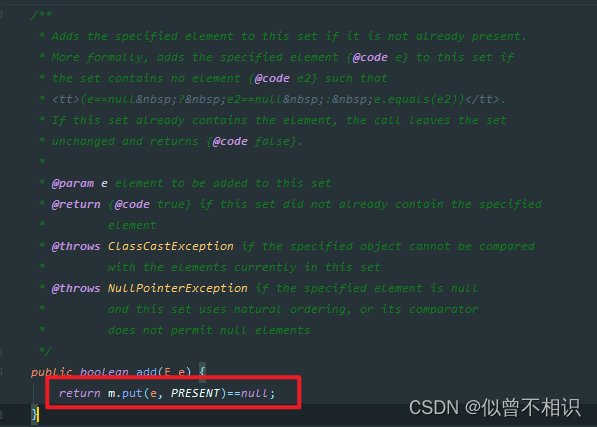
添加方法add()
类似于HashSet,TreeSet底层在调用add()方法添加元素时,实际上是在通过内部持有的m属性——TreeMap对象,调用put()方法,将当前元素E的值作为key传递,并将value值的位置使用同一个Object对象PRESENT进行填充。
Collections工具类
Collections工具类,包含大量的静态方法,用于对集合进行查找、赋值、取最大/小值、返回线程安全的集合对象、返回只读的集合对象等操作。
虽然Collections类的构造器被private修饰,无法直接通过new关键字创建对象,但是,通常的我们只需要通过`Collections.静态方法名`的方式,直接去使用该类提供的静态方法即可。
示例代码如下,
import java.util.*;
public class Collections_Class {
//properties
//methods
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//addAll
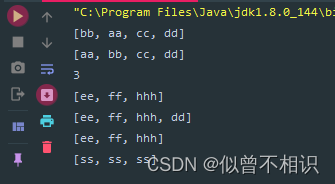
Collections.addAll(list,"bb","aa","cc","dd");
System.out.println(list);
//sort()-排序操作-指定比较器-[方法引用]-【如果不指定,默认是升序的排列】
Collections.sort(list, String::compareTo);
System.out.println(list);
//binarySearch-二分查找-返回下标值-[前提:集合是有序的]
int binarySearch = Collections.binarySearch(list, "dd");
System.out.println(binarySearch);
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list1,"ee","ff","hhh");
System.out.println(list1);
//会将list1中相同下标处的内容,覆盖到list中
Collections.copy(list,list1);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list1);
//fill-填充-[会将所有的元素都替换为ss]
Collections.fill(list1,"ss");
System.out.println(list1);
}
}

![[datawhale202211]跨模态神经搜索实践:前端简介 Streamlit](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/616b18f61a3149b2bd541f5b00c48bfb.png)
![[python]basemap后安装后hello world代码](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c5f2b969eb034153b300e1044a2ca431.png)

![[Apollo Cyber RT] Timer实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e38e5bbff45d4bc3b313c029f0569d5b.png)