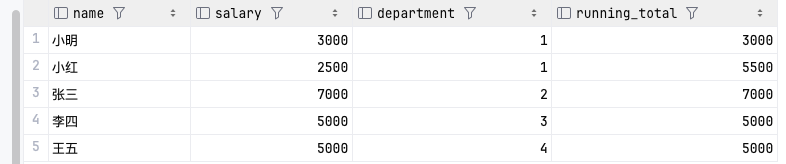
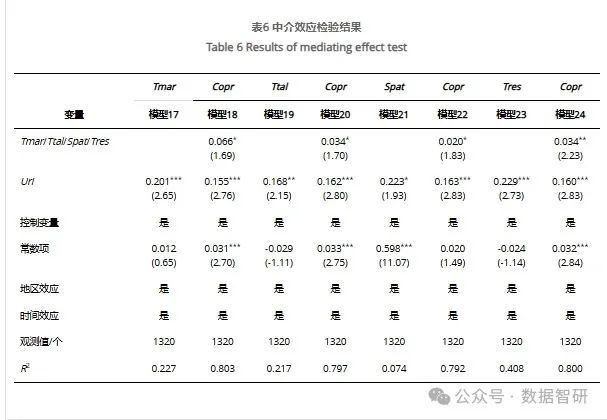
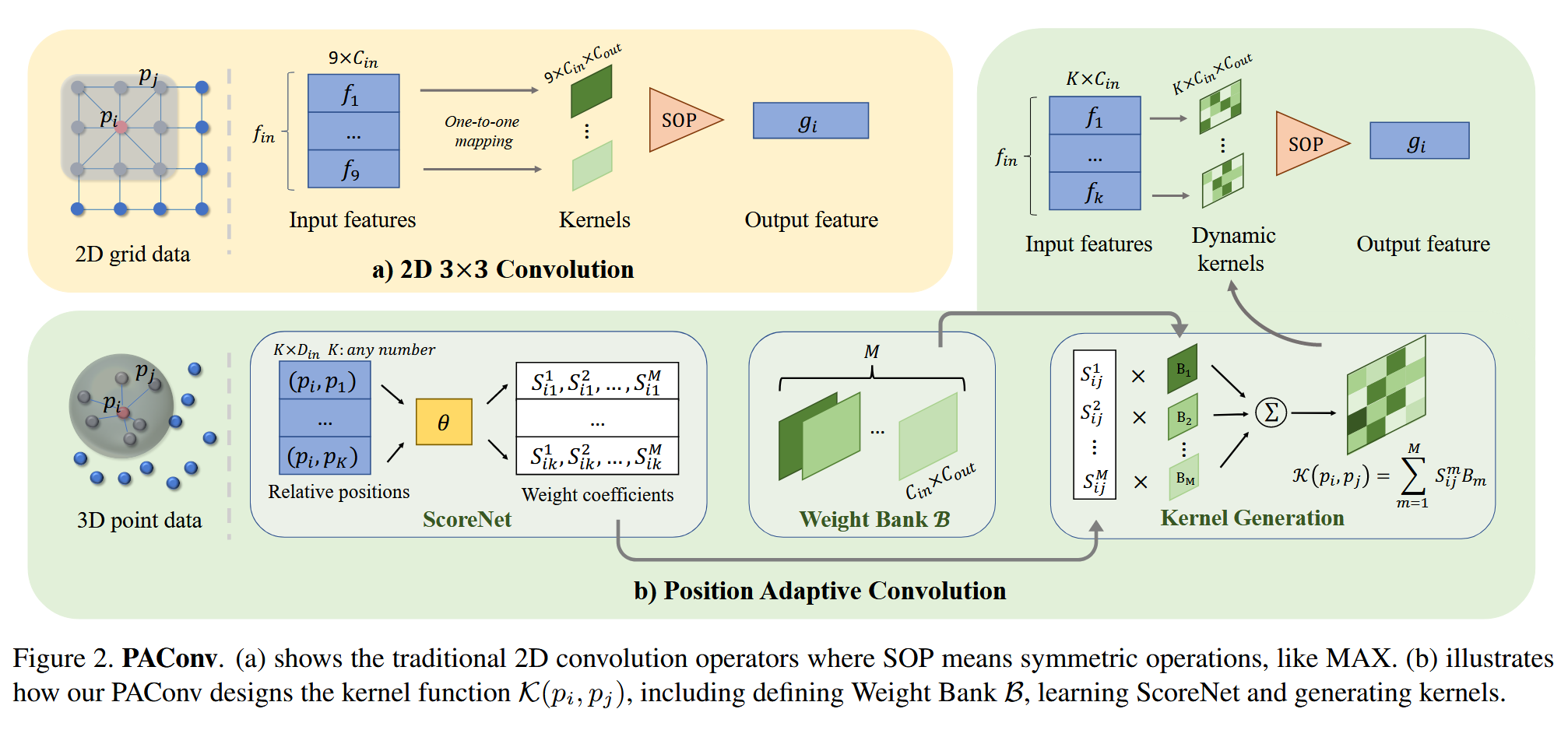
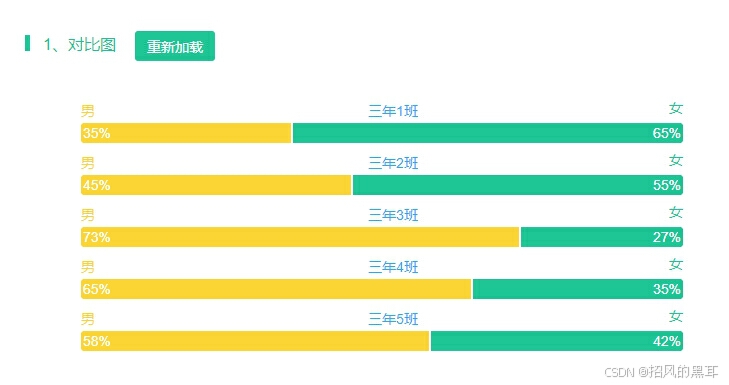
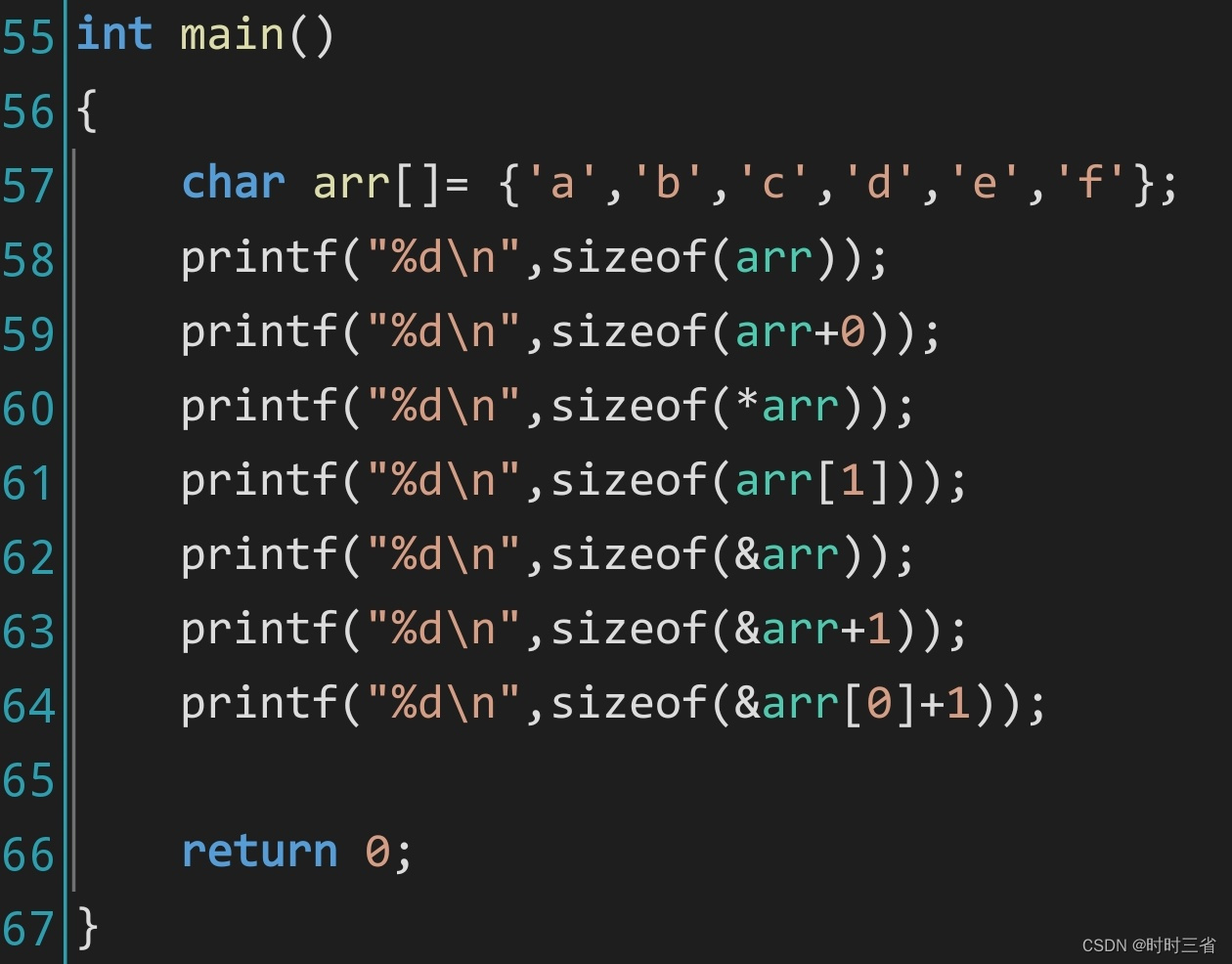
自行实现Mystring类
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class mystring
{
public:
mystring()
{
len = 0;
str = nullptr;
}
mystring(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, s);
}
mystring(const mystring& other)
{
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, other.str);
}
~mystring()
{
delete[] str;
}
mystring& operator=(const mystring& other)
{
if (this != &other)
{
len = other.len;
delete[] str;
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, other.str);
}
return *this;
}
mystring operator+(const mystring& other)
{
mystring s;
s.len = len + other.len;
s.str = new char[s.len + 1];
strcpy(s.str, str);
strcat(s.str, other.str);
return s;
}
bool operator!=(const mystring& other)
{
if(strcmp(str, other.str)!= 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator==(const mystring& other)
{
if(strcmp(str, other.str) == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator<(const mystring& other)
{
if(strcmp(str, other.str) < 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator>(const mystring& other)
{
if(strcmp(str, other.str) > 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator<=(const mystring& other)
{
if(strcmp(str, other.str) <= 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const mystring& other)
{
if(strcmp(str, other.str) >= 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
const char* data() const
{
return str;
}
bool empty() const
{
return len == 0;
}
int size() const
{
return len;
}
int length() const
{
return len;
}
char at(int index) const
{
if (index < 0 || index >= len)
{
throw out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
return str[index];
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream& L, const mystring &R);
friend istream &operator>>(istream& L, mystring &R);
private:
char* str;
int len;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& L, const mystring &R)
{
L << R.str<<endl;
return L;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& L,mystring &R)
{
L >> R.str;
return L;
}
int main()
{
mystring s1("hello");
mystring s2(s1);
cout << s1.data() << endl;
cout << s2.data() << endl;
s2 = mystring("world");
cout << s1.data() << endl;
cout << s2.data() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s1.empty() << endl;
cout << s2.empty() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s2.length() << endl;
try {
cout << s1.at(0) << endl;
cout << s2.at(0) << endl;
} catch (const out_of_range& e) {
cerr << e.what() << endl;
}
s1 = s1 + s2;
cout << s1.data() << endl;
cout << s2.data() << endl;
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 != s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 <= s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 >= s2) << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}