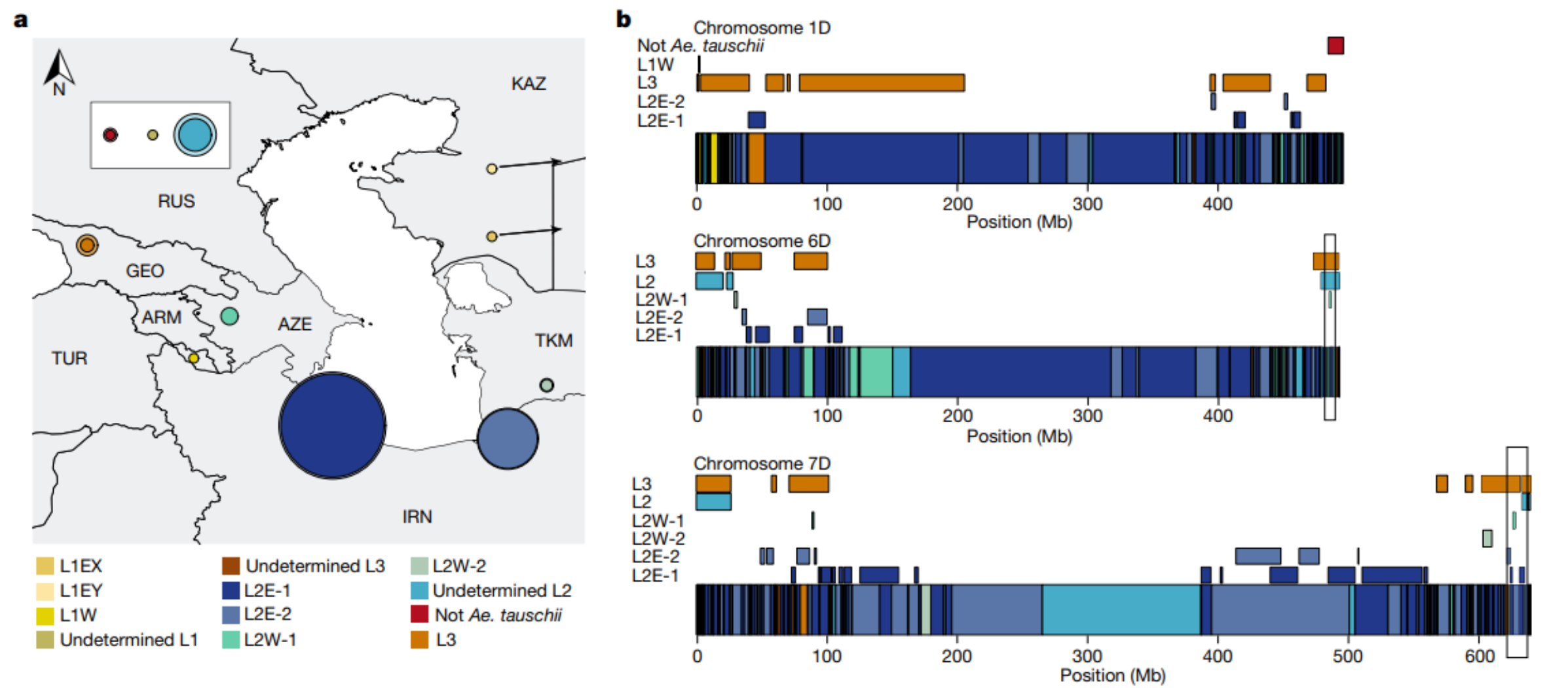
Linux系统之jobs命令的基本使用
- 一、jobs命令介绍
- 二、jobs命令的使用帮助
- 2.1 jobs命令的help帮助信息
- 2.2 jobs命令的语法解释
- 三、jobs命令的基本使用
- 3.1 运行一个后台任务
- 3.2 列出后台所有的作业
- 3.3 列出进程ID
- 3.4 只列出进程ID
- 3.5 终止后台任务
- 3.6 只显示运行任务
- 3.7 只显示停止任务
- 3.8 将后台任务转到前台
- 3.9 将前台任务放到后台:
- 3.10 终止后台作业
- 四、注意事项

👨💻 江湖有缘
🚀 一名在运维领域不懈探索的学习者。
🌟 认证与成就
🔴 红帽 RHCE 认证
🟠 华为 HCIP 数通认证
🔵 华为 HCIE 云计算认证
…以及其他多项专业认证
🌐 个人主页
🔗 CSDN个人主页
📢 公众号
🏷️ 【运维江湖客】
👥 交流社群
💬 欢迎同行及爱好者加入我们的QQ群:
🏷️ 群号【942602415】
📝 人生格言
“人可以被毁灭,但不能被打败。”
—— 海明威
一、jobs命令介绍
jobs 命令在 Linux 和类 Unix 系统中是一个非常实用的工具,它允许用户管理后台运行的任务。当你启动一个程序但不希望它占用终端窗口时,或者你想让程序在后台继续运行时,jobs 命令就派上用场了。
二、jobs命令的使用帮助
2.1 jobs命令的help帮助信息
使用–help,查看jobs的帮助信息。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs --help
jobs: jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs -x command [args]
Display status of jobs.
Lists the active jobs. JOBSPEC restricts output to that job.
Without options, the status of all active jobs is displayed.
Options:
-l lists process IDs in addition to the normal information
-n lists only processes that have changed status since the last
notification
-p lists process IDs only
-r restrict output to running jobs
-s restrict output to stopped jobs
If -x is supplied, COMMAND is run after all job specifications that
appear in ARGS have been replaced with the process ID of that job's
process group leader.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option is given or an error occurs.
If -x is used, returns the exit status of COMMAND.
2.2 jobs命令的语法解释
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -l | 列出进程ID,除了正常的作业信息之外 |
| -n | 只列出自从上次通知以来状态发生变化的进程 |
| -p | 只列出进程ID |
| -r | 只输出为正在运行的作业 |
| -s | 只输出为已停止的作业 |
jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] 或 jobs -x command [args]
- 选项:
-l: 列出进程ID,除了正常的作业信息之外。-n: 只列出自从上次通知以来状态发生变化的进程。-p: 只列出进程ID。-r: 只输出为正在运行的作业。-s: 只输出为已停止的作业。
三、jobs命令的基本使用
3.1 运行一个后台任务
执行以下命令,运行一个后台任务。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
[1] 47372
3.2 列出后台所有的作业
直接使用jobs命令,列出后台所有作业情况。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs
[1]+ Running ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
3.3 列出进程ID
使用
-l选项,列出进程ID,可以看到编号为1的任务进程ID为47372。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs -l
[1]+ 47372 Running ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
3.4 只列出进程ID
使用
-p选项,只显示进程ID。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs -p
47372
3.5 终止后台任务
- 重新启动一个任务
[root@openEuler-test ~]# sleep 1000 &
[2] 47474
- 暂停该任务
[root@openEuler-test ~]# kill -s STOP 47474
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000
- 查看当前后台任务
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs
[1]- Running ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000
3.6 只显示运行任务
使用-r选项,只显示后台正在运行任务。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs -r
[1]- Running ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
3.7 只显示停止任务
使用-s选项,只显示后台停止的任务。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs -s
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000
3.8 将后台任务转到前台
使用 fg 命令将后台任务转到前台:
fg %1

3.9 将前台任务放到后台:
如果已经开始运行一个任务,并且想要把它放到后台,可以使用 Ctrl+Z 快捷键来暂停它,然后使用下面的命令将其移至后台:
[root@openEuler-test ~]# bg %1
[1]+ ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs
[1]- Running ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000

3.10 终止后台作业
使用kill命令,终止后台作业。
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs
[1]- Running ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null &
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000
[root@openEuler-test ~]# kill %1
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs
[1]- Terminated ping www.baidu.com > /dev/null
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000
[root@openEuler-test ~]# jobs
[2]+ Stopped sleep 1000
四、注意事项
- 使用
&符号可使命令在后台运行,而Ctrl+Z可暂停并将命令发送到后台。 - 作业标识符
%1、%2等用于引用作业列表中的第一个、第二个等作业。 - 默认情况下,
jobs命令列出所有活动作业;使用-l选项显示更多详细信息,如进程ID。 - 使用
fg %job_number可将后台作业转到前台继续执行,而bg %job_number则将其移至后台。 - 通过
kill %job_number或killall command_name可以终止后台作业或所有同名进程。 - 使用
Ctrl+C或kill命令时需小心,以免意外中断或影响其他进程。 - 不同 shell 对作业控制的支持可能不同,请熟悉您正在使用的 shell。
- 长时间运行的作业应定期检查资源使用情况,避免过度占用系统资源。
- 作业继承启动它的 shell 的环境,确保作业在正确的上下文中运行。
- 可以编写 shell 脚本自动管理和控制后台作业。
【原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jks212454/article/details/141232763】







![Python入门级 序列全集 [ 继上篇 进阶版 持续更新中哞哞哞!!! ]例题较多](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d749eb05e78b49d096b4fffb9bf7bcab.png)