正片从现在开始了。
1.结构体关联
当DDR初始化后,整个内存就可以访问了。但是需要合理的管理,防止内存碎片以及安全相关的问题。因此需要对物理内存进行严格的管理。
物理内存分为:页, 分区,内存节点。DMA需要连续的内存,因此需要单独的内存。(大概16MB)。

物理页帧结构体,每个物理块都通过一个struct page描述。
- 定义头文件:include/linux/mm_type.h 描述不同类型的页。
- 每个物理页帧page frame 都使用结构体page表示。
- 结构体struct page核心成员分析。
- 思考
-
- 物理页帧和struct page之间的关系:通过page结构体找到对应的页帧号。因为page结构体是线性存放。
- 不同类型的page分别有什么作用。
- 物理页帧号pfn 和物理地址的关系:通过页帧号找到对应的page结构体。
- struct page存储在哪里。page本身是需要占用内存的,每个页空间,都会用page结构体描述它。比如说系统总共有1024个page,那么就需要1024个page结构体来描述整个系统内存。此时需要类似struct page mm_map[1024]的信息来保存。
- 全局变量:mem_map。它保存了系统所有page的地址,因为系统所有的page都有对应的地址,需要这么一块内存指向它。
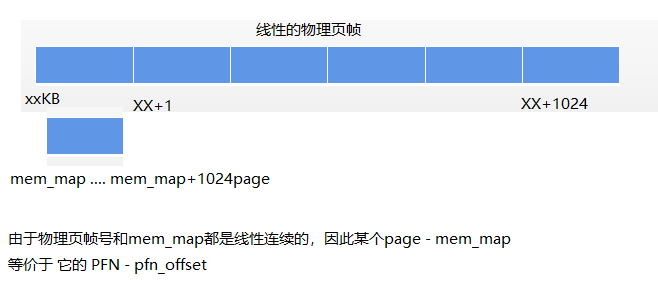
假设物理页帧号是0x10240000,0x10250000,0x10260000 ... 0x20470000, 如果用arr[1024]数组保存它,arr[0] = 0x10240000,arr[1] = 0x10250000, ... arr[1023] = 0x20470000。因此物理页帧号对应存放的地址:__page_to_pfn(page) ==> (page - mem_map)
示例1:如果已知page,要去求pfn
struct page my_page=mem_map[22]
my_page_pfn = (my_page - mem_map) + ARCH_PFN_OFFSET示例2:如果已知某个pfn,去求page
my_pfn = 0x10250000
struct page my_page = mem_map + (pfn - ARCH_FPN_OFFSET)
2.内存页:page结构体
struct page 是 Linux 内核中的一个重要数据结构,用于表示和管理物理内存页。struct page 结构体的设计非常复杂,因为它必须能够适应多种不同的用途,包括但不限于页缓存、匿名页面、页表管理、内存池管理、内存控制组等。为了支持这些多样的用途,struct page 中包含了多个 union 联合体。

unsigned long flags 这个成员包含了一些标志位,用于表示页面的状态,如是否可写、是否脏、是否被锁定等。
struct page {
unsigned long flags; /* 用于表示页面的状态,如是否可写、是否脏、是否被锁定等。
/*
* Five words (20/40 bytes) are available in this union.
* WARNING: bit 0 of the first word is used for PageTail(). That
* means the other users of this union MUST NOT use the bit to
* avoid collision and false-positive PageTail().
*/
union {
struct { /* Page cache and anonymous pages */
/**
* @lru: Pageout list, eg. active_list protected by
* pgdat->lru_lock. Sometimes used as a generic list
* by the page owner.
*/
struct list_head lru;
/* See page-flags.h for PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS */
struct address_space *mapping;
pgoff_t index; /* Our offset within mapping. */
/**
* @private: Mapping-private opaque data.
* Usually used for buffer_heads if PagePrivate.
* Used for swp_entry_t if PageSwapCache.
* Indicates order in the buddy system if PageBuddy.
*/
unsigned long private;
};
struct { /* page_pool used by netstack */
/**
* @dma_addr: might require a 64-bit value on
* 32-bit architectures.
*/
unsigned long dma_addr[2];
};
struct { /* slab, slob and slub */
union {
struct list_head slab_list;
struct { /* Partial pages */
struct page *next;
#ifdef CONFIG_64BIT
int pages; /* Nr of pages left */
int pobjects; /* Approximate count */
#else
short int pages;
short int pobjects;
#endif
};
};
struct kmem_cache *slab_cache; /* not slob */
/* Double-word boundary */
void *freelist; /* first free object */
union {
void *s_mem; /* slab: first object */
unsigned long counters; /* SLUB */
struct { /* SLUB */
unsigned inuse:16;
unsigned objects:15;
unsigned frozen:1;
};
};
};
struct { /* Tail pages of compound page */
unsigned long compound_head; /* Bit zero is set */
/* First tail page only */
unsigned char compound_dtor;
unsigned char compound_order;
atomic_t compound_mapcount;
unsigned int compound_nr; /* 1 << compound_order */
};
struct { /* Second tail page of compound page */
unsigned long _compound_pad_1; /* compound_head */
atomic_t hpage_pinned_refcount;
/* For both global and memcg */
struct list_head deferred_list;
};
struct { /* Page table pages */
unsigned long _pt_pad_1; /* compound_head */
pgtable_t pmd_huge_pte; /* protected by page->ptl */
unsigned long _pt_pad_2; /* mapping */
union {
struct mm_struct *pt_mm; /* x86 pgds only */
atomic_t pt_frag_refcount; /* powerpc */
};
#if ALLOC_SPLIT_PTLOCKS
spinlock_t *ptl;
#else
spinlock_t ptl;
#endif
};
struct { /* ZONE_DEVICE pages */
/** @pgmap: Points to the hosting device page map. */
struct dev_pagemap *pgmap;
void *zone_device_data;
/*
* ZONE_DEVICE private pages are counted as being
* mapped so the next 3 words hold the mapping, index,
* and private fields from the source anonymous or
* page cache page while the page is migrated to device
* private memory.
* ZONE_DEVICE MEMORY_DEVICE_FS_DAX pages also
* use the mapping, index, and private fields when
* pmem backed DAX files are mapped.
*/
};
/** @rcu_head: You can use this to free a page by RCU. */
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
};
union { /* This union is 4 bytes in size. */
/*
* If the page can be mapped to userspace, encodes the number
* of times this page is referenced by a page table.
*/
atomic_t _mapcount;
/*
* If the page is neither PageSlab nor mappable to userspace,
* the value stored here may help determine what this page
* is used for. See page-flags.h for a list of page types
* which are currently stored here.
*/
unsigned int page_type;
unsigned int active; /* SLAB */
int units; /* SLOB */
};
/* Usage count. *DO NOT USE DIRECTLY*. See page_ref.h */
atomic_t _refcount;
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG
union {
struct mem_cgroup *mem_cgroup;
struct obj_cgroup **obj_cgroups;
};
#endif
/*
* On machines where all RAM is mapped into kernel address space,
* we can simply calculate the virtual address. On machines with
* highmem some memory is mapped into kernel virtual memory
* dynamically, so we need a place to store that address.
* Note that this field could be 16 bits on x86 ... ;)
*
* Architectures with slow multiplication can define
* WANT_PAGE_VIRTUAL in asm/page.h
*/
#if defined(WANT_PAGE_VIRTUAL)
void *virtual; /* Kernel virtual address (NULL if
not kmapped, ie. highmem) */
#endif /* WANT_PAGE_VIRTUAL */
#ifdef LAST_CPUPID_NOT_IN_PAGE_FLAGS
int _last_cpupid;
#endif
} _struct_page_alignment;
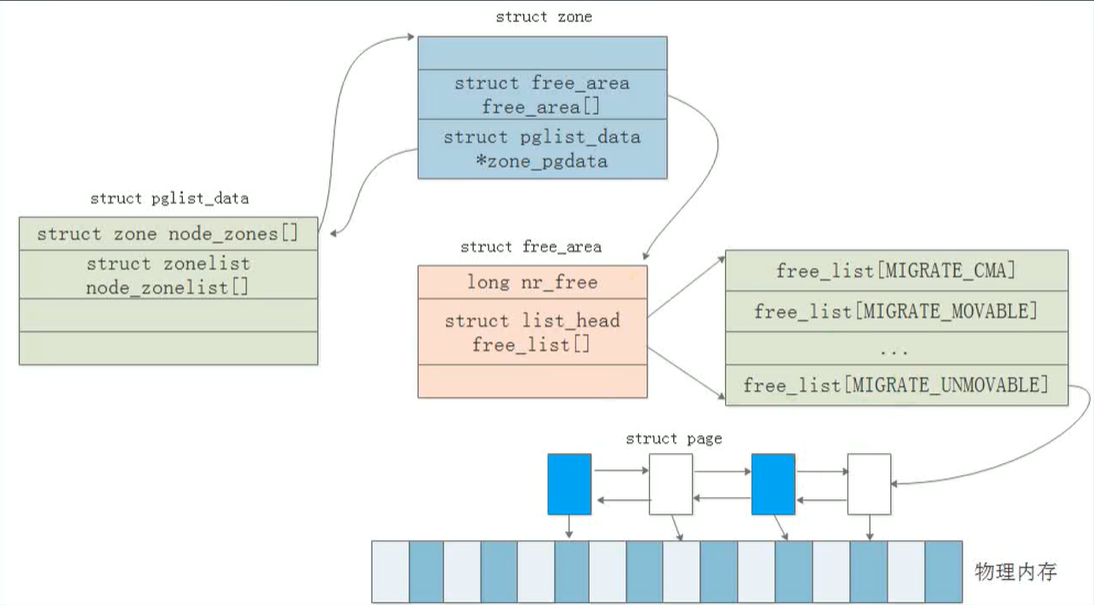
3.内存区域:struct zone
- 定义:mmzone.h
- 重要结构体成员:_watermark watermark_boost zone_start_pfn present_pages free_area
-
- zone_start_pfn 起始页帧号 present_pages 该zone当前有多少个页
- lowmem_reseve备用内存,怎么理解??
- 初始化:zone_sizes_init

zone_type
enum zone_type {
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
ZONE_DMA,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA32
ZONE_DMA32,
#endif
ZONE_NORMAL,
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
ZONE_HIGHMEM,
#endif
ZONE_MOVABLE,
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DEVICE
ZONE_DEVICE,
#endif
__MAX_NR_ZONES
};
struct zone
struct zone {
/* Read-mostly fields */
/* zone watermarks, access with *_wmark_pages(zone) macros */
unsigned long _watermark[NR_WMARK]; 表示该内存区域的水印阈值,用于内存管理策略。
unsigned long watermark_boost; 用于提高水印阈值的临时值。
unsigned long nr_reserved_highatomic; 表示为高原子操作预留的页面数量。
long lowmem_reserve[MAX_NR_ZONES]; 用于保留低内存区域的页面数量,以防上层内存充足而下层内存不足的情况。
#ifdef CONFIG_NEED_MULTIPLE_NODES
int node; 表示该内存区域所在的 NUMA 节点编号。
#endif
struct pglist_data *zone_pgdat; 用于描述整个内存区域的元数据。
struct per_cpu_pageset __percpu *pageset;
#ifndef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM
unsigned long *pageblock_flags; 用于标记页面块的标志,例如页面是否可移动等。
#endif /* CONFIG_SPARSEMEM */
/* zone_start_pfn == zone_start_paddr >> PAGE_SHIFT */
unsigned long zone_start_pfn; 示该内存区域起始的物理页号。
atomic_long_t managed_pages; 表示该内存区域中由 buddy 系统管理的页面数量。
unsigned long spanned_pages; 表示该内存区域覆盖的总页数,包括空洞区域。
unsigned long present_pages; 表示该内存区域存在的物理页数,不包括空洞区域。
const char *name;
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_ISOLATION
unsigned long nr_isolate_pageblock;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG
/* see spanned/present_pages for more description */
seqlock_t span_seqlock;
#endif
int initialized; 表示该内存区域是否已经初始化。
/* Write-intensive fields used from the page allocator */
ZONE_PADDING(_pad1_)
/* free areas of different sizes */
struct free_area free_area[MAX_ORDER]; 用于表示不同大小的空闲页面区域。
/* zone flags, see below */
unsigned long flags; 包含该内存区域的标志位,如是否支持 NUMA 等
/* Primarily protects free_area */
spinlock_t lock;
/* Write-intensive fields used by compaction and vmstats. */
ZONE_PADDING(_pad2_)
/*
* When free pages are below this point, additional steps are taken
* when reading the number of free pages to avoid per-cpu counter
* drift allowing watermarks to be breached
*/
unsigned long percpu_drift_mark;
#if defined CONFIG_COMPACTION || defined CONFIG_CMA
/* pfn where compaction free scanner should start */
unsigned long compact_cached_free_pfn;
/* pfn where compaction migration scanner should start */
unsigned long compact_cached_migrate_pfn[ASYNC_AND_SYNC];
unsigned long compact_init_migrate_pfn;
unsigned long compact_init_free_pfn;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPACTION
unsigned int compact_considered;
unsigned int compact_defer_shift;
int compact_order_failed;
#endif
#if defined CONFIG_COMPACTION || defined CONFIG_CMA
/* Set to true when the PG_migrate_skip bits should be cleared */
bool compact_blockskip_flush; 表示是否应清除 PG_migrate_skip 标志。
#endif
bool contiguous; 表示该内存区域是否支持连续内存分配。
ZONE_PADDING(_pad3_)
/* Zone statistics */
atomic_long_t vm_stat[NR_VM_ZONE_STAT_ITEMS]; 维护关于该内存区域的各种统计信息。
atomic_long_t vm_numa_stat[NR_VM_NUMA_STAT_ITEMS]; 维护关于该内存区域的 NUMA 相关统计信息。
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
4.内存节点:node(struct pglist_data)
- 内存模型:uma numa
- struct pglist_data 表示node中的内存资源
- 定义:include/linux/mmzone.h
- 结构体:struct pglist_data
- node_data数组:保存所有node的的pglist_data结构体

物理内存管理架构:
- 在numa系统中,每个node节点将有一个pglist_data结构体去描述它。如果在uma上,这里将只有一个pglist_data.
- 接下来就是zone:一般分为dma区,nomal区和highmem区,当然这里是不一定的。
- zone区通过struct zone结构体描述,unsigned long zone_start_pfn;描述具体page页帧号。