0 前言
curl是一款综合性网络传输工具,既可以上传也可以下载,支持HTTP、HTTPS、FTP等30余种常见协议。
Linux和Windows都提供了curl命令。
D:\>curl --help
Usage: curl [options...] <url>
-d, --data <data> HTTP POST data
-f, --fail Fail fast with no output on HTTP errors
-h, --help <category> Get help for commands
-i, --include Include protocol response headers in the output
-o, --output <file> Write to file instead of stdout
-O, --remote-name Write output to a file named as the remote file
-s, --silent Silent mode
-T, --upload-file <file> Transfer local FILE to destination
-u, --user <user:password> Server user and password
-A, --user-agent <name> Send User-Agent <name> to server
-v, --verbose Make the operation more talkative
-V, --version Show version number and quit
This is not the full help, this menu is stripped into categories.
Use "--help category" to get an overview of all categories.
For all options use the manual or "--help all".
D:\>curl --help category
Usage: curl [options...] <url>
auth Different types of authentication methods
connection Low level networking operations
curl The command line tool itself
dns General DNS options
file FILE protocol options
ftp FTP protocol options
http HTTP and HTTPS protocol options
imap IMAP protocol options
misc Options that don't fit into any other category
output Filesystem output
pop3 POP3 protocol options
post HTTP Post specific options
proxy All options related to proxies
scp SCP protocol options
sftp SFTP protocol options
smtp SMTP protocol options
ssh SSH protocol options
telnet TELNET protocol options
tftp TFTP protocol options
tls All TLS/SSL related options
upload All options for uploads
verbose Options related to any kind of command line output of curl
D:\>相对于Windows 系统中的curl,Linux下的curl命令选项超多,在学习笔记68和69中,我们列举了该命令的部分实例,今天继续通过实例来研究curl命令的功能和用法。
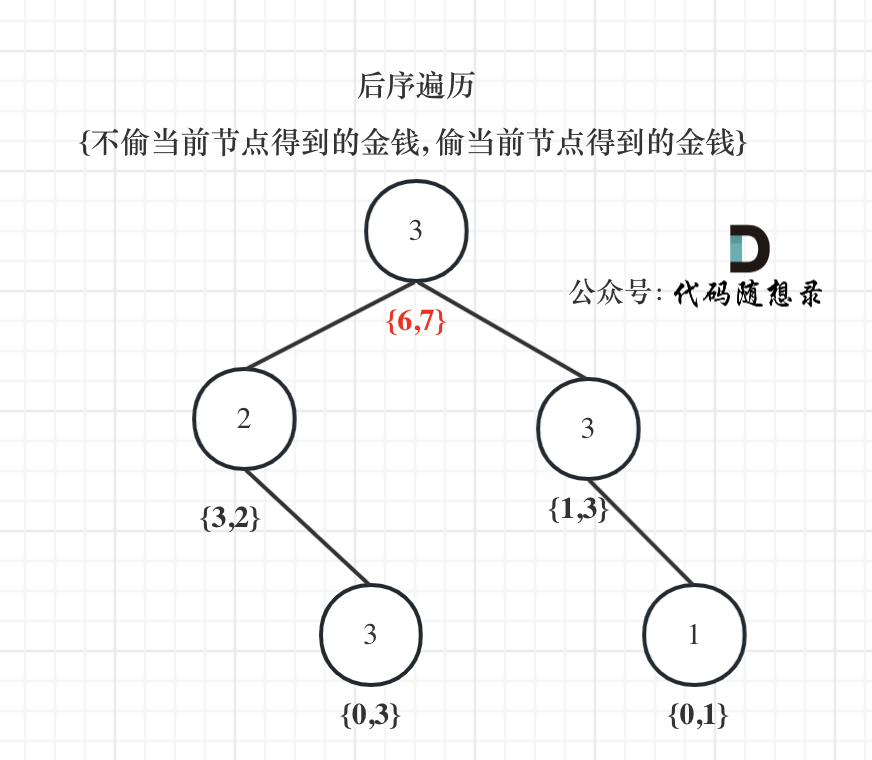
1 curl命令应用实例
1.1 只查看将把header(头部信息)写入指定文件:curl -I 统一资源定位符
我们可以使用命令 curl -i 网址 来显示header信息和资源内容,如果我们只想想看header信息,可以使用-I选项。
1.1.1 查看g.cn的header信息
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -I g.cn
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://google.cn/
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Server: sffe
Content-Length: 215
X-XSS-Protection: 0
Date: Mon, 12 Aug 2024 14:10:09 GMT
Expires: Mon, 12 Aug 2024 14:40:09 GMT
Cache-Control: public, max-age=1800
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Age: 1673
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] 
1.1.2 查看网络文件 https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 的header信息
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -I https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: image/png
Content-Length: 46323
Connection: keep-alive
Server: OBS
ETag: "1da8da89c801747e0d8427b9ac0461e1"
Date: Fri, 09 Aug 2024 11:23:54 GMT
Last-Modified: Thu, 01 Aug 2024 05:07:57 GMT
Expires: Sun, 08 Sep 2024 11:23:54 GMT
Accept-Ranges: bytes
x-obs-request-id: 0000019136E184B5EBE8705BEFA1430C
Content-Disposition: inline
x-obs-tagging-count: 0
x-obs-id-2: 32AAAQAAEAABAAAQAAEAABAAAQAAEAABCS3bAzJG6eJ1F/gKjkvPPj8zfb3tQv+l
x-link-via: bjct01:443;xianymp09:80;
X-Cache-Status: HIT from KS-CLOUD-XIANY-MP-09-04
X-Cache-Status: HIT from KS-CLOUD-BJ-CT-01-02
X-Cdn-Request-ID: 4edfdd9d8d4ff2cebf5e274fa0ae5a4b

1.2 将把header(头部信息)写入指定文件:curl -D 文件名 统一资源定位符
我们可以使用命令 curl -I 网址 来显示header信息,如果我们想把header信息保存到文件中,可以使用-D选项。
例如,我们要把http://g.cn的头部信息写入当前目录下的文件 h.txt中。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -D h.txt http://g.cn
<HTML><HEAD><meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<TITLE>301 Moved</TITLE></HEAD><BODY>
<H1>301 Moved</H1>
The document has moved
<A HREF="https://google.cn/">here</A>.
</BODY></HTML>
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] ls
Code h.txt
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] cat h.txt
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://google.cn/
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Server: sffe
Content-Length: 215
X-XSS-Protection: 0
Date: Mon, 12 Aug 2024 14:21:12 GMT
Expires: Mon, 12 Aug 2024 14:51:12 GMT
Cache-Control: public, max-age=1800
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Age: 530
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] 
首先,我们使用命令 curl -D h.txt http://g.cn 来将header信息保存到当前目录下的文件h.txt中
然后,我们使用ls命令查看当前目录下的内容,可以看到在当前目录下,有一个目录code,还有一个文件h.txt。
接着,我们使用 cat命令查看文件h.txt的内容,正是g.cn的header信息。
1.3 下载文件时保存原始时间:curl -R -o 文件名 统一资源定位符
通常我们将网络中的文件下载保存到本地,那么本地的文件的时间会是实际保存时间,如果我们希望下载到本地的文件仍然保存网络中远程文件的原始时间,那么可以使用-R选项。
我们以下载1.1.2 中的网络文件 https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png为例。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -o 1.png https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 46323 100 46323 0 0 180k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 180k
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] ls -l --full-time 1.png
-rw-rw-r-- 1 csdn csdn 46323 2024-08-12 23:01:08.213754613 +0800 1.png
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -R -o 2.png https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 46323 100 46323 0 0 204k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 204k
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] ls -l --full-time 2.png
-rw-rw-r-- 1 csdn csdn 46323 2024-08-01 13:07:57.000000000 +0800 2.png
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] 
首先,我们使用命令curl -o 1.png https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 将 远程文件https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 下载为本地文件1.png
然后我们使用命令 ls -l --full-time 1.png 查看文件1.png的时间信息,即:
2024-08-12 23:01:08.213754613 +0800
在 1.1.2 中,我们可以看到网络文件 https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 的时间信息,即:
Thu, 01 Aug 2024 05:07:57 GMT
可以看到, 本地文件1.png的时间信息与 网络文件 https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png是不同的。
接着,我们使用命令 curl -R -o 2.png https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 将 远程文件https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 下载为本地文件2.png
随后,我们使用命令 ls -l --full-time 2.png 查看文件2.png的时间信息,即:
2024-08-01 13:07:57.000000000 +0800
可以看到,这显然不是文件写入磁盘的时间。
这是由于我们在命令curl -R -o 2.png https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 中一了 -R选项,所以本地文件2.png的与 网络文件 https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f2734cc485764a9fa75c46b697f40081.png 的时间信息都是2024-08-01 。
1.4 查看邮件:curl -u 用户名:密码 imap服务器url
我们以imap://mail.163.com为例。
在命令行上直接输入密码可能并不安全,所以我们也可以只在命令行上输入用户名,然后再根据提示输入密码。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -u purpleendurer imap://mail.163.com
Enter host password for user 'purpleendurer':
curl: (7) Failed connect to mail.163.com:143; Connection timed out
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] 
1.5 查阅使用手册:curl -M | more
curl命令的帮助信息还是比较简略的,我们还可以使用 -M 选项查阅使用手册,获取更详细的说明。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ] curl -M | more
_ _ ____ _
Project ___| | | | _ \| |
/ __| | | | |_) | |
| (__| |_| | _ <| |___
\___|\___/|_| \_\_____|
NAME
curl - transfer a URL
SYNOPSIS
curl [options] [URL...]
DESCRIPTION
curl is a tool to transfer data from or to a server, using one of the
supported protocols (DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, GOPHER, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP,
IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, SMTPS,
TELNET and TFTP). The command is designed to work without user inter-
action.
curl offers a busload of useful tricks like proxy support, user authen-
tication, FTP upload, HTTP post, SSL connections, cookies, file trans-
fer resume, Metalink, and more. As you will see below, the number of
features will make your head spin!
curl is powered by libcurl for all transfer-related features. See
libcurl(3) for details.
URL
The URL syntax is protocol-dependent. You'll find a detailed descrip-
tion in RFC 3986.
You can specify multiple URLs or parts of URLs by writing part sets
within braces as in:
http://site.{one,two,three}.com
--More--



![[Megagon Labs] Annotating Columns with Pre-trained Language Models](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/dd7f7081717b4cb094a6fb563cfd0a6d.png)





![[C++][opencv]基于opencv实现photoshop算法可选颜色调整](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e99672cffc4f4999b41ebd88fe91636b.gif)