openblas提供的sgemm有两种方式,一种是通过cblas,另一种是直接声明并调用 sgemm_
其中,cblas方式是更正规调用方法;
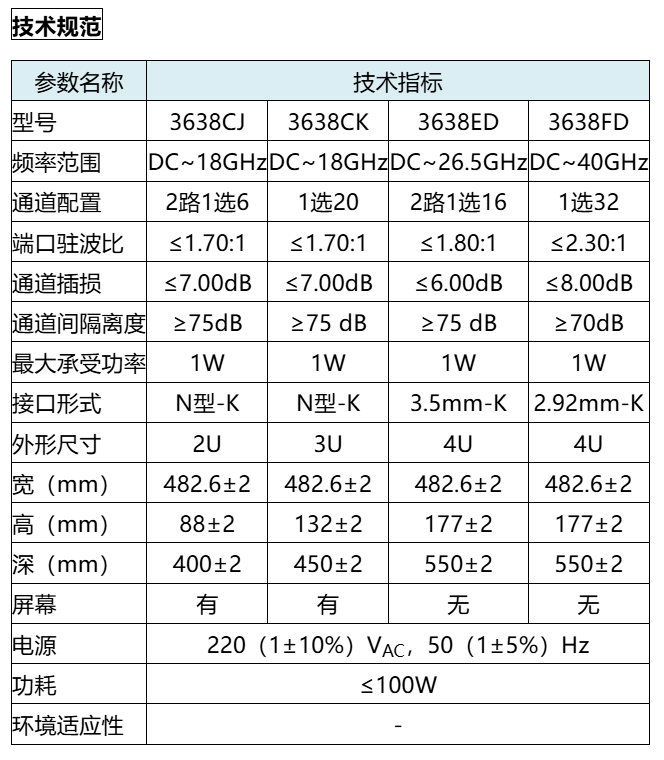
1,调用openblas的 sgemm 的两种方式
1.1 c语言程序中使用 sgemm
hello_sgemm.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
//#define CBLAS_USE 1
#ifdef CBLAS_USE
#include "cblas.h"
#else
//extern "C"{
void sgemm_( char * const transpa, char * const transpb, int *m, int *n,
int *k, float *alpha, float *a, int *lda, float *b, int *ldb,
float *beta, float *c, int *ldc );
//}
#endif
void init_matrix(int M, int N, float* A, int lda, int seed)
{
srand(seed);
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
for(int j=0; j<N; j++){
A[i + j*lda] = (float)rand()/RAND_MAX;
}
}
}
void print_matrix(int M, int N, float* A, int lda)
{
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
for(int j=0; j<N; j++){
printf(" %7.4f ", A[i + j*lda]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int M = 3;
int N = 3;
int K = 3;
float* A = NULL;
float* B = NULL;
float* C = NULL;
int lda = M;
int ldb = K;
int ldc = M;
A = (float*)malloc(lda*K* sizeof(float));
B = (float*)malloc(ldb*N* sizeof(float));
C = (float*)malloc(ldc*N* sizeof(float));
init_matrix(M, K, A, lda, 2023); printf("\nA =\n"); print_matrix(M, K, A, lda);
init_matrix(K, N, B, ldb, 2024); printf("\nB =\n"); print_matrix(K, N, B, ldb);
init_matrix(M, N, C, ldc, 2025); printf("\nC =\n"); print_matrix(M, N, C, ldc);
float alpha = 1.0f;
float beta = 0.0f;
#ifdef CBLAS_USE
cblas_sgemm(CblasColMajor, CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, M, N, K, 1.0, A, lda, B, ldb, 0.0, C, ldc);
printf("C = alpha*A*B + beta*C =cblas_sgemm()=\n"); print_matrix(M, N, C, ldc);
#else
sgemm_("N", "N", &M, &N, &K, &alpha, A, &lda, B, &ldb, &beta, C, &ldc);
printf("C = alpha*A*B + beta*C = sgemm_()=\n"); print_matrix(M, N, C, ldc);
#endif
return 0;
}
运行效果:
$ gcc -DCBLAS_USE hello_sgemm.c -L ../tdd/third-party/openblas/local/lib/ -lopenblas -o hello_sgemm_c
$ gcc hello_sgemm.c -L ../tdd/third-party/openblas/local/lib/ -lopenblas -o hello_sgemm_c

可见调用 sgemm_() 与调用 cblas_sgemm() 的结果相同;
需要注意sgemm_()函数的声明方式,参数全部都是指针:
void sgemm_( char * const transpa, char * const transpb, int *m, int *n,
int *k, float *alpha, float *a, int *lda, float *b, int *ldb,
float *beta, float *c, int *ldc );
1.2 cpp 语言程序中调用 sgemm
相较于 c 语言中,cpp 程序中增加了 extern "C"{ 修饰;
否则编译无法通过,由于c++的特性。
hello_sgemm.cpp
#if CBLAS_USE
#include "cblas.h"
#else
extern "C"{
void sgemm_( char * const transpa, char * const transpb, int *m, int *n,
int *k, float *alpha, float *a, int *lda, float *b, int *ldb,
float *beta, float *c, int *ldc );
}
#endif
2. cpp 中的sgemm_声明为何需要 extern "C"
extern "C" 的作用:
在 C++ 源代码文件中,使用 extern "C" 的作用是告诉编译器按照 C 语言的方式对函数进行链接,而不是 C++ 的方式。这在与其他语言或库进行交互时非常有用,特别是在 C++ 代码中调用 C 语言编写的函数时。
当您使用 extern "C" 修饰一个函数声明时,编译器会按照 C 语言的命名约定来生成函数符号,这样可以确保 C++ 代码和 C 代码之间的函数调用能够正确链接。在 C++ 中,函数名可能会经过名称修饰(name mangling)以支持函数重载和其他特性,比如在函数末尾加上参数类型缩写,而 C 语言没有这种面向对象的语法概念和需求。
如下图可见,
print_matrix函数的名字,在 cpp中被加了前缀和后缀,而 c语言文件中,函数名字依然为
print_matrix