Title
题目
Improving breast cancer diagnostics with deep learning for MRI
用深度学习改进乳腺癌MRI诊断
01
文献速递介绍
乳腺磁共振成像(MRI)是一种检测乳腺癌的高度敏感的方式,报告的敏感性超过80%。传统上,其在筛查中的使用仅限于高风险患者。新的证据支持在中等风险和平均风险女性中进行筛查MRI的作用。诊断性MRI对于解决问题和新近确诊乳腺癌患者等其他适应症也很有用。随着接受乳腺MRI的患者数量不断增加,保持高特异性和阳性预测值(PPV)以尽量减少不必要的活检和后续建议变得非常重要。在针对中等风险和平均风险女性的筛查MRI研究中,活检推荐的PPV范围为19.6%至35.7%。这意味着每进行一次恶性结果的活检,就要进行两到四次良性结果的活检。因此,需要开发经过良好测试的工具来提高MRI的性能并提升护理质量。此外,还需要开发考虑临床医生或患者偏好的工具,例如在决定是否进行活检时。
Abstract
摘要
动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)在检测乳腺癌方面具有很高的敏感性,但往往导致不必要的活检和患者的进一步检查。我们使用深度学习(DL)系统来提高乳腺癌诊断的整体准确性,并个性化管理接受DCE-MRI检查的患者。在内部测试集中(n = 3936次检查),我们的系统在受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUROC)上达到了0.92(95% CI:0.92至0.93)。在一项回顾性读片研究中,五位持证乳腺放射科医师与DL系统之间没有统计学上显著差异(P = 0.19)(DL系统的平均ΔAUROC值高出+0.04)。当放射科医师的预测与DL系统的预测平均值结合时,放射科医师的表现有所提高【平均ΔAUPRC(精确度-召回曲线下面积)提高了+0.07】。我们使用来自波兰和美国的多个数据集证明了DL系统的通用性。在波兰数据集上的另一项读片研究表明,DL系统对分布变化的鲁棒性与放射科医师相当。在亚组分析中,我们观察到在不同的癌症亚型和患者人口统计学中结果一致。通过决策曲线分析,我们显示DL系统可以在临床相关风险阈值范围内减少不必要的活检。这可以使高达20%的BI-RADS 4类病变患者避免活检,且结果为良性。最后,我们进行了错误分析,研究DL预测大多数错误的情况。这项探索性工作为基于DL的乳腺MRI模型的部署和前瞻性分析奠定了基础。
Method
方法
The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate a DL system for predicting the probability of breast cancer in DCE-MRI. To do so, we collected a dataset of 21,537 DCE-MRI examinations from the NYU Langone Health sites. We used it to train, validate, and test the system. In addition, we used three independent, international datasets for external validation of our model. The DL system is based on a modified 3D-ResNet18 architecture, which uses 3D convolutions to learn spatiotemporal features. Our training procedure used elements of transfer learning, multitask learning, and both train-time augmentation and test-time augmentation (TTA). The final DL system is an ensemble of the most accurate 20 models selected from a larger pool of models trained with different hyperparameters. Beyond analyzing the system’s standalone performance, we simulated a “hybrid performance” by averaging radiologists’ and system’s predictions. Last, we used DCA methodology to demonstrate that system’s predictions can accurately identify low-risk BI-RADS category 4 lesions and help in avoiding unnecessary biopsies. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board, and the informed consent requirement was waived.
本研究的目的是开发和评估一个用于预测DCE-MRI中乳腺癌概率的深度学习(DL)系统。为此,我们收集了来自NYU Langone Health站点的21,537次DCE-MRI检查数据,用于训练、验证和测试系统。此外,我们使用了三个独立的国际数据集对我们的模型进行外部验证。DL系统基于修改后的3D-ResNet18架构,使用3D卷积来学习时空特征。我们的训练过程采用了迁移学习、多任务学习、训练时增强和测试时增强(TTA)等元素。最终的DL系统是从使用不同超参数训练的大量模型中选出的最准确的20个模型的集成。除了分析系统的独立性能外,我们还通过平均放射科医生和系统的预测来模拟“混合性能”。最后,我们使用决策曲线分析(DCA)方法,证明系统的预测可以准确识别低风险的BI-RADS 4类病变,并帮助避免不必要的活检。该研究获得了机构审查委员会的批准,并豁免了知情同意要求。
Results
结果
The DL system described in this study (Fig. 1) was trained in a supervised manner, that is, the machine learning model was provided with many examples of inputs and correct outputs. The inputs of this system were DCE-MRI pre- and postcontrast sequences, all stored as three-dimensional (3D) volumes. This approach mimics clinical practice, in which radiologists evaluate changes in contrast enhancement in breast to correctly identify suspicious areas. DCE-MRI volumes are passed through the model, which generates predictions of the breast-level probability of malignancy (POM). That is, for each of the patient’s breasts, the system produces a number in a range between 0 and 1. The underlying neural network of the system performs 3D convolutions, which are mathematical operations that ultimately allow it to extract spatiotemporal features of the inputs.
本研究中描述的深度学习(DL)系统(图1)采用监督学习的方式进行训练,即为机器学习模型提供了大量输入和正确输出的示例。该系统的输入是DCE-MRI对比增强前后的序列,所有序列均存储为三维(3D)体积。这种方法模拟了临床实践中放射科医生评估乳腺中对比增强变化以正确识别可疑区域的过程。DCE-MRI体积数据通过模型处理,模型生成乳腺层面的恶性概率(POM)预测。也就是说,对于每位患者的每个乳腺,系统会生成一个介于0和1之间的数值。该系统的底层神经网络执行3D卷积,这是一种数学运算,最终使其能够提取输入的时空特征。
Figure
图
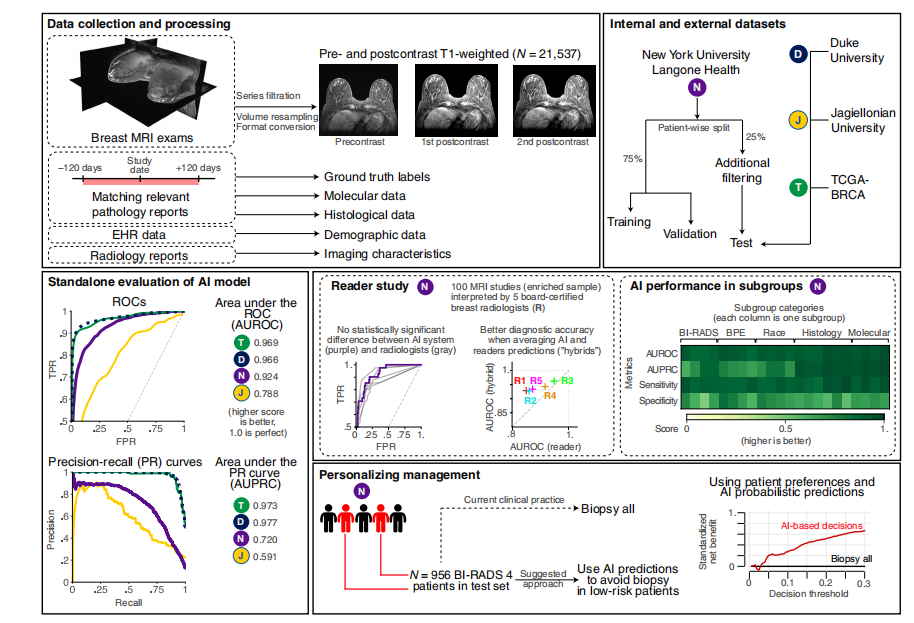
Fig. 1. Overview of the study. In this work, we trained and evaluated a DL system based on deep neural networks that predict the probability of breast cancer in DCE-MRI examinations. Data collection and processing: To build the system, we collected 21,537 DCE-MRI imaging exams, consisting of one precontrast and two postcontrast T1-weighted fat-saturated sequences. We also collected diagnosis information from breast pathology reports to generate ground truth labels. Auxiliary information on patient demographics, tumor histological data, and radiological features enabled extensive subgroup analysis. Internal and external datasets: The internal dataset was collected from the NYU Langone Health system and divided into training (n = 14,198), validation (n = 3403), and test (n = 3936) subsets. We applied additional filtering on the test subset of NYU dataset to reduce potential label noise. To evaluate our system on data that the model had not seen before, we acquired three external datasets from Duke University (United States; n = 922), JU (Poland; n = 394), and TCGA-BRCA (United States; n = 131). Standalone evaluation of DL model: Using the NYU Langone training data subset, we trained deep neural networks to predict the probability of malignancy in MRI examinations. Our model was validated using standard metrics area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC). The plot presents ROC curves for all datasets. Reader study: To compare the performance of DL system to experts, five readers and the DL system interpreted 100 random MRI examinations and provided their predictions of probability of breast cancer presence in MRI examinations. We also simulated combining DL and radiologists’ predictions by averaging them into a “hybrid” prediction. DL performance in subgroups: To confirm that our model works well in all subgroups, we performed an analysis of the model’s performance across various subsets (with respect to demographic data, imaging features, and histological features). The grid subplot presents DL model performance in each subgroup (columns) across four metrics (rows). Detailed results are presented in the “Subgroup analyses” section. Personalizing management: We simulated a scenario that assessed whether the model could correctly identify low-risk patients with BI-RADS 4 lesions who might avoid an unnecessary biopsy (that is, a biopsy yielding benign results). This simulation included 956 patients from the NYU dataset and used a decision curve analysis (DCA) methodology. AI, artificial intelligence; EHR, electronic health record; FPR, false positive rate; TPR, true positive rate.
图1. 研究概述。在本研究中,我们训练并评估了一个基于深度神经网络的DL系统,该系统预测DCE-MRI检查中乳腺癌的概率。数据收集与处理:为了构建该系统,我们收集了21,537次DCE-MRI成像检查,包括一个对比增强前和两个对比增强后T1加权脂肪抑制序列。我们还从乳腺病理报告中收集诊断信息以生成真实标签。患者人口统计学信息、肿瘤组织学数据和放射学特征的辅助信息使得广泛的亚组分析成为可能。内部和外部数据集:内部数据集来自NYU Langone Health系统,并被分为训练集(n = 14,198)、验证集(n = 3403)和测试集(n = 3936)。我们对NYU数据集的测试集进行了额外筛选,以减少潜在的标签噪声。为了评估系统在模型未见过的数据上的表现,我们获取了来自杜克大学(美国;n = 922)、JU(波兰;n = 394)和TCGA-BRCA(美国;n = 131)的三个外部数据集。DL模型的独立评估:使用NYU Langone训练数据子集,我们训练了深度神经网络以预测MRI检查中的恶性概率。我们的模型使用标准指标受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUROC)和精确-召回曲线下面积(AUPRC)进行验证。该图展示了所有数据集的ROC曲线。读片研究:为了比较DL系统与专家的表现,五位读片医师和DL系统解读了100次随机MRI检查,并提供了他们对MRI检查中乳腺癌存在概率的预测。我们还通过将DL和放射科医生的预测平均化为“混合”预测来模拟结合DL和放射科医生预测的情况。DL在各亚组中的表现:为了确认我们的模型在所有亚组中都表现良好,我们对模型在不同子集(关于人口统计数据、成像特征和组织学特征)中的表现进行了分析。网格子图展示了DL模型在各亚组(列)中四个指标(行)中的表现。详细结果在“亚组分析”部分中呈现。个性化管理:我们模拟了一个评估模型能否正确识别具有BI-RADS 4类病变且可能避免不必要活检(即活检结果为良性)的低风险患者的情景。该模拟包括来自NYU数据集的956名患者,并使用决策曲线分析(DCA)方法。AI,人工智能;EHR,电子健康记录;FPR,假阳性率;TPR,真阳性率。
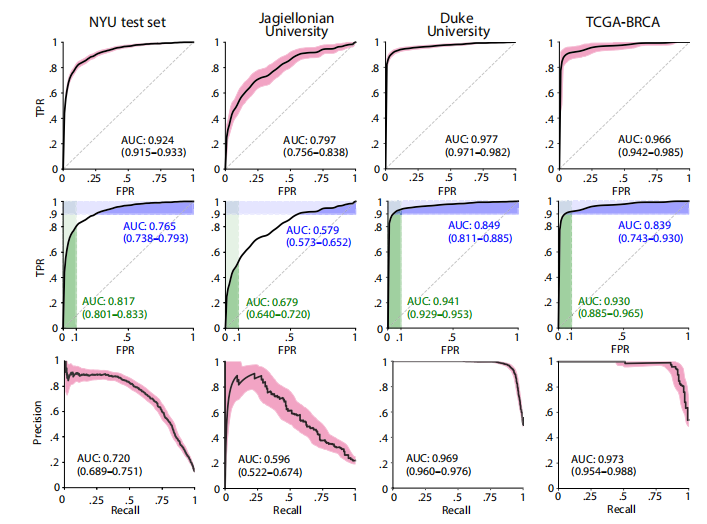
Fig. 2. DL system performance on all internal and external test sets. (Top) ROC curves with 95% CIs calculated with bootstrapping. (Middle) ROC curves with partial AUC (pAUC). The AUCs in green represent the pAUC for specificity of 90 to 100%. The AUCs in blue represent the pAUC for sensitivity of 90 to 100%. (Bottom) PRCs with 95% CIs.
图2. DL系统在所有内部和外部测试集上的表现。(顶部)通过重复抽样法计算的具有95%置信区间的ROC曲线。(中部)具有部分AUC(pAUC)的ROC曲线。绿色表示90%到100%特异性的pAUC,蓝色表示90%到100%敏感性的pAUC。(底部)具有95%置信区间的PRC曲线。
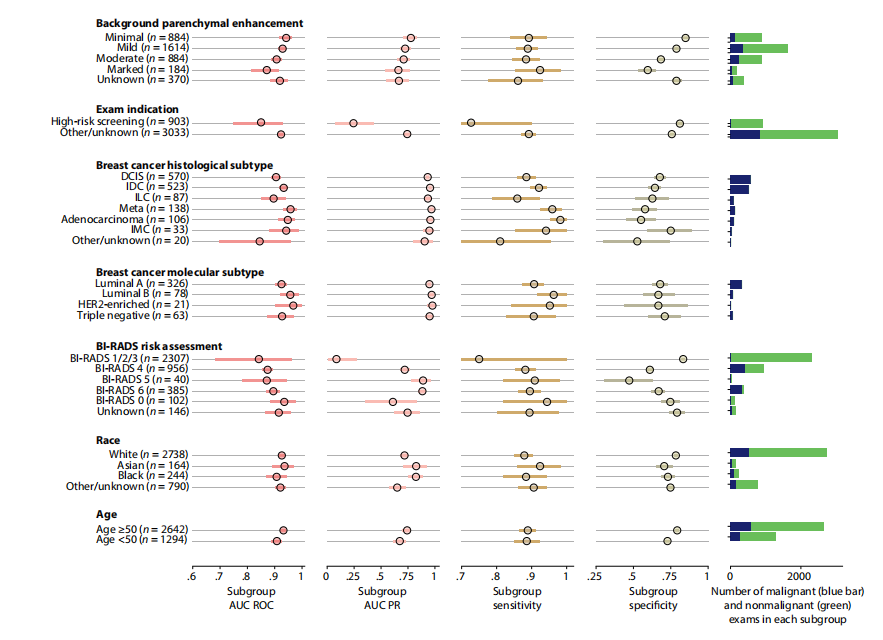
Fig. 3. System performance in key subgroups on the internal test set. Each subgroup was evaluated using four metrics: area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC ROC), area under the precision-recall curve (AUC PR), sensitivity, and specificity. Blue (malignant cases) and green (nonmalignant cases) bars to the right represent the number of examinations in each subgroup. Values for all subgroups and metrics are presented with 95% CIs calculated by bootstrap (N = 2000 replicates). To calculate the sensitivity and specificity, we selected a decision threshold such that the DL system’s sensitivity closely matches the average reader sensitivity. Full numerical values for each subgroup are available in table S4. Examinations with BI-RADS categories 1, 2, and 3 were aggregated because there were no MRI exams associated with malignant diagnoses in BI-RADS 1 and 2 categories; thus, AUROC would be undefined in those subgroups. HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; IDC, invasive ductal carcinoma; ILC, invasive lobular carcinoma; IMC, invasive mammary carcinoma.
图3. 内部测试集中关键子组的系统性能。每个子组使用四个指标进行评估:受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC ROC)、精确-召回曲线下面积(AUC PR)、敏感性和特异性。右侧的蓝色(恶性病例)和绿色(非恶性病例)条表示每个子组中的检查次数。所有子组和指标的数值均以通过重复抽样法计算的95%置信区间表示(N = 2000次重复)。为了计算敏感性和特异性,我们选择了一个决策阈值,使DL系统的敏感性与平均读片医师的敏感性相匹配。每个子组的完整数值见表S4。由于在BI-RADS 1和2类中没有与恶性诊断相关的MRI检查,因此将BI-RADS 1、2和3类的检查合并,因为在这些子组中AUROC将无法定义。HER2,人类表皮生长因子受体2;DCIS,导管原位癌;IDC,浸润性导管癌;ILC,浸润性小叶癌;IMC,浸润性乳腺癌。
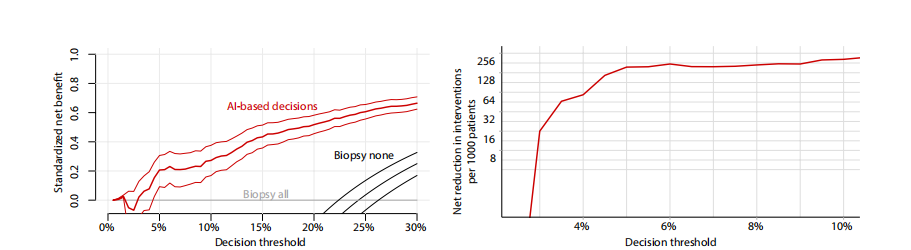
Fig. 4. Results of the DCA support using the DL system for making diagnostic decisions in low-risk patients with BI-RADS 4 lesions. (Left) Standardized net benefit values (y axis) were higher when decisions are made based on the DL system’s predictions (red curve) compared to the default biopsy-all approach (gray curve at x = 0) across all relevant decision thresholds (x axis). The black curve is a biopsy-none approach. The net benefit curve is presented with 95% bootstrapped CIs (N = 2000 replicates). (Right) Net interventions avoided per 1000 patients with BI-RADS 4 findings (y axis). Benefits were highest when decision threshold (x axis) was above 3%.
图4. 使用DL系统在低风险患者中针对BI-RADS 4病变做出诊断决策的DCA支持结果。(左)在所有相关决策阈值(x轴)范围内,当基于DL系统的预测做出决策时(红色曲线),标准化净效益值(y轴)比默认的全部活检方法(x = 0的灰色曲线)更高。黑色曲线表示不进行活检的方法。净效益曲线以95%的重复抽样置信区间(N = 2000次重复)表示。(右)每1000名BI-RADS 4患者中避免的净干预数(y轴)。当决策阈值(x轴)高于3%时,效益最高。
Table
表
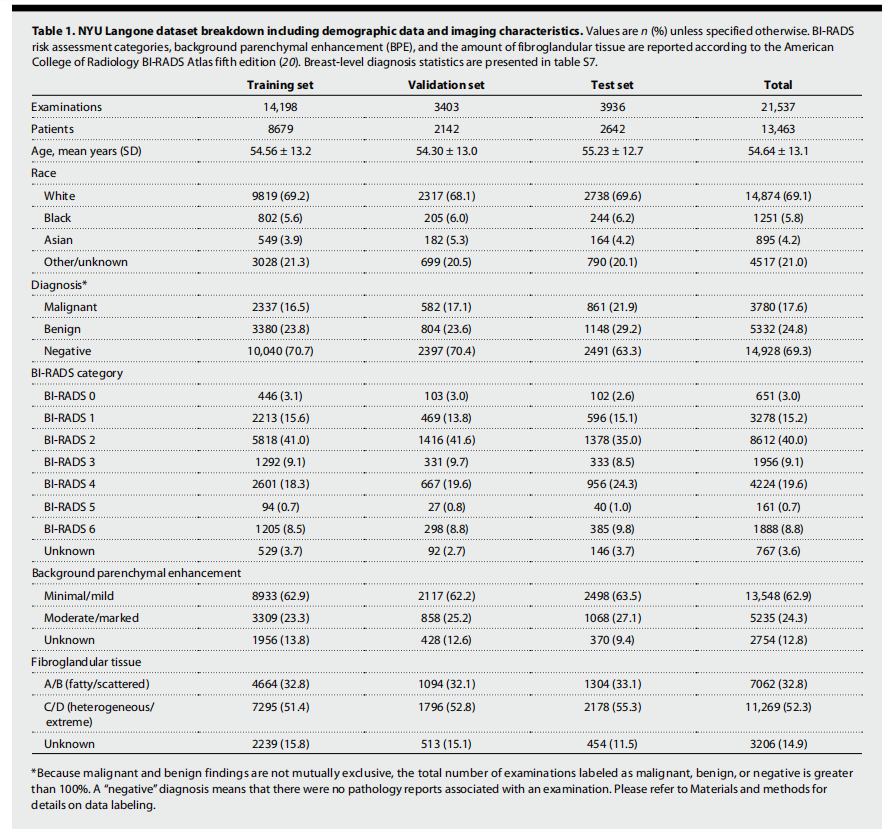
Table 1. NYU Langone dataset breakdown including demographic data and imaging characteristics. Values are n (%) unless specified otherwise. BI-RADS risk assessment categories, background parenchymal enhancement (BPE), and the amount of fibroglandular tissue are reported according to the American College of Radiology BI-RADS Atlas fifth edition (20). Breast-level diagnosis statistics are presented in table S7.
表1. NYU Langone数据集的细分,包括人口统计数据和成像特征。除非另有说明,数值以n (%)表示。BI-RADS风险评估类别、背景实质增强(BPE)和纤维腺体组织的数量根据美国放射学会BI-RADS Atlas第五版报告(20)。乳腺层级诊断统计数据见表S7。
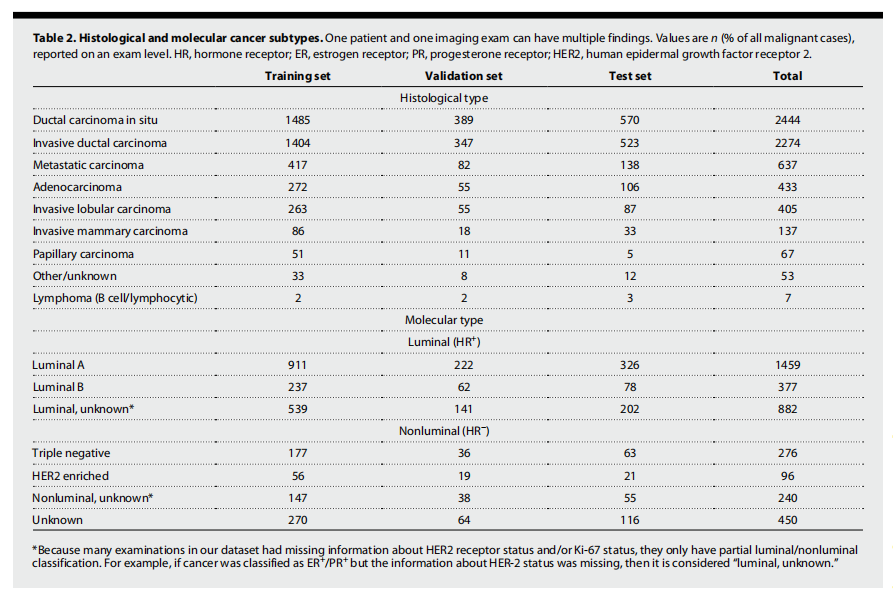
Table 2. Histological and molecular cancer subtypes. One patient and one imaging exam can have multiple findings. Values are n (% of all malignant cases), reported on an exam level. HR, hormone receptor; ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2.
表2. 组织学和分子癌症亚型。一个患者和一个成像检查可以有多种发现。数值以n(占所有恶性病例的百分比)表示,按检查级别报告。HR,激素受体;ER,雌激素受体;PR,孕激素受体;HER2,人类表皮生长因子受体2。
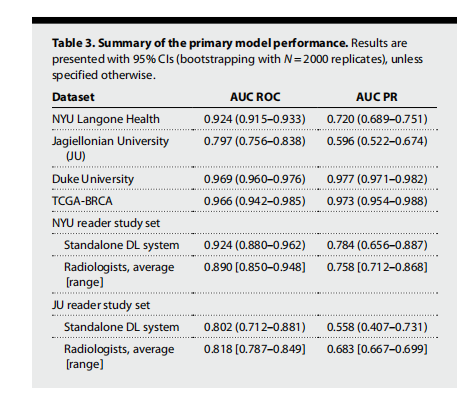
Table 3. Summary of the primary model performance. Results are presented with 95% CIs (bootstrapping with N = 2000 replicates), unless specified otherwise.
表3. 主要模型性能总结。除非另有说明,结果以95%置信区间(通过N = 2000次重复抽样法计算)表示。