阅读提示:本篇文章的代码为在普通GAN代码上实现人脸图片生成的修改,文章内容仅包含修改内容,全部代码讲解需结合下面的文章阅读。
相关资料链接为:使用PyTorch构建GAN生成对抗
本次训练代码使用了本地GPU计算。
1 CelebADataset类的修改
原则上这一类不需要修改,但为了提升模型运行速度,可以对图片周边适当裁剪,保留五官等重要内容。
# 设置裁剪功能(辅助函数)
def crop_centre(img, new_width, new_height):
height, width, _ = img.shape
startx = width//2 - new_width//2
starty = height//2 - new_height//2
return img[ starty:starty + new_height, startx:startx + new_width, :]
上面这个函数可以用来从图像的中心裁剪。该函数接收三个参数:
- img:原始图像,需要是 numpy 数组形式
- new_width:裁剪后图像的新宽度
- new_height:裁剪后图像的新高度
该函数通过计算原始图像的中心位置,以及所需裁剪图像的起始位置,从而在 numpy 数组上实现裁剪。最后,函数返回裁剪后的图像。
有了这个函数后,可以在类中预置对图像的裁剪功能,需要对类的__getitem__方法和plot_image方法进行优化。
class CelebADataset(Dataset):
def __getitem__(self, index):
if index >= len(self.dataset):
raise IndexError()
img = numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index) + '.jpg'])
img = crop_centre(img, 128, 128)
return torch.cuda.FloatTensor(img).permute(2,0,1).view(1,3,128,128) / 255.0
def plot_image(self, index):
img = numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index)+'.jpg'])
img = crop_centre(img, 128, 128)
plt.imshow(img, interpolation='nearest')
2 鉴别器类的修改
鉴别器的网络结构是卷积GAN需要重点修改的地方。此次的卷积GAN设置了3个卷积层和1个全连接层。
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Conv2d(256, 3, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
View(3*10*10),
nn.Linear(3*10*10, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
经过裁剪的图片的小为128*128;
第一个卷积层使用了256个卷积核,每个卷积核大小为8,步长为2。这一卷积层将会输出256个特征图,特征图的大小为
128
−
8
2
+
1
\frac{128-8}{2}+1
2128−8+1 ,即61*61;
第二个卷积层使用了256个卷积核,每个卷积核大小为8,步长为2。这一卷积层将会输出256个特征图,特征图的大小为
61
−
8
2
+
1
\frac{61-8}{2}+1
261−8+1 ,即27*27;
第二个卷积层使用了3个卷积核,每个卷积核大小为8,步长为2。这一卷积层将会输出3个特征图,特征图的大小为
27
−
8
2
+
1
\frac{27-8}{2}+1
227−8+1 ,即10*10;
经过了3层的卷积后,图片的大小已经降到了(3*10*10)。
3 鉴别器测试
修改完鉴别器之后,可以使用真实图像和随即图像,初步判断鉴别器的能力与测试这部分修改后的代码是否存在BUG。
# 鉴别器类建立
D = Discriminator()
D.to(device)
# 测试鉴别器
for image_data_tensor in celeba_dataset:
# real data
D.train(image_data_tensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))
# fake data
D.train(generate_random_image((1,3,128,128)), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0]))
pass
同样,可以查看损失函数的变化情况并使用测试集进行测试。
for image_data_tensor in celeba_dataset:
# real data
D.train(image_data_tensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))
# fake data
D.train(generate_random_image((1,3,128,128)), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0]))
pass
D.plot_progress()
for i in range(4):
image_data_tensor = celeba_dataset[random.randint(0,20000)]
print( D.forward( image_data_tensor ).item() )
pass
for i in range(4):
print( D.forward( generate_random_image((1,3,128,128))).item() )
pass
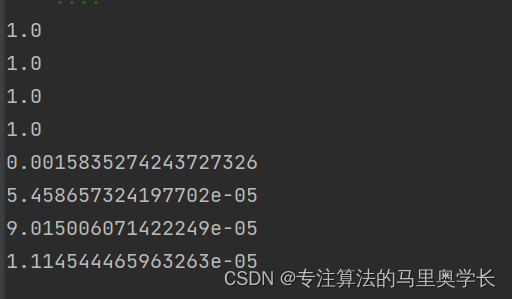
可以看出,鉴别器对于数据的判断非常有信息。
之后还需对生成器进行同步修改,并使用代码生成图像,这部分内容将放在下篇。
此部分的完整代码可在文末留言申请或在博主的资源区自行下载。