栈的定义
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶
可以把他想象成一个水杯
栈代码的实现
结构的定义,以及函数声明
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int QueueNodeType;
struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
QueueNodeType data;
}typedef QueueNode;
//队列只需要在队尾插入,队头删除,不需要改变里面的内容
//所以只需要改变头尾
struct Queue {
struct QueueNode* head;
struct QueueNode* tail;
size_t _size;
}typedef Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QueueNodeType data);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// 获取队列头部元素
QueueNodeType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QueueNodeType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
size_t QueueSize(Queue* q);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
接口的实现
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->_size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
while (q->head)
{
QueueNode* next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
q->tail = NULL;
q->_size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QueueNodeType data)
{
assert(q);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
//尾插
if (q->tail == NULL)
{
q->tail = q->head = newnode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = newnode;
q->tail = q->tail->next;
}
q->_size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
QueueNode* newhead = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = newhead;
if (q->head == NULL)
{
q->tail = NULL;
}
q->_size--;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL;
}
QueueNodeType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
QueueNodeType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->_size;
}
队列的定义
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
队列代码的实现
结构的定义,以及函数声明
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int QueueNodeType;
struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
QueueNodeType data;
}typedef QueueNode;
//队列只需要在队尾插入,队头删除,不需要改变里面的内容
//所以只需要改变头尾
struct Queue {
struct QueueNode* head;
struct QueueNode* tail;
size_t _size;
}typedef Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QueueNodeType data);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// 获取队列头部元素
QueueNodeType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QueueNodeType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
size_t QueueSize(Queue* q);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
接口的实现
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->_size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
while (q->head)
{
QueueNode* next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
q->tail = NULL;
q->_size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QueueNodeType data)
{
assert(q);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
//尾插
if (q->tail == NULL)
{
q->tail = q->head = newnode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = newnode;
q->tail = q->tail->next;
}
q->_size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
QueueNode* newhead = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = newhead;
if (q->head == NULL)
{
q->tail = NULL;
}
q->_size--;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL;
}
QueueNodeType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
QueueNodeType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->_size;
}
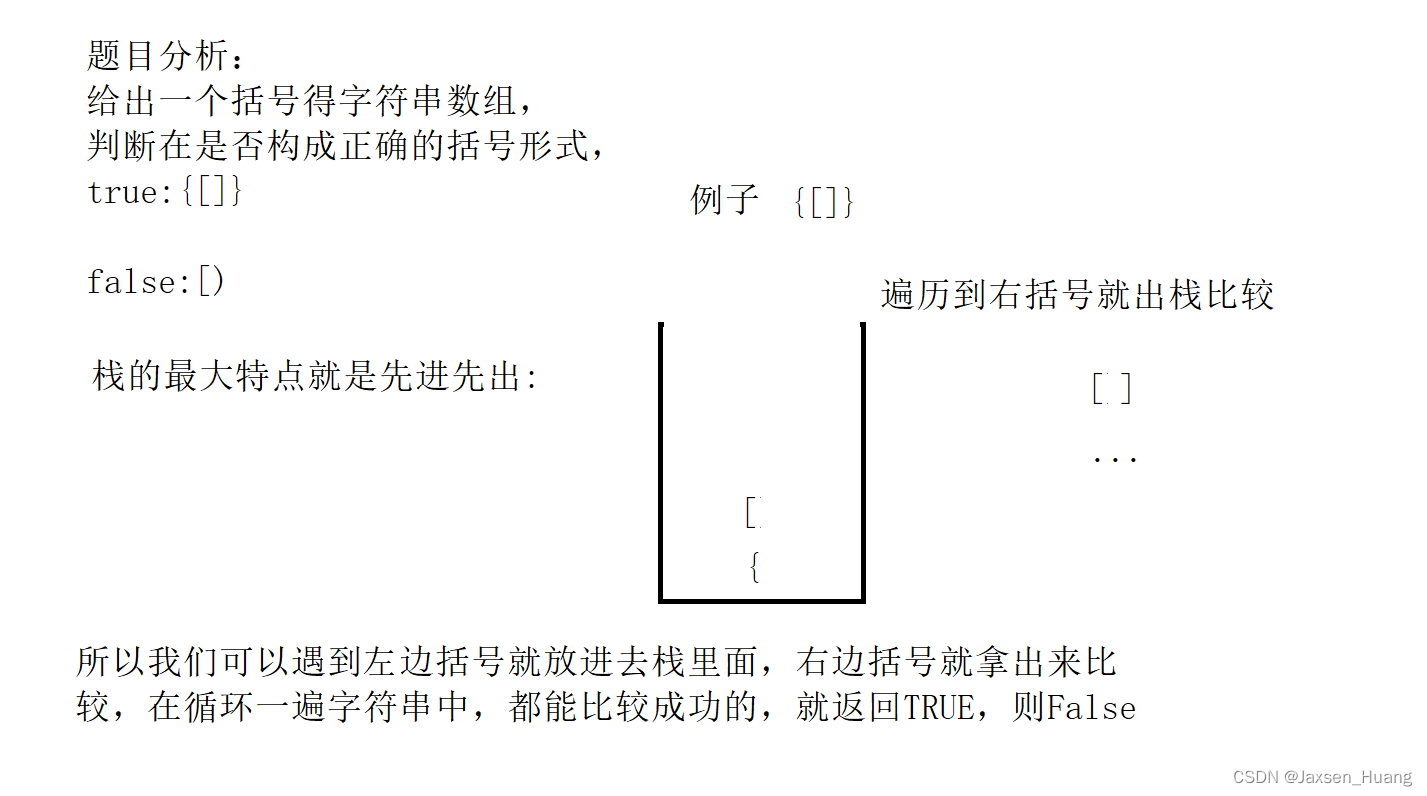
题目1:括号匹配问题
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/description/

思路详解:
参考代码
typedef char StackType;
struct Stack {
StackType* _a;
int _top;
int _capacity;
}typedef Stack;
//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pStack);
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pStack,StackType data);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pStack);
//获取栈顶元素
StackType StackTop(const Stack* pStack);
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(const Stack* pStack);
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pStack);
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pStack);
void StackInit(Stack* pStack)
{
pStack->_a = NULL;
pStack->_capacity = 0;
pStack->_top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* pStack,StackType data)
{
assert(pStack);
if (pStack->_top == pStack->_capacity)
{
int newCapacity = pStack->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : pStack->_capacity * 2;
StackType* newa = NULL;
newa = (StackType*)realloc(pStack->_a, sizeof(StackType) * newCapacity);
if (newa == NULL)
{
perror("StackPush():: realloc::");
return;
}
pStack->_a = newa;
pStack->_capacity = newCapacity;
}
pStack->_a[pStack->_top] = data;
pStack->_top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* pStack)
{
assert(pStack);
assert(!StackEmpty(pStack));
pStack->_top--;
}
StackType StackTop(const Stack* pStack)
{
// 因为top的初始值为0 ,而插入一个数据后为1,
// 但是所对应的数组下标为0
assert(pStack);
assert(!StackEmpty(pStack));
return pStack->_a[pStack->_top - 1];
}
int StackSize(const Stack* pStack)
{
return pStack->_top;
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pStack)
{
assert(pStack);
return pStack->_top == 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* pStack)
{
free(pStack->_a);
pStack->_capacity = 0;
pStack->_top = 0;
pStack->_a = NULL;
}
//这里题目实现,上面都是栈的实现和接口,因为是C语言的关系没有STL库所以要自己造轮子
bool isValid(char* s)
{
Stack stack = { 0 };
StackInit(&stack);
while (*s)
{
if (*s == '(' || *s == '{' || *s == '[')
{
StackPush(&stack, *s);
s++;
}
else
{
//第一个字符为有括号,证明不是有效括号,直接返回NULL
if(StackEmpty(&stack))
{
//特殊案例如果是 [[]]],这里如果直接返回的话就会导致内存泄露
StackDestroy(&stack);
return false;
}
StackType top = StackTop(&stack);
StackPop(&stack);
if (top == '(' && *s != ')'
|| top == '{' && *s != '}'
|| top == '[' && *s != ']'
)
{
StackDestroy(&stack);
return false;
}
else
{
s++;
}
}
}
bool ret = StackEmpty(&stack);
StackDestroy(&stack);
return ret;
// return true;
}
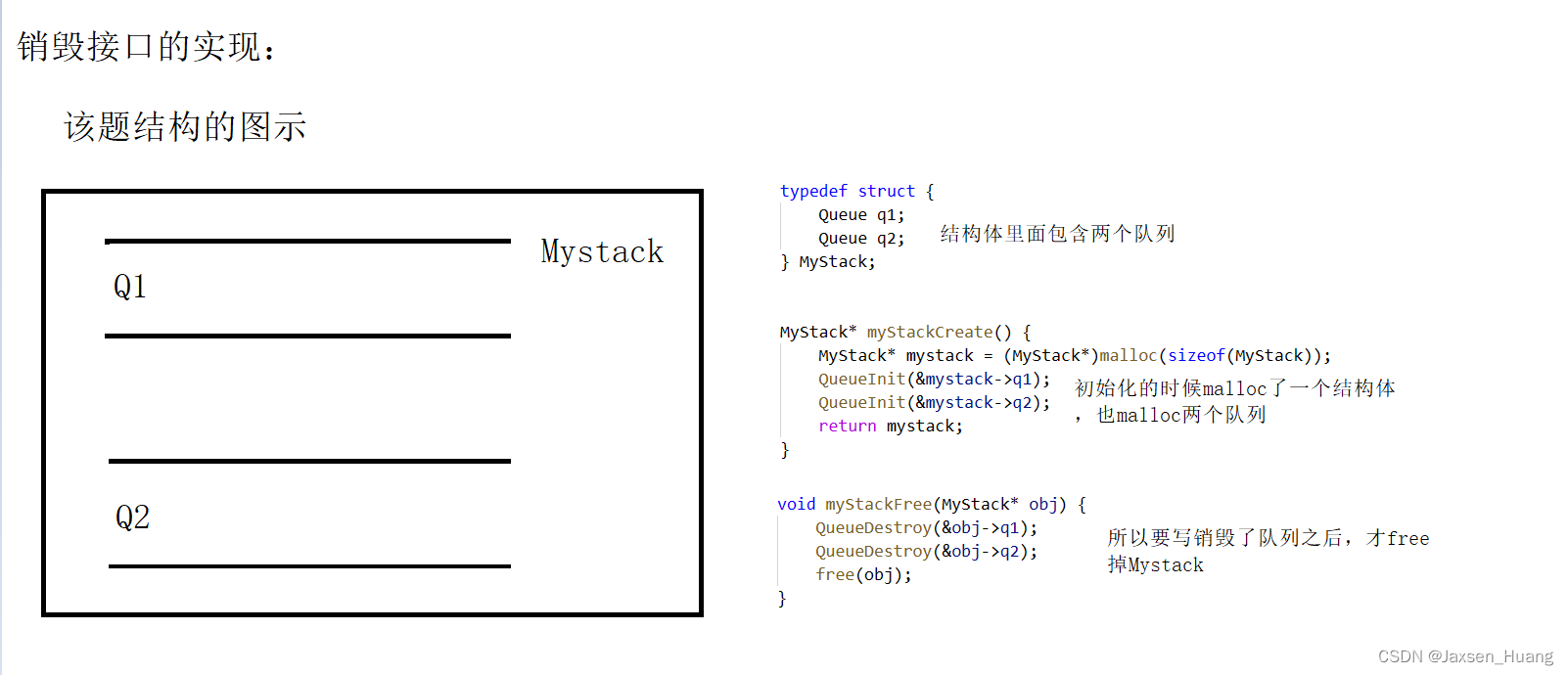
题目2:用队列实现栈
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/

思路详解:

参考代码:
typedef int QueueNodeType;
struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
QueueNodeType data;
}typedef QueueNode;
//队列只需要在队尾插入,队头删除,不需要改变里面的内容
//所以只需要改变头尾
struct Queue {
struct QueueNode* head;
struct QueueNode* tail;
size_t _size;
}typedef Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QueueNodeType data);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// 获取队列头部元素
QueueNodeType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QueueNodeType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
size_t QueueSize(Queue* q);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->_size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
while (q->head)
{
QueueNode* next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
q->tail = NULL;
q->_size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QueueNodeType data)
{
assert(q);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
//尾插
if (q->tail == NULL)
{
q->tail = q->head = newnode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = newnode;
q->tail = q->tail->next;
}
q->_size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
QueueNode* newhead = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = newhead;
if (q->head == NULL)
{
q->tail = NULL;
}
q->_size--;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL;
}
QueueNodeType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
QueueNodeType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->_size;
}
//上面是队列的接口,从这里下面才开始对栈的实现
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* mystack = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&mystack->q1);
QueueInit(&mystack->q2);
return mystack;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
//找那个是为空队列
Queue* emptyQueue = &obj->q1;
Queue* nonEmptyQueue = &obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
emptyQueue = &obj->q2;
nonEmptyQueue = &obj->q1;
}
//保留非空队列中的最后一个元素,其余元素转移到空队列里面
while(QueueSize(nonEmptyQueue) > 1)
{
QueuePush(emptyQueue,QueueFront(nonEmptyQueue));
QueuePop(nonEmptyQueue);
}
int ret = QueueFront(nonEmptyQueue);
QueuePop(nonEmptyQueue);
return ret;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
//两个队列中,非空的那个队列的队尾就是栈顶
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
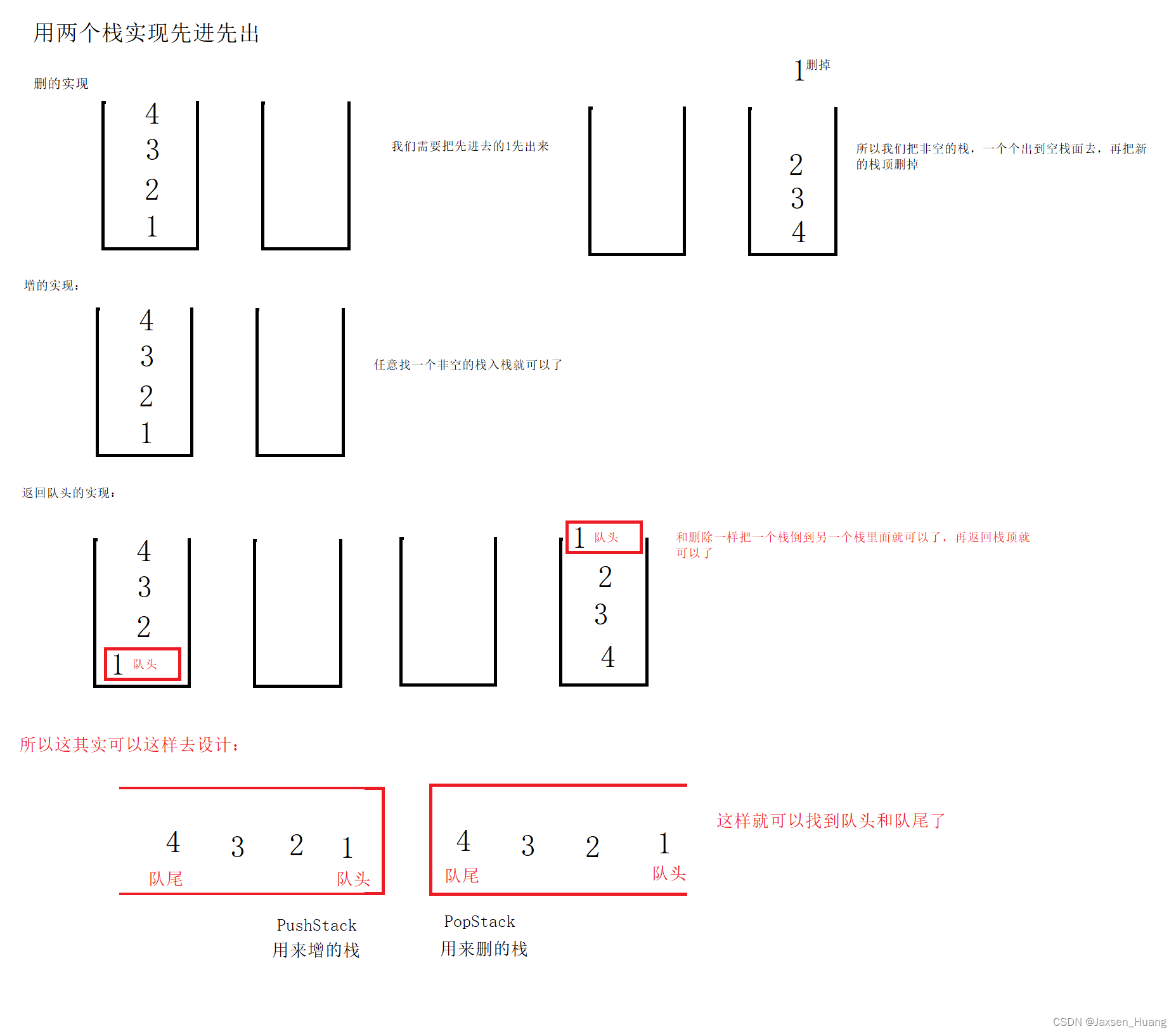
题目3:用栈实现队列
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/

思路详解:
参考代码:
typedef char StackType;
struct Stack {
StackType* _a;
int _top;
int _capacity;
}typedef Stack;
//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pStack);
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pStack,StackType data);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pStack);
//获取栈顶元素
StackType StackTop(Stack* pStack);
//获取栈底元素
StackType StackBottom(Stack* pStack);
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* pStack);
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pStack);
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pStack);
void StackInit(Stack* pStack)
{
pStack->_a = NULL;
pStack->_capacity = 0;
pStack->_top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* pStack,StackType data)
{
assert(pStack);
if (pStack->_top == pStack->_capacity)
{
int newCapacity = pStack->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : pStack->_capacity * 2;
StackType* newa = NULL;
newa = (StackType*)realloc(pStack->_a, sizeof(StackType) * newCapacity);
if (newa == NULL)
{
perror("StackPush():: realloc::");
return;
}
pStack->_a = newa;
pStack->_capacity = newCapacity;
}
pStack->_a[pStack->_top] = data;
pStack->_top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* pStack)
{
assert(pStack);
assert(!StackEmpty(pStack));
pStack->_top--;
}
StackType StackTop(Stack* pStack)
{
assert(pStack);
assert(!StackEmpty(pStack));
// 因为top的初始值为0 ,而插入一个数据后为1,
// 但是所对应的数组下标为0
return pStack->_a[pStack->_top - 1];
}
StackType StackBottom(Stack* pStack)
{
assert(pStack);
assert(!StackEmpty(pStack));
return pStack->_a[0];
}
int StackSize(Stack* pStack)
{
return pStack->_top;
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pStack)
{
assert(pStack);
return pStack->_top == 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* pStack)
{
free(pStack->_a);
pStack->_capacity = 0;
pStack->_top = 0;
pStack->_a = NULL;
}
//这里开始才是实现队列的代码
typedef struct {
Stack PushStack;
Stack PopStack;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* queue= (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&queue->PushStack);
StackInit(&queue->PopStack);
return queue;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
StackPush(&obj->PushStack,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->PopStack))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->PushStack))
{
StackPush(&obj->PopStack,StackTop(&obj->PushStack));
StackPop(&obj->PushStack);
}
}
int popTop = StackTop(&obj->PopStack);
StackPop(&obj->PopStack);
return popTop;
}
//返回队头
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->PopStack))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->PushStack))
{
StackPush(&obj->PopStack,StackTop(&obj->PushStack));
StackPop(&obj->PushStack);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->PopStack);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return StackEmpty(&obj->PushStack) && StackEmpty(&obj->PopStack);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestroy(&obj->PopStack);
StackDestroy(&obj->PushStack);
free(obj);
}
题目4:设计循环队列
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/

思路详解:
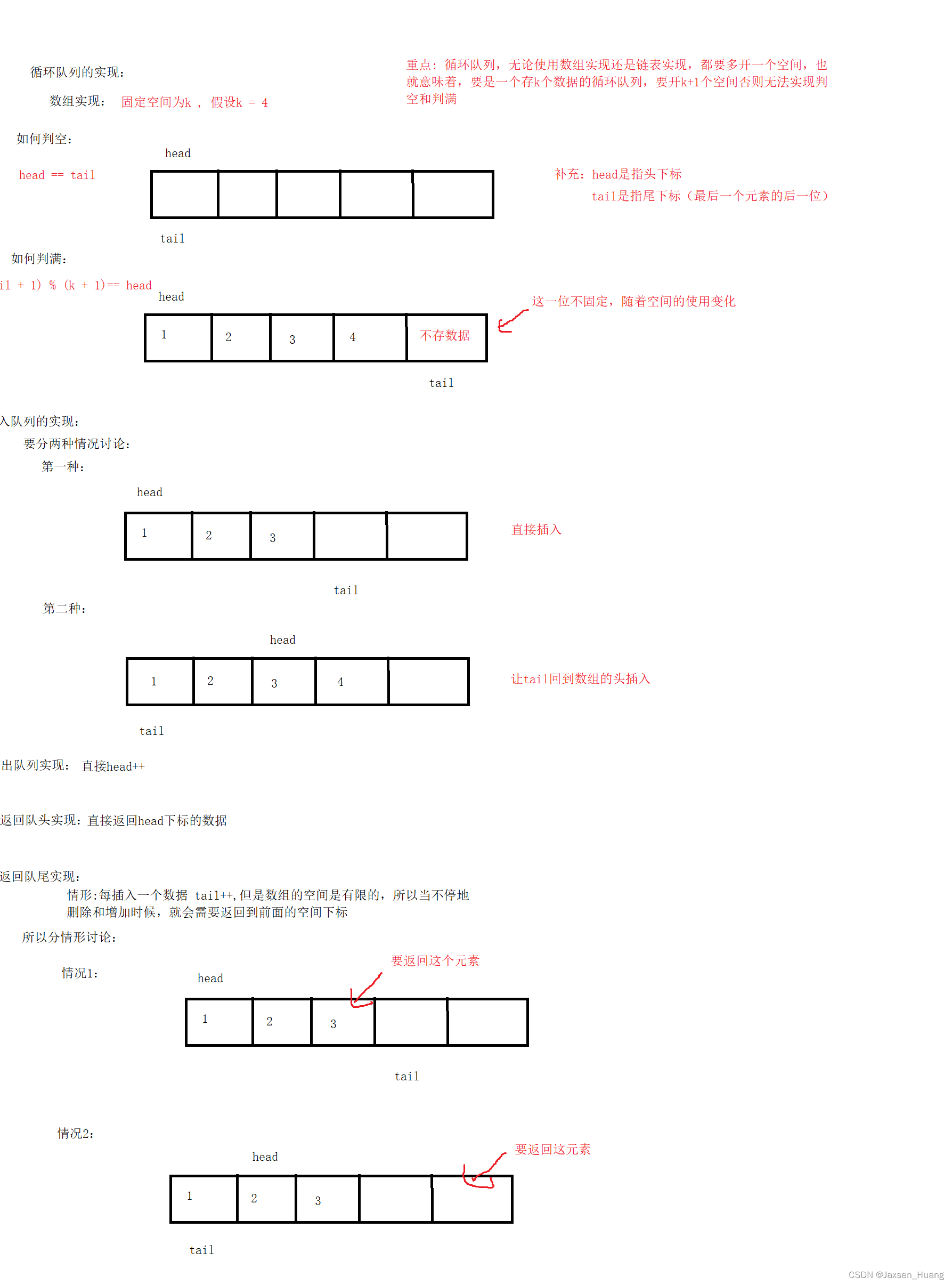
参考代码:
用数组实现:
typedef struct {
int* _a; //数组
int _head; //头下标
int _tail; //尾下标
int _k; //存储的元素个数
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);
// 初始化
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* cq = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
assert(cq);
cq->_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1));
assert(cq->_a);
cq->_head = 0;
cq->_tail = 0;
cq->_k = k;
return cq;
}
// 入队列
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue * obj, int value) {
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
else
{
obj->_a[obj->_tail] = value;
if (obj->_tail >= obj->_k)
{
obj->_tail = 0;
}
else
{
obj->_tail++;
}
return true;
}
}
//删队列
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
if (obj->_head >= obj->_k)
{
obj->_head = 0;
return true;
}
else
{
obj->_head++;
return true;
}
}
//队头
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->_a[obj->_head];
}
//队尾
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
//方法1;
if (obj->_tail == 0)
{
return obj->_a[obj->_k];
}
else
{
return obj->_a[obj->_tail - 1];
}
//方法2:
/*int i = (obj->_tail + obj->_k) % (obj->_k + 1);
return obj->_a[i];*/
}
//判空
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return obj->_head == obj->_tail;
}
//判满
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return (obj->_tail + 1) % (obj->_k + 1) == obj->_head;
}
//销毁
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
free(obj->_a);
free(obj);
}












![【2024最新华为OD-C/D卷试题汇总】[支持在线评测] 中文分词模拟器(200分) - 三语言AC题解(Python/Java/Cpp)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/563238f533cc4f3b8e6d812d064adbf1.png)


