第一:启动
在shell下敲gdb命令即可启动gdb,启动后会显示下述信息,出现gdb提示符。
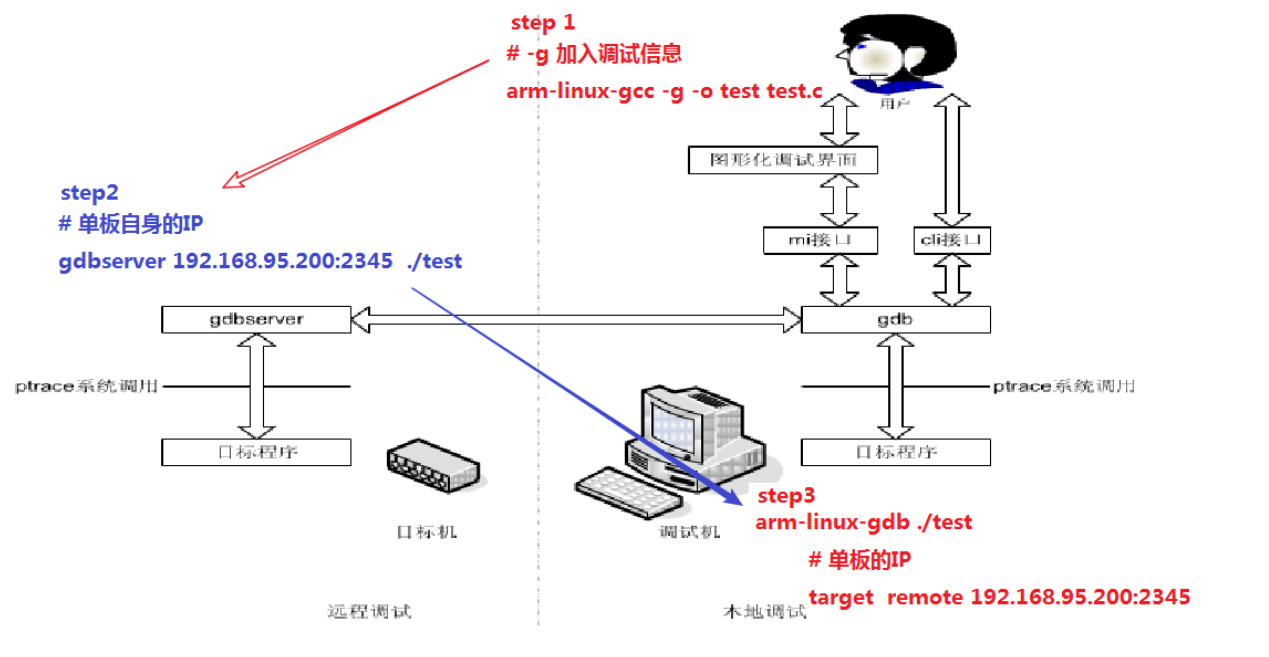
添加编译指令:gcc -g a.c -o test
打开指令:gdb test
或者 gdb 然后输入:file test
➜ example gdb GNU gdb (Ubuntu 8.1.1-0ubuntu1) 8.1.1 Copyright (C) 2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html> This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details. This GDB was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu". Type "show configuration" for configuration details. For bug reporting instructions, please see: <http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>. Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>. For help, type "help". Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word". (gdb)
测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
int minus(int a,int b){
printf("In minus():\n");
int c = a-b;
return c;
}
int sum(int a, int b) {
printf("In sum():\n");
int c = a+b;
return c;
}
void print(int xx, int *xxptr) {
printf("In print():\n");
printf(" xx is %d and is stored at %p.\n", xx, &xx);
printf(" ptr points to %p which holds %d.\n", xxptr, *xxptr);
int c = sum(2,3);
int d = minus(3,2);
}
int main(void) {
int x = 10;
int *ptr = &x;
printf("In main():\n");
printf(" x is %d and is stored at %p.\n", x, &x);
printf(" ptr points to %p which holds %d.\n", ptr, *ptr);
print(x, ptr);
return 0;
}
第二:设置断点
可以在函数名和行号等上设置断点。程序运行后,到达断点就会自动暂停运行。此时可以查看该时刻的变量值、显示栈帧、重新设置断点或重新运行等。断点命令(break)可以简写为b。
格式
break 断点
举例
(gdb) b main Breakpoint 1 at 0x758: file gdb_example.c, line 9.
格式
break 函数名 break 行号 break 文件名:行号 break 文件名:函数名 break + 偏移量 break - 偏移量 break * 地址
举例
(gdb) b print Breakpoint 2 at 0x709: file gdb_example.c, line 4. (gdb) b gdb_example.c:5 Breakpoint 3 at 0x715: file gdb_example.c, line 5. (gdb) b +3 Note: breakpoint 2 also set at pc 0x709. Breakpoint 4 at 0x709: file gdb_example.c, line 4. (gdb) b *0x709 Note: breakpoints 2 and 4 also set at pc 0x709. Breakpoint 5 at 0x709: file gdb_example.c, line 4. (gdb)
上面的例子分别对print函数,gdb_example.c第5行,现在暂停位置往后第3行,地址0x709设置断点。
设置好的断点可以通过info break 确认
(gdb) info break Num Type Disp Enb Address What 1 breakpoint keep y 0x0000000000000758 in main at gdb_example.c:9 2 breakpoint keep y 0x0000000000000709 in print at gdb_example.c:4 3 breakpoint keep y 0x0000000000000715 in print at gdb_example.c:5 4 breakpoint keep y 0x0000000000000709 in print at gdb_example.c:4 5 breakpoint keep y 0x0000000000000709 in print at gdb_example.c:4
第三:显示栈帧
backtrace命令可以在遇到断点而暂停执行时显示栈帧。该命令简写为bt。此外, backtrace的别名还有where和info stack(简写为info s)。
backtrace bt
显示所有栈帧
backtrace N bt N
只显示开头N个栈帧
backtrace -N bt -N
只显示最后N个栈帧
backtrace full bt full backtrace full N bt full N backtrace full -N bt full -N
举例
(gdb) b 4
Breakpoint 1 at 0x714: file gdb_example.c, line 4.
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/zhongyi/code/example/gdb_example
In main():
x is 10 and is stored at 0x7fffffffe2fc.
ptr points to 0x7fffffffe2fc which holds 10.
In print():
xx is 10 and is stored at 0x7fffffffe2cc.
ptr points to 0x7fffffffe2fc which holds 10.
In sum():
In minus():
Breakpoint 1, minus (a=3, b=2) at gdb_example.c:4
4 int c = a-b;
# 显示栈帧
(gdb) bt
#0 minus (a=3, b=2) at gdb_example.c:4
#1 0x00005555555547c0 in print (xx=10, xxptr=0x7fffffffe2fc) at gdb_example.c:17
#2 0x0000555555554841 in main () at gdb_example.c:28
#只显示前2个栈帧
(gdb) bt 2
#0 minus (a=3, b=2) at gdb_example.c:4
#1 0x00005555555547c0 in print (xx=10, xxptr=0x7fffffffe2fc) at gdb_example.c:17
(More stack frames follow...)
# 从外向内显示2个栈帧,及其局部变量
(gdb) bt full -2
#1 0x00005555555547c0 in print (xx=10, xxptr=0x7fffffffe2fc) at gdb_example.c:17
c = 5
d = 21845
#2 0x0000555555554841 in main () at gdb_example.c:28
x = 10
ptr = 0x7fffffffe2fc
(gdb)
显示栈帧后,就可以确认程序在何处停止,及程序的调用路径。
第四:显示变量
格式
print 变量
举例
(gdb) p x $1 = 10 (gdb) p ptr $2 = (int *) 0x7fffffffe2fc (gdb)
第五:显示寄存器
举例
(gdb) info reg rax 0xc 12 rbx 0x0 0 rcx 0x7ffff7af2104 140737348837636 rdx 0x7ffff7dcf8c0 140737351841984 rsi 0x555555756260 93824994337376 rdi 0x1 1 rbp 0x7fffffffe310 0x7fffffffe310 rsp 0x7fffffffe2f0 0x7fffffffe2f0 r8 0x7ffff7fe14c0 140737354011840 r9 0x0 0 r10 0x0 0 r11 0x246 582 r12 0x5555555545f0 93824992232944 r13 0x7fffffffe3f0 140737488348144 r14 0x0 0 r15 0x0 0 rip 0x555555554841 0x555555554841 <main+123> eflags 0x202 [ IF ] cs 0x33 51 ss 0x2b 43 ds 0x0 0 es 0x0 0 fs 0x0 0 gs 0x0 0
寄存器前加$,可以显示寄存器的内容。
(gdb) p $rdi $7 = 1 (gdb) p $rax $8 = 12 (gdb)
显示寄存器可以用以下格式
p/格式 变量
| 格式 | 说明 |
| x | 显示为16进制数 |
| d | 显示为十进制数 |
| u | 显示为无符号十进制数 |
| o | 显示为八进制数 |
| t | 显示为二进制数 |
| a | 地址 |
| c | 显示为ascii |
| f | 浮点小数 |
| s | 显示为字符串 |
| i | 显示为机器语言(仅在显示内存的x命令中可用) |
显示内存
x命令可以显示内存的内容
格式
x/格式 地址
举例
(gdb) x $r12 0x5555555545f0 <_start>: xor %ebp,%ebp (gdb) x $r8 0x7ffff7fe14c0: rclb $0xf7,(%rsi,%rdi,8) (gdb)
x/i 可以显示汇编指令。一般用x命令时,格式为x/NFU ADDR。此处ADDR为希望显示的地址,N为重复次数。F为前面讲过的格式,u代表的单位如下。
| 单位 | 说明 |
| b | 字节 |
| h | 半字(2字节) |
| w | 字(4字节) |
| g | 双字(8字节) |
下面显示从rsp开始的10条指令。
(gdb) x/10i $rsp 0x7fffffffe2f0: (bad) 0x7fffffffe2f1: rex.W push %rbp 0x7fffffffe2f3: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe2f4: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe2f5: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe2f6: add %al,(%rax) 0x7fffffffe2f8: lock rex.RB push %r13 0x7fffffffe2fb: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe2fc: or (%rax),%al 0x7fffffffe2fe: add %al,(%rax)
显示反汇编
格式
disassemble disassemble 程序计数器 disassemble 开始地址 结束地址
格式1为反汇编当前整个函数,2为反汇编程序计数器所在函数的整个函数。3为反汇编从开始地址到结束地址的部分。
(gdb) disassemble Dump of assembler code for function sum: 0x0000555555554722 <+0>: push %rbp 0x0000555555554723 <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp 0x0000555555554726 <+4>: sub $0x20,%rsp 0x000055555555472a <+8>: mov %edi,-0x14(%rbp) 0x000055555555472d <+11>: mov %esi,-0x18(%rbp) 0x0000555555554730 <+14>: lea 0x1bd(%rip),%rdi # 0x5555555548f4 0x0000555555554737 <+21>: callq 0x5555555545b0 <puts@plt> => 0x000055555555473c <+26>: mov -0x14(%rbp),%edx 0x000055555555473f <+29>: mov -0x18(%rbp),%eax 0x0000555555554742 <+32>: add %edx,%eax 0x0000555555554744 <+34>: mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp) 0x0000555555554747 <+37>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%eax 0x000055555555474a <+40>: leaveq 0x000055555555474b <+41>: retq End of assembler dump.
第六:单步执行
执行源代码中的一行:next 进入函数内部执行:step 逐条执行汇编指令:nexti,stepi
第七:继续运行
格式
continue continue 次数
指定次数可以忽略断点,例如,continue 5 则5次遇到断点不会停止,第6次遇到断点才会停止。
第八:监视点
格式
watch <表达式>
<表达式>发生变化时暂停运行,<表达式>意思是常量或变量
awatch <表达式>
<表达式>被访问,改变时暂停运行
rwatch <表达式>
<表达式>被访问时暂停运行
举例
(gdb) watch c Hardware watchpoint 2: c (gdb) c Continuing. Hardware watchpoint 2: c Old value = 21845 New value = 5 sum (a=2, b=3) at gdb_example.c:10 10 return c; (gdb)
格式
删除断点和监视点
delete <编号>
<编号>指的是断点或监视点
举例
(gdb) info b
Num Type Disp Enb Address What
1 breakpoint keep y 0x000055555555473c in sum at gdb_example.c:9
breakpoint already hit 1 time
2 hw watchpoint keep y c
breakpoint already hit 1 time
(gdb) delete 2
(gdb) info b
Num Type Disp Enb Address What
1 breakpoint keep y 0x000055555555473c in sum at gdb_example.c:9
breakpoint already hit 1 time
(gdb)
第九:改变变量的值
格式
set variable <变量>=<表达式>
举例
(gdb) p c $1 = 5 (gdb) set variable c=0 (gdb) p c $2 = 0 (gdb)
第十:生成内核转储文件
(gdb) generate-core-file warning: Memory read failed for corefile section, 4096 bytes at 0xffffffffff600000. Saved corefile core.2380
有了内核转储文件,即使退出了GDB也能查看生成转储文件时的运行历史。
gcore 'pidof gdb_example'
该命令无需停止正在运行的程序,可以直接从命令行直接生成转储文件。当需要在其他机器上单独分析问题原因时,或者是分析客户现场问题时十分有用。
第十一:条件断点
break 断点 if 条件
如果条件为真,则暂停运行
condition 断点编号 condition 断点编号 条件
第一条指令删除指定断点编号的触发条件,第二条指令给断点添加触发条件
第十二:反复执行
ignore 断点编号 次数
在编号指定的断点,监视点忽略指定的次数
continue与ignore一样,也可以指定次数,达到指定次数前,执行到断点时不暂停。
continue次数 step 次数 stepi 次数 next 次数 nexti 次数
finish until until 地址
finish 执行完当前函数后暂停,until命令执行完当前函数等代码块后暂停,常用于跳出循环。、
第十三:删除断点或禁用断点
clear clear 函数名 clear 行号 clear 文件名:行号 clear 文件名:函数名 delete [breakpoints] 断点编号
clear 用于删除已定义的断点
disable [breakpoints] disable [breakpoints] 断点编号 disable display 显示编号 disable mem 内存区域
disable 临时禁用断点。第3种格式禁用display命令定义的自动显示,第4种格式禁用mem命令定义的内存区域。
enable enable [breakpoints] 断点编号 enable [breakpoints] once 断点编号 enable [breakpoints] delete 断点编号 enable disable display 显示编号 enable mem 内存区域
once 使指定的断点只启用一次。delete表示在运行暂停后删除断点。
第十四:断点命令
格式
commands 断点编号 命令 ... end
程序在指定的断点处暂停,就会自动执行命令。
举例
(gdb) b 17 Breakpoint 3 at 0x5555555547b1: file gdb_example.c, line 17. (gdb) command 3 Type commands for breakpoint(s) 3, one per line. End with a line saying just "end". >p c >end (gdb) r Starting program: /home/zhongyi/code/example/gdb_example -e 'p 1' In main(): x is 10 and is stored at 0x7fffffffe2ec. ptr points to 0x7fffffffe2ec which holds 10. In print(): xx is 10 and is stored at 0x7fffffffe2bc. ptr points to 0x7fffffffe2ec which holds 10. In sum(): Breakpoint 3, print (xx=10, xxptr=0x7fffffffe2ec) at gdb_example.c:17 17 int d = minus(3,2); $1 = 5
上例表示在17行暂停后打印c的值。
与前面的条件断点组合使用,可以在断点暂停时执行复杂的动作。
举例
break 17 if c==5 commands silent printf “x is %d\n”,x cont end
第十五:常用命令及其缩略形式
| 命令 | 简写形式 | 说明 |
| backtrace | bt/where | 显示backtrace |
| break | 设备断点 | |
| continue | c/cont | 继续运行 |
| delete | d | 删除断点 |
| finish | 运行到函数结束 | |
| info breakpoints | 显示断点信息 | |
| next | n | 执行下一行 |
| | p | 显示表达式 |
| run | r | 运行程序 |
| step | s | 一次执行一行,包括函数内部 |
| x | 显示内存内容 | |
| until | u | 执行到指定行 |
| directory | dir | 插入目录 |
| disable | dis | 禁用断点 |
| down | do | 在当前栈帧中选择要显示的栈帧 |
| edit | e | 编辑文件或函数 |
| frame | f | 选择要显示的栈帧 |
| forward-search | fo | 向前搜索 |
| generate-core-file | gcore | 生成内核转储 |
| help | h | 显示帮助文档 |
| info | i | 显示信息 |
| list | l | 显示函数行 |
| nexti | ni | 执行下一行(以汇编代码为单位) |
| print-object | po | 显示目标信息 |
| sharedlibrary | share | 加载共享库的符号 |
| stepi | si | 执行下一行 |
第十六:值的历史
通过print命令显示过的值会记录在内部的值历史中,这些值可以在其他表达式中使用。
举例
(gdb) b 16 Breakpoint 1 at 0x79f: file gdb_example.c, line 16. (gdb) b 17 Breakpoint 2 at 0x7b1: file gdb_example.c, line 17. (gdb) b 29 Breakpoint 3 at 0x841: file gdb_example.c, line 29. (gdb) r Starting program: /home/zhongyi/code/example/gdb_example In main(): x is 10 and is stored at 0x7fffffffe2fc. ptr points to 0x7fffffffe2fc which holds 10. In print(): xx is 10 and is stored at 0x7fffffffe2cc. ptr points to 0x7fffffffe2fc which holds 10. Breakpoint 1, print (xx=10, xxptr=0x7fffffffe2fc) at gdb_example.c:16 16 int c = sum(2,3); (gdb) p c $1 = 1431651824 (gdb) c Continuing. In sum(): Breakpoint 2, print (xx=10, xxptr=0x7fffffffe2fc) at gdb_example.c:17 17 int d = minus(3,2); (gdb) p c $2 = 5 (gdb) c Continuing. In minus(): Breakpoint 3, main () at gdb_example.c:29 29 return 0;
最后的值可以使用$ 访问。
通过show values 可以显示历史中的最后10个值
举例
(gdb) show values $1 = 1431651824 $2 = 5 $3 = 10 $4 = 10 (gdb)
值的历史的访问变量和说明
| 变量 | 说明 |
| $ | 值历史中的最后一个值 |
| $n | 值历史的第n个值 |
| $$ | 值历史的倒数第二个值 |
| $$n | 值历史的倒数第n个值 |
| $_ | x命令显示过的最后的地址 |
| $__ | x命令显示过的最后的地址的值 |
| $_exitcode | 调试中的程序的返回代码 |
| $bpnum | 最后设置的断点的编号 |
可以随意定义变量。变量以$开头,有英文和数字组成。
举例
(gdb) set $i=0 (gdb) p $i $5 = 0 (gdb)
第十七:命令历史
可以把命令保存在文件中,保存命令历史后,就可以在其他调试会话中使用。默认命令历史文件位于./.gdb_history
set history expansion show history expansion
可以使用csh风格的!字符
set history filename 文件名 show history filename
可将命令历史保存到文件中,可以通过环境变量GDBHISTFILE改变默认文件。
set history save show history save
启用命令历史保存到文件和恢复的功能。
set history size 数字 show history size
设置保存到命令历史中的命令数量,默认为256。
第十八:初始化文件(.gdbinit)
Linux下gdb初始化文件为.gdbinit。如果存在.gdbinit文件,GDB在启动之前将其作为命令文件运行。
顺序如下:
- $HOME/.gdbinit
- 运行命令行选项
- ./.gdbinit
- 加载通过-x选项给出的命令文件
第十九:命令定义
用define可以自定义命令,用document可以给自定义的命令加说明,利用help 命令名可以查看定义的命令。
define格式:
define 命令名 命令 ………… end
document格式:
document 命令名 说明 end
help格式:
help 命令名
以下示例定义了名为li的命令。
举例
(gdb) define li Type commands for definition of "li". End with a line saying just "end". >x/10i $rbp >end (gdb) document li Type documentation for "li". End with a line saying just "end". >list machine instruction >end (gdb) li 0x7fffffffe310: (bad) 0x7fffffffe311: rex.W push %rbp 0x7fffffffe313: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe314: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe315: push %rbp 0x7fffffffe316: add %al,(%rax) 0x7fffffffe318: xchg %edi,(%rax,%riz,4) 0x7fffffffe31b: idiv %edi 0x7fffffffe31d: jg 0x7fffffffe31f 0x7fffffffe31f: add %al,(%rcx) (gdb) help li list machine instruction
还可以把各种设置写在文件中,运行调试器时读取这些文件。
source 文件名
总结
本文只是对gdb命令脚本做了一个粗浅的介绍,旨在起到抛砖引玉的效果。如果大家想更深入地了解这部分知识,可以参考gdb手册的相关章节:Extending GDB (https://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Extending-GDB.html)。
最后向大家推荐一个github上的.gdbinit文件:https://github.com/gdbinit/Gdbinit,把这个弄懂,相信gdb脚本文件就不在话下了。