1.Tensor操作
Tensor是PyTorch中最基本的数据结构,类似于NumPy的数组,但可以在GPU上运行加速计算。
示例:创建和操作Tensor
import torch
# 创建一个零填充的Tensor
x = torch.zeros(3, 3)
print(x)
# 加法操作
y = torch.ones(3, 3)
z = x + y
print(z)
# 在GPU上创建Tensor
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
x = torch.zeros(3, 3, device=device)
print(x)
运行结果: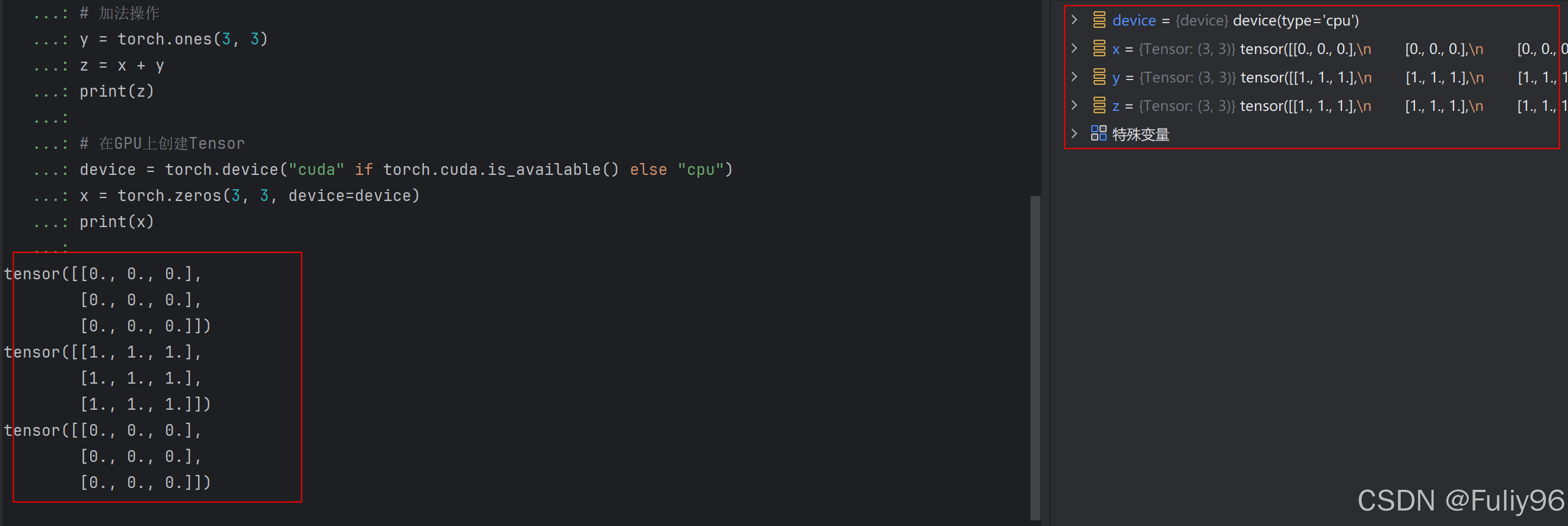
2. nn.Module和自定义模型
nn.Module是PyTorch中定义神经网络模型的基类,所有的自定义模型都应该继承自它。
示例:定义一个简单的全连接神经网络模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 自定义模型类
class SimpleNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleNet, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(10, 5) # 线性层:输入维度为10,输出维度为5
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# 创建模型实例
model = SimpleNet()
print(model)
运行结果:

3. DataLoader和Dataset
DataLoader用于批量加载数据,Dataset定义了数据集的接口,自定义数据集需继承自它。
示例:加载自定义数据集
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
# 自定义数据集类
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data, targets):
self.data = data
self.targets = targets
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, index):
x = self.data[index]
y = self.targets[index]
return x, y
# 假设有一些数据和标签
data = torch.randn(100, 10) # 100个样本,每个样本10维
targets = torch.randint(0, 2, (100,)) # 100个随机标签,0或1
# 创建数据集实例
dataset = CustomDataset(data, targets)
# 创建数据加载器
batch_size = 10
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
# 打印一个batch的数据
for batch in dataloader:
inputs, labels = batch
print(inputs.shape, labels.shape)
break
运行结果:

4. 优化器和损失函数
优化器用于更新模型参数以减少损失,损失函数用于计算预测值与实际值之间的差异。
示例:使用优化器和损失函数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
# 定义模型(假设已定义好)
model = SimpleNet()
# 定义损失函数
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 前向传播、损失计算、反向传播和优化过程请参考前面完整示例的训练循环部分。
运行结果:
5. nn.functional中的函数
nn.functional提供了各种用于构建神经网络的函数,如激活函数、池化操作等。
示例:使用ReLU激活函数
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 创建一个Tensor
x = torch.randn(3, 3)
# 使用ReLU激活函数
output = F.relu(x)
print(output)
运行结果: