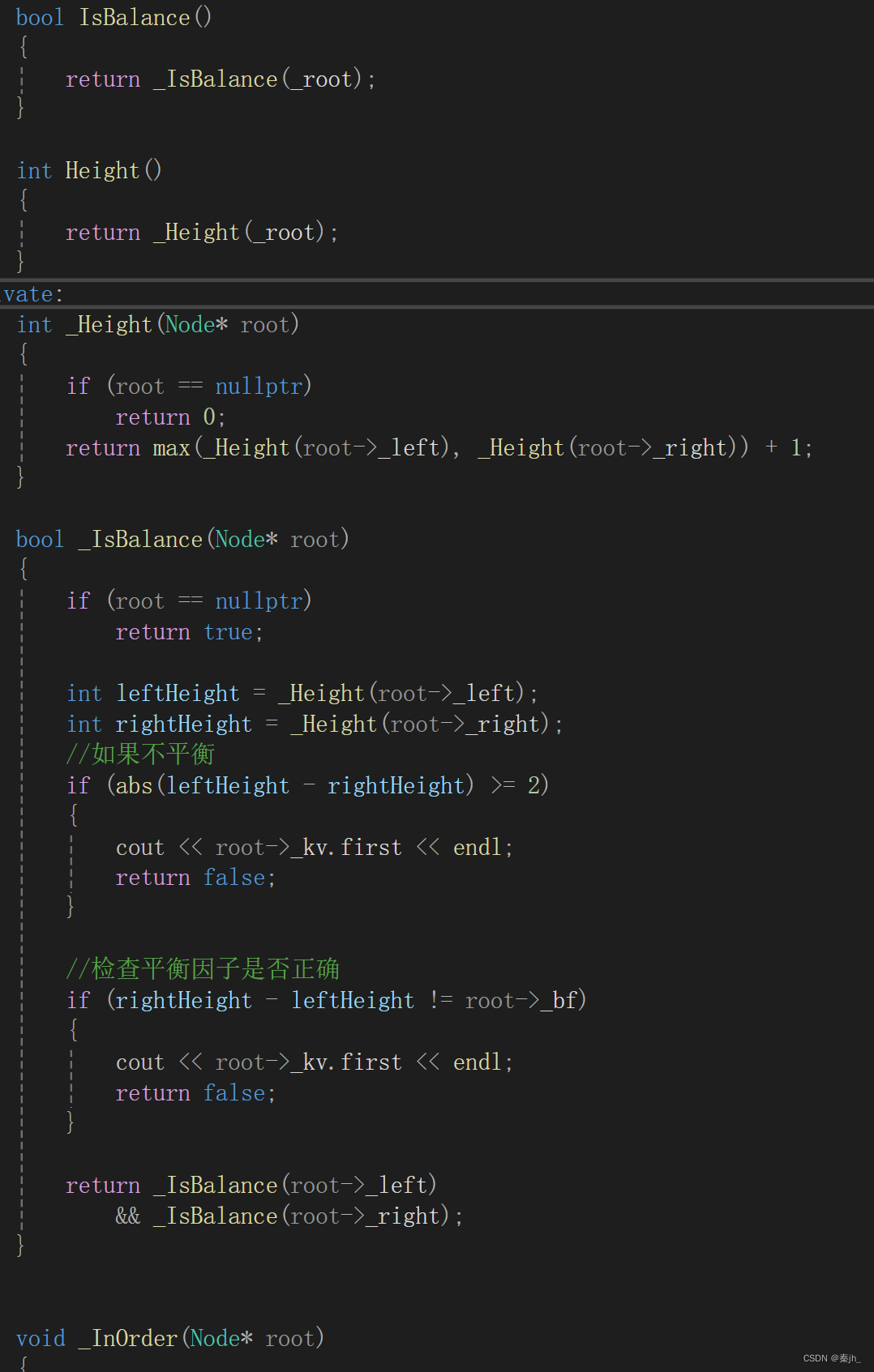
二叉搜索树:
- 非线性的,树是层级结构。
- 基本单位是节点,每个节点最多2个子节点。
- 有序。每个节点,其左子节点都比它小,其右子节点都比它大。
- 每个子树都是一个二叉搜索树。每个节点及其所有子节点形成子树。
- 可以是空树。
C语言实现:(使用链表实现,不使用递归)
创建结构体数据类型(记录二叉搜索树的根节点和数据个数):
typedef struct Link
{
LinkNode *root; // 根节点
int length; // 统计有多少数据
} LinkBST; // 别名创建二叉搜索树,并初始化:
LinkBST bst;
bst.root = NULL; // 根节点,初始化为NULL
bst.length = 0; // 数据个数,初始化为0
创建节点(结构体数据类型),并创建具体节点实例的函数:
// 节点(结构体数据类型)
typedef struct Node
{
int value; // 数据类型为整型
struct Node *left; // 左子节点
struct Node *right; // 右子节点
} LinkNode; // 别名// 函数:创建节点
LinkNode *createNode(int data)
{
LinkNode *node = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode)); // 分配节点内存空间
if(node == NULL)
{
perror("Memory allocation failed");
exit(-1);
}
node->value = data; // 数据
node->left = NULL; // 左子节点,初始化为NULL
node->right = NULL; // 右子节点,初始化为NULL
return node;
}
添加元素:
从根节点开始,比对数值。若比它小,往左子树比对;若比它大,往右子树比对;直到找到为空,则为新元素的位置。
void add(LinkBST *bst, int data) // add a element to the tree
{
LinkNode *newNode = createNode(data);
// 若是空树,根节点就是新节点
if(bst->root == NULL)
{
bst->root = newNode;
bst->length++;
return ;
}
// 非空树,比根节点数值小,往左边比对,比根节点数值大,往右边比对
LinkNode *cur = bst->root;
while(1)
{
if(data == cur->value) return ;
if(data < cur->value)
{
if(cur->left == NULL)
{
cur->left = newNode;
bst->length++;
return ;
}
cur = cur->left;
}
else if(data > cur->value)
{
if(cur->right == NULL)
{
cur->right = newNode;
bst->length++;
return ;
}
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}删除元素:
- 若删除的节点为叶子节点(即无子节点),则直接删除。
- 若删除的节点只有左子节点,则左子节点替代删除节点。
- 若删除的节点只有右子节点,则右子节点替代删除节点。
- 若删除的节点既有左子节点又有右子节点,则找到直接前驱(即删除节点的左子树中的最大值,即删除节点的左子节点的最右节点),直接前驱的值替代删除节点的值,删除直接前驱节点。
void delete(LinkBST *bst,int data) // delete a element from the tree
{
// 函数:删除节点的具体操作
LinkNode *del(LinkNode *node)
{
// 只有右子节点,右子节点替代删除节点
if(node->left == NULL)
{
bst->length--;
return node->right;
}
// 只有左子节点,左子节点替代删除节点
if(node->right == NULL)
{
bst->length--;
return node->left;
}
// 左右子节点都有,直接前驱(左子节点的最右节点,即左子树中最大值)替代删除节点,删除直接前驱
if(node->left && node->right)
{
LinkNode *tmp = node, *cur = node->left;
while(cur->right)
{
tmp = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
node->value = cur->value;
bst->length--;
if(tmp != node) tmp->right = cur->left;
else tmp->left = cur->left;
return node;
}
}
// 函数:找到删除节点
void delNode(int data)
{
LinkNode *parent, *cur = bst->root;
while(1)
{
if(cur == NULL) return ;
if(data == cur->value)
{
// 删除节点若是根节点,根节点接收删除后的节点
if(cur == bst->root) bst->root = del(cur);
// 删除节点若是左子节点,父节点的左子节点接收删除后的节点
else if(data < parent->value) parent->left = del(cur);
// 删除节点若是右子节点,父节点的右子节点接收删除后的节点
else if(data > parent->value) parent->right = del(cur);
return ;
}
if(data < cur->value)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->left;
}
else if(data > cur->value)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
// 空树,直接退出程序
if(bst->root == NULL) return ;
delNode(data);
}遍历元素:
前序遍历:(顺序:根节点、左子节点、右子节点)
使用数组实现栈(后进先出),数量:一个栈。
1、起始栈中元素为根节点。2、栈中元素依次出栈(并打印),找到元素的右节点和左节点依次入栈(注意:先右后左)。3、重复2,直到栈为空。
void pretraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(root,left,right)
{
LinkNode *cur = NULL;
// 指针数组(数组元素是指针),实现栈(后进先出)
LinkNode *arr[bst->length];
int n = 1;
arr[n-1] = bst->root;
printf("pretravel: ");
while(n != 0)
{
cur = arr[n-1];
printf("%d ", cur->value);
n--;
if(cur->right)
{
arr[n] = cur->right;
n++;
}
if(cur->left)
{
arr[n] = cur->left;
n++;
}
}
printf("\n");
}中序遍历:(顺序:左子节点、根节点、右子节点)
使用数组实现栈(后进先出),数量:一个栈。
1、从根节点开始遍历,根节点入栈。2、找左节点依次入栈,找到最左节点后,栈中元素依次出栈(并打印),找右节点入栈。3、重复2,直到节点不存在或者栈为空。
void midtraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(left,root,right)
{
printf("midtravel: ");
LinkNode *cur = bst->root;
// 指针数组(数组元素是指针),实现栈(后进先出)
LinkNode *arr[bst->length];
int n = 0;
while(cur || n != 0)
{
if(cur)
{
arr[n] = cur;
n++;
cur = cur->left;
}
else
{
cur = arr[n-1];
printf("%d ", cur->value);
n--;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
printf("\n");
}后序遍历:(顺序:左子节点、右子节点、根节点)
使用数组实现栈(后进先出),数量:两个栈(辅助栈,目标栈)。
1、辅助栈中起始元素为根节点。2、辅助栈中元素依次出栈(并入栈目标栈),找到元素的左节点和右节点依次入栈辅助栈(注意:先左后右)。3、重复2,直到辅助栈为空。4、遍历目标栈,并打印。
void posttraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(left,right,root)
{
LinkNode *cur = NULL;
// 指针数组(数组元素是指针),实现栈(后进先出)
LinkNode *arr[bst->length]; // 辅助栈
LinkNode *brr[bst->length]; // 目标栈
int n = 1, m = 0;
arr[n-1] = bst->root;
while(n != 0)
{
cur = brr[m] = arr[n-1]; // 辅助栈出栈,目标栈入栈
n--;
m++;
if(cur->left)
{
arr[n] = cur->left; // 辅助栈入栈
n++;
}
if(cur->right)
{
arr[n] = cur->right; // 辅助栈入栈
n++;
}
}
// 遍历目标栈
printf("posttravel: ");
for(int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
printf("%d ", brr[i]->value);
}
printf("\n");
}广度遍历(层级遍历):
使用链表实现队列(先进先出),数量:一个队列。
1、队列中起始元素为根节点。2、队列中元素依次从队头出队(并打印),找到元素的左节点和右节点依次从队尾入队(注意:先左后右)。3、重复2,直到队列为空。
void breadthtraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(levels)
{
printf("threadtravel: ");
// 链表:实现队列(先进先出),注:链表的函数在bstqueue.c(完整代码中展示)
Queue queue;
queue.header = createQnode(bst->root); // 头指针,指向第一个元素
queue.tail = NULL; // 尾指针,指向最后一个元素
LinkNode *cur = NULL;
while(queue.header)
{
cur = queue.header->bstnode;
printf("%d ", cur->value);
popQnode(&queue); // 从队头出队(函数在bstqueue.c)
if(cur->left)
{
addQnode(&queue, cur->left); // 从队尾入队(函数在bstqueue.c)
}
if(cur->right)
{
addQnode(&queue, cur->right); // 从队尾入队(函数在bstqueue.c)
}
}
printf("\n");
}查找元素:
从根节点开始,比对数值。若比它小,往左子树查找;若比它大,往右子树查找;直到找到该元素,则返回1(true),若没有,则返回0(false)。
int find(LinkNode *node, int data) // if find data,return 1(true),or return 0(false)
{
LinkNode *cur = node;
while(cur)
{
if(data == cur->value) return 1;
if(data < cur->value) cur = cur->left;
else if(data > cur->value) cur = cur->right;
}
return 0;
}完整代码:(bstree.c,bstqueue.c(链表实现的队列,用于广度遍历))
// bstree.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "bstqueue.c" // 引入链表实现的队列,用于广度遍历
/* structure */
typedef struct Node // node of the binary search tree(bst)
{
int value; // data type is integer
struct Node *left; // left child node
struct Node *right; // right child node
} LinkNode;
typedef struct Link //bst(Linkedlist)
{
LinkNode *root; // root node
int length; // the number of the tree
} LinkBST;
/* function prototype */
void add(LinkBST *, int); // add a element
void delete(LinkBST *,int); // delete a element
void pretraverse(LinkBST *); // show element one by one,(root,left,right)
void midtraverse(LinkBST *); // show element one by one,(left,root,right)
void posttraverse(LinkBST *); // show element one by one,(left,right,root)
void breadthtraverse(LinkBST *); // show element one by one,(levels)
int find(LinkNode *, int); // if find data,return 1(true),or return 0(false)
/* main function */
int main(void)
{
// create binary search tree and initialization
LinkBST bst;
bst.root = NULL;
bst.length = 0;
printf("isempty(1:true, 0:false): %d, length is %d\n", bst.root==NULL, bst.length);
add(&bst, 15);
add(&bst, 8);
add(&bst, 23);
add(&bst, 19);
add(&bst, 10);
add(&bst, 6);
add(&bst, 9);
add(&bst, 12);
printf("isempty(1:true, 0:false): %d, length is %d\n", bst.root==NULL, bst.length);
pretraverse(&bst);
midtraverse(&bst);
posttraverse(&bst);
breadthtraverse(&bst);
printf("find 10(1:true, 0:false): %d\n", find(bst.root, 10));
printf("find 11(1:true, 0:false): %d\n", find(bst.root, 11));
delete(&bst, 23);
delete(&bst, 15);
delete(&bst, 6);
printf("isempty(1:true, 0:false): %d, length is %d\n", bst.root==NULL, bst.length);
pretraverse(&bst);
midtraverse(&bst);
posttraverse(&bst);
breadthtraverse(&bst);
return 0;
}
/* subfunction */
LinkNode *createNode(int data) // create a node of the binary search tree
{
LinkNode *node = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
if(node == NULL)
{
perror("Memory allocation failed");
exit(-1);
}
node->value = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
void add(LinkBST *bst, int data) // add a element to the tree
{
LinkNode *newNode = createNode(data);
// if empty, root is newNode
if(bst->root == NULL)
{
bst->root = newNode;
bst->length++;
return ;
}
// if not empty, smaller,to left, biger,to right
LinkNode *cur = bst->root;
while(1)
{
if(data == cur->value) return ;
if(data < cur->value)
{
if(cur->left == NULL)
{
cur->left = newNode;
bst->length++;
return ;
}
cur = cur->left;
}
else if(data > cur->value)
{
if(cur->right == NULL)
{
cur->right = newNode;
bst->length++;
return ;
}
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
void delete(LinkBST *bst,int data) // delete a element from the tree
{
// subfunction: delete the node
LinkNode *del(LinkNode *node)
{
// if only right child, return right child node
if(node->left == NULL)
{
bst->length--;
return node->right;
}
// if only left child, return left child node
if(node->right == NULL)
{
bst->length--;
return node->left;
}
// both left and right, the max on the left replace the delete node and delete it
if(node->left && node->right)
{
LinkNode *tmp = node, *cur = node->left;
while(cur->right)
{
tmp = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
node->value = cur->value;
bst->length--;
if(tmp != node) tmp->right = cur->left;
else tmp->left = cur->left;
return node;
}
}
// subfunction: find the delete node
void delNode(int data)
{
LinkNode *parent, *cur = bst->root;
while(1)
{
if(cur == NULL) return ;
if(data == cur->value)
{
// delete node is root,root receive the node after delete
if(cur == bst->root) bst->root = del(cur);
// delete node is left,left child of parent receive the node after delete
else if(data < parent->value) parent->left = del(cur);
//delete node is right,right child of parent receive the node after delete
else if(data > parent->value) parent->right = del(cur);
return ;
}
if(data < cur->value)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->left;
}
else if(data > cur->value)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
if(bst->root == NULL) return ;
delNode(data);
}
void pretraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(root,left,right)
{
LinkNode *cur = NULL;
// pointer array(stack:LIFO): array, each element is a pointer(point to node)
LinkNode *arr[bst->length];
int n = 1;
arr[n-1] = bst->root;
printf("pretravel: ");
while(n != 0)
{
cur = arr[n-1];
printf("%d ", cur->value);
n--;
if(cur->right)
{
arr[n] = cur->right;
n++;
}
if(cur->left)
{
arr[n] = cur->left;
n++;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
void midtraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(left,root,right)
{
printf("midtravel: ");
LinkNode *cur = bst->root;
// pointer array(stack:LIFO): array, each element is a pointer(point to node)
LinkNode *arr[bst->length];
int n = 0;
while(cur || n != 0)
{
if(cur)
{
arr[n] = cur;
n++;
cur = cur->left;
}
else
{
cur = arr[n-1];
printf("%d ", cur->value);
n--;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
void posttraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(left,right,root)
{
LinkNode *cur = NULL;
// pointer array(stack:LIFO): array, each element is a pointer(point to node)
LinkNode *arr[bst->length];
LinkNode *brr[bst->length];
int n = 1, m = 0;
arr[n-1] = bst->root;
while(n != 0)
{
cur = brr[m] = arr[n-1];
n--;
m++;
if(cur->left)
{
arr[n] = cur->left;
n++;
}
if(cur->right)
{
arr[n] = cur->right;
n++;
}
}
printf("posttravel: ");
for(int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
printf("%d ", brr[i]->value);
}
printf("\n");
}
void breadthtraverse(LinkBST *bst) // show element one by one,(levels)
{
printf("threadtravel: ");
// queue(FIFO): use Linkedlist implement
Queue queue;
queue.header = createQnode(bst->root);
queue.tail = NULL;
LinkNode *cur = NULL;
while(queue.header)
{
cur = queue.header->bstnode;
printf("%d ", cur->value);
popQnode(&queue);
if(cur->left)
{
addQnode(&queue, cur->left);
}
if(cur->right)
{
addQnode(&queue, cur->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int find(LinkNode *node, int data) // if find data,return 1(true),or return 0(false)
{
LinkNode *cur = node;
while(cur)
{
if(data == cur->value) return 1;
if(data < cur->value) cur = cur->left;
else if(data > cur->value) cur = cur->right;
}
return 0;
}// bstqueue.c
#include <stdlib.h>
/* structure */
typedef struct queueNode // node of the queue
{
void *bstnode; // data type is bst node
struct queueNode *next; // point to next node
} Qnode;
typedef struct queue // queue(Linkedlist)
{
Qnode *header; // point to the top node
Qnode *tail; // point to the last node
} Queue;
/* subfunction */
Qnode *createQnode(void *bstnode) // create a node of the queue
{
Qnode *node = (Qnode *)malloc(sizeof(Qnode));
if(node == NULL)
{
perror("Memory allocation failed");
exit(-1);
}
node->bstnode = bstnode;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
void addQnode(Queue *queue, void *node) // add a element to the end of the queue
{
Qnode *qnode = createQnode(node);
if(queue->tail == NULL) queue->tail = queue->header = qnode;
else
{
queue->tail->next = qnode;
queue->tail = qnode;
}
}
void popQnode(Queue *queue) // delete a element from the top of the queue
{
queue->header = queue->header->next;
if(queue->header == NULL) queue->tail = NULL;
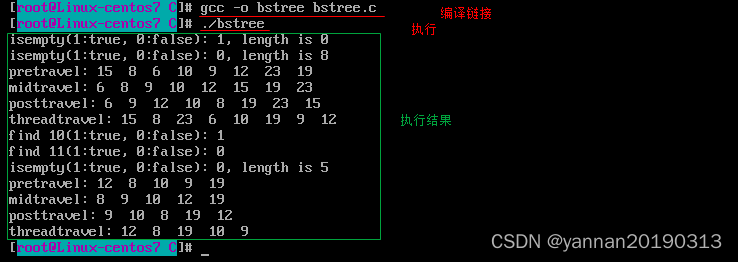
}编译链接: gcc -o bstree bstree.c
执行可执行文件: ./bstree