文章目录
- 前言
- 一. linux下文件删除原理
- 1.1 文件删除原理的简单介绍
- 1.2 测试inode号是否容易被覆盖?
- 二. 实验测试过程
- 2.1 实验环境:
- 2.2 新增一块硬盘测试
- 2.3 对磁盘分区
- 2.3.1 分区(使用fdisk分区)
- 2.3.2 格式化,创建目录挂载
- 2.3.3 创建测试文件
- 2.3.4 删除文件测试
- 2.3.5 安装工具extundelte
- 2.3.6 使用工具去恢复数据
- 写在最后
前言
如果你一不小心删除了文件,该如何恢复? \textcolor{red}{如果你一不小心删除了文件,该如何恢复? } 如果你一不小心删除了文件,该如何恢复?
这句话已经成了面试官口中的高频面试题,作为运维的你,真的知道如何恢复吗?快来跟我一起查缺补漏,通过一个实战案例来实现误删除文件的恢复吧。
一. linux下文件删除原理
1.1 文件删除原理的简单介绍
简单的说,文件系统由文件名,inode,block 三部分组成。
当一个文件要申请inode,首先GDT检索然后跳到inode位图看哪的inode空闲,把stat存到inode,然后开始写文件内容。
如果要删除文件,其实就是将数据块block bit map置0,inodebitmap置0,所以删除很快,而数据内容在磁盘还在相应的数据块。
在inode中并没有文件名这个信息, 因为电脑是根据inode来判断文件的。
那么文件名存放在什么位置呢?
答案是: 存在目录中,根目录的inode默认为2,寻找文件名会从根目录开始:
一般的寻址过程,找到目录的数据块,匹配记录项,文件名,再找到inode编号。
这里有两个通识:
- 删除文件其实删除的inode
- inode号一旦释放,若有其他文件申请到了这个刚刚释放的inode号,对应这个inode号位置的数据就会被覆盖。
1.2 测试inode号是否容易被覆盖?
## 创建测试 目录
[root@mufeng71 ~]# mkdir test
# 创建测试文件
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch a.txt
## 查看文件的inode
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i a.txt
34503763 a.txt
## 删除文件后,再次创建a.txt,看是否还是原来的inode号
[root@mufeng71 ~]# rm -rf a.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch a.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i a.txt
33803902 a.txt
## 如果第一次与原来不同,可能是正好有缺省的inode,可以再次测试
[root@mufeng71 ~]# rm -rf a.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch a.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i a.txt
33803902 a.txt
## 这里第二次测试的时候,发现inode和被删除时候的inode一致
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch b.txt
## 创建一个不同的文件名测试
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i b.txt
33803903 b.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# rm -rf b.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch b.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i b.txt
33803903 b.txt
##测试创建文件名不同,占用inode是相同的吗?
[root@mufeng71 ~]# rm -rf b.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch c.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch b.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i b.txt
33803903 b.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i c.txt
33803901 c.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# rm -rf c.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch d.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls -i d.txt
33803901 d.txt
## 可以看到即使文件名不同,inode也有可能相同
根据以上代码测试,我们总结出一个规律:
- inode的申请是随机的,申请到的必然是空闲的inode
- inode指向block (真正存放数据的地方)
那我们是否可以通过inode号来恢复数据?
二. 实验测试过程
2.1 实验环境:
[root@mufeng71 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.9 (Final)
2.2 新增一块硬盘测试
选择硬盘-添加添加,如下图:
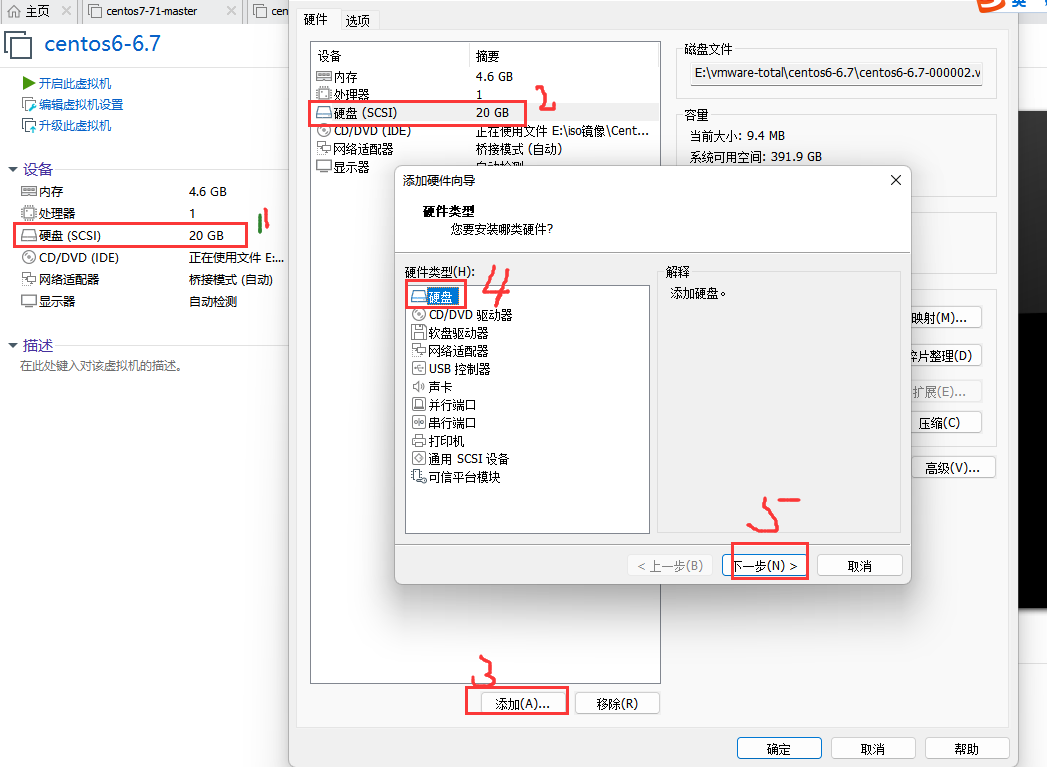
创建新的磁盘
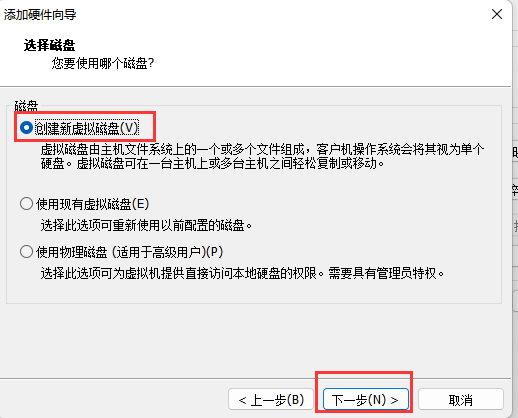
指定磁盘容量并设置存储为单个文件
新增磁盘结束之后,开启虚拟机
2.3 对磁盘分区
2.3.1 分区(使用fdisk分区)
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ll /dev/sdb*
brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 5月 18 23:16 /dev/sdb
[root@mufeng71 ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x95ad17d7.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
...
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +5G
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x95ad17d7
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 654 5253223+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ll /dev/sdb*
brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 5月 18 23:19 /dev/sdb
brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 17 5月 18 23:19 /dev/sdb1
2.3.2 格式化,创建目录挂载
创建挂载目录
[root@mufeng71 ~]# mkdir /tmp/sdb1
开始格式化
[root@mufeng71 ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
文件系统标签=
操作系统:Linux
块大小=4096 (log=2)
分块大小=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
328656 inodes, 1313305 blocks
65665 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
第一个数据块=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1346371584
41 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8016 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
正在写入inode表: 完成
Creating journal (32768 blocks): 完成
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: 完成
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 36 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
进行目录挂载
挂载目录:
[root@mufeng71 ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /tmp/sdb1
[root@mufeng71 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 20G 3.5G 15G 20% /
tmpfs 2.2G 72K 2.2G 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 190M 40M 140M 23% /boot
/dev/sdb1 4.9G 11M 4.6G 1% /tmp/sdb1
2.3.3 创建测试文件
[root@mufeng71 ~]# cp /etc/passwd /tmp/sdb1
[root@mufeng71 ~]# cp /etc/hosts /tmp/sdb1
[root@mufeng71 ~]# echo aaa > a.txt
[root@mufeng71 ~]# mkdir -p /tmp/sdb1/a/b/c
[root@mufeng71 ~]# cp a.txt /tmp/sdb1/a
[root@mufeng71 ~]# cp a.txt /tmp/sdb1/a/b
[root@mufeng71 ~]# touch !$/kong.txt
touch /tmp/sdb1/a/b/kong.txt
/etc/passwd
创建完成后查看目录结构:
## 镜像挂载
[root@mufeng71 sdb1]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt
mount: block device /dev/sr0 is write-protected, mounting read-only
## 安装tree命令
[root@mufeng71 sdb1]# yum install tree*
## 使用tree命令查看
[root@mufeng71 sdb1]# tree
.
├── a
│ ├── a.txt
│ └── b
│ ├── a.txt
│ ├── c
│ └── kong.txt
├── hosts
├── lost+found
└── passwd
4 directories, 5 files
2.3.4 删除文件测试
将文件全部删掉,并查看:
[root@mufeng71 sdb1]# ls
a hosts lost+found passwd
[root@mufeng71 sdb1]# rm -rf ./*
删除文件后,为了防止数据被覆盖掉:
卸载分区,或者设置为只读,我们再此处用卸载分区的方法:
[root@mufeng71 ~]# umount /dev/sdb1
[root@mufeng71 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 20G 3.5G 15G 20% /
tmpfs 2.2G 72K 2.2G 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 190M 40M 140M 23% /boot
/dev/sr0 3.7G 3.7G 0 100% /mnt
[root@mufeng71 ~]#
2.3.5 安装工具extundelte
使用工具 extundelete进行数据恢复,可以提前下载好,然后用rz命令上传。
若没有rz命令,需要提前使用 yum进行安装
[root@mufeng71 ~]# yum install lr*
安装完成后,执行rz,然后选择你要上传的包即可, 传完后可以在虚拟机查看到此文件:
上传完成:
[root@mufeng71 ~]# ls extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2
extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2
安装extundelete
安装环境:
[root@mufeng71 ~]# yum install gcc*
[root@mufeng71 extundelete-0.2.4]# yum install e2fsprogs-devel
解压并开始进行安装
[root@mufeng71 ~]# tar xf extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2
[root@mufeng71 ~]# cd extundelete-0.2.4
开始编译安装
[root@mufeng71 extundelete-0.2.4]# ./configure
Configuring extundelete 0.2.4
Writing generated files to disk
[root@mufeng71 extundelete-0.2.4]# make && make install
2.3.6 使用工具去恢复数据
1. 查看之前被删除的文件的inode号
[root@mufeng71 test]# extundelete /dev/sdb1 --inode 2
NOTICE: Extended attributes are not restored.
Loading filesystem metadata ... 41 groups loaded.
Group: 0
Contents of inode 2:
................
File name | Inode number | Deleted status
. 2
.. 2
lost+found 11 Deleted
passwd 12 Deleted
hosts 13 Deleted
a 128257 Deleted
[root@mufeng71 test]#
2. 通过inode号来恢复
目前inode 12 是passwd文件,我们直接用inode号进行恢复即可:
[root@mufeng71 test]# extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-inode 12
NOTICE: Extended attributes are not restored.
Loading filesystem metadata ... 41 groups loaded.
Loading journal descriptors ... 62 descriptors loaded.
[root@mufeng71 test]# ls
RECOVERED_FILES
[root@mufeng71 test]# cd RECOVERED_FILES/
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# ls
file.12
## 使用md5测试,发现和源文件一致
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# md5sum file.12 /etc/passwd
53baee54724c650df260e45099a82100 file.12
53baee54724c650df260e45099a82100 /etc/passwd
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]#
3. 通过文件名来恢复
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-file passwd
NOTICE: Extended attributes are not restored.
Loading filesystem metadata ... 41 groups loaded.
Loading journal descriptors ... 62 descriptors loaded.
Successfully restored file passwd
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# cd RECOVERED_FILES/
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# ls
passwd
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# md5sum passwd /etc/passwd
53baee54724c650df260e45099a82100 passwd
53baee54724c650df260e45099a82100 /etc/passwd
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]#
4. 通过目录名字来恢复
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-directory a
NOTICE: Extended attributes are not restored.
Loading filesystem metadata ... 41 groups loaded.
Loading journal descriptors ... 62 descriptors loaded.
Searching for recoverable inodes in directory a ...
8 recoverable inodes found.
Looking through the directory structure for deleted files ...
4 recoverable inodes still lost.
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# cd RECOVERED_FILES/
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# ls
a
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# tree a
a
├── a.txt
└── b
└── a.txt
1 directory, 2 files
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]#
5. 一次性恢复所有文件
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-all
NOTICE: Extended attributes are not restored.
Loading filesystem metadata ... 41 groups loaded.
Loading journal descriptors ... 62 descriptors loaded.
Searching for recoverable inodes in directory / ...
8 recoverable inodes found.
Looking through the directory structure for deleted files ...
0 recoverable inodes still lost.
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# cd RECOVERED_FILES/
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# ls
a hosts passwd
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]# tree
.
├── a
│ ├── a.txt
│ └── b
│ └── a.txt
├── hosts
└── passwd
2 directories, 4 files
[root@mufeng71 RECOVERED_FILES]#

有没有发现空文件和空目录没有被恢复? 这是因为 在ext4系统中,默认会认为空文件和空目录没有恢复的必要。但在XFS系统中,由于有默认的备份机制,空文件和空目录是可以恢复的。
写在最后
✨ 原创不易,还希望各位大佬支持一下 \textcolor{blue}{原创不易,还希望各位大佬支持一下} 原创不易,还希望各位大佬支持一下
👍 点赞,你的认可是我创作的动力! \textcolor{green}{点赞,你的认可是我创作的动力!} 点赞,你的认可是我创作的动力!
⭐️ 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向! \textcolor{green}{收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!} 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✏️ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富! \textcolor{green}{评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!} 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!