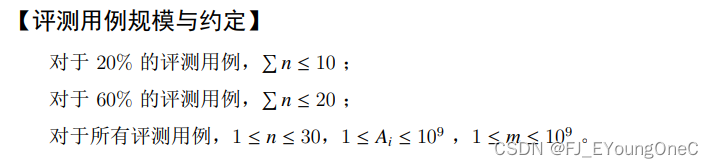
70pts
题目要求我们在给定的瓜中选择一些瓜,可以选择将瓜劈成两半,使得最后的总重量恰好等于 m m m。我们的目标是求出至少需要劈多少个瓜。
首先,我们注意到每个瓜的重量最多为 1 0 9 10^9 109,而求和的重量 m m m 也最多为 1 0 9 10^9 109,每个瓜的重量最多只能被分为两份。同时,由于每个瓜可以选择劈或者不劈,所以我们可以使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来遍历所有可能的组合。
在深度优先搜索的过程中,我们需要记录当前考虑到的瓜的序号 u,当前已经选中瓜的总重量 s 以及已经劈开的瓜的数量 cnt。当满足以下条件之一时,当前搜索分支可以提前结束:
- 当前已选瓜的总重量
s大于目标重量m; - 已经劈开的瓜的数量
cnt大于等于目标重量m,因为劈开的瓜越多,总重量越小,不可能达到m。
当我们遍历到最后一个瓜时,检查当前选中瓜的总重量 s 是否等于目标重量 m,如果等于,则更新答案 res 为 cnt 和 res 中的较小值。
时间复杂度:
由于每个瓜都有三种选择,所以时间复杂度为 O ( 3 n ) O(3^n) O(3n),其中 n n n 是瓜的个数。
95pts
由于 70pts 速度过慢,故需要优化,用了两个 DFS 函数(折半搜索),dfs_1 和 dfs_2,先对前一半的瓜进行搜索,将搜索结果存储在哈希表 h 中,然后对后一半的瓜进行搜索,同时在搜索过程中与哈希表 h 中的结果进行匹配,以找到满足条件的组合。
时间复杂度:
由于每个瓜都有三种选择,所以时间复杂度为 O ( 3 n 2 ) O(3^\frac{n}{2}) O(32n),其中 n n n 是瓜的个数。同时,由于在搜索过程中进行了剪枝,实际运行时间会小于 O ( 3 n 2 ) O(3^\frac{n}{2}) O(32n),又由于哈希表的常数过大,会导致程序缓慢,故无法通过所有数据。
100pts
本题要求从给定的瓜中选择一些瓜,可以对瓜进行劈开,使得最后选出的瓜的总重量恰好为 m m m,求最少需要劈开的瓜的个数。题目可以使用分治和二分查找的思路来解决。
首先,将所有的瓜按照重量进行排序。然后,将瓜分为两部分,前 n / 2 n/2 n/2 个瓜和后 n / 2 n/2 n/2 个瓜。对于每一部分,求出所有可能的瓜的重量组合以及对应的劈开的瓜的个数。接着,将前半部分的所有重量组合排序,方便后续使用二分查找。最后,遍历后半部分的所有重量组合,使用二分查找在前半部分寻找恰好使得总重量为 m m m 的组合,并记录最少需要劈开的瓜的个数。
具体实现如下:
- 读入瓜的个数
n和目标重量m,将目标重量m乘以 2 2 2,将题目转换成求瓜的重量恰好为 2 m 2m 2m 的组合。 - 读入每个瓜的重量,将瓜的重量也乘以 2 2 2。
- 对瓜的重量进行排序。
- 计算分界点
tn,将瓜分为前后两部分,前半部分为[0, tn),后半部分为[tn, n)。 - 使用深度优先搜索遍历前半部分的所有组合,记录每种组合的总重量和需要劈开的瓜的个数,保存在数组
alls中。 - 对
alls数组进行排序,然后去重。 - 使用深度优先搜索遍历后半部分的所有组合,对于每种组合,使用二分查找在前半部分寻找恰好使得总重量为 2 m 2m 2m 的组合,并记录最少需要劈开的瓜的个数。
- 输出最少需要劈开的瓜的个数,如果不存在这样的组合,则输出
-1。
时间复杂度:
本题的时间复杂度主要取决于深度优先搜索和二分查找的复杂度。在最坏情况下,深度优先搜索需要遍历所有可能的组合,因此时间复杂度为 O ( 3 n 2 ) O(3^\frac{n}{2}) O(32n)。二分查找的时间复杂度为 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn)。所以总的时间复杂度为 O ( 3 n 2 log 3 n 2 + 3 n 2 ) O(3^\frac{n}{2} \log 3^\frac{n}{2} + 3^\frac{n}{2}) O(32nlog32n+32n)。
手写哈希表
由于部分平台数据较强,可能无法通过 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据,文末补充手写哈希表的做法,实测可通过 100 % 100\% 100% 数据。
AC_Code
- C++(70%)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 35;
int n, m, tn;
int w[N];
int res = 50;
void dfs(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m || cnt >= m)
return;
if (s == m)
{
res = cnt;
return;
}
if (u == n)
return;
dfs(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
dfs(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m, m *= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i )
cin >> w[i], w[i] *= 2;
dfs(0, 0, 0);
cout << (res == 50? -1: res) << endl;
return 0;
}
- Java(70%)
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
private static final int N = 35;
private static int n, m;
private static int[] w = new int[N];
private static int res = 50;
public static void dfs(int u, long s, int cnt) {
if (s > m || cnt >= m) {
return;
}
if (s == m) {
res = cnt;
return;
}
if (u == n) {
return;
}
dfs(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
dfs(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
m *= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
w[i] = in.nextInt();
w[i] *= 2;
}
dfs(0, 0, 0);
System.out.println((res == 50 ? -1 : res));
}
}
- Python(65%)
from sys import stdin
N = 35
def dfs(u, s, cnt):
if s > m or cnt >= m:
return
if s == m:
global res
res = cnt
return
if u == n:
return
dfs(u + 1, s, cnt)
dfs(u + 1, s + w[u] // 2, cnt + 1)
dfs(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt)
n, m = map(int, stdin.readline().split())
m *= 2
w = [int(x) * 2 for x in stdin.readline().split()]
res = 50
dfs(0, 0, 0)
print(-1 if res == 50 else res)
- C++(95%)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 35;
int n, m, tn;
int w[N];
int res = 50;
unordered_map<int, int> h;
void dfs_1(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m)
return;
if (u == tn)
{
if (h.count(s))
h[s] = min(h[s], cnt);
else
h[s] = cnt;
return;
}
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
}
void dfs_2(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m || cnt > res)
return;
if (u == n)
{
if (h.count(m - s))
res = min(res, h[m - s] + cnt);
return;
}
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m, m *= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i )
cin >> w[i], w[i] *= 2;
sort(w, w + n);
tn = max(0, n / 2 - 2);
dfs_1(0, 0, 0);
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0);
cout << (res == 50? -1: res) << endl;
return 0;
}
- Java(95%)
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static final int N = 35;
private static int n, m, tn;
private static int[] w = new int[N];
private static int res = 50;
private static HashMap<Integer, Integer> h = new HashMap<>();
public static void dfs_1(int u, long s, int cnt) {
if (s > m) {
return;
}
if (u == tn) {
h.put((int)s, h.getOrDefault((int)s, cnt));
return;
}
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
}
public static void dfs_2(int u, long s, int cnt) {
if (s > m || cnt > res) {
return;
}
if (u == n) {
if (h.containsKey((int)(m - s))) {
res = Math.min(res, h.get((int)(m - s)) + cnt);
}
return;
}
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
m *= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
w[i] = in.nextInt();
w[i] *= 2;
}
Arrays.sort(w, 0, n);
tn = Math.max(0, n / 2 - 2);
dfs_1(0, 0, 0);
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0);
System.out.println((res == 50 ? -1 : res));
}
}
- Python(80%)
from itertools import combinations
def dfs_1(u, s, cnt):
if s > m:
return
if u == tn:
if s in h:
h[s] = min(h[s], cnt)
else:
h[s] = cnt
return
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt)
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] // 2, cnt + 1)
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt)
def dfs_2(u, s, cnt):
global res # 声明 res 为全局变量
if s > m or cnt > res:
return
if u == n:
if m - s in h:
res = min(res, h[m - s] + cnt)
return
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt)
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] // 2, cnt + 1)
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt)
n, m = map(int, input().split())
m *= 2
w = list(map(int, input().split()))
w = [x * 2 for x in w]
w.sort()
tn = max(0, n // 2 - 2)
h = {}
res = 50
dfs_1(0, 0, 0)
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0)
print(-1 if res == 50 else res)
- C++(100%)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 35;
int n, m, tn, t;
int w[N];
int res = 50;
PII alls[1 << 21];
void dfs_1(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m)
return;
if (u == tn)
{
alls[t ++] = {s, cnt};
return;
}
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
}
void dfs_2(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m || cnt >= res)
return;
if (u == n)
{
int l = 0, r = t - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (alls[mid].x + s >= m)
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
if (alls[l].x + s == m)
res = min(res, alls[l].y + cnt);
return;
}
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m, m *= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i )
cin >> w[i], w[i] *= 2;
sort(w, w + n);
tn = max(0, n / 2 - 2);
dfs_1(0, 0, 0);
sort(alls, alls + t);
int k = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < t; ++ i )
if (alls[i].x != alls[i - 1].x)
alls[k ++] = alls[i];
t = k;
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0);
cout << (res == 50? -1: res) << endl;
return 0;
}
- Java(100%)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static final int N = 35;
private int n, m, tn, t;
private int[] w = new int[N];
private int res = 50;
private Pair[] alls = new Pair[1 << 21];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main main = new Main();
main.solve();
}
private void solve() throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] input = in.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(input[1]) * 2;
input = in.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
w[i] = Integer.parseInt(input[i]) * 2;
}
Arrays.sort(w, 0, n);
tn = Math.max(0, n / 2 - 2);
dfs_1(0, 0, 0);
Arrays.sort(alls, 0, t, Comparator.comparingInt(Pair::getX));
int k = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < t; ++i) {
if (alls[i].x != alls[i - 1].x) {
alls[k++] = alls[i];
}
}
t = k;
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0);
out.println(res == 50 ? -1 : res);
out.flush();
}
private void dfs_1(int u, long s, int cnt) {
if (s > m)
return;
if (u == tn) {
alls[t++] = new Pair((int) s, cnt);
return;
}
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
}
private void dfs_2(int u, long s, int cnt) {
if (s > m || cnt >= res)
return;
if (u == n) {
int l = 0, r = t - 1;
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (alls[mid].x + s >= m)
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
if (alls[l].x + s == m)
res = Math.min(res, alls[l].y + cnt);
return;
}
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
}
static class Pair {
int x, y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
int getX() {
return x;
}
}
}
- Python(100%)
import sys
from typing import List, Tuple
N = 35
n, m, tn, t = 0, 0, 0, 0
w = [0] * N
res = 50
alls: List[Tuple[int, int]] = [(0, 0)] * (1 << 21)
def dfs_1(u: int, s: int, cnt: int):
global t, alls
if s > m:
return
if u == tn:
alls[t] = (s, cnt)
t += 1
return
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt)
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt)
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] // 2, cnt + 1)
def dfs_2(u: int, s: int, cnt: int):
global res, alls
if s > m or cnt >= res:
return
if u == n:
l, r = 0, t - 1
while l < r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
if alls[mid][0] + s >= m:
r = mid
else:
l = mid + 1
if alls[l][0] + s == m:
res = min(res, alls[l][1] + cnt)
return
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt)
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt)
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] // 2, cnt + 1)
def main():
global n, m, tn, t, w, alls, res
n, m = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split())
m *= 2
w = list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split()))
w = [x * 2 for x in w]
w.sort()
tn = max(0, n // 2 - 2)
dfs_1(0, 0, 0)
alls = sorted(alls[:t], key=lambda x: x[0])
k = 1
for i in range(1, t):
if alls[i][0] != alls[i - 1][0]:
alls[k] = alls[i]
k += 1
t = k
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0)
print(-1 if res == 50 else res)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- C++(手写哈希表 100%)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 35, M = 1e7 + 7, null = 2e9 + 7;
int n, m, tn, t;
int w[N];
int res = N;
PII h[M];
int find(int s)
{
int k = s % M;
while (h[k].x != s && h[k].x != null)
{
k ++;
if (k == M)
k = 0;
}
return k;
}
void dfs_1(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m)
return;
if (u == tn)
{
int k = find(s);
h[k] = {s, min(h[k].y, cnt)};
return;
}
dfs_1(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
dfs_1(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
}
void dfs_2(int u, LL s, int cnt)
{
if (s > m || cnt >= res)
return;
if (u == n)
{
int tar = m - s;
int k = find(tar);
if (h[k].x != null)
res = min(res, cnt + h[k].y);
return;
}
dfs_2(u + 1, s, cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u], cnt);
dfs_2(u + 1, s + w[u] / 2, cnt + 1);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m, m <<= 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i )
cin >> w[i], w[i] <<= 1;
for (int i = 1; i < M; ++ i )
h[i] = {null, null};
sort(w, w + n);
tn = max(0, n / 2 - 1);
dfs_1(0, 0, 0);
dfs_2(tn, 0, 0);
cout << (res == N? -1: res) << '\n';
return 0;
}
【在线测评】










![[SAP ABAP] 数据字典](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/482fc68b72ae40b8ad511ed1d07fc264.png)