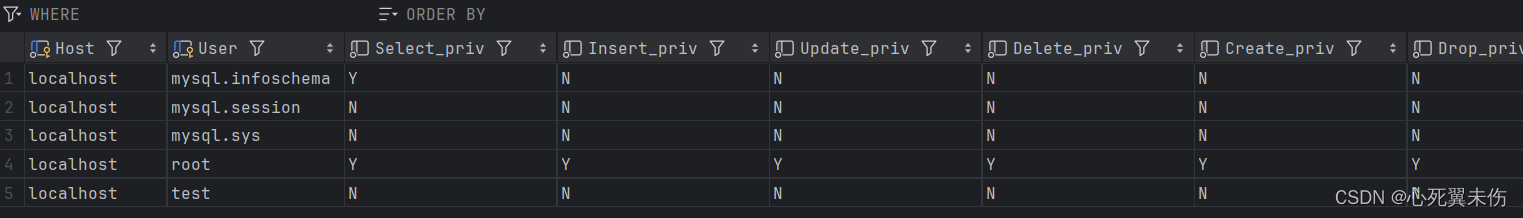
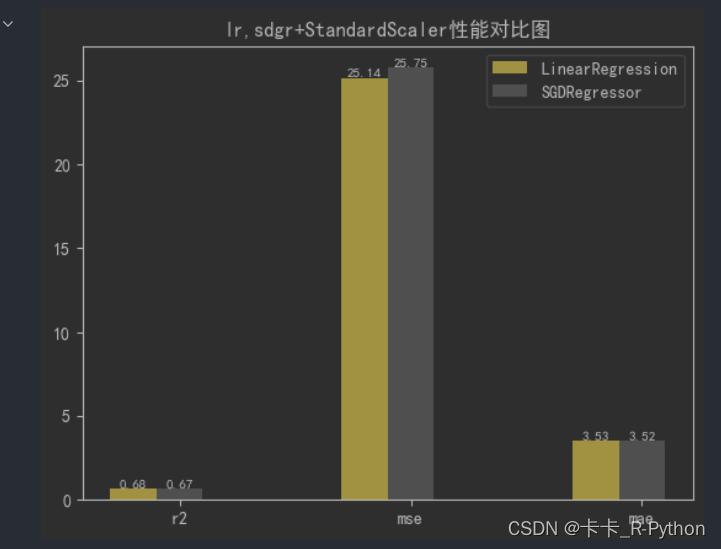
VAL树的特性
- 左右子树高度差的绝对值不超过1。(即左右子树高度差取值为-1,0,1)
- 且左右子树均为VAL树
- 右子树的值大于左子树的值
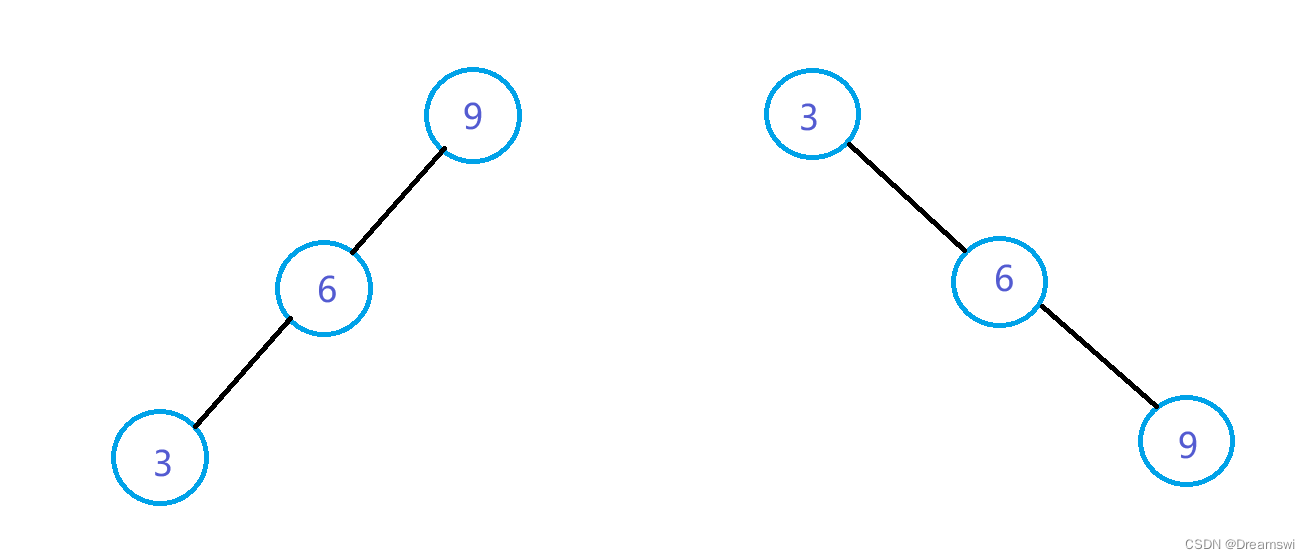
在搜索二叉树中我们提及了搜索二叉树的退化问题。
当有序(升序或降序)地插入时,搜索二叉树就会出现下图的情况,搜索次数从树的高度次退化成n次。而平衡搜索二叉树就解决了这一问题。
平衡方法
在解决方案中,左右子树的差值被定为平衡因子,所以上述例子用平衡二叉搜索树的角度来看如下图。此时出现了不被允许的2和-2,意味着平衡被打破,需要进行调整平衡。
插入时平衡因子的变化逻辑
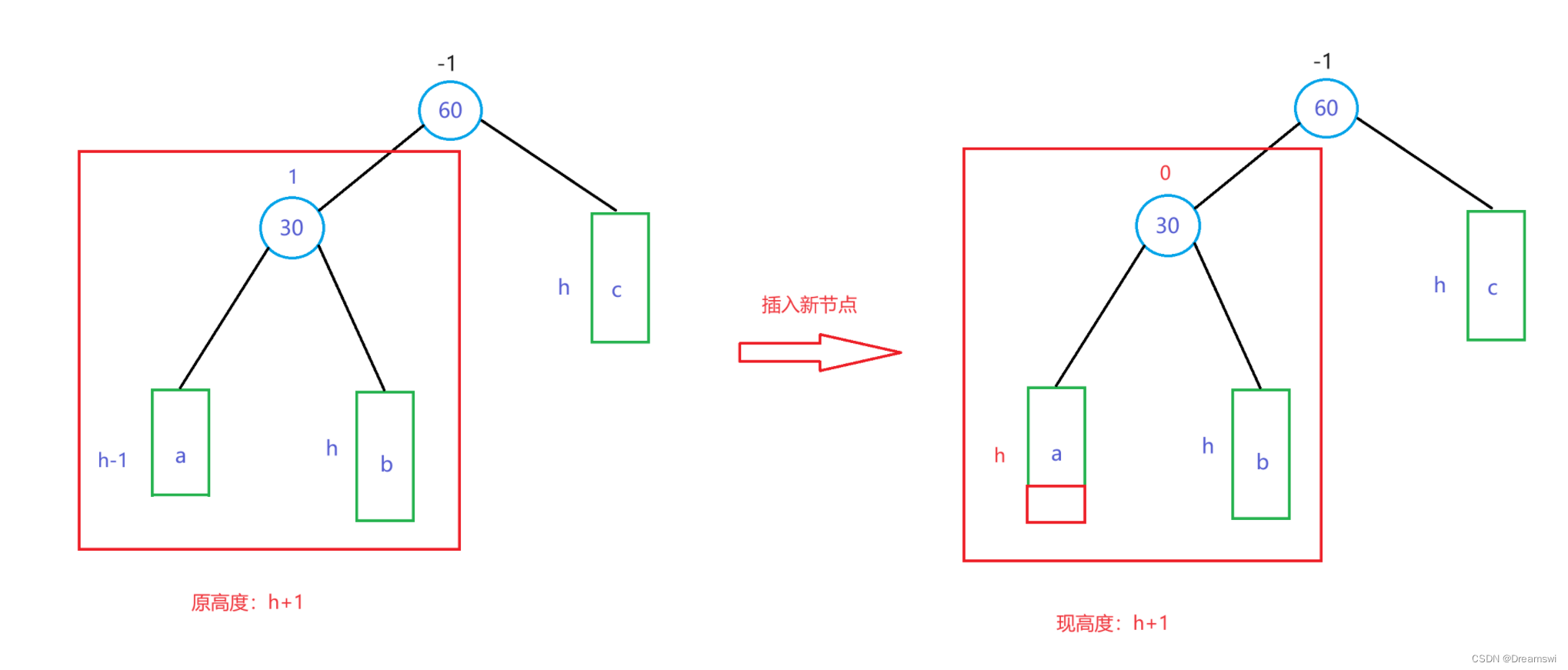
以下绿色方框代表一棵子树,h为其高度,且h>=0,具体节点上方的数字为平衡因子。
因为插入节点,导致60这个节点的左右子树失衡了。
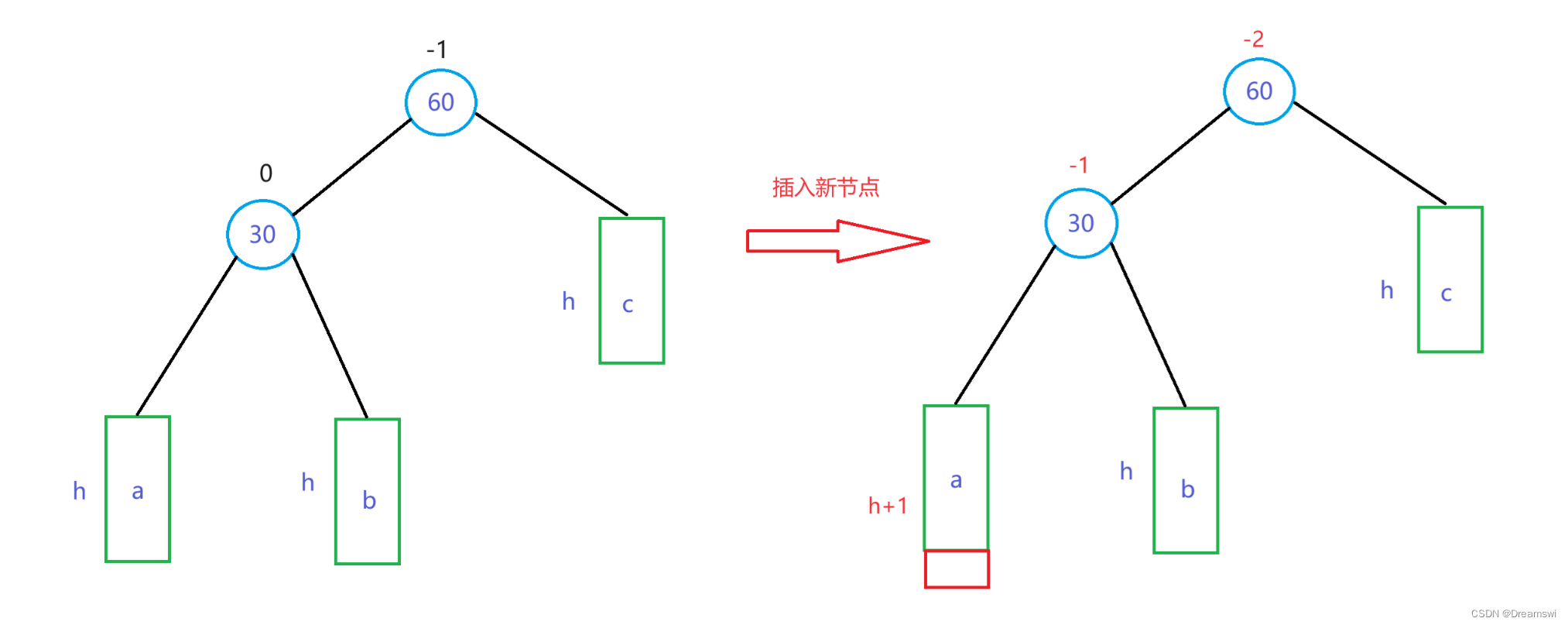
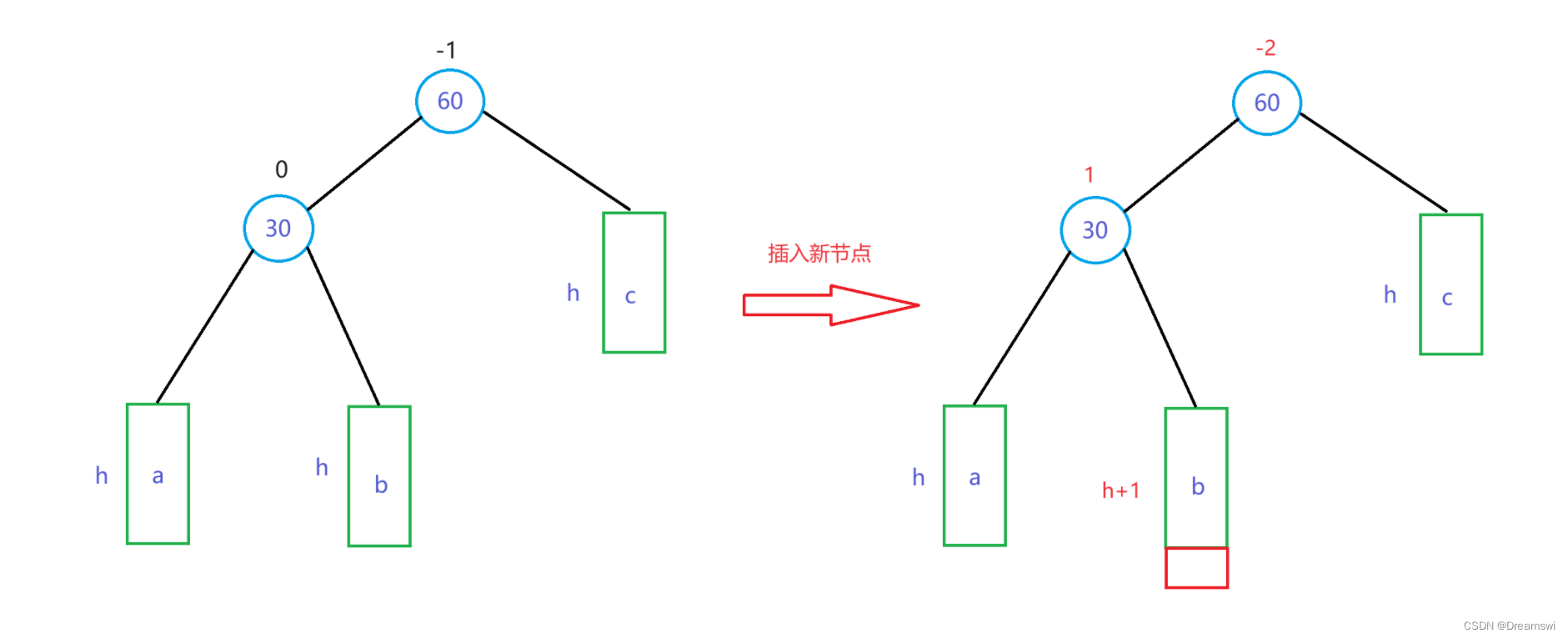
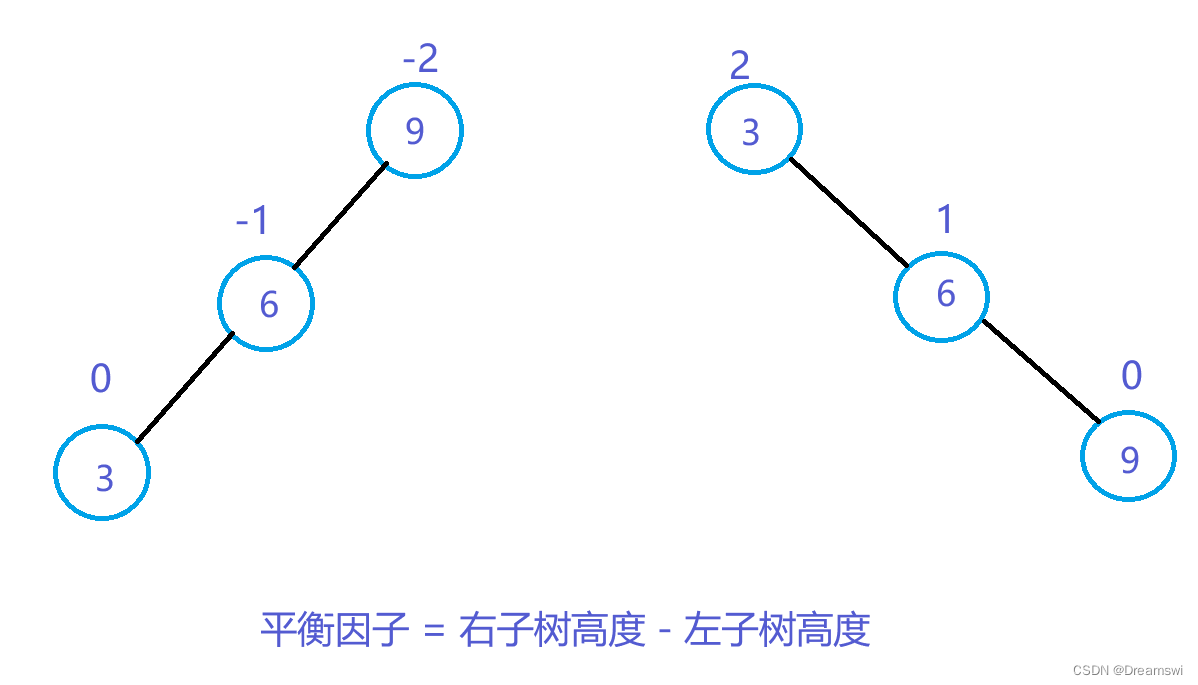
如图我们可以看到,根据插入位置的不同,其父节点的平衡因子的变化也不同。因为此处我使用的平衡因子 = 右子树高度 - 左子树高度。所以当插入到右子树时,父节点平衡因子+1,插入到左子树时,父节点平衡因子-1。
了解完插入时平衡因子的变化,我们再来了解一下变化的两种情况。
(1)插入后父节点平衡因子变为1或-1的,那么其原来的平衡因子是0,意味着该父节点原本平衡,插入节点后打破了平衡使该父节点为根的整棵子树高度产生变化,此时平衡因子需要继续向上更新,于是60这个节点也受其影响改变了,此时出现了不被允许的失衡,此时就要旋转调整平衡。
(2)第二种情况比较简单,插入后父节点平衡因子变为0,意味着其原本有一些失衡,但还在允许范围内,但插入后完全平衡了,此时无需再继续更新,因为高度没有改变。
总结:亚健康(-1、1)到健康(0)不用管,反之健康到亚健康要去向上更新平衡因子,因为其父节点可能直接就生病了。
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_pRoot == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = new Node(data);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _pRoot;
while (cur)
{
if (data > cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else if (data < cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
if (parent->_data < data)
{
parent->_pRight = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_pLeft = cur;
}
cur->_pParent = parent;
//调整平衡因子
while (parent)
{
if (cur == parent->_pLeft)
{
parent->_bf--;
}
else
{
parent->_bf++;
}
//插入后恰好平衡了,跳出循环
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
break;
} //高度出现变化但还未失衡,向上走进行判断
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
} //已经失衡需要进行调整
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
//右单旋
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
//左单旋
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
//右左双旋
RotateRL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
//左右双旋
RotateLR(parent);
}
break;
}
else
{
//理论而言不可能出现这个情况(此时小于-2或大于2)
assert(false);
}
}
return true;
}旋转调整
有了前面插入时平衡因子变化逻辑的铺垫,失衡时的情况就简化成了:
失衡节点无非是-2或2,造就失衡节点的子节点无非是-1,1(产生高度变化)。排列组合后就出现了四种情况。于是出现四种旋转方式与其一一对应。
右单旋
此时的失衡情况为:左左(插入在失衡节点的左节点的左子树中),此时失衡节点平衡因子为-2,产生高度变化的子节点平衡因子为-1。
所以右单旋适用于“左左”,即parent的平衡因子为-2,高度变化的子节点的平衡因子为-1。
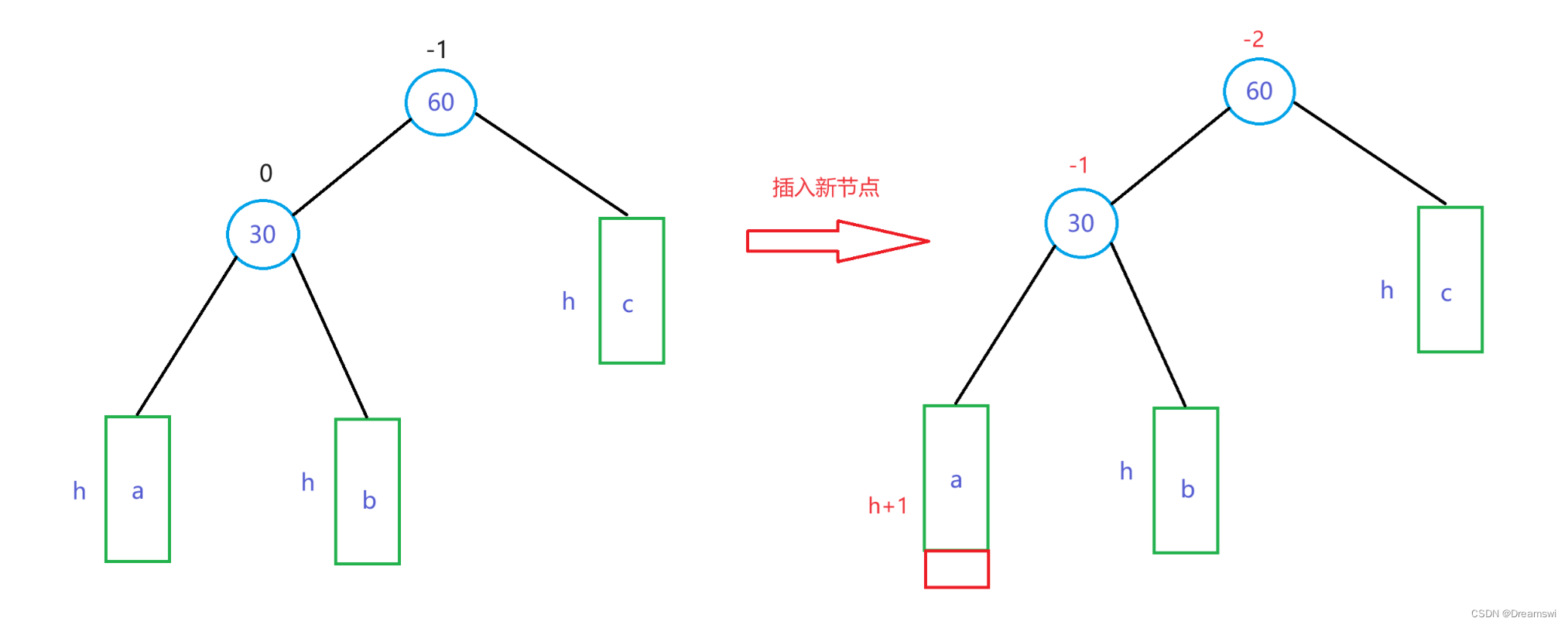
右单旋过程:
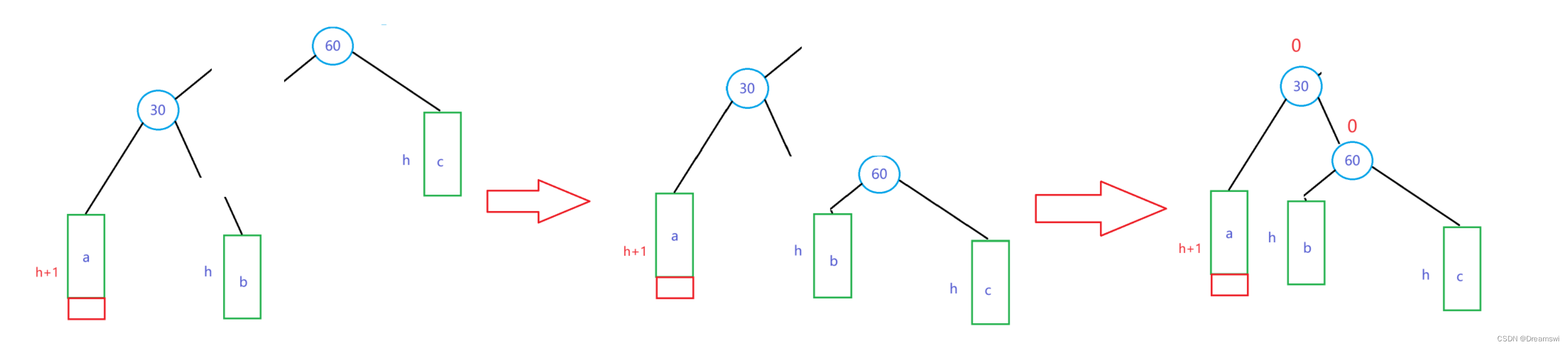
可以看到,调整后30和60这两个节点的平衡因子都为0了。
那么为什么要这么做?
现在我们先来分析一下他们的大小关系。
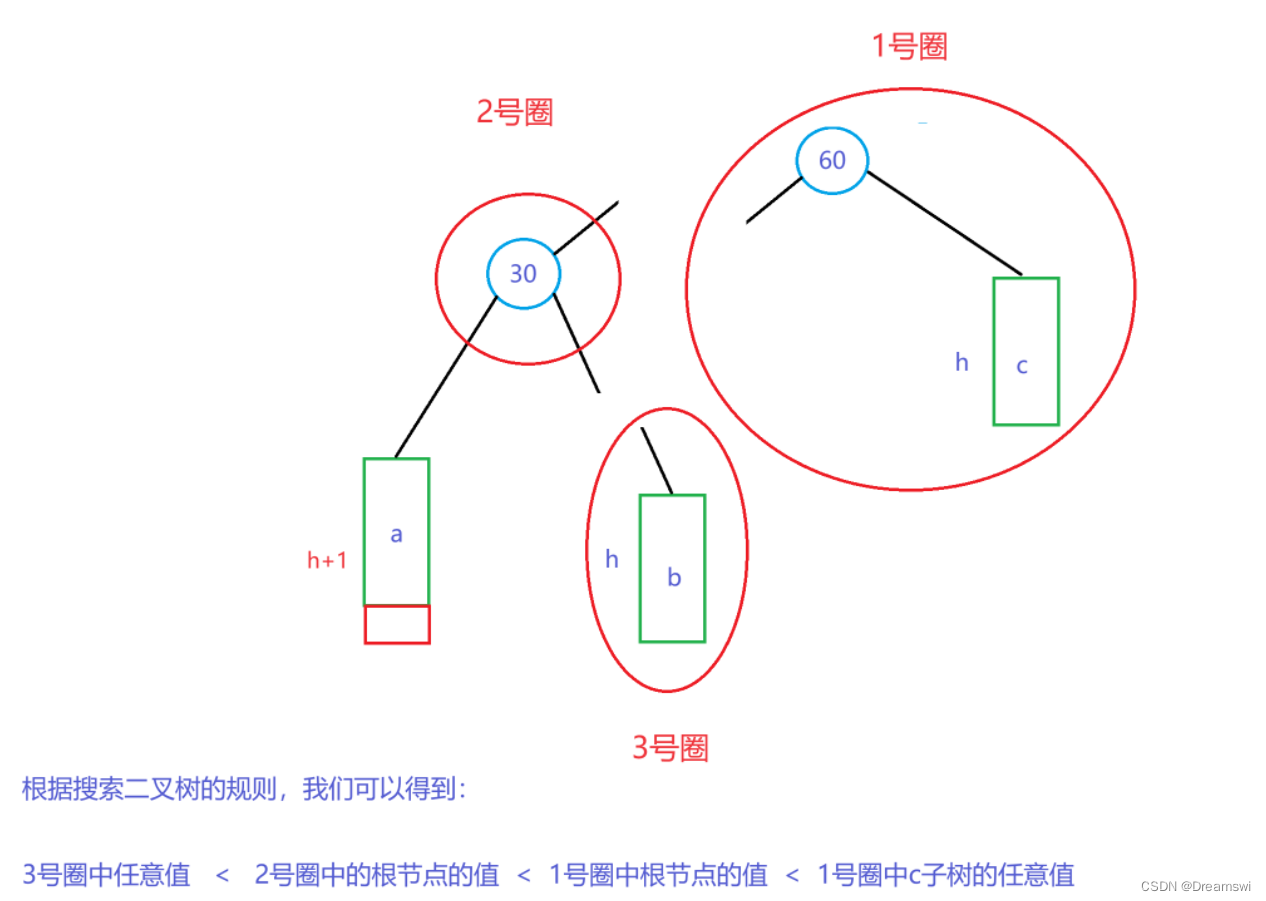
比较大小后发现,60非常适合当作30的右子树根节点,同时又做b子树的父节点,因为60>b子树任意值>30。
所以右单旋就是将失衡节点及其右子树下压,当作高度出现变化的节点的右子树,再连接上b子树和60这个节点,就使30的左右子树高度一致了。左子树高度是h+1(1为插入的节点),右边也是h+1(1为原父节点),此时30成为新父节点。
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;
pParent->_pLeft = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_pParent = pParent;
subL->_pRight = pParent;
Node* temp = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = subL;
//pParent有可能为根,右单旋后应该更新根节点指向。
if (pParent == _pRoot)
{
_pRoot = subL;
_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (temp->_pLeft == pParent)
{
temp->_pLeft = subL;
}
else
{
temp->_pRight = subL;
}
subL->_pParent = temp;
}
pParent->_bf = subL->_bf = 0;
}左单旋
与右单旋同理,不过多赘述。
左单旋适用于“右右”,即parent的平衡因子为2,高度变化的子节点的平衡因子为1。
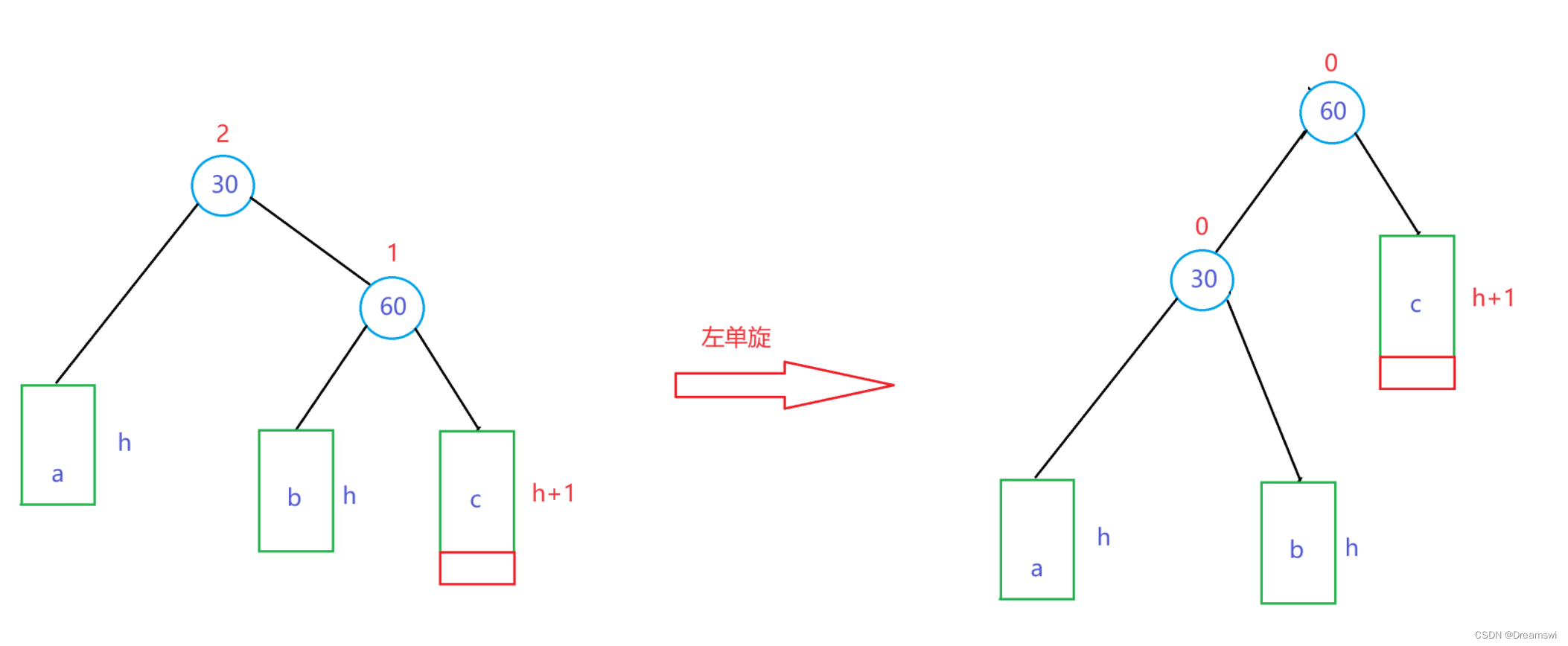
旋转过程:
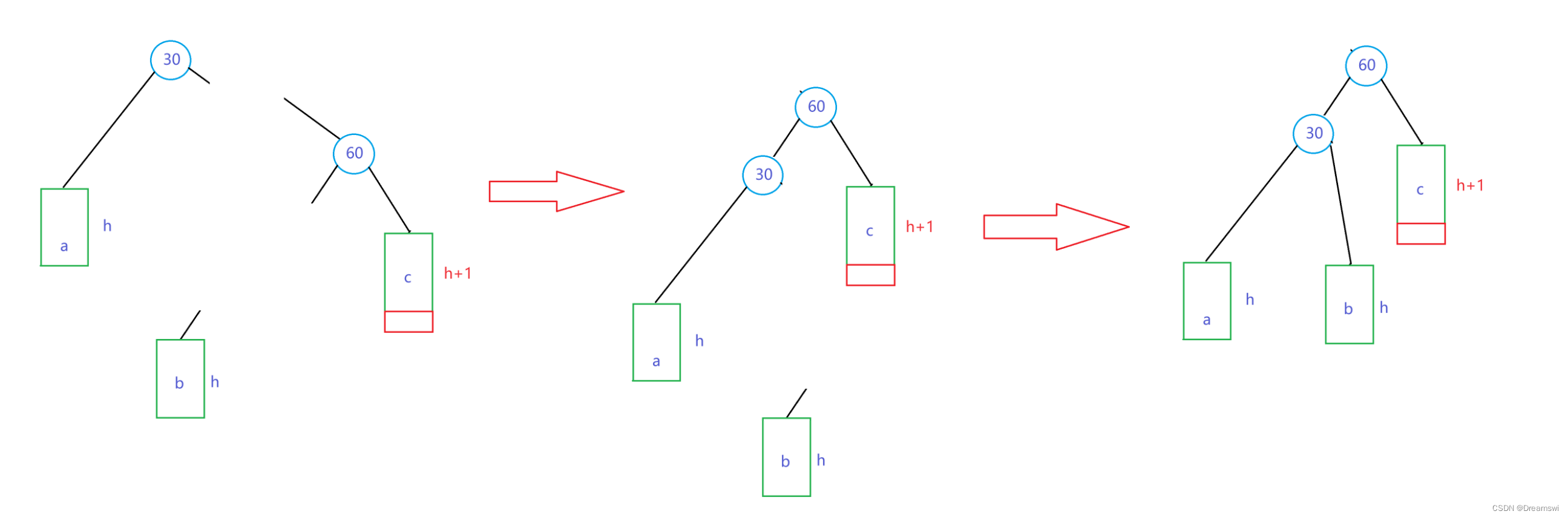
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;
pParent->_pRight = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_pParent = pParent;
subR->_pLeft = pParent;
Node* temp = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = subR;
//pParent有可能为根,右单旋后应该更新根节点指向。
if (pParent == _pRoot)
{
_pRoot = subR;
_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (temp->_pLeft == pParent)
{
temp->_pLeft = subR;
}
else
{
temp->_pRight = subR;
}
subR->_pParent = temp;
}
pParent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;
}左右双旋
如图所示,当出现插入节点在失衡节点(90)其左孩子(30)的右孩子(60)下的子树时,就需要用到左右双旋,单旋是无法解决的。
即:失衡节点平衡因子为-2,且其左孩子的平衡因子为1时使用左右双旋,以下简称“左右”。
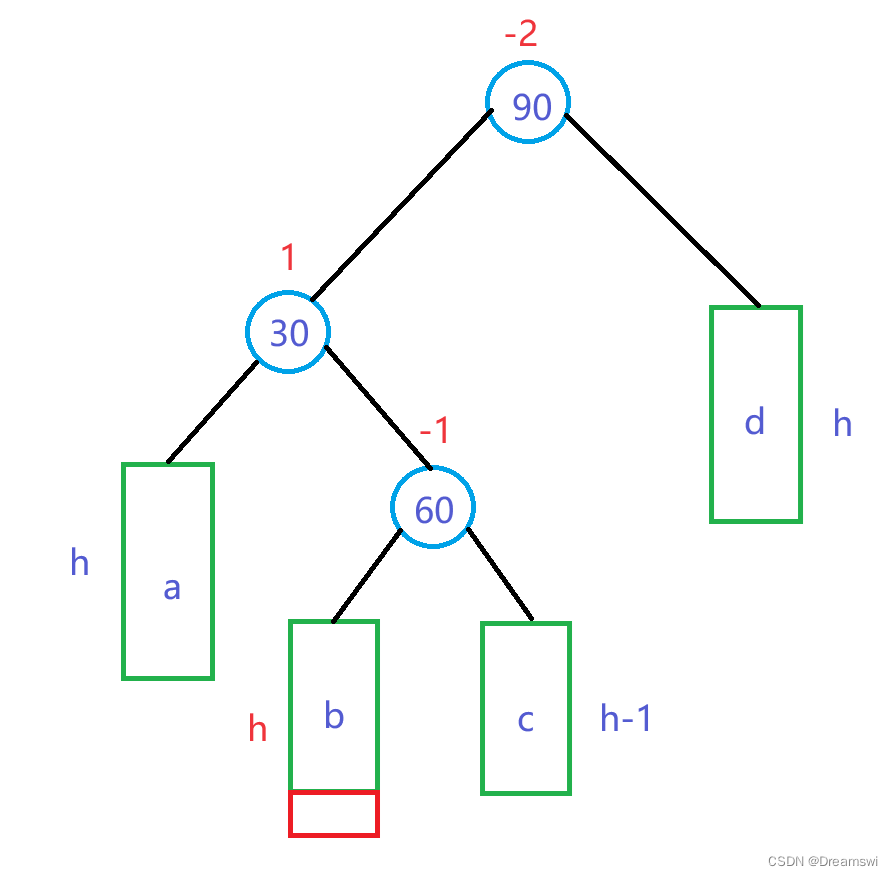
第一步,我们对30为根的子树进行左单旋。(第一次旋转后,失衡的状况从“左右”变成了可以使用右单旋的“左左”)
第二步,我们对90为根的子树进行右单旋。
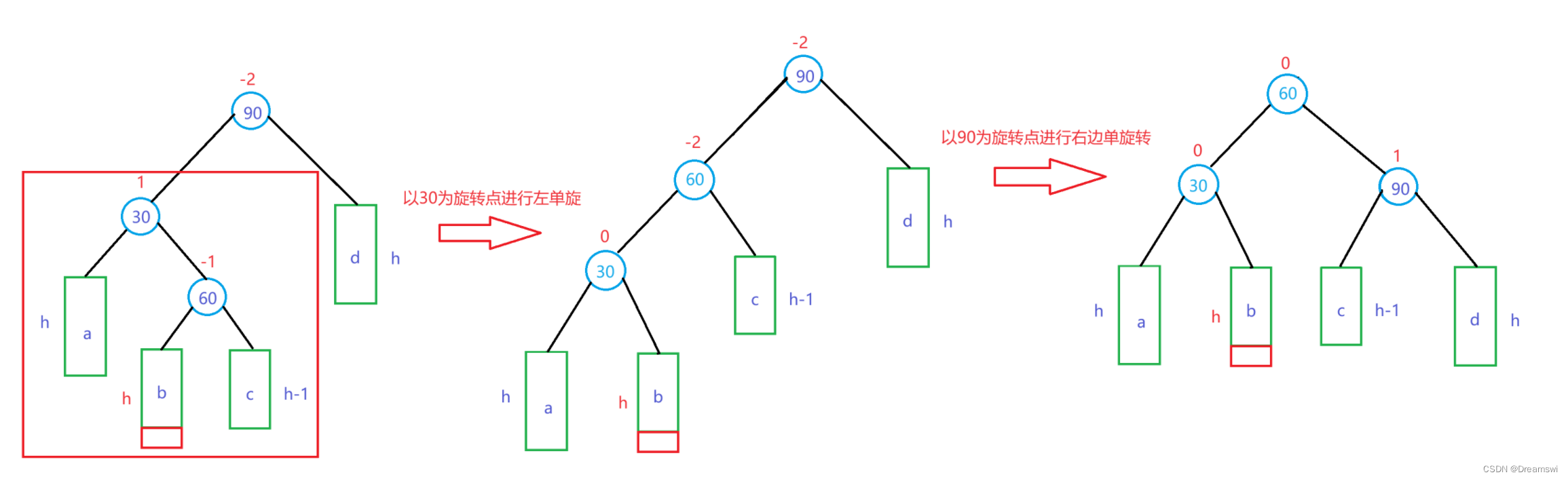
代码实际上是对左单旋和右单旋的复用,然后再处理节点间的连接关系。
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;
int bf = subLR->_bf;
RotateL(subL);
RotateR(pParent);
subLR->_bf = 0;
if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = -1;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 1;
subL->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = 0;
}
}右左双旋
失衡节点平衡因子为2,且其左孩子的平衡因子为-1时使用左右双旋。
第一步,我们对90为根的子树进行右单旋。(第一次旋转后,失衡的状况从“右左”变成了可以使用左单旋的“右右”)
第二步,我们对30为根的子树进行左单旋。
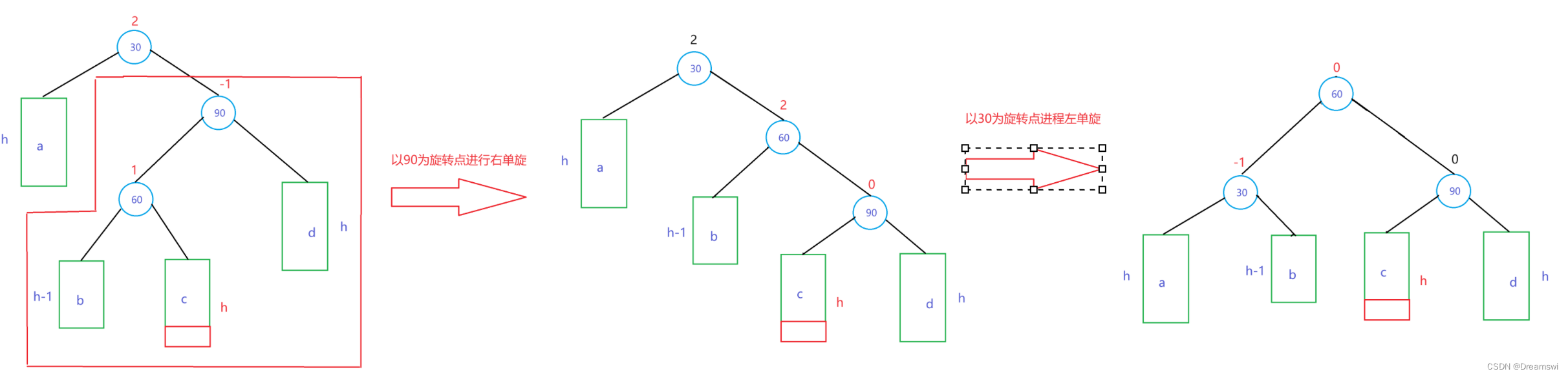
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;
int bf = subRL->_bf;
RotateR(subR);
RotateL(pParent);
subRL->_bf = 0;
if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = -1;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 1;
}
else
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
}完整代码实现
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace VAL
{
template<class T>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr)
, _pRight(nullptr)
, _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _bf(0)
{}
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;
T _data;
int _bf; // 节点的平衡因子
};
// AVL: 二叉搜索树 + 平衡因子的限制
template<class T>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
AVLTree()
: _pRoot(nullptr)
{}
Node* Find(const T& data)
{
Node* cur = _pRoot;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_data < data)
{
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else if (cur->_data > data)
{
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_pRoot == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = new Node(data);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _pRoot;
while (cur)
{
if (data > cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else if (data < cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
if (parent->_data < data)
{
parent->_pRight = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_pLeft = cur;
}
cur->_pParent = parent;
//调整平衡因子
while (parent)
{
if (cur == parent->_pLeft)
{
parent->_bf--;
}
else
{
parent->_bf++;
}
//插入后恰好平衡了,跳出循环
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
break;
} //高度出现变化但还未失衡,向上走进行判断
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
} //已经失衡需要进行调整
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateRL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateLR(parent);
}
break;
}
else
{
// 理论而言不可能出现这个情况
assert(false);
}
}
return true;
}
// AVL树的验证
bool IsAVLTree()
{
return _IsAVLTree(_pRoot);
}
int Size()
{
return _Size(_pRoot);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_pRoot);
cout << endl;
}
size_t Height()
{
return _Height(_pRoot);
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_pLeft);
cout << root->_data << endl;
_InOrder(root->_pRight);
}
bool _IsAVLTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_pLeft);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_pRight);
// 不平衡
if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) >= 2)
{
cout << root->_data << endl;
return false;
}
// 顺便检查一下平衡因子是否正确
if (rightHeight - leftHeight != root->_bf)
{
cout << root->_data << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsAVLTree(root->_pLeft)
&& _IsAVLTree(root->_pRight);
}
size_t _Height(Node* _pRoot)
{
if (_pRoot == nullptr) return 0;
return max(_Height(_pRoot->_pLeft), _Height(_pRoot->_pRight)) + 1;
}
int _Size(Node* root)
{
return root == nullptr ? 0 : _Size(root->_pLeft) + _Size(root->_pRight) + 1;
}
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;
pParent->_pLeft = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_pParent = pParent;
subL->_pRight = pParent;
Node* temp = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = subL;
//pParent有可能为根,右单旋后应该更新根节点指向。
if (pParent == _pRoot)
{
_pRoot = subL;
_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (temp->_pLeft == pParent)
{
temp->_pLeft = subL;
}
else
{
temp->_pRight = subL;
}
subL->_pParent = temp;
}
pParent->_bf = subL->_bf = 0;
}
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;
pParent->_pRight = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_pParent = pParent;
subR->_pLeft = pParent;
Node* temp = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = subR;
//pParent有可能为根,右单旋后应该更新根节点指向。
if (pParent == _pRoot)
{
_pRoot = subR;
_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (temp->_pLeft == pParent)
{
temp->_pLeft = subR;
}
else
{
temp->_pRight = subR;
}
subR->_pParent = temp;
}
pParent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;
}
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;
int bf = subRL->_bf;
RotateR(subR);
RotateL(pParent);
subRL->_bf = 0;
if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = -1;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 1;
}
else
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
}
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;
int bf = subLR->_bf;
RotateL(subL);
RotateR(pParent);
subLR->_bf = 0;
if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = -1;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 1;
subL->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = 0;
}
}
private:
Node* _pRoot;
};
}




![[数据集][目标检测]婴儿状态睡觉哭泣检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式7109张3类别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d51f7da7b67c480a8879c3064d26d018.png)