SpringBoot总体流程
当我们启动一个SpringBoot程序的时候,只需要一个main方法就可以启动,但是对于其中流程时如何执行的,以及如何调用spring的IOC和AOP机制,本篇带着这个问题来整体体系化的梳理下流程。
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// test
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApp.class);
}
}
实际调用的是如下,也就是run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
// 调用重载的run方法,将传递的Class对象封装为了一个数组
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// 创建了一个SpringApplication对象,并调用其run方法
// 1.先看下构造方法中的逻辑
// 2.然后再看run方法的逻辑
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
基本可以分为两块,一个是构造方法,一个是run。
SpringBootApplication 构造方法
构造方法中,其实主要完成的工作,设置主启动类 primarySources,判断当前应用类型 servlet类型。通过公共方法,getSpringFactoriesInstances 进行获取目标类。然后设置到对应的初始化器以及监听器对象中。
然后通过堆栈信息获取主启动类
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 传递的resourceLoader为null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 记录主方法的配置类名称 用set进行去重复
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 记录当前项目的类型 servlet类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 加载配置在spring.factories文件中的ApplicationContextInitializer对应的类型并实例化
// 并将加载的数据存储在了 initializers 成员变量中。
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 初始化监听器 并将加载的监听器实例对象存储在了listeners成员变量中
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 反推main方法所在的Class对象 并记录在了mainApplicationClass对象中
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
其他的比较简单,主要分析下getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法
getSpringFactoriesInstances
整体流程,其实就是根据入参,从spring.factorties中 根据key获取对应的权限定类集合。
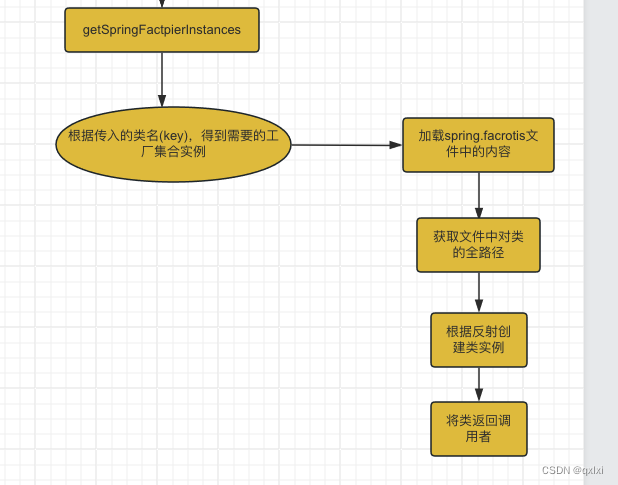
getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 根据入参类型 返回一个集合对象
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
// 获取当前上下文类加载器 默认是app类加载
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// 获取到的扩展类名存入set集合中防止重复
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 创建扩展点实例
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
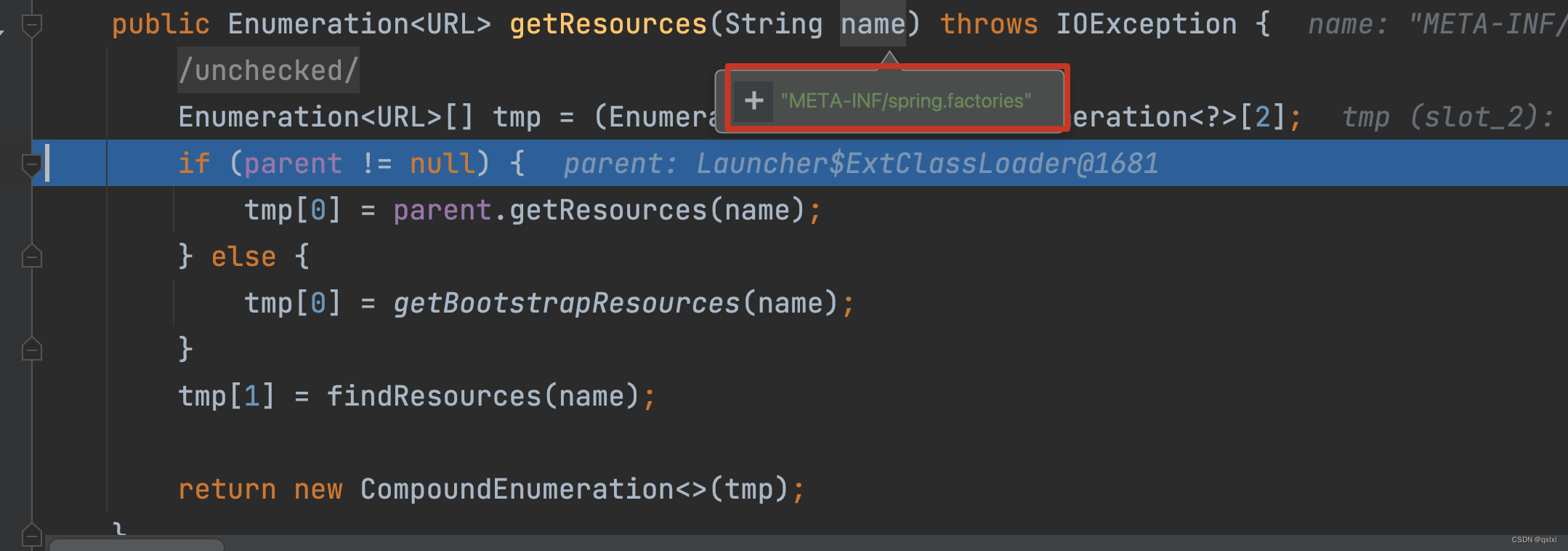
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames
通过调用loadSpringFactories 从META-INF/spring.factories处读取相应配置文件,key是对应的 factoryTypeName value是多个类名。
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 根据Class获取名称
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 先查询缓存是否有 第一次进来是空
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
// 判断classLoader是否为空
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
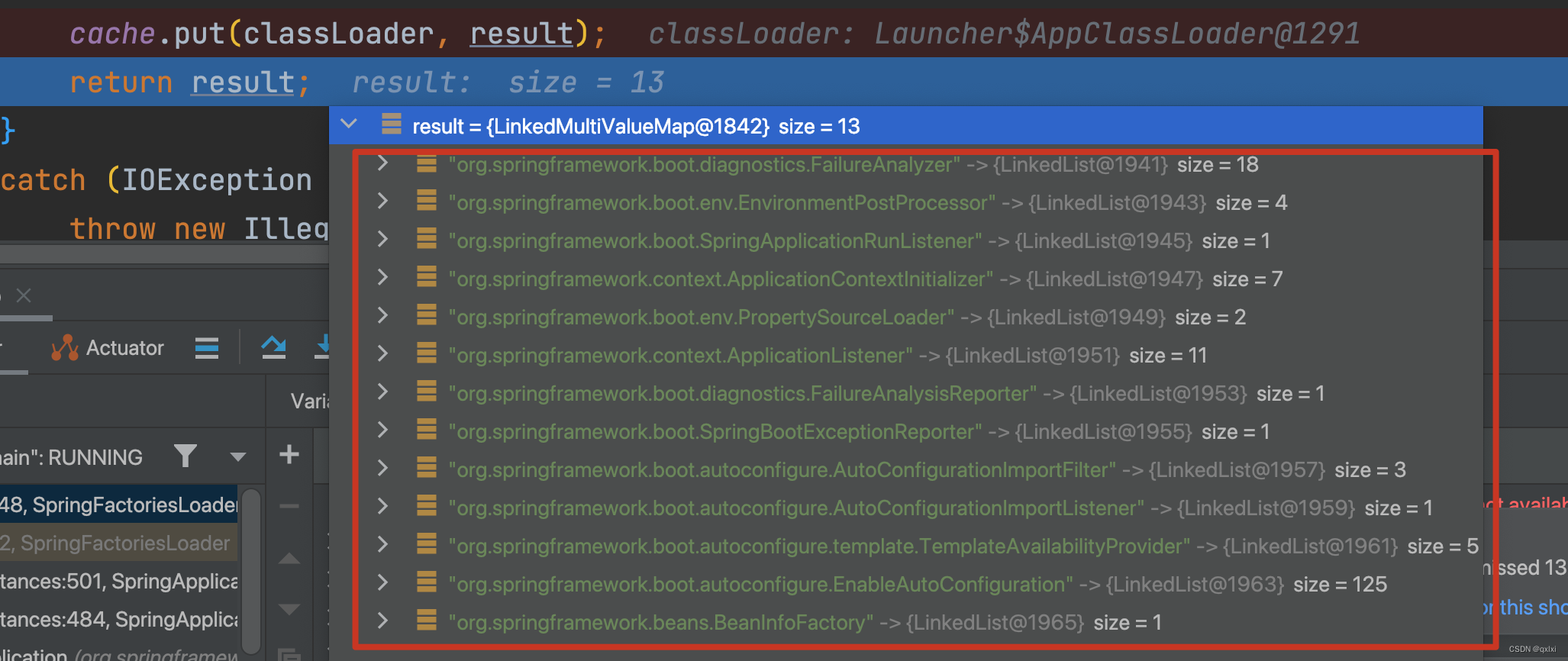
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
前面获取到所有类,然后进行反射进行实例化,添加到instances 集合中 返回。
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
// 创建实例的集合容器
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
// 通过反射将扩展点实例实例化
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
所以这个过程有设置了两个 ApplicationContextInitializer、ApplicationListener 会对配置中的类进行初始化。
构造方法就执行如下方法。

run方法
run方法比较核心,其中主要包含初始化环境变量、事件发布等,应用参数设置、打印banner、创建上下文对象,异常处理器、刷新前操作、刷新操作、刷新后操作、监听器运行等。好了,我们分析下主要的流程。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 创建一个任务执行观察器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
// 开始执行记录执行时间
stopWatch.start();
// 声明 ConfigurableApplicationContext 对象
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 声明集合容器用来存储 SpringBootExceptionReporter 启动错误的回调接口
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 设置了一个名为java.awt.headless的系统属性
// 其实是想设置该应用程序,即使没有检测到显示器,也允许其启动.
//对于服务器来说,是不需要显示器的,所以要这样设置.
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 获取 SpringApplicationRunListener 加载的是 EventPublishingRunListener
// 获取启动时的监听器---》 事件发布器 发布相关事件的 11个监听器 谁去发布事件?
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 触发启动事件 发布 starting 事件 --》 那么监听starting事件的监听器就会触发
listeners.starting();
try {
// 构造一个应用程序的参数持有类 java -jar xx.jar a
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 创建并配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 配置需要忽略的BeanInfo信息
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 输出的Banner信息
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建应用上下文对象 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
// 加载配置的启动异常处理器
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 刷新前操作
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新应用上下文 完成Spring容器的初始化
refreshContext(context);
// 刷新后操作 功能拓展进行使用
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 结束记录启动时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 事件广播 启动完成了
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 事件广播启动出错了
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 监听器运行中
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 返回上下文对象--> Spring容器对象
return context;
}
getRunListeners 获取监听器
这里会获取spring.factories 的中的SpringApplicationRunListener 类,然后实例化。并且调用start()进行启动执行。这里以 LoggingApplicationListener 为例子,执行了 日志的操作。
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
// getSpringFactoriesInstances 读取spring.factories 文件中key 为 SpringApplicationRunListener 类型的
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
void starting() {
// 发布器 EventPulishingRunListener
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
public void starting() {
// System.out.println("EventPublishingRunListener ----》starting ");
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
private void onApplicationStartingEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
this.loggingSystem = LoggingSystem.get(event.getSpringApplication().getClassLoader());
this.loggingSystem.beforeInitialize();
}
prepareEnvironment 环境准备
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
// 创建并且配置 Environment servlet context config \ systemt config等信息
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置PropertySources和activeProfiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 加载 configurationProperties 配置信息
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 在配置环境信息之前发布事件 配置相关 这里会在执行监听器的 environmentPrepared
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 把相关的配置信息绑定到Spring容器中
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 配置PropertySources对它自己的递归依赖
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
会再次执行
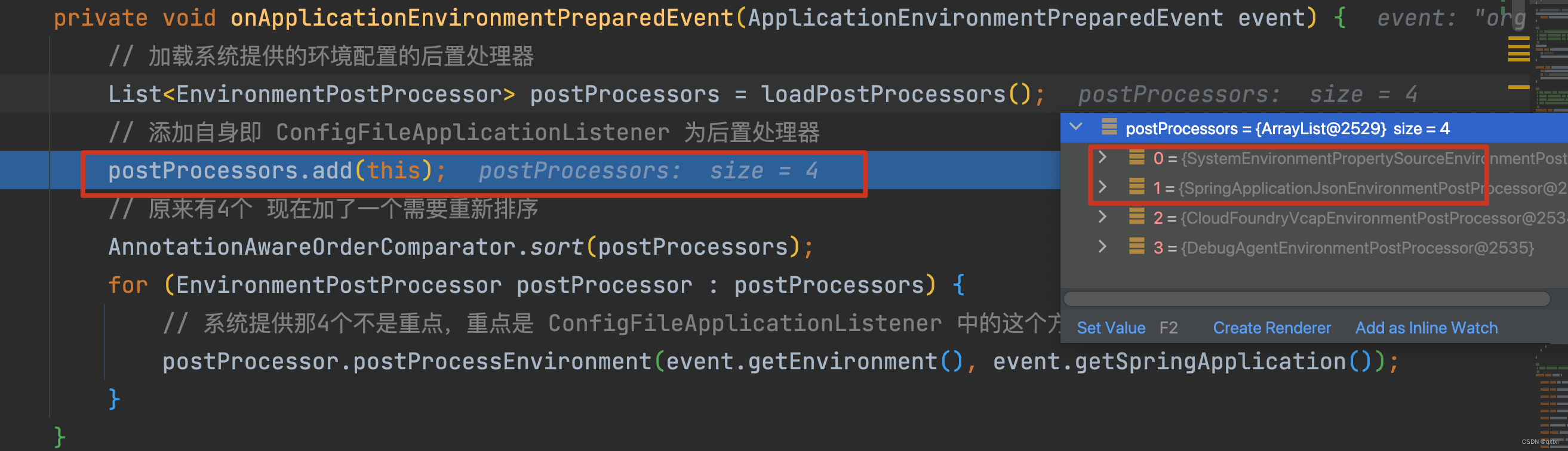
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
// 加载系统提供的环境配置的后置处理器
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
// 添加自身即 ConfigFileApplicationListener 为后置处理器
postProcessors.add(this);
// 原来有4个 现在加了一个需要重新排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
// 系统提供那4个不是重点,重点是 ConfigFileApplicationListener 中的这个方法处理
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
createApplicationContext 创建容器
这里比较简单根据webApplicationType的类型,选择创建对应的容器对象,这里是 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 并且进行实例化。调用默认构造器进行初始化了两个对象,AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader、ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 后续会使用到
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET: // AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
// 在实例化的时候 调用构造方法 创建两个对象 reader和scanner
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
//
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
Spring容器前置处理
将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化配置奠定基础。
这里其实主要做的两件事,一个是执行吃书画方法,将容器中的Initializer执行初始化操作,以及将主类,通过注解的方式添加到spring的beanDefinitionMap中。
// 1.设置环境属性
// 2.设置postprocess
// 3.启动类config信息 准备上下文环境工作
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 设置环境变量属性
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// 转换方法
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 应用初始化器 核心⭐️ 执行容器中的ApplicationContextInitializer(包括 spring.factories和自定义的实例)
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
// 获取bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 注册 springApplicationArguments 参数对象
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
// 注册banner
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// spring底层使用就是这个
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 核心⭐️
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
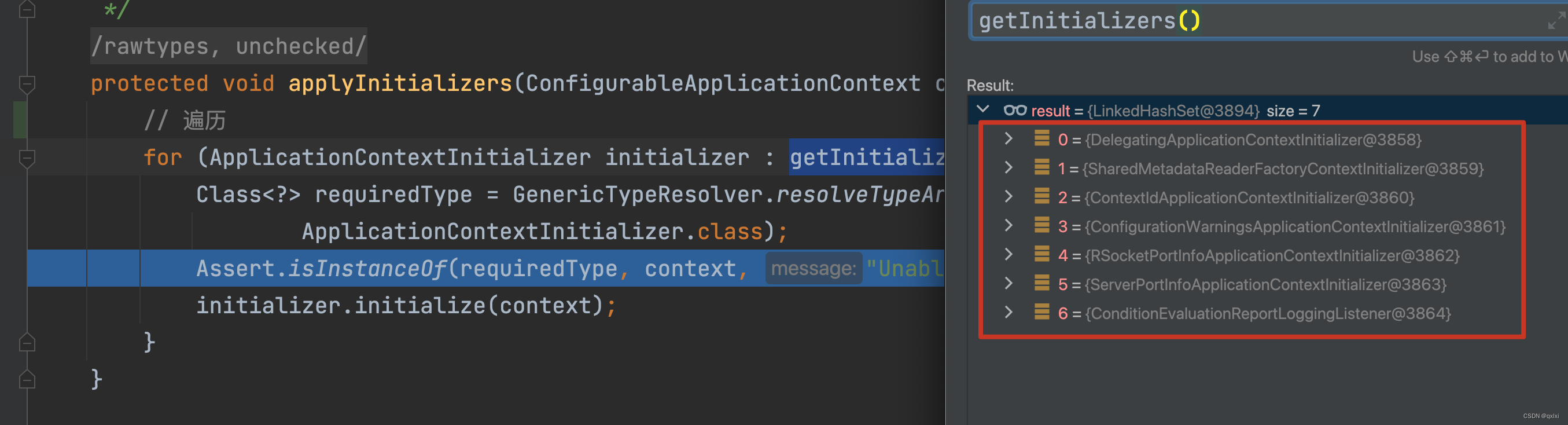
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 遍历
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(),
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
// 执行初始化方法
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
// ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer 执行了将ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor 添加到容器中 BFPP 等待容器进行刷新的BFPP的时候执行。
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 加入对象
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor(getChecks()));
}
loader.load();
int load() {
int count = 0;
for (Object source : this.sources) {
count += load(source);
}
return count;
}
// 加载
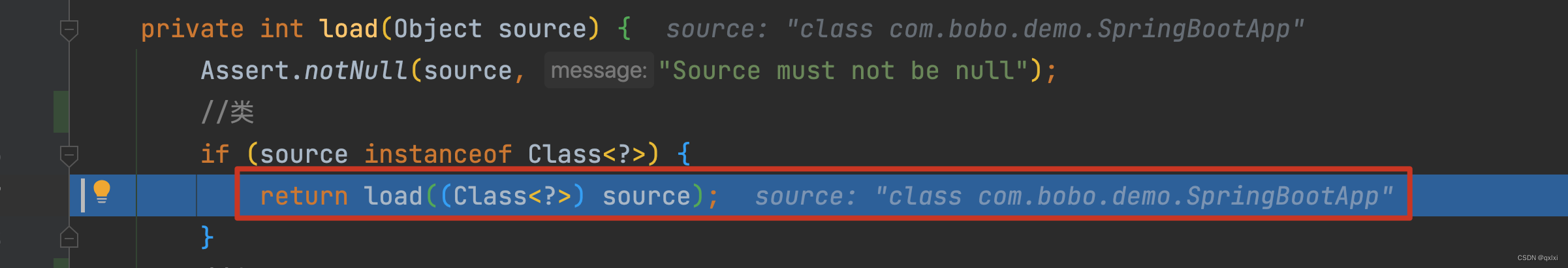
private int load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
//类
if (source instanceof Class<?>) {
return load((Class<?>) source);
}
//资源
if (source instanceof Resource) {
return load((Resource) source);
}
//包
if (source instanceof Package) {
return load((Package) source);
}
//
if (source instanceof CharSequence) {
return load((CharSequence) source);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
if (isComponent(source)) { // 是否包含compoent注解
// 注册SpringBootApp类到ioc 容器中
this.annotatedReader.register(source);
return 1;
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
refreshContext(context);
这里其实就是调用spring的refresh() 由于整体过于庞大,先不讲解。后续在补坑。
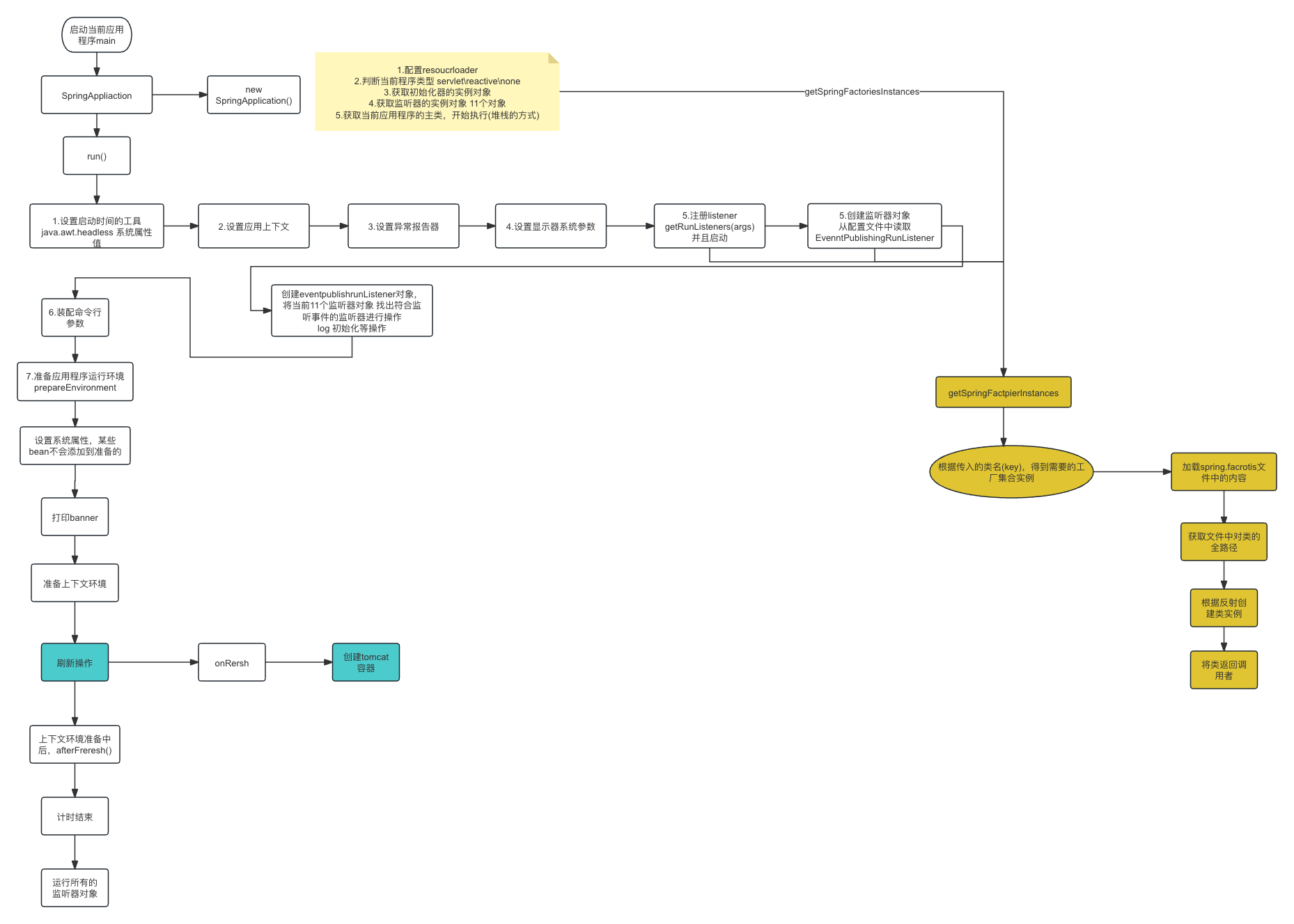
小总结








![[leetcode hot 150]第一百二十二题,买卖股票的最佳时机Ⅱ](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3333a1aa25c34a05a96d91f557599220.png)