在现代应用程序开发中,数据可视化是一个关键部分。本文将介绍如何使用 Java Swing 和 XChart 库创建各种类型的图表。XChart 是一个轻量级的图表库,支持多种类型的图表,非常适合在 Java 应用中进行快速的图表绘制。
1、环境配置
在开始之前,我们需要确保项目中包含了 XChart 的依赖。以下是在 Maven 项目中的 pom.xml 文件中添加 XChart 依赖的方法:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.knowm.xchart</groupId>
<artifactId>xchart</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</dependency>
2、创建不同类型的图表
以下是如何使用 XChart 创建不同类型的图表的示例代码。
面积图
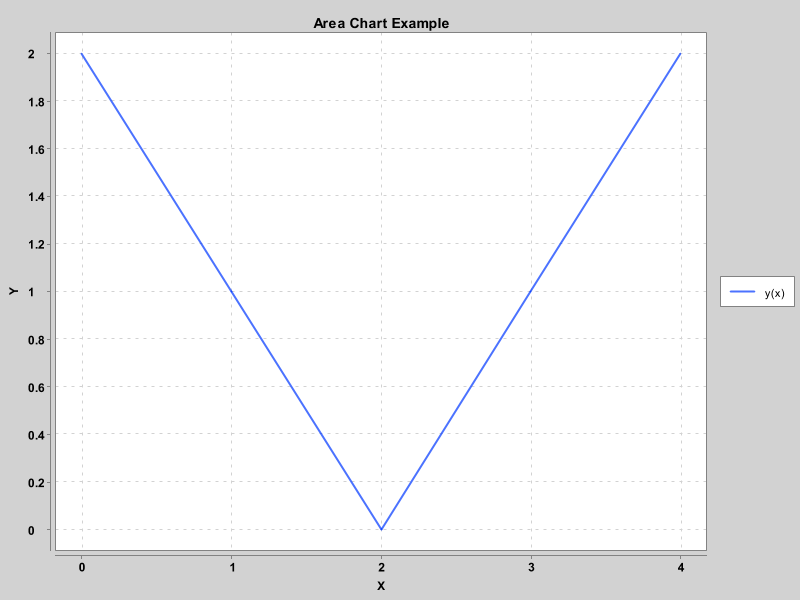
public class AreaChartExample extends JFrame {
public AreaChartExample() {
// 创建图表
XYChart chart = new XYChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Area Chart Example").xAxisTitle("X").yAxisTitle("Y").build();
// 添加数据
double[] xData = new double[] {0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0};
double[] yData = new double[] {2.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0};
chart.addSeries("y(x)", xData, yData).setMarker(SeriesMarkers.NONE).setFillColor(new Color(0, 0, 255, 50));
// 将图表面板添加到 JFrame
JPanel chartPanel = new XChartPanel<>(chart);
getContentPane().add(chartPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
AreaChartExample example = new AreaChartExample();
example.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
example.pack();
example.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
柱状图
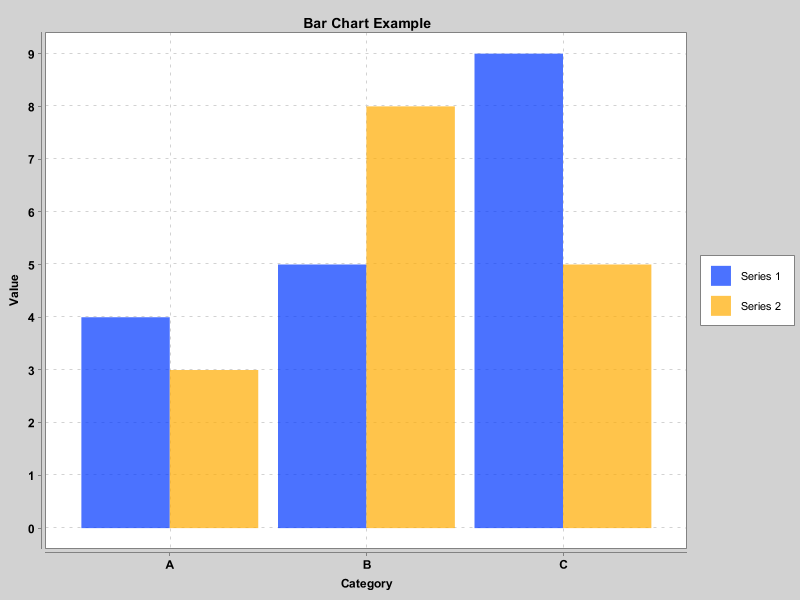
public class BarChartExample extends JFrame {
public BarChartExample() {
// 创建图表
CategoryChart chart = new CategoryChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Bar Chart Example").xAxisTitle("Category").yAxisTitle("Value").build();
// 添加数据
List<String> categories = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C");
List<Number> series1Values = Arrays.asList(4, 5, 9);
List<Number> series2Values = Arrays.asList(3, 8, 5);
chart.addSeries("Series 1", categories, series1Values);
chart.addSeries("Series 2", categories, series2Values);
// 将图表面板添加到 JFrame
JPanel chartPanel = new XChartPanel<>(chart);
getContentPane().add(chartPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
BarChartExample example = new BarChartExample();
example.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
example.pack();
example.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
气泡图
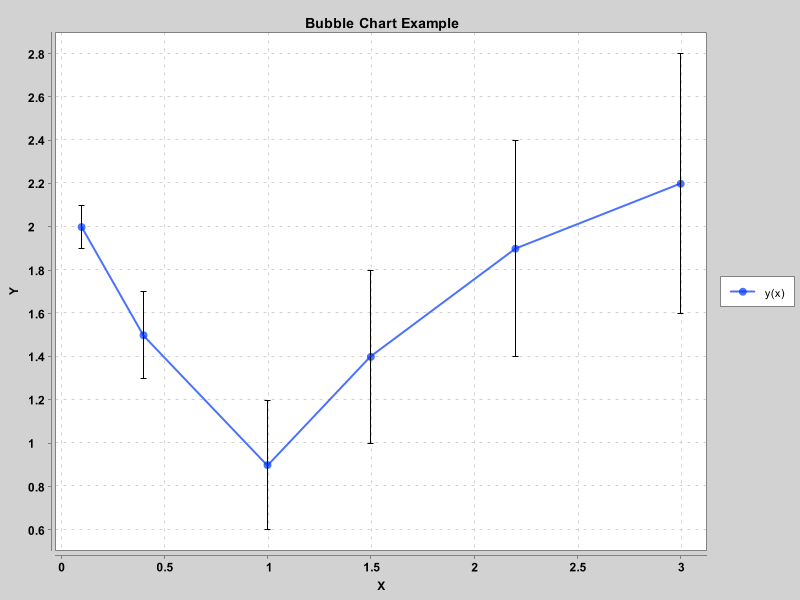
public BubbleChartExample() {
// 创建图表
XYChart chart = new XYChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Bubble Chart Example").xAxisTitle("X").yAxisTitle("Y").build();
// 添加数据
double[] xData = new double[] {0.1, 0.4, 1.0, 1.5, 2.2, 3.0};
double[] yData = new double[] {2.0, 1.5, 0.9, 1.4, 1.9, 2.2};
double[] bubbleSize = new double[] {0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6};
chart.addSeries("y(x)", xData, yData, bubbleSize).setMarker(SeriesMarkers.CIRCLE);
// 将图表面板添加到 JFrame
JPanel chartPanel = new XChartPanel<>(chart);
getContentPane().add(chartPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
BubbleChartExample example = new BubbleChartExample();
example.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
example.pack();
example.setVisible(true);
});
}
折线图
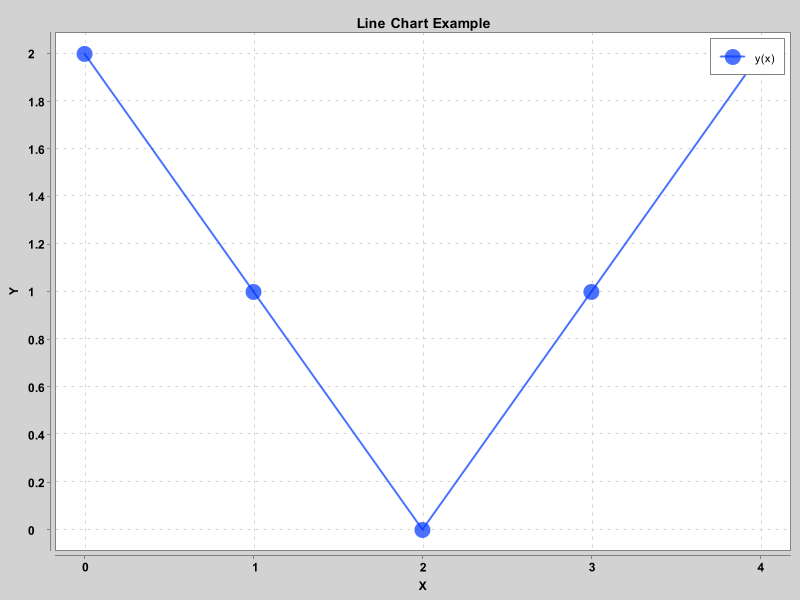
public class LineChartExample extends JFrame {
public LineChartExample() {
// 创建图表
XYChart chart = new XYChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Line Chart Example").xAxisTitle("X").yAxisTitle("Y").build();
// 自定义图表样式
chart.getStyler().setLegendPosition(Styler.LegendPosition.InsideNE);
chart.getStyler().setMarkerSize(16);
// 添加数据
double[] xData = new double[] {0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0};
double[] yData = new double[] {2.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0};
chart.addSeries("y(x)", xData, yData);
// 将图表面板添加到 JFrame
JPanel chartPanel = new XChartPanel<>(chart);
getContentPane().add(chartPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
LineChartExample example = new LineChartExample();
example.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
example.pack();
example.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
饼图
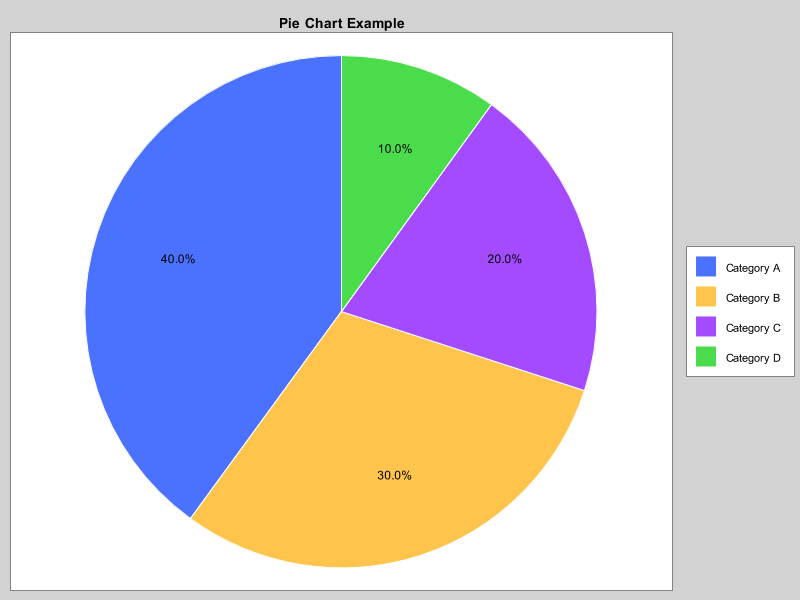
public class PieChartExample extends JFrame {
public PieChartExample() {
// 创建图表
PieChart chart = new PieChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Pie Chart Example").build();
// 添加数据
chart.addSeries("Category A", 40);
chart.addSeries("Category B", 30);
chart.addSeries("Category C", 20);
chart.addSeries("Category D", 10);
// 将图表面板添加到 JFrame
JPanel chartPanel = new XChartPanel<>(chart);
getContentPane().add(chartPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
PieChartExample example = new PieChartExample();
example.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
example.pack();
example.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
阶梯图
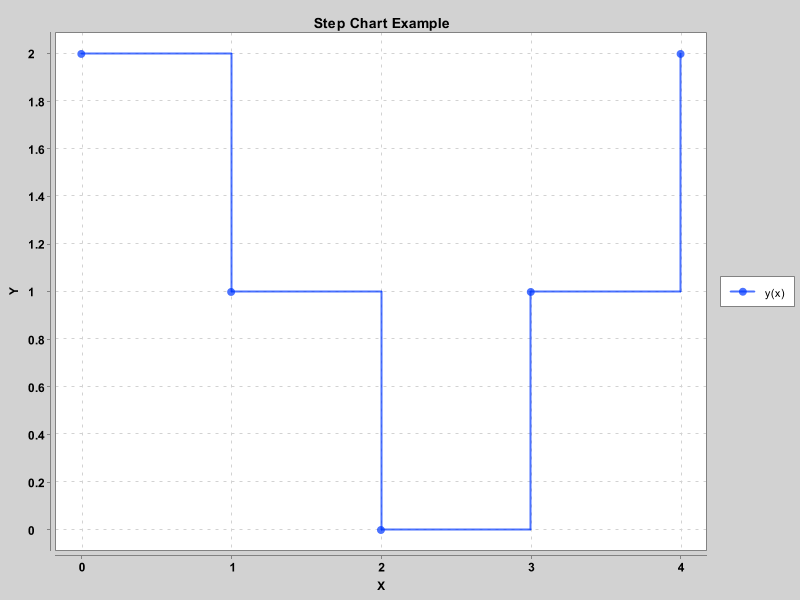
public class StepChartExample extends JFrame {
public StepChartExample() {
// 创建图表
XYChart chart = new XYChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Step Chart Example").xAxisTitle("X").yAxisTitle("Y").build();
// 添加数据
double[] xData = new double[] {0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0};
double[] yData = new double[] {2.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0};
chart.addSeries("y(x)", xData, yData).setXYSeriesRenderStyle(XYSeries.XYSeriesRenderStyle.Step);
// 将图表面板添加到 JFrame
JPanel chartPanel = new XChartPanel<>(chart);
getContentPane().add(chartPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
StepChartExample example = new StepChartExample();
example.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
example.pack();
example.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
3、总结
通过本文的示例代码,您可以在 Java 应用程序中轻松创建多种类型的图表。XChart 提供了简单且强大的 API,能够满足大多数数据可视化需求。希望这些示例能帮助您更好地理解如何使用 XChart 进行数据可视化。