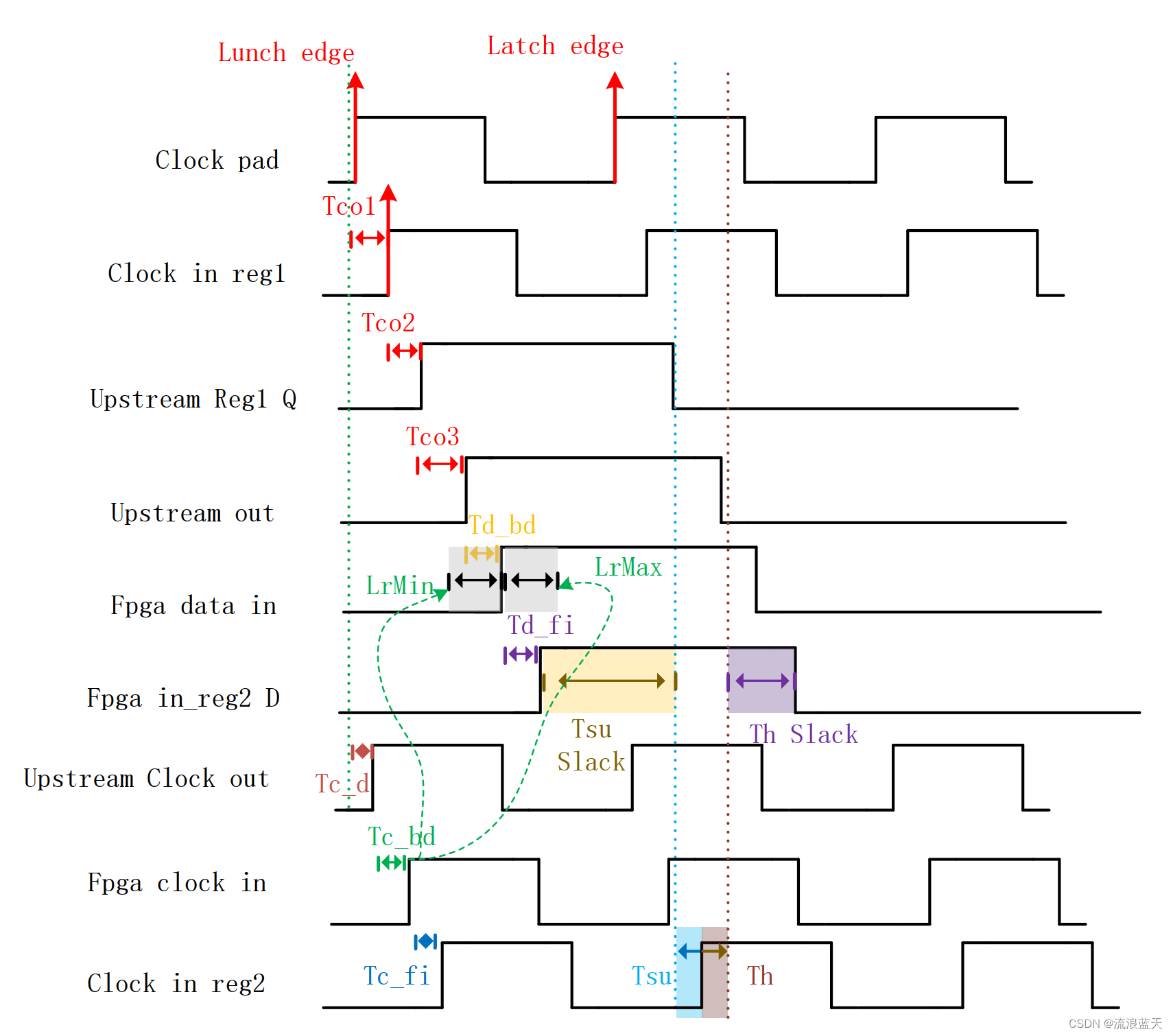
gici-open学习日记——GNSS RTK图优化
- 前言
- 初始化RTK的调用
- `rearrangePhasesAndCodes`
- 双差构造`formPhaserangeDDPair`
- 周跳探测`cycleSlipDetectionSD`
- 添加参数块
- 模糊度参数部分`addSdAmbiguityParameterBlocks`
- 添加双差伪距残差`addDdPseudorangeResidualBlocks`
- 添加双差相位残差`addDdPhaserangeResidualBlocks`
- 添加多普勒观测残差`addDopplerResidualBlocks`
- 其他一些参数块的添加
- 伪距双差残差`PseudorangeErrorDD`
- `EvaluateWithMinimalJacobians`
- 相位双差残差`PseudorangeErrorDD`
- `EvaluateWithMinimalJacobians`
- 多普勒残差`DopplerError`
- `EvaluateWithMinimalJacobians`
- 添加相对残差
- 更新DOP值`updateGdop`
前言
自己其实很久没有看这个框架了,包括后续代码好像也更新了不少,不过正好过一阵可能就要准备找工作了,这里就当简单把RTK的知识稍微看一下吧。如果和最新版本的代码有冲突的地方还请以最新版本为主
初始化RTK的调用
这个的调用流程和SPP是一样的,只不过相当于是在SPP调用的上一层,具体在GnssImuInitializer::addMeasurement函数里
bool GnssImuInitializer::addMeasurement(const EstimatorDataCluster& measurement)
{
/* 这部分不关注的代码 */
if (sub_gnss_estimator_->addMeasurement(*measurement.gnss)) {
/* 这部分不关注的代码 */
}
事实上,在进行具体的RTK解算之前,需要进行SPP提供给RTK解算的初值,所以才会在RtkEstimator::addGnssMeasurementAndState函数的最前面先进行SPP观测的添加以及SPP的解算
关于RtkEstimator::addGnssMeasurementAndState这个函数,大概的流程在gici-open学习日记(5):runMeasurementAddin函数引申——初始化这篇文章的“GNSS/INS初始化补充1:RtkEstimator流程”这里梳理过,所以这里不再梳理具体的流程,重点关注具体的参数块添加和解算
rearrangePhasesAndCodes
我的理解是这个函数是删除重复的相位,让每个观测值只对应一个相位的函数。这里面的核心是把载波相位和期对应的伪距码对应起来,如果不对应的情况,就把伪距观测值根据不同的DCB对应到同一个基础下,我在原函数的基础上加了一点点注释,就不特别详细地展开记录了。
void rearrangePhasesAndCodes(GnssMeasurement& measurement, bool accept_coarse)
{
CodeBiasPtr code_bias = measurement.code_bias;
for (auto& sat : measurement.satellites) {
std::string prn = sat.first;
char system = prn[0];
Satellite& satellite = sat.second;
std::unordered_map<int, Observation>& observations = satellite.observations;
std::unordered_map<int, Observation> arranged_observations; // 重新排序的观测
for (auto it = observations.begin(); it != observations.end(); it++) {
std::pair<int, Observation> arranged_observation;
int code = it->first;
Observation observation = it->second;
int phase_id = getPhaseID(system, code);
int default_code = 0;
#define MAP(S, P, C) \
if (system == S && phase_id == P) { default_code = C; }
PHASE_CHANNEL_TO_DEFAULT_CODE; // 为每个载波相位分配默认的码
#undef MAP
bool can_add = true;
// do not need to arrange
if (default_code == code) arranged_observation = *it;
// arrange to default code
else {
double bias = code_bias->getCodeBias(prn, code, accept_coarse);
double default_bias =
code_bias->getCodeBias(prn, default_code, accept_coarse);
// do not have code bias
if (bias == 0.0 || default_code == 0.0) {
// consider DCBs in the same frequency are zeros
if (accept_coarse) {
arranged_observation = std::make_pair(default_code, observation);
}
// cannot arrange
else {
// pass
can_add = false;
}
}
// use code bias to arrange
else {
observation.pseudorange += bias - default_bias; // 相当于把伪距观测值也对齐到默认码下面
arranged_observation = std::make_pair(default_code, observation);
}
}
// add to observations
if (can_add) {
if (arranged_observations.find(default_code) == arranged_observations.end()) {
arranged_observations.insert(arranged_observation);
}
}
}
satellite.observations = arranged_observations;
}
}
双差构造formPhaserangeDDPair
双差的公式manual里有给出了,这里不再详细记录

formPhaserangeDDPair进行了观测值双差的构建,其调用的参数有三个
const GnssMeasurement& measurement_rov, // 流动站观测值
const GnssMeasurement& measurement_ref, // 基准站观测值
const GnssCommonOptions& options // GNSS基本的配置选项
函数先对接收机之间做了一次单差
GnssMeasurementSDIndexPairs sd_pairs = formPhaserangeSDPair(
measurement_rov, measurement_ref, options); // 先对接收机间做一个单差
接下来先定义了5个变量,不过有一个目前来看是没有用到的。代码的话就是针对每一个变量进行赋值
/**
* prn_to_number_phases 卫星和载波相位数对应起来
* prn_to_index 每一个卫星prn所对应的在单差sd_pairs的索引
* prn_to_phases prn和载波相位对应起来
* system_to_num_phases 卫星系统和载波相位的对应,每一种系统挑出载波观测最多的以可卫星
*/
std::map<char, int> system_to_num_phases;
std::multimap<char, double> system_to_phases; // FIXME 没用到
std::map<std::string, int> prn_to_number_phases;
std::multimap<std::string, double> prn_to_phases;
std::multimap<std::string, int> prn_to_indexes;
然后// Find base satellites for each system and phases,这里就是为形成双差挑选一颗基础卫星,操作和RTKLIB是一样的,也是找出卫星高度角最大的。
std::map<char, std::string> system_to_base_prn;
for (size_t i = 0; i < getGnssSystemList().size(); i++) {
char system = getGnssSystemList()[i];
double max_elevation = 0.0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < sd_pairs.size(); j++) {
if (sd_pairs[j].rov.prn[0] != system) continue;
// we only select satellites with max phase number
if (prn_to_number_phases.at(sd_pairs[j].rov.prn) !=
system_to_num_phases.at(system)) continue;
double elevation = satelliteElevation( // 相对参考站的卫星高度角
measurement_ref.getSat(sd_pairs[j].ref).sat_position,
measurement_ref.position);
if (max_elevation < elevation) {
system_to_base_prn[system] = sd_pairs[j].rov.prn;
max_elevation = elevation; // 找到最大的卫星高度角
}
}
}
最后就是形成双差了,这里也是只是形成了双差的结构,但没有完成具体的双差计算
GnssMeasurementDDIndexPairs dd_pairs;
for (size_t i = 0; i < sd_pairs.size(); i++) {
char system = sd_pairs[i].rov.prn[0];
std::string prn = sd_pairs[i].rov.prn;
std::string prn_base = system_to_base_prn.at(system);
if (prn == prn_base) continue; // 同一颗卫星无法形成双差
for (auto it = prn_to_indexes.lower_bound(prn_base);
it != prn_to_indexes.upper_bound(prn_base); it++) {
GnssMeasurementSDIndexPair& sd_pair_base = sd_pairs[it->second];
int phase_id_base = getPhaseID(system, sd_pair_base.rov.code_type);
int phase_id = getPhaseID(system, sd_pairs[i].rov.code_type);
if (phase_id_base == phase_id) {
dd_pairs.push_back(GnssMeasurementDDIndexPair( // 形成了双差结构
sd_pairs[i].rov, sd_pairs[i].ref, sd_pair_base.rov, sd_pair_base.ref));
break;
}
}
}
周跳探测cycleSlipDetectionSD
周跳的精确探测可以确保正确的模糊度参数化,包括整周模糊度的搜索准则,所以也是RTK解算的一个重要部分。
- GICI和RTKLIB一样,也是在一上来利用LLI对周跳进行探测。LLI(Loss of Lock Indicator)表示失锁标识符,和接收机板卡的性能有关系。但在实际GNSS处理中,有些板卡也会把不是周跳通过LLI探测成周跳,周跳的过探测对后边的固定率影响也比较大,所以这个选项是可以根据自己的需要进行修改的,不过那都是很特殊的需求了。
cycleSlipDetectionLLI(measurement_rov_pre, measurement_rov_cur);
cycleSlipDetectionLLI(measurement_ref_pre, measurement_ref_cur);
关于cycleSlipDetectionLLI函数,就是根据当前历元的LLI标志和上一历元LLI与当前历元LLI是否一致判断的。
void cycleSlipDetectionLLI(GnssMeasurement& measurement_pre,
GnssMeasurement& measurement_cur)
{
for (auto& sat : measurement_cur.satellites) { // 先根据当前历元的LLI判断有没有周跳
for (auto& obs : sat.second.observations) {
Observation& observation = obs.second;
if (observation.LLI & 1) {
observation.slip = true;
continue;
}
// detect slip by parity unknown flag transition in LLI
uint8_t LLI_cur = observation.LLI; // 再根据两个历元的LLI是否一样判断
auto it_sat = measurement_pre.satellites.find(sat.first);
if (it_sat == measurement_pre.satellites.end()) continue;
auto it_obs = it_sat->second.observations.find(obs.first);
if (it_obs == it_sat->second.observations.end()) continue;
uint8_t LLI_pre = it_obs->second.LLI;
if (((LLI_pre & 2) && !(LLI_cur & 2)) || (!(LLI_pre & 2) && (LLI_cur & 2))) {
observation.slip = true;
#if LOG_CYCLE_SLIP
LOG(INFO) << "Detected cycle slip by LLI at " << sat.second.prn << ".";
#endif
}
}
}
}
-
接下来分别生成了上一历元与当前历元的单差观测值,这里不仅构造了
GnssMeasurementSDIndexPairs单差类型的变量,还完成了具体单差观测值的计算。 -
然后根据GF组合进行了周跳探测
Under not disturbed ionospheric conditions, the geometry-free combination performs as a very precise and smooth test signal,
driven by the ionospheric refraction. Although, for instance, the jump produced by a simultaneous one-cycle slip in both signals is smaller in this combination than in the original signals (λ2-λ1 =5.4cm), it can provide reliable detection even for small jumps
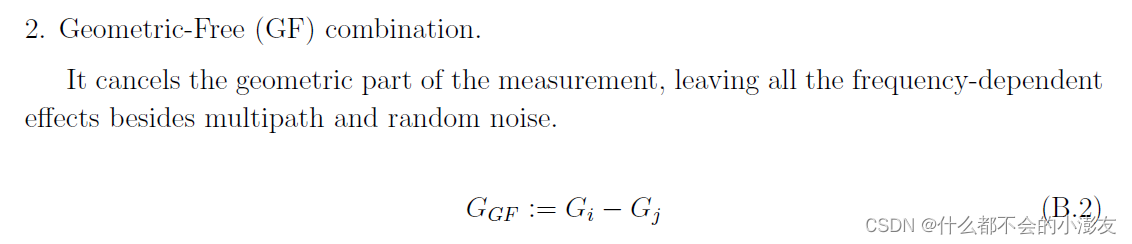
代码也很简单,就是分别计算得到了上一历元和当前历元的GF值,然后作差和阈值比较,大于阈值就认为发生了周跳。具体的计算内容在
cycleSlipDetectionGF(measurement_sd_pre, measurement_sd_cur, options.gf_sd_slip_thres);
- 根据时间间隔判断是否周跳
这个的核心就在于cycleSlipDetectionTimeGap中的一行代码
cycleSlipDetectionTimeGap(measurement_sd_pre, measurement_sd_cur, options.period * 1.5);
// cycleSlipDetectionTimeGap函数中
if (measurement_cur.timestamp - measurement_pre.timestamp < max_time_gap) {
return;
}
如果时间间隔大于设置的阈值,然后接下来又在代码中判断确认是单频率,就直接认为发生了周跳
- 最后就是周跳的汇总了,当流动站和参考站中有一个发生周跳的时候,就会认为当前的历元发生了周跳
for (size_t i = 0; i < pairs_cur.size(); i++) {
Observation& observation_sd = measurement_sd_cur.getObs(pairs_cur[i].rov);
Observation& observation_rov = measurement_rov_cur.getObs(pairs_cur[i].rov);
Observation& observation_ref = measurement_ref_cur.getObs(pairs_cur[i].ref);
observation_rov.slip |= observation_sd.slip;
observation_ref.slip |= observation_sd.slip;
}
添加参数块
模糊度参数部分addSdAmbiguityParameterBlocks
addSdAmbiguityParameterBlocks(curGnssRov(),
curGnssRef(), index_pairs, curGnssRov().id, curAmbiguityState());
前几个参数很好理解,就是当前的流动站、基准站、双差以及ID,最后一个参数得到的是模糊度状态容器ambiguity_states_(定义在gnss_estimator_base.h里)的最后一个变量,这里只是加入到参数块之中,具体的解算也在后面
- 函数上来先利用之前形成的双差关系得到了一些变量,在后边可能会用到
const Satellite& satellite = // 先利用双差得到了一些之后可能会用的变量
measurement_rov.getSat(index_pair.rov);
// 。。。这里省略了一些变量
- 然后根据ID判断在图优化中是否已经存在了
double code = index_pair.rov.code_type;
double wavelength = observation.wavelength; // FIXME 没用到啊
double phase_id = gnss_common::getPhaseID(system, code);
BackendId ambiguity_id = createGnssAmbiguityId(satellite.prn, phase_id, id);
CHECK(!graph_->parameterBlockExists(ambiguity_id.asInteger()))
<< "Ambiguity parameter for " << satellite.prn << " in phase "
<< phase_id << " has already been added!";
- 接下来用伪距和载波相位观测值给了个初值,其实原理就是用两个观测方程减一下就得到了

- TODO:事实上前面定义了波长的变量,按理说这里给初值用这个变量好一点,不过这里没有用到。我觉得用一下是不是比较好?
double phaserange = observation.phaserange; // 这里利用伪距和载波观测给了个初值
double pseudorange = observation.pseudorange;
double phaserange_ref = observation_ref.phaserange;
double pseudorange_ref = observation_ref.pseudorange;
double ambiguity = phaserange - phaserange_ref -
(pseudorange - pseudorange_ref);
// TODO ambiguity /= wavelength;
- 接下来就是构建模糊度参数并加到图中了
Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1> init;
init[0] = ambiguity;
std::shared_ptr<AmbiguityParameterBlock> ambiguity_parameter_block =
std::make_shared<AmbiguityParameterBlock>(init, ambiguity_id.asInteger());
CHECK(graph_->addParameterBlock(ambiguity_parameter_block));
state.ids.push_back(ambiguity_id);
- 因为形成双差是需要一颗
base_satellite的,所以接下来就是对这个卫星再进行一遍类似的操作
BackendId ambiguity_base_id = // 这里为作为基础的那颗卫星添加参数块
createGnssAmbiguityId(satellite_base.prn, phase_id, id);
if (!graph_->parameterBlockExists(ambiguity_base_id.asInteger()))
{
phaserange = observation_base.phaserange;
pseudorange = observation_base.pseudorange;
phaserange_ref = observation_ref_base.phaserange;
pseudorange_ref = observation_ref_base.pseudorange;
ambiguity = phaserange - phaserange_ref -
(pseudorange - pseudorange_ref);
// TODO 同理,这里是不是也可以利用上波长信息作为初值?
/**
* wavelength = observation_base.wavelength;
* ambiguity /= wavelength;
*/
Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1> init_base;
init_base[0] = ambiguity;
std::shared_ptr<AmbiguityParameterBlock> ambiguity_base_parameter_block =
std::make_shared<AmbiguityParameterBlock>(
init_base, ambiguity_base_id.asInteger());
CHECK(graph_->addParameterBlock(ambiguity_base_parameter_block));
state.ids.push_back(ambiguity_base_id);
- 最后添加模糊度的残差
addAmbiguityResidualBlock(ambiguity_base_id, init_base[0], // 在构建误差的时候会执行setInformation的操作
gnss_base_options_.error_parameter.initial_ambiguity);
添加双差伪距残差addDdPseudorangeResidualBlocks
这个函数也是进行了参数块的添加,关于参数块的核心计算步骤不在这个函数里,也是分为了ECEF和ENU两种框架下
// 这里用ENU框架下的代码举例子
else {
is_state_pose_ = true; // ENU框架下
BackendId pose_id = state.id_in_graph;
std::shared_ptr<PseudorangeErrorDD<7, 3>> pseudorange_error =
std::make_shared<PseudorangeErrorDD<7, 3>>( // 主要是进行构建这个残差
measurement_rov, measurement_ref,
index_pair.rov, index_pair.ref, index_pair.rov_base, index_pair.ref_base,
gnss_base_options_.error_parameter);
pseudorange_error->setCoordinate(coordinate_);
graph_->addResidualBlock(pseudorange_error,
huber_loss_function_ ? huber_loss_function_.get() : nullptr,
graph_->parameterBlockPtr(pose_id.asInteger()),
graph_->parameterBlockPtr(gnss_extrinsics_id_.asInteger()));
}
添加双差相位残差addDdPhaserangeResidualBlocks
这个和上一个函数没啥区别,不过是相位观测的话残差的维度会变多(模糊度),这里就不再重复记录了
// Add phaserange residual blocks
addDdPhaserangeResidualBlocks(curGnssRov(), curGnssRef(), index_pairs, curState()); // 相位双差残差
添加多普勒观测残差addDopplerResidualBlocks
这个其实和前两个也没什么不同,不过就是添加进去的残差信息换成多普勒观测量的了,关于多普勒的残差因子可以看manual的3.4.3节,这里代码也没有什么特别的东西,不再重复记录
if (rtk_options_.estimate_velocity) {
addDopplerResidualBlocks(curGnssRov(), curState(), num_valid_satellite); // 多普勒残差
}
其他一些参数块的添加
其实剩下添加的一些残差块都差不多,核心都在于残差构建的地方,那就不在具体的添加残差的函数里了,所以这里就不一一详细记录了,只是大概列一下都加了哪些
if (!isFirstEpoch()) {
if (!rtk_options_.estimate_velocity) {
// position
addRelativePositionResidualBlock(lastState(), curState()); // 相对位置残差
}
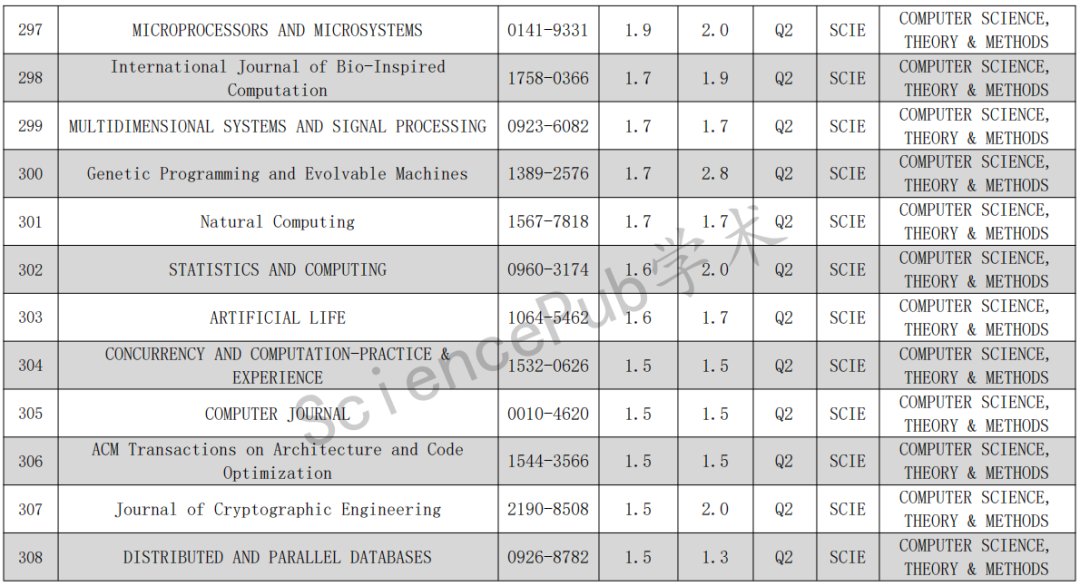
else {
// position and velocity
addRelativePositionAndVelocityBlock(lastState(), curState()); // 速度和位置
// frequency
addRelativeFrequencyBlock(lastState(), curState()); // 频率
}
// ambiguity
addRelativeAmbiguityResidualBlock( // 模糊度残差
lastGnssRov(), curGnssRov(), lastAmbiguityState(), curAmbiguityState());
}
伪距双差残差PseudorangeErrorDD
关于双差伪距残差的几种形式,注释里也给出了比较详细的解释
// Group 1: P1. receiver position in ECEF (3)
// Group 2: P1. body pose in ENU (7), P2. relative position from body to receiver
// in body frame (3)
// Group 3: Group 1 + P2. troposphere delay at rov (1), P3. troposphere delay at ref (1)
// P4. ionosphere delay (1), P5. ionosphere delay of base satellite (1)
// Group 4: Group 2 + P3. troposphere delay at rov (1), P4. troposphere delay at ref (1),
// P5. ionosphere delay (1), P6. ionosphere delay of base satellite (1)
构造函数也是判断了具体是哪种形式,以及调用setInfoemation设置了信息矩阵
EvaluateWithMinimalJacobians
残差和雅可比矩阵的计算在这个函数里
- 首先是得到了在ECEF下的坐标
if (!is_estimate_body_) // ECEF框架下
{
t_WR_ECEF = Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(parameters[0]);
}
else
{
// pose in ENU frame
t_WS_W = Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(¶meters[0][0]);
q_WS = Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond>(¶meters[0][3]);
// relative position
t_SR_S = Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(parameters[1]);
// receiver position
Eigen::Vector3d t_WR_W = t_WS_W + q_WS * t_SR_S;
if (!coordinate_) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Coordinate not set!";
}
if (!coordinate_->isZeroSetted()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Coordinate zero not set!";
}
t_WR_ECEF = coordinate_->convert(t_WR_W, GeoType::ENU, GeoType::ECEF);
}
- 然后计算了卫星到接收机的距离,因为是双差所以也是分为
base satellite和使用到的另一颗
double rho_rov = gnss_common::satelliteToReceiverDistance( // 接收机和卫星的距离
satellite_rov_.sat_position, t_WR_ECEF);
double rho_ref = gnss_common::satelliteToReceiverDistance(
satellite_ref_.sat_position, measurement_ref_.position);
double rho_rov_base = gnss_common::satelliteToReceiverDistance( // 接收机和base卫星的距离
satellite_rov_base_.sat_position, t_WR_ECEF);
double rho_ref_base = gnss_common::satelliteToReceiverDistance(
satellite_ref_base_.sat_position, measurement_ref_.position);
- 然后和距离一样,计算对应的高度角
double elevation_rov = gnss_common::satelliteElevation(
satellite_rov_.sat_position, t_WR_ECEF);
double elevation_ref = gnss_common::satelliteElevation(
satellite_ref_.sat_position, measurement_ref_.position);
double elevation_rov_base = gnss_common::satelliteElevation(
satellite_rov_base_.sat_position, t_WR_ECEF);
double elevation_ref_base = gnss_common::satelliteElevation(
satellite_ref_base_.sat_position, measurement_ref_.position);
- 在短基线的情况下,认为大气延迟都被双差模型消除了,就不再计算大气相关的延迟量了;而如果选择估计大气延迟,就要计算对应的延迟量
if (!is_estimate_atmosphere_)
{
// We think all atmosphere delays are eliminated by double-difference
}
else
{
// use estimated atomspheric delays
double zwd_rov = 0.0, zwd_ref = 0.0;
double dionosphere_delay_cur = 0.0, dionosphere_delay_base = 0.0;
if (!is_estimate_body_) {
zwd_rov = parameters[1][0];
zwd_ref = parameters[2][0];
dionosphere_delay_cur = parameters[3][0];
dionosphere_delay_base = parameters[4][0];
}
else {
zwd_rov = parameters[2][0];
zwd_ref = parameters[3][0];
dionosphere_delay_cur = parameters[4][0];
dionosphere_delay_base = parameters[5][0];
}
// troposphere hydro-static delay
double zhd_rov = gnss_common::troposphereSaastamoinen(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, PI / 2.0);
double zhd_ref = gnss_common::troposphereSaastamoinen(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, PI / 2.0);
double zhd_rov_base = gnss_common::troposphereSaastamoinen(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, PI / 2.0);
double zhd_ref_base = gnss_common::troposphereSaastamoinen(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, PI / 2.0);
// mapping
gnss_common::troposphereGMF( // 投影函数模型
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, elevation_rov, &gmf_hydro_rov, &gmf_wet_rov);
gnss_common::troposphereGMF(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, elevation_ref, &gmf_hydro_ref, &gmf_wet_ref);
gnss_common::troposphereGMF(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, elevation_rov_base, &gmf_hydro_rov_base, &gmf_wet_rov_base);
gnss_common::troposphereGMF(
timestamp, t_WR_ECEF, elevation_ref_base, &gmf_hydro_ref_base, &gmf_wet_ref_base);
dtroposphere_delay = zhd_rov * gmf_hydro_rov - zhd_ref * gmf_hydro_ref -
zhd_rov_base * gmf_hydro_rov_base + zhd_ref_base * gmf_hydro_ref_base +
zwd_rov * gmf_wet_rov - zwd_ref * gmf_wet_ref -
zwd_rov * gmf_wet_rov_base + zwd_ref * gmf_wet_ref_base;
// ionosphere
dionosphere_delay_cur = gnss_common::ionosphereConvertFromBase(
dionosphere_delay_cur, observation_rov_.wavelength);
dionosphere_delay_base = gnss_common::ionosphereConvertFromBase(
dionosphere_delay_base, observation_rov_base_.wavelength);
dionosphere_delay = dionosphere_delay_cur - dionosphere_delay_base;
}
- 接下来就是计算残差以及赋权了
double dpseudorange_estimate = rho_rov - rho_ref - rho_rov_base + rho_ref_base
+ dtroposphere_delay + dionosphere_delay;
// Compute error
double dpseudorange = observation_rov_.pseudorange - observation_ref_.pseudorange -
observation_rov_base_.pseudorange + observation_ref_base_.pseudorange;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1> error =
Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>(dpseudorange - dpseudorange_estimate);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1> > weighted_error(residuals);
weighted_error = square_root_information_ * error; // 利用在构造函数中得到的权重进行赋权的操作
- 计算雅可比矩阵,对应着manual的3.8.3节中的第一个残差,具体的雅可比计算在3.4.1节中的
Formulation 11形式里,待估参数形式:
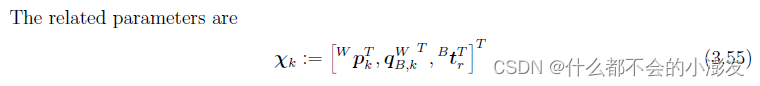
- 残差形式:
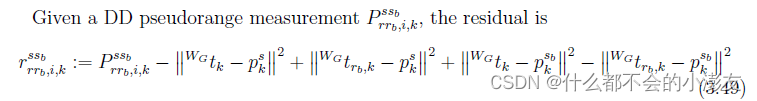
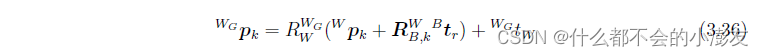
- 雅可比的形式:
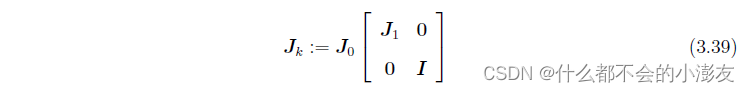
- 具体的J0以及J1:


相位双差残差PseudorangeErrorDD
相位双差主要比伪距残差多了一维模糊度的参数,但是具体形式的分类和伪距是一样的,也是根据是否估计大气延迟进行分类的。在具体的构造函数中,选择了残差的形式并利用setInfomation设置了信息矩阵以及对应的权重。
EvaluateWithMinimalJacobians
这里和伪距残差的部分也没什么不同,多的模糊度的部分雅可比对应到manual里的公式(3.80)又是-1和1

Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1> J_amb = -Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(1, 1); // 模糊度对应的雅可比部分
Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1> J_amb_base = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(1, 1);
剩下的和伪距残差没有特别大的区别,对应3.8.3中的第二个残差,具体可以参考manual的3.4.2小节,这里就不再详细记录了
多普勒残差DopplerError
如果需要对速度进行估计的情况下就会用到多普勒观测量,这个时候也就需要计算对应的多普勒残差。多普勒的残差只根据框架分为了ECEF框架下和ENU框架下两种形式,构造函数则是可以选择是否设置角速度的值,如果选择设置角度速的值,就会在执行完正常的构造函数后再给角速度赋值
template<int... Ns>
DopplerError<Ns ...>::DopplerError(
const GnssMeasurement& measurement,
const GnssMeasurementIndex index,
const GnssErrorParameter& error_parameter,
const Eigen::Vector3d& angular_velocity)
: DopplerError(measurement, index, error_parameter)
{
angular_velocity_ = angular_velocity;
}
关于具体调用哪种形式,也是根据框架来的,如果是ECEF框架下就不会设置,反之就会设置这个值
// gnss_estimator_base.cpp
if (parameter_id.type() == IdType::gPosition) {
/* 无关的代码 */
std::shared_ptr<DopplerError<3, 3, 1>> doppler_error =
std::make_shared<DopplerError<3, 3, 1>>(measurement,
GnssMeasurementIndex(satellite.prn, obs.first),
gnss_base_options_.error_parameter);
/* 无关的代码 */
}
// pose in ENU for fusion
else {
/* 无关的代码 */
std::shared_ptr<DopplerError<7, 9, 3, 1>> doppler_error =
std::make_shared<DopplerError<7, 9, 3, 1>>(measurement,
GnssMeasurementIndex(satellite.prn, obs.first),
gnss_base_options_.error_parameter, angular_velocity);
/* 无关的代码 */
}
EvaluateWithMinimalJacobians
残差和雅可比的计算也是对照着手册来就可以了,对应着manual残差中的第三部分,具体到3.4.3小节,在ENU融合框架的形式下:
- 待估参数的形式为:

- 残差的计算:
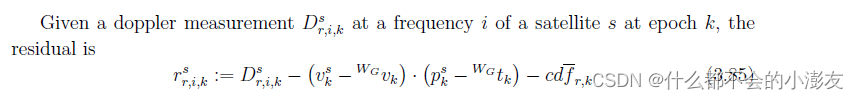
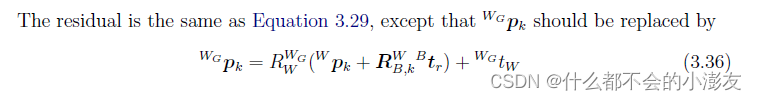
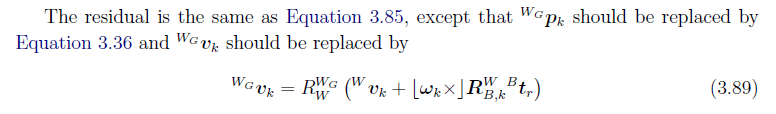
- 具体的雅可比计算
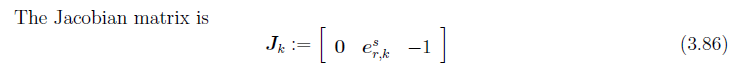
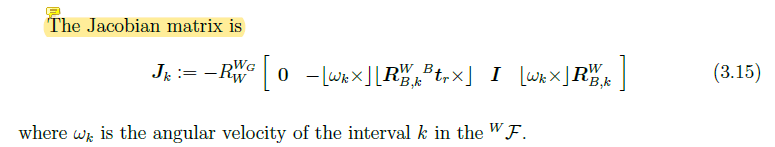
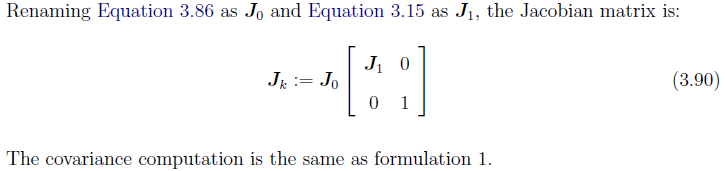
添加相对残差
相对残差的概念在manual 3.7.3有介绍
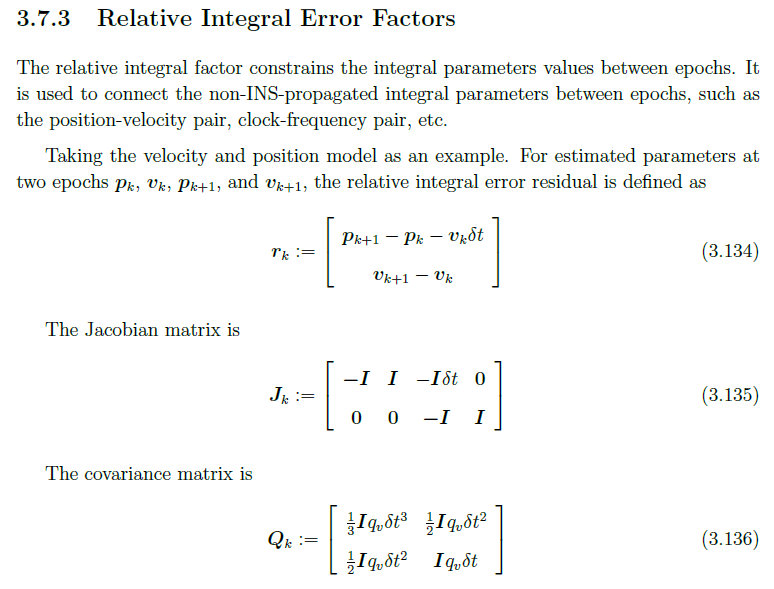
关于这部分的代码可以在RelativeConstError和RelativeIntegrationError找到,比如对应到公式(3.136)的这个
RelativeIntegrationError(const Eigen::Matrix<double, Dim, Dim>& psd, double dt) { // 设置权阵
Eigen::MatrixXd covariance = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(2*Dim, 2*Dim);
covariance.topLeftCorner(Dim, Dim) = psd * pow(dt, 3) / 3.0;
covariance.topRightCorner(Dim, Dim) = psd * pow(dt, 2) / 2.0;
covariance.bottomLeftCorner(Dim, Dim) = psd * pow(dt, 2) / 2.0;
covariance.bottomRightCorner(Dim, Dim) = psd * dt;
setCovariance(covariance);
dt_ = dt;
}
更新DOP值updateGdop
DOP (dilution of precision)值,代表着精度因子,是用来判断卫星相对于观测者的几何位置所造成误差(卫星几何效应)的单位,会随卫星和接受器间的相对移动而变化,通常值越低代表误差越小。在GICI中,DOP值的计算是在函数gnss_common::computeDops中
inline void updateGdop(
const GnssMeasurement& measurement_rov, const GnssMeasurementDDIndexPairs& indexes) {
gdop_ = gnss_common::computeDops(
measurement_rov, indexes, gnss_base_options_.common).x();
}
这个函数核心的计算部分是调用了RTKLIB的dops函数
dops(ns, azel, degreeToRad(options.min_elevation), Dops.data());
关于这部分的原理,其实很简单,就只是一种精度的评价方式