文章目录
- 目标
- 过程与代码
- 监听窗口的滚动
- 窗口上事件监听的移除
- 封装到一个hook
- 回调函数法(不推荐)
- 返回值法(推荐)
- 效果
- 总代码
- 修改或添加的文件
- hooks的useScroll
- home-content
- 参考
本项目博客总结:【前端】Vue项目:旅游App-博客总结
目标
监听窗口的滚动,滚动到底部则动态地加载houseList数据。

过程与代码
监听窗口的滚动
首先要监听窗口的滚动。
注意,滚动有两种:窗口滚动和页面滚动,关于如何区分它们:【前端】如何判断是页面滚动还是窗口滚动
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
// 当前位置到顶部的距离
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// 屏幕的长度
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
// 页面总体长度
const scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight
// 滚动到底部:提前一点刷新
if (scrollHeight <= scrollTop + clientHeight + 1) {
homeStore.fetchHouseList()
console.log('滚动到底部')
}
})
效果:滚动到底部后就加载出了新的数据。

窗口上事件监听的移除
写到这里我们要进行一些思考:滚动到底部就加载数据 这一事件是绑定到整个App的窗口上的,但我们只需要它在home页面上绑定。
当我们切换到其他页面,如favor页面时,我们需要remove这个事件。也就是说,我们在写这个代码的时候要考虑到生命周期。
生命周期选项 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)
生命周期钩子 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)
在unmounted时移除此事件:
const scrollBottomListener = () => {
// 当前位置到顶部的距离
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// 屏幕的长度
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
// 页面总体长度
const scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight
// 滚动到底部:提前一点刷新
if (scrollHeight <= scrollTop + clientHeight + 1) {
homeStore.fetchHouseList()
console.log('滚动到底部')
}
}
window.addEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
onUnmounted(() => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
那么自然会想到我们只在mounted时添加此事件的监听。
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
封装到一个hook
写到这里我们会发现,并不是只有home页面需要有监听滚动到底部的功能,别的页面也可能需要。因此,我们可以把这个功能抽取出来。
useScoll.js:
// 关于滚动到底部的代码逻辑
import { onMounted, onUnmounted } from "@vue/runtime-core";
export default function useScroll() {
const scrollBottomListener = () => {
// 当前位置到顶部的距离
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// 屏幕的长度
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
// 页面总体长度
const scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight
// 滚动到底部:提前一点刷新
if (scrollHeight <= scrollTop + clientHeight + 1) {
homeStore.fetchHouseList()
console.log('滚动到底部')
}
}
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
}
接下来我们只需要在 需要用到监听滚动到底部 这一功能的地方调用 这一函数即可。
这里,我们在home页面需要调用此函数,当判定滚动到底部后需要进行的操作是:动态加载更多的houselist。
接下来将讲两种实现这个功能的方法(名字随便取的):
- 回调函数法
- 返回值法
回调函数法(不推荐)
回调函数法,就是在useScoll中传入一个回调函数,来让滚动到底部时调用callback。这样我们就可以每次传入不同的callback来实现不同的功能。
useScroll.js:滚到底部时调用callback
// 关于滚动到底部的代码逻辑
import { onMounted, onUnmounted } from "@vue/runtime-core";
export default function useScroll(callback) {
const scrollBottomListener = () => {
// 当前位置到顶部的距离
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// 屏幕的长度
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
// 页面总体长度
const scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight
// 滚动到底部:提前一点刷新
if (scrollHeight <= scrollTop + clientHeight + 1) {
console.log('滚动到底部')
if (callback) callback()
}
}
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
}
home-content:
useScroll(() => {
homeStore.fetchHouseList()
})
效果:可以实现。
但是这个方法有弊端:
- 回调函数不好管理
- 不同功能可能需要传入不同数量的回调函数
总而言之,可以实现,但不推荐。
返回值法(推荐)
既然传入一个回调函数并不方便,那么我们可不可以让hook传出一个值,我们根据这个值在对应页面中实现各自的功能?答案是可以的。
useScroll.js:
// 关于滚动到底部的代码逻辑
import { onMounted, onUnmounted } from "@vue/runtime-core";
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default function useScroll() {
// 初始默认为没有到底
const isReachBottom = ref(false)
const scrollBottomListener = () => {
// 当前位置到顶部的距离
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// 屏幕的长度
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
// 页面总体长度
const scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight
// 滚动到底部:提前一点刷新
if (scrollHeight <= scrollTop + clientHeight + 1) {
console.log('滚动到底部')
isReachBottom.value = true
}
}
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
return { isReachBottom }
}
home-content:
这里我们用watch来监听数据的变化:Vue.js中 watch(深度监听)的最易懂的解释 - 星期九 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
const { isReachBottom } = useScroll()
watch(isReachBottom, (newValue) => {
if (newValue) {
homeStore.fetchHouseList()
isReachBottom.value = false
}
})
对于homeStore.fetchHouseList()更好的写法是:在它返回promise之后再修改isReachBottom的值:这样意味着它先加载了新数据,再使标记变为“没有到底”。
const { isReachBottom } = useScroll()
watch(isReachBottom, (newValue) => {
if (newValue) {
homeStore.fetchHouseList().then(() => {
isReachBottom.value = false
})
}
})
效果
达成目标。
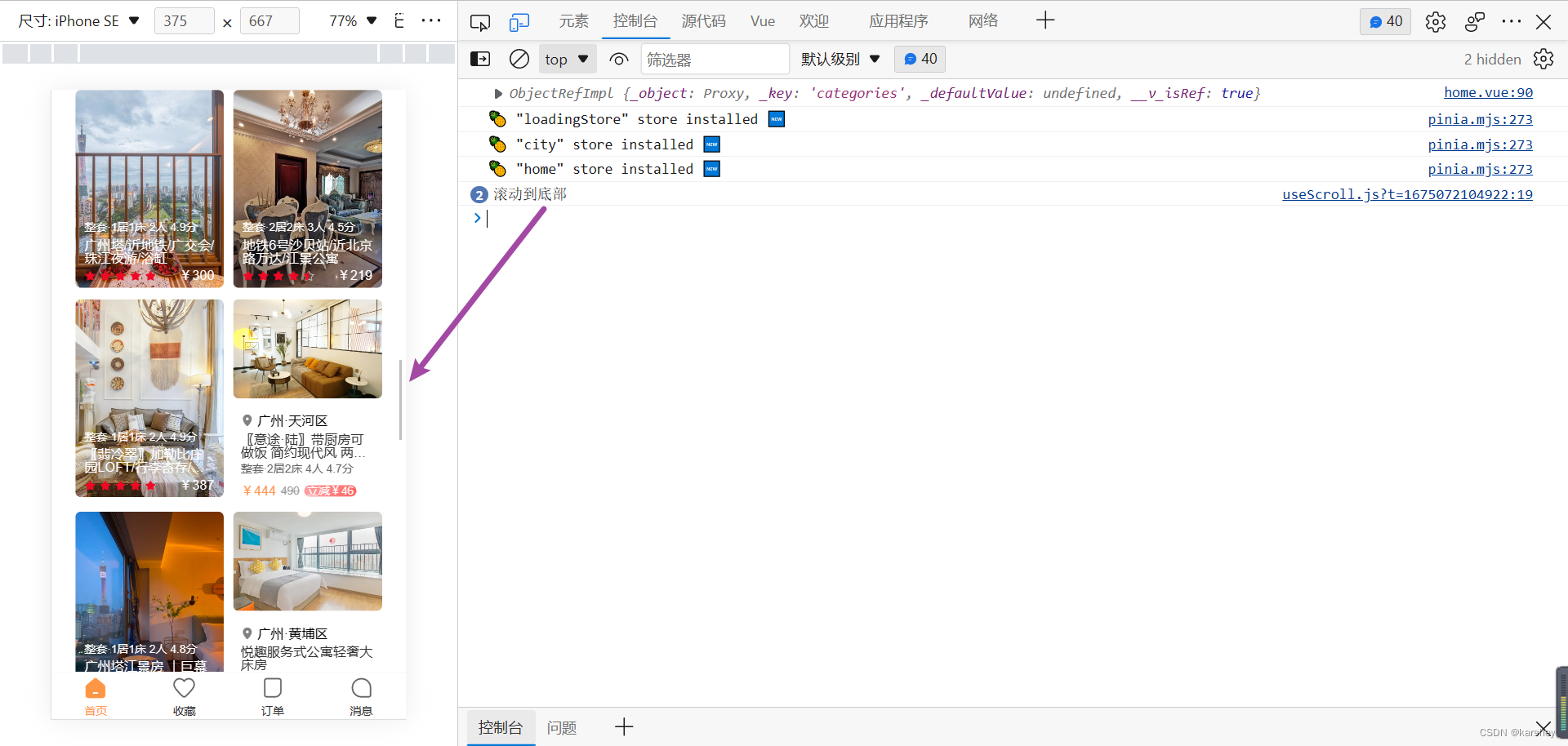
总代码
修改或添加的文件
hooks的useScroll
将监听窗口滚动到底部的逻辑抽取到hooks。
// 关于滚动到底部的代码逻辑
import { onMounted, onUnmounted } from "@vue/runtime-core";
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default function useScroll() {
// 初始默认为没有到底
const isReachBottom = ref(false)
const scrollBottomListener = () => {
// 当前位置到顶部的距离
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// 屏幕的长度
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
// 页面总体长度
const scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight
// 滚动到底部:提前一点刷新
if (scrollHeight <= scrollTop + clientHeight + 1) {
console.log('滚动到底部')
isReachBottom.value = true
}
}
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollBottomListener)
})
return { isReachBottom }
}
home-content
调用hooks。
<template>
<div class="content">
<h2>热门精选</h2>
<div class="list">
<template v-for="(item, index) in houseList" :key="item.data.houseId">
<houseItemV9 v-if="item.discoveryContentType === 9" :item="item.data"></houseItemV9>
<houseItemV3 v-else-if="item.discoveryContentType === 3" :item="item.data"></houseItemV3>
</template>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
import useHomeStore from "../../../store/modules/home";
import houseItemV9 from "../../../components/house-item/house-item-v9.vue";
import houseItemV3 from "../../../components/house-item/house-item-v3.vue";
import useScroll from '@/hooks/useScroll.js'
import { watch } from 'vue'
const homeStore = useHomeStore()
homeStore.fetchHouseList()
const { houseList } = storeToRefs(homeStore)
// console.log(houseList)
const { isReachBottom } = useScroll()
watch(isReachBottom, (newValue) => {
if (newValue) {
homeStore.fetchHouseList().then(() => {
isReachBottom.value = false
})
}
})
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.content {
padding: 0 20px;
h2 {
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: 700;
}
.list {
margin-top: 20px;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
}
</style>
参考
Element.scrollTop - Web API 接口参考 | MDN (mozilla.org)
Element - Web API 接口参考 | MDN (mozilla.org)
【前端】如何判断是页面滚动还是窗口滚动_karshey的博客-CSDN博客
Vue.js中 watch(深度监听)的最易懂的解释 - 星期九 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
生命周期选项 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)
生命周期钩子 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)




![[Lua实战]整理Lua中忽略的问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/720df27435104c098057007dd895507e.png)