论文:BEIT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.00184
Introduction
- BEIT(Bidirectional Encoder representation from Image Transformers)
- Motivation: 启发于BERT的自编码方式(随机mask进行token预测)
- 难点:没有视觉词表,无法简单应用softmax分类器预测candidates。
- 直观感受是将该问题视为回归问题,预测masked patch的每个像素点,但是这会导致浪费模型能力在建立短程依赖和高频细节上。(waste modeling capability on pre-training shortrange dependencies and high-frequency details)
- 最终解决方案
1) Overview
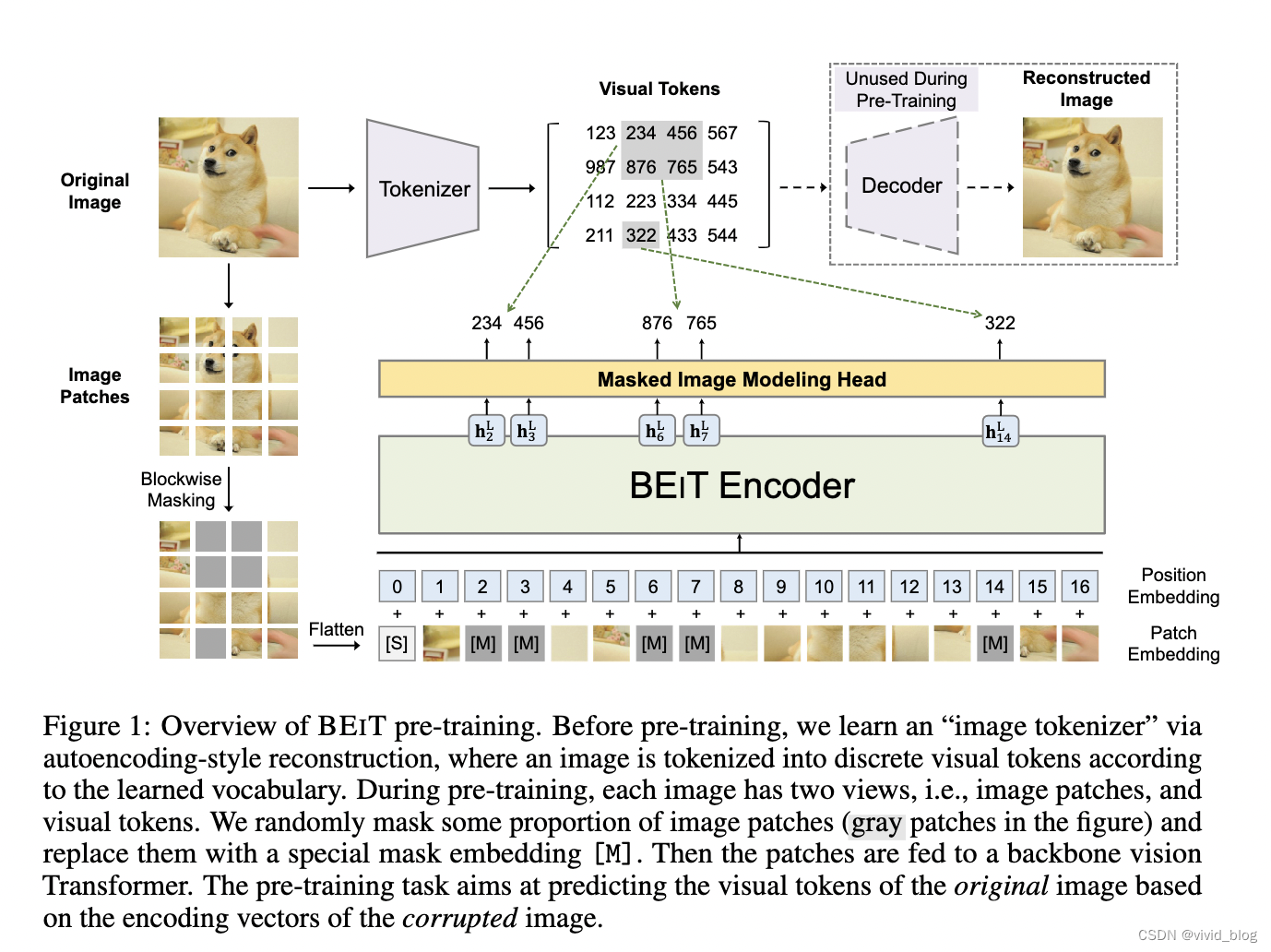
2)两种view,image patches and visual tokens。首先将图像划分为patches并随机mask作为模型输入。然后通过VAE将图像tokenize为离散的视觉token。模型最终学习目标为,recover the visual tokens not pixels of masked patches。
3)实验结果:BEIT 优于从头开始训练和以前的强自监督模型
Details
- Image Patch,输入图像维度 x ∈ R H ∗ W ∗ C x \in R^{H*W*C} x∈RH∗W∗C,reshape成为 N = H W / P 2 N=HW/P^2 N=HW/P2个patch, x p ∈ R N ∗ ( P 2 C ) x^p\in\mathbb{R}^{N*(P^2C)} xp∈RN∗(P2C),C为通道数。在该实验中,split 224 × 224 image into a 14 × 14 grid of image patches, where each patch is 16 × 16.
- Visual Token,直接将图像tokenize为 z = [ z 1 , . . . z N ] ∈ V h ∗ w z=[z_1,...z_N]\in \mathbb{V}^{h*w} z=[z1,...zN]∈Vh∗w,tokenizer为训练好的discrete variational autoencoder (dVAE),该自编码器包括encoder和decoder两部分,encoder负责将图像输入映射到视觉词表,decoder负责根据encoder的结果重建输入。在本文中仅需要使用训练好的encoder部分作为tokenizer以及对应词表。词表大小为8192
- Backbone Network: Image Transformer,在输入前加入special token [S]。
- Pre-Training BEIT: Masked Image Modeling(MIM) 。随机mask40%的patches,masked位置由[M] token替代。
训练目标为感觉masked patch预测相应位置的visual token:
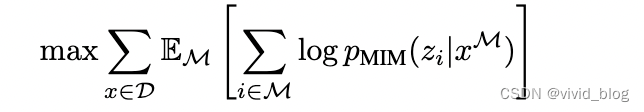
- blockwise masking,类似于bert中的n gram mask,先随机生成块大小,再选定纵横比 :

- blockwise masking,类似于bert中的n gram mask,先随机生成块大小,再选定纵横比 :
实验
- 参数设置:ImageNet-1K,1.2M图像。12-layer Transformer with 768 hidden size, and 12 attention heads,intermediate size of feed-forward networks is 3072,16 × 16 input patch size,视觉词表8192. 图像处理包括随机调整大小的裁剪,水平翻转,颜色抖动。2k batch size,800epoch。500k training steps take about five days using 16 Nvidia Telsa V100 32GB GPU cards。
- 下游任务微调:
- 在图像分类任务上,加入一个简单的线性分类器作为任务层,使用average pooling作为最终表示过softmax。
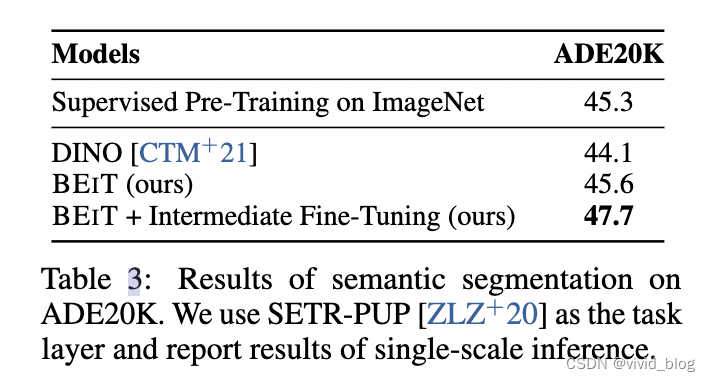
- 在语义分割上,引入几个反卷积层
- Intermediate fine-tuning,进一步进行beit的微调应用于下游任务
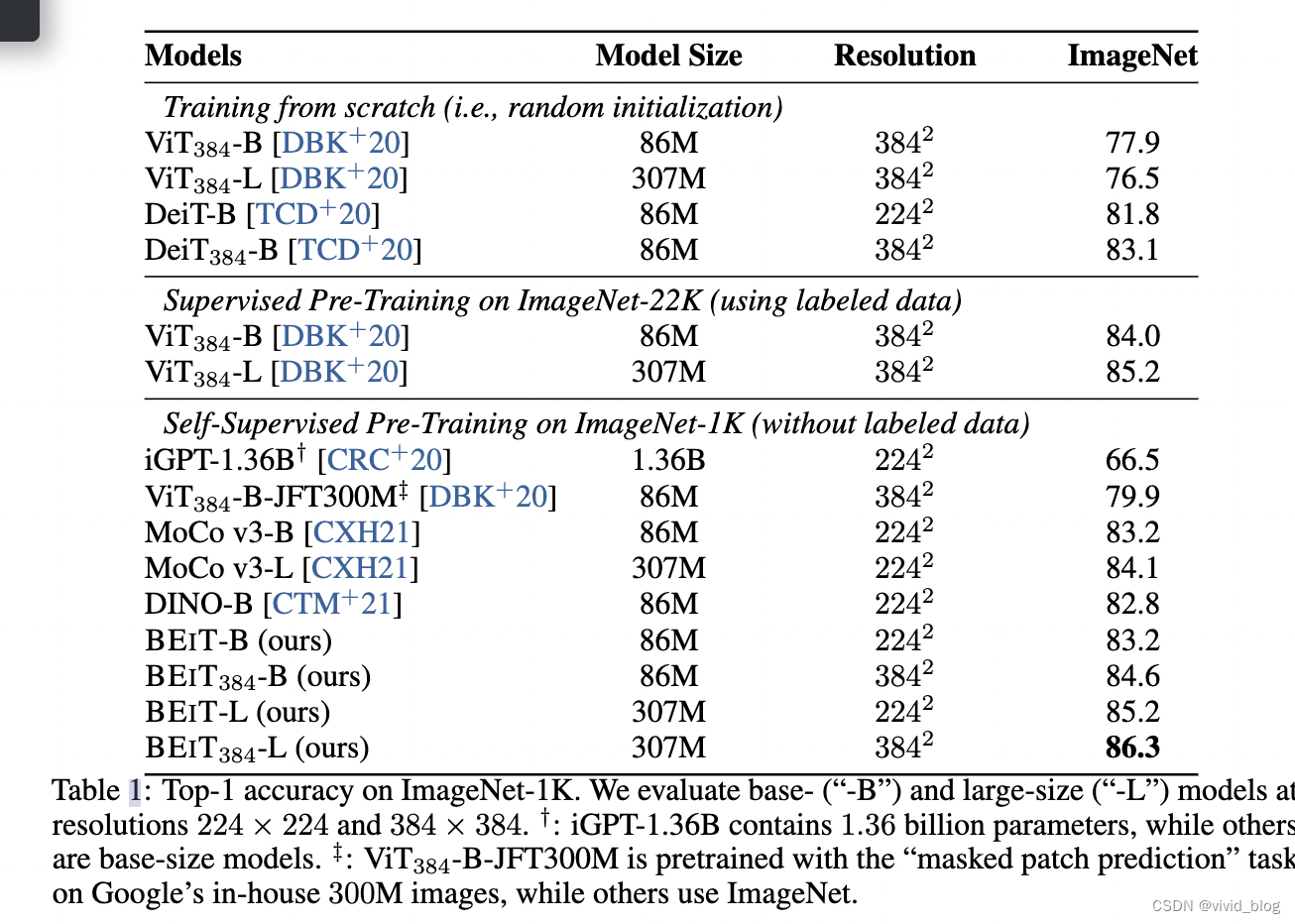
- 主要对比实验,384为输入图像大小
- 收敛实验,BEiT收敛速度更快

- 语义分割实验
- 消融实验,预测visual tokem最重要

- 可视化结果