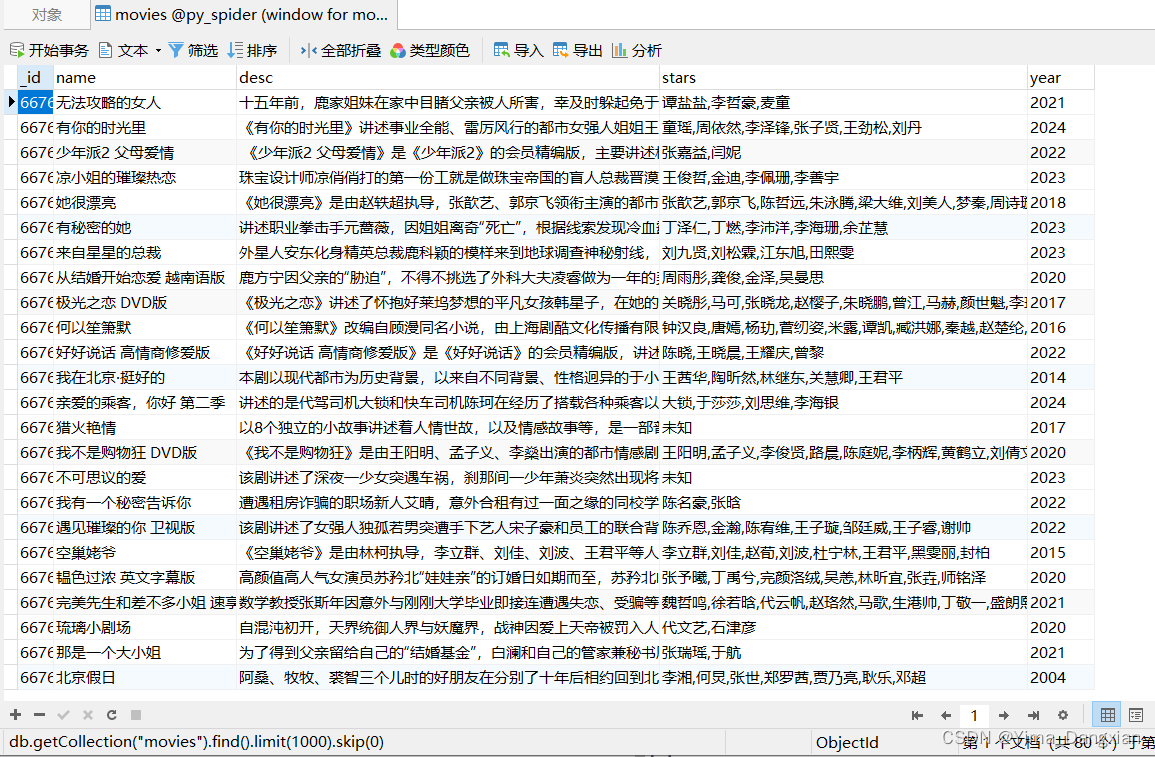
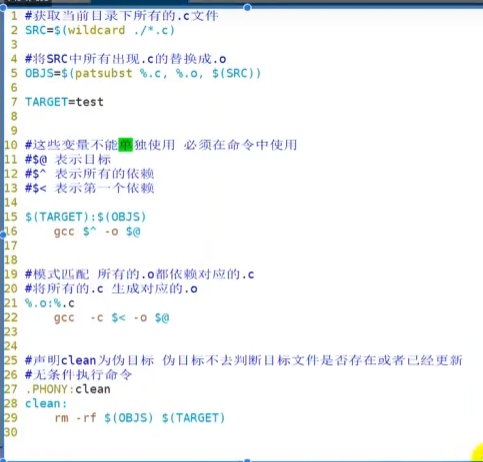
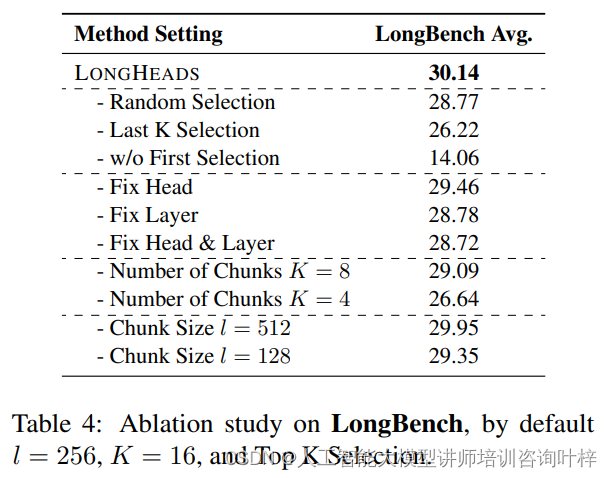
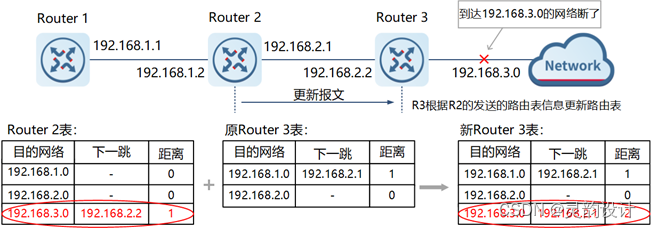
Jetpack的数据绑定(DataBinding)库为我们提供了一个强大而灵活的工具,用于将UI组件与数据源绑定在一起。本文将深入探讨数据绑定的高级用法,包括双向绑定、自定义Binding
Adapter、使用LiveData和ViewModel,以及如何处理复杂数据结构和事件绑定。
双向数据绑定
双向数据绑定允许UI组件和数据源互相同步。这在处理用户输入时特别有用。例如,当用户在EditText
中输入数据时,数据源可以实时更新。
示例
在XML布局中使用@=语法实现双向绑定:
<EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@={viewModel.username}" />
在ViewModel中定义一个MutableLiveData变量:
class UserViewModel : ViewModel() {
val username = MutableLiveData<String>()
}
在Activity或Fragment中进行绑定:
val viewModel: UserViewModel by viewModels()
binding.viewModel = viewModel
binding.lifecycleOwner = this
自定义Binding Adapter
自定义Binding Adapter允许我们为特定的UI组件创建自定义属性绑定逻辑。这在处理复杂的UI更新时非常有用,例如加载图片。
示例
定义一个自定义Binding Adapter来加载图片:
@BindingAdapter("imageUrl")
fun loadImage(view: ImageView, url: String?) {
url?.let {
Glide.with(view.context)
.load(it)
.into(view)
}
}
在布局文件中使用自定义属性:
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:imageUrl="@{viewModel.imageUrl}" />
数据绑定与LiveData和ViewModel结合
将数据绑定与LiveData和ViewModel结合使用,可以实现更清晰和模块化的架构。ViewModel持有UI相关的数据,并在数据变化时自动通知UI更新。
示例
定义ViewModel:
class UserViewModel : ViewModel() {
val username = MutableLiveData<String>()
val imageUrl = MutableLiveData<String>()
}
在Activity或Fragment中设置数据绑定:
val viewModel: UserViewModel by viewModels()
binding.viewModel = viewModel
binding.lifecycleOwner = this
在布局文件中使用ViewModel的数据:
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<data>
<variable name="viewModel" type="com.example.app.UserViewModel" />
</data>
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@={viewModel.username}" />
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:imageUrl="@{viewModel.imageUrl}" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
处理复杂数据结构
数据绑定可以处理复杂的数据结构,例如嵌套的对象和集合。我们可以通过定义Observable对象和集合,并在布局文件中使用适当的表达式来绑定它们。
示例
定义嵌套的数据结构:
data class Address(val street: String, val city: String)
data class User(val name: String, val address: Address)
在ViewModel中使用Observable对象:
class UserViewModel : ViewModel() {
val user = MutableLiveData<User>()
}
在布局文件中绑定嵌套对象:
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable name="viewModel" type="com.example.app.UserViewModel" />
</data>
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{viewModel.user.name}" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{viewModel.user.address.street}" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{viewModel.user.address.city}" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
事件绑定
数据绑定不仅可以用于数据,还可以用于事件处理。我们可以在布局文件中直接绑定事件处理方法,从而减少样板代码。
示例
在ViewModel中定义事件处理方法:
class UserViewModel : ViewModel() {
fun onButtonClick() {
// 处理按钮点击事件
}
}
在布局文件中绑定事件处理方法:
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="@{() -> viewModel.onButtonClick()}" android:text="Click Me" />
使用BindingAdapter处理复杂逻辑
有时我们需要在XML中处理复杂的逻辑,BindingAdapter可以帮助我们实现这一点。
示例
定义一个BindingAdapter来处理复杂逻辑:
@BindingAdapter("app:formattedText")
fun setFormattedText(view: TextView, value: Int) {
view.text = "Formatted value: $value"
}
在布局文件中使用:
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:formattedText="@{viewModel.someValue}" />
总结
Jetpack的数据绑定是一个强大且灵活的工具,它不仅简化了UI和数据之间的绑定过程,还提供了处理复杂逻辑和自定义需求的能力。通过深入理解和应用数据绑定的各种高级特性,开发者可以大大提高开发效率,编写出更加简洁、可维护的代码。
希望本文能帮助你深入理解Jetpack数据绑定的高级用法,并在实际开发中灵活运用这些技巧。
感谢阅读,Best regards!