1、== 和 equals的区别
- == 是操作符
- ==操作符专门用来比较变量的值是否相同。
- 对于基本类型变量来说,只能使用 == ,因为基本类型的变量没有方法。使用==比较是值比较。
- 对于引用类型的变量来说,==比较的两个引用对象的地址是否相等。
- equals 是方法
- equals方法常用来比较对象的内容是否相同。 Java当中所有的类都是继承于Object这个超类的,在Object类中定义的equals方法:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
- 未重写equals方法的类:
Object中的equals方法实际使用的也是==操作符,比较的是他们的内存地址是否同一地址。本质上还是使用的 == - 重写了equals方法的类:使用该类自己的equals方法比较逻辑(一般是比较对象的内容是否相同)。比如:
- String:比较字符串内容,内容相同则相同;
- Integer:比较对应的基本数据类型int的值是否相同(==操作符)。
2、Integer值 == 和 equals的判断
示例代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 999;
Integer b = 999;
System.out.println(a == b);
Integer c = 99;
Integer d = 99;
System.out.println(c == d);
}
结果是什么呢?引用数据类型 == 是比较的是对象地址,两次输出的结果都是false,对不对?非也!!!

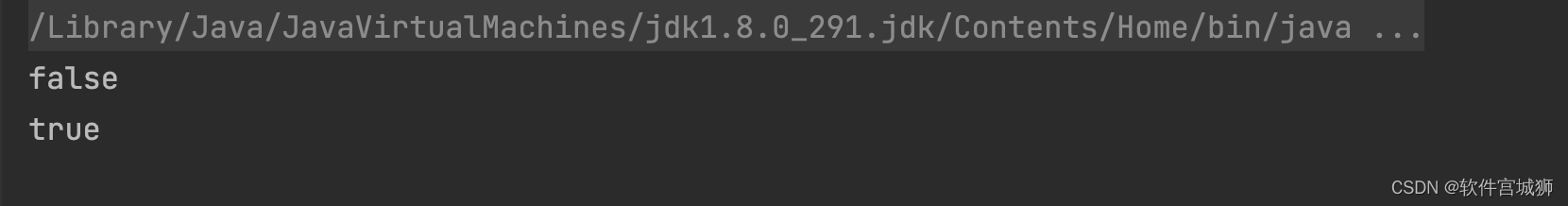
从上图可以清楚地看到:
- 1、第一次输出的结果是false
- 2、第二次输出的结果是true
看到此处有点懵了,为什么呢?
源码解析
在执行Integer a=999;时会调用Integer类的静态方法public static Integer valueOf(int i)进行自动装箱,其源码如下:
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
该方法的主要逻辑如下:
- 如果i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high则调用IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]
- 如果i的值不满足i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high则调用new Integer(i)
继续探究Integer缓存IntegerCache。IntegerCache是Integer类中的静态内部类,用于缓存数据便于节省内存、提高性能。其源码如下:
/**
* Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between
* -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS.
*
* The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache
* may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option.
* During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property
* may be set and saved in the private system properties in the
* sun.misc.VM class.
*/
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
从这里我们可以看出 :
- IntegerCache.low = -128
- IntegerCache.high = 127
- 缓冲区cache是一个Integer类型的数组
也就是说:IntegerCache缓存区间为[-128,127]。所以,在调用Integer.valueOf(int i)方法进行自动装箱时假若i的值在[-128,127]区间则生成的Integer对象会被存入缓冲区。当再次对该值进行装箱时会先去缓冲区中获取;如果取到则返回,如果没有取到则创建包装类对象存入缓存区并返回。
这里就可以理解之前的那小段代码了。
Integer c = 99;
Integer d = 99;
因为 99 在 [-128,127] 区间中,所以 c 对象会被存入缓冲区, 当 d 再次 对 99 进行装箱时,会先去缓冲区去获取。所以 c 和 d 的引用地址是相同的。
Tips : Byte 、Short、Long、Character 也有类似于Integer 的 缓存区