map和set可以采用两套红黑树实现,也可以用同一个红黑树,就需要对前面的结构进行修改
迭代器的好处是可以方便遍历,是数据结构的底层实现与用户透明。如果想要给红黑树增加迭代器,需要考虑以前问题:
- begin()和end()
stl明确规定,begin和edn代表的是一段前闭后开的区间,而对红黑树进行中序遍历后,可以得到一个有序序列,因此:begin可以放在红黑树中最小节点(即最左侧节点)的位置,end放在最大结点(最右侧节点)的下一个位置,关键是最大节点的下一个位置在哪?如果给成nullptr,end的–操作要能找到最后一个元素的位置,最好的方式是将end放在头节点的位置
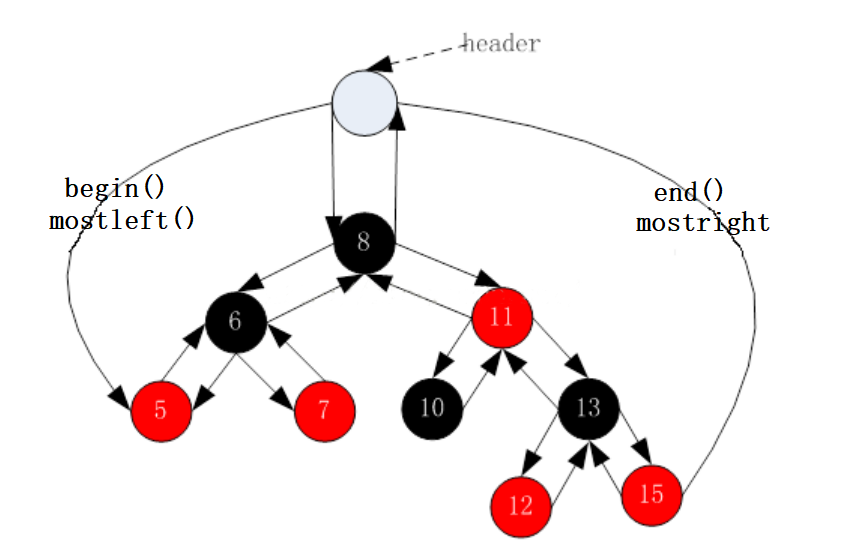
迭代器结构
在红黑树中提供一个迭代器类,提供基本的*,->,++,–等运算符重载。变量时一个节点指针,用节点来初始化迭代器
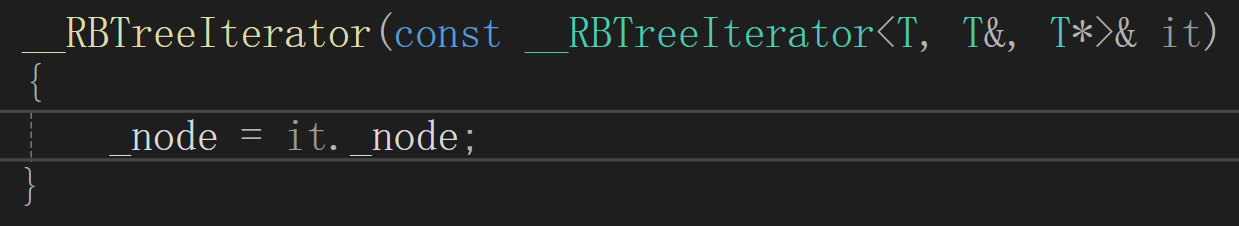
加入上面构造的好处
固定的普通迭代器初始化这个迭代器类,参数模板都用T,如果T传入的是普通迭代器,就是拷贝构造,如果是cosnt迭代器,就支持用普通迭代器隐式转换常量迭代器,保证set的key不能修改
++和–
迭代器的++是按中序遍历的顺序找到下一个元素,遵循中序的原则。规则是:当前节点判断它的右节点有没有节点,如果有,就找到右子树中最小的,也就是最左的结点。如果是空,就看它是双亲的左还是右,如果是左,按中序原则就到它的父亲位置,如果是右,说明这颗子树遍历完毕,向上重复直到找到cur是par的左节点的时候,如果到end的位置就结束
self& operator++()
{
//1.右不为空,找右树最左节点
if (_node->_right != nullptr)
{
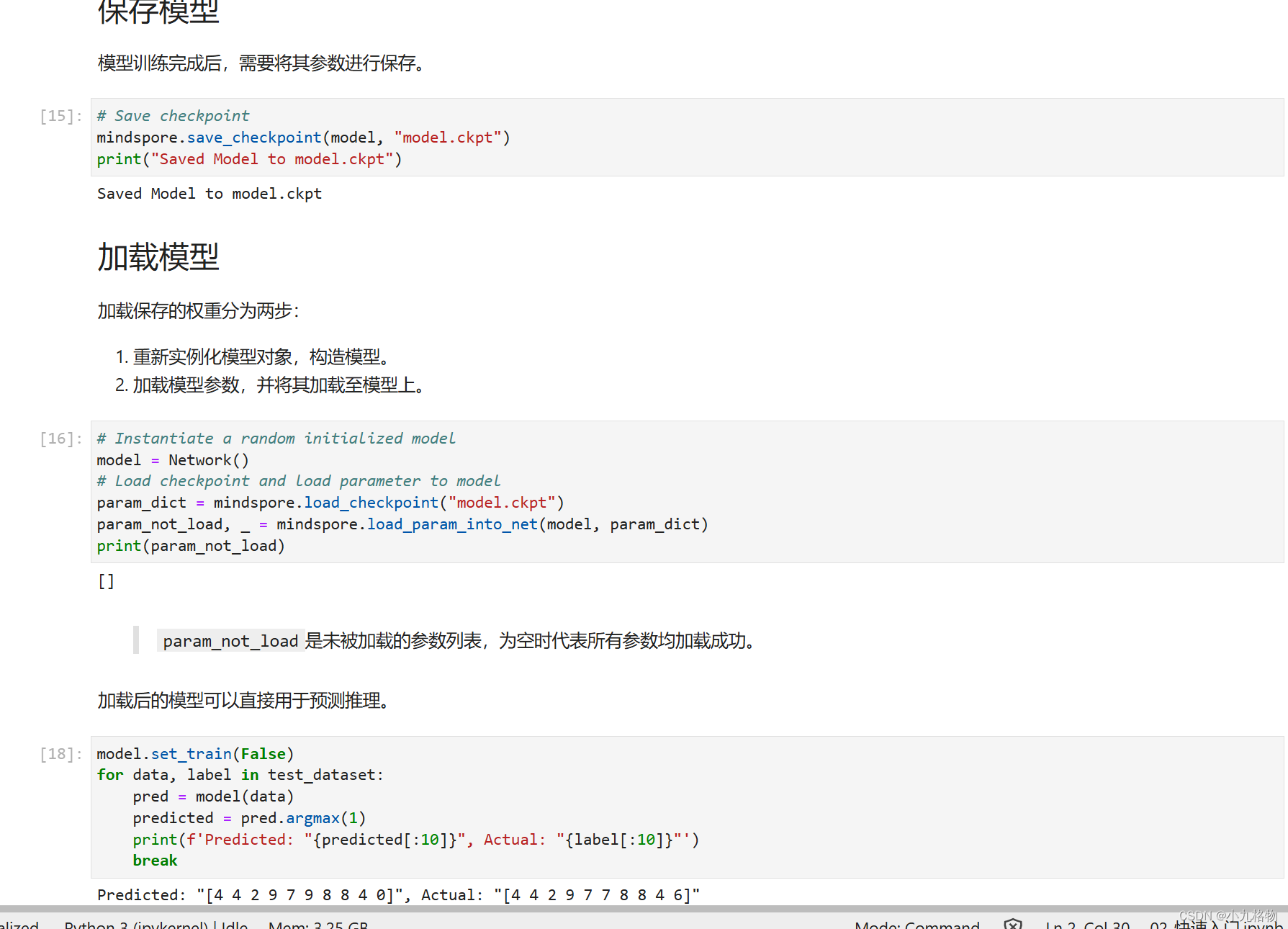
node* subleft = _node->_right;
while (subleft->_left)
{
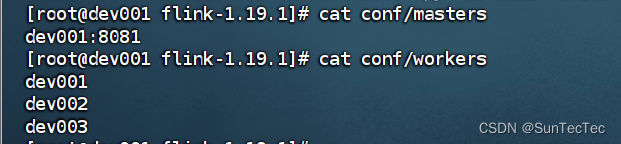
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
_node = subleft;
}
else
{
//2.右为空,沿着路径找孩子是父亲左的祖先
node* cur = _node;
node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
–和++的操作是镜像的,左为空,找是右子树的结点
self& operator--()
{
//1.左不为空,找左树最右节点
if (_node->_left != nullptr)
{
node* subright = _node->_left;
while (subright->_right)
{
subright = subright->_right;
}
_node = subright;
}
else
{
//2.左为空,沿着路径找孩子是父亲右的祖先
node* cur = _node;
node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
全
enum color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template <class T>
struct TreeNode
{
struct TreeNode<T>* _parent;
struct TreeNode<T>* _left;
struct TreeNode<T>* _right;
T _data;
color _col;
TreeNode(T data)
:_parent(nullptr), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr)
, _data(data), _col(RED)
{}
};
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef TreeNode<T> node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(node* cur)
:_node(cur)
{}
//普通迭代器,当迭代器是普通时是拷贝构造,是const迭代器时支持普通转换const
__RBTreeIterator(const __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*>& it)
{
_node = it._node;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const self& x)
{
return x._node != _node;
}
self& operator++()
{
//1.右不为空,找右树最左节点
if (_node->_right != nullptr)
{
node* subleft = _node->_right;
while (subleft->_left)
{
subleft = subleft->_left;
}
_node = subleft;
}
else
{
//2.右为空,沿着路径找孩子是父亲左的祖先
node* cur = _node;
node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
self& operator--()
{
//1.左不为空,找左树最右节点
if (_node->_left != nullptr)
{
node* subright = _node->_left;
while (subright->_right)
{
subright = subright->_right;
}
_node = subright;
}
else
{
//2.左为空,沿着路径找孩子是父亲右的祖先
node* cur = _node;
node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
};
begin和end
红黑树提供begin和end功能,begin返回最左的元素,也就是最小的值。end返回空迭代器
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
//中序第一个,最左节点
node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//中序第一个,最左节点
node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
insert返回值
insert的返回值返回pair,第一个参数是iterator,第二个参数插入成功或失败,如果插入成功,就返回插入位置,插入失败,就返回已经存在的数据位置
insert比较
set是比较key的值,而map传入的值是pair,pair本身的比较规则是先比较first,first相等比较second。而我们想要的是只比较first,所以要统一两个的比较方法

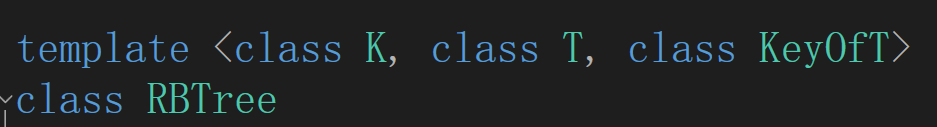
模板里传入一个KeyOfT,是一个仿函数,根据不同的T的类型,取到set和map用于比较的元素
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return std::make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
node* parent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(data) > kot(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return std::make_pair(iterator(cur), false);;
}
}
//插入
cur = new node(data);
node* newnode = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
if (data < parent->_data)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
//父节点是红色调整
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
node* gdparent = parent->_parent;
node* uncle;
if (gdparent->_left == parent)
{
uncle = gdparent->_right;
//第一种情况 叔叔节点是红色,变色
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
//第二种情况 分左右
// g
// par un
// cur
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateRight(gdparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
// g
// par un
// cur
else
{
RotateLeft(parent);
RotateRight(gdparent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
parent->_col = RED;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
uncle = gdparent->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateLeft(gdparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
// g
// par un
// cur
else
{
RotateRight(parent);
RotateLeft(gdparent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
//parent->_col = RED;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
cur = gdparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//根必须是黑色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return std::make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);;
}
set和map的仿函数如下:
struct SetOfK
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
struct SetOfV
{
const K& operator()(const std::pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
全
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
#include <queue>
template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef TreeNode<T> node;
public:
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
//中序第一个,最左节点
node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//中序第一个,最左节点
node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
node* find(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(key) < kot(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(key) > kot(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return std::make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
node* parent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(data) > kot(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return std::make_pair(iterator(cur), false);;
}
}
//插入
cur = new node(data);
node* newnode = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
if (data < parent->_data)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
//父节点是红色调整
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
node* gdparent = parent->_parent;
node* uncle;
if (gdparent->_left == parent)
{
uncle = gdparent->_right;
//第一种情况 叔叔节点是红色,变色
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
//第二种情况 分左右
// g
// par un
// cur
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateRight(gdparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
// g
// par un
// cur
else
{
RotateLeft(parent);
RotateRight(gdparent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
parent->_col = RED;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
uncle = gdparent->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateLeft(gdparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
// g
// par un
// cur
else
{
RotateRight(parent);
RotateLeft(gdparent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
//parent->_col = RED;
gdparent->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
cur = gdparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//根必须是黑色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return std::make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);;
}
void RotateLeft(node* parent)
{
node* sub = parent->_right;
node* subl = sub->_left;
sub->_left = parent;
parent->_right = subl;
//父节点修改
node* Pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = sub;
//有子节点改变指向
if (subl)
{
subl->_parent = parent;
}
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = sub;
}
else
{
//原parent在父节点的左右
if (Pparent->_left == parent)
{
Pparent->_left = sub;
}
else
{
Pparent->_right = sub;
}
}
sub->_parent = Pparent;
}
void RotateRight(node* parent)
{
node* sub = parent->_left;
node* subr = sub->_right;
sub->_right = parent;
parent->_left = subr;
if (subr)
{
subr->_parent = parent;
}
node* Pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = sub;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = sub;
}
else
{
if (Pparent->_left == parent)
{
Pparent->_left = sub;
}
else
{
Pparent->_right = sub;
}
}
sub->_parent = Pparent;
}
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root->_col == RED)
{
std::cout << "根节点是红色" << std::endl;
return false;
}
int refVal = 0; //记录最左路径黑色节点的数量,用来参考
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
refVal++;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _IsBalance(_root, 0, refVal);
}
bool _IsBalance(node* cur, int blackNum, int refVal)
{
if (cur == nullptr)
{
//判断每条路径黑色节点数量正常
if (blackNum != refVal)
{
std::cout << "黑色节点数量不相等" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
blackNum++;
}
if (cur->_col == RED && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
std::cout << cur->_kv.first << " 连续红色节点" << std::endl;
}
return _IsBalance(cur->_left, blackNum, refVal)
&& _IsBalance(cur->_right, blackNum, refVal);
}
void layer()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
std::queue<node*> q;
q.push(_root);
int lay = 1;
while (!q.empty())
{
std::cout << "第" << lay << "层: ";
int num = q.size();
while (num--)
{
node* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
std::cout << cur->_kv.first << " 颜色:" << cur->_col << " ";
if (cur->_left != nullptr)
{
q.push(cur->_left);
}
if (cur->_right != nullptr)
{
q.push(cur->_right);
}
}
lay++;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void inorder()
{
_inorder(_root);
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void _inorder(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_inorder(root->_left);
std::cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_inorder(root->_right);
}
int size()
{
return _size(_root);
}
int _size(node* node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
return _size(node->_left) + _size(node->_right) + 1;
}
int TreeHeight()
{
return _TreeHeight(_root);
}
int _TreeHeight(node* node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
int lhight = _TreeHeight(node->_left);
int rhight = _TreeHeight(node->_right);
return lhight > rhight ? lhight + 1 : rhight + 1;
}
private:
node* _root = nullptr;
};
set

两个参数都用K初始化,传入仿函数
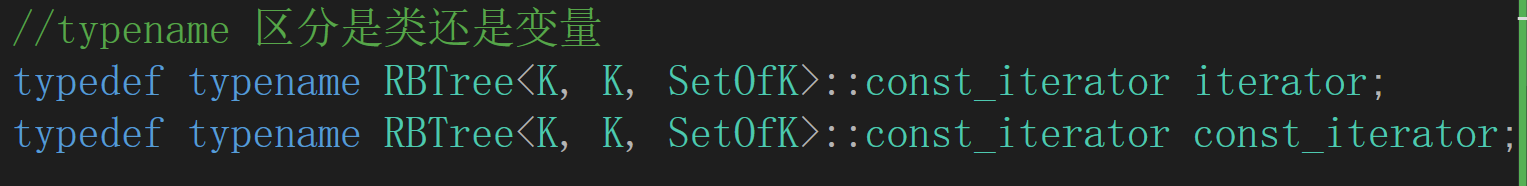
普通迭代器也用const,保证key不被修改,typename用来区分是一个类还是变量类型
全
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
template <class K>
class set
{
struct SetOfK
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//typename 区分是类还是变量
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetOfK>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetOfK>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetOfK> _t;
};
map

map第一个是K,用来erase,find等函数接口是key,它的数据类型是pair
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
std::pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
map提供[]操作,返回key位置的值,并可以对自身修改
全
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include "RBTree.h"
template <class K, class V>
class map
{
struct SetOfV
{
const K& operator()(const std::pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, std::pair<const K, V>, SetOfV>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const std::pair<const K, V> kv)
{
return _t.insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
std::pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, std::pair<const K, V>, SetOfV> _t;
};