前端异步编程规范
- Promise介绍
- 手写Promise(resolve,reject)
- 手写Promise(then)
- Promise相关 API实现
- all
- race
- allSettled
- any
- async/await和Promise的关系
- async/await的使用
Promise介绍
Promise是一个类,可以翻译为承诺、期约
Promise 就像一个容器,里面存放着未来才会结束,返回结果的容器,返回的结果只需要在出口处接收就好了。从语法上讲,Promise
是一个对象,从它可以获取异步操作的消息。
当通过new创建Promise实例时,需要传入一个回调函数,我们称之为executor
- 这个回调函数会被立刻执行,并传入两个回调参数resolve、reject
- 当调用resolve回调函数时,会执行 Promise 对象的then()第一个方法传入的回调
- 当调用reject回调函数时,会执行 Promise 对象的then()第二个方法或catch方法传入的回调
Promise是一个状态机,分为 3 种状态:
- pending:待定状态,执行了 executor 后,处于该状态
- fulfilled:兑现(成功)状态,调用resolve()后,Promise 的状态更改为 fullfilled,且无法再次更改
- rejected:拒绝状态,调用reject()后,Promise 的状态更改为 rejected,且无法再次更改
Promise 的状态,只可能是其中一种状态,从进行中变为成功或失败状态之后,状态就固定了,不会再发生改变。
const p = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
reject('error message')
},1000)
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res)//不执行
},err1=>{
console.log('err1',err1)//1秒后打印 err1 error message 不会打印err2 error message 先被then的err1输出结果
}).catch(err2=>{
console.log('err2',err2)//如果没有err1 1秒后打印err2 error message
})
手写Promise(resolve,reject)
Promise使用:

从Promise的使用上看,整理一下思路:Promise有三种状态。pending,fulfilled,rejected,且
- 执行了resolve,Promise状态会变成fulfilled;
- 执行了reject,Promise状态会变成rejected;
- Promise状态不可逆,第一次成功就永久为fulfilled,第一次失败就永远状态为rejected;只会执行resolve或reject其中一个
- Promise中有throw的话,就相当于执行了reject;
先来实现1和2
- 构建 Promise 对象时,需要传入一个 executor 函数,Promise 的主要业务流程都在 executor 函数中执行。
- 如果运行在 excutor 函数中的业务执行成功了,会调用 resolve 函数;如果执行失败了,则调用 reject 函数。
class MyPromise{
constructor(executor){
this.initValue()
//执行传进来的执行函数
// let executor =(resolve,reject)=>{
// setTimeout(()=>{
// reject('error message')
// },1000)
// }
// executor()
executor(this.resolve,this.reject)//resolve,reject
}
//先创建Promise初始化
initValue(){
this.PromiseState='pending'//Promise的状态
this.PromiseResult=null//Promise的输出结果
}
resolve(value){
console.log('resolve')
this.PromiseState='fulfilled'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window,
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
}
reject(value){
console.log('reject')
this.PromiseState='rejected'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
}
}
let p1 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
// console.log('MyPromise',this)//此时的this是window
resolve('success')//如果没有改变resolve函数内部的this指向,内部的this是没有PromiseState和PromiseResult属性的
// reject('fail')
})
console.log('p1', p1)
报错,resolve和reject内部的this是undefined,此时的resolve和reject在p1的原型对象上,如图
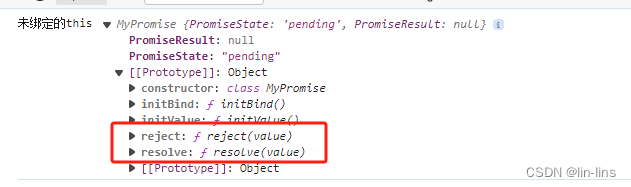
new的时候只会把构造函数里的类属性指向实例,类原型对象上方法不会指向实例
p1.resolve()可以调用,但是我们使用是resolve(),没有调用者。所以我们需要改变resolve函数的this指向,让resolve函数指向实例,才能访问实例上的属性(原型对象不能指回实例,原型对象和实例是1对多的关系,不清楚原型和实例关系的可以去本专栏的第一篇)
改变resolve函数的this指向,有三种方式call,apply,bind(详细可以看专栏第二篇),我们采用bind(只改变函数指向,先不执行)
class MyPromise{
constructor(executor){
this.initValue()
this.initBind()
//执行传进来的执行函数
executor(this.resolve,this.reject)//resolve,reject
// let executor =(resolve,reject)=>{
// setTimeout(()=>{
// reject('error message')
// },1000)
// }
// executor()
}
// 先创建Promise初始化
initValue(){
this.PromiseState='pending'//Promise的状态
this.PromiseResult=null//Promise的输出结果
}
//绑定this指向
initBind(){
//console.log('未绑定的this',this)//没有改变resolve和reject的this指向,此时resolve和reject函数是在class上,也就是实例的原型上
this.resolve = this.resolve.bind(this)//对class上的resolve函数,改变this指向,指向实例。this是实例,resolve不在实例上,实例上找不到,顺着在实例的原型上找
//等价于 this.resolve =this.__proto__.resolve.bind(this) ,在实例上创建一个函数,函数赋值原型上的函数resolve,此时函数内部的this指向是实例
this.reject = this.reject.bind(this)
console.log('绑定后的this',this)
}
resolve(value){
console.log('resolve')
this.PromiseState='fulfilled'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window,
//所以需要将resolve的this指向指向PromiseState的同一个实例,构造函数里的属性会挂在new出来的实例,也就是,要指向p1
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
}
reject(value){
console.log('reject')
this.PromiseState='rejected'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
}
}
let p1 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('MyPromise',this)//此时的this是window
resolve('success')//resolve的调用者是window,如果没有改变resolve函数内部的this指向,内部的this是没有PromiseState和PromiseResult属性的
reject('fail')
})
console.log('p1', p1)
绑定后,实例上不仅有俩个属性,还多了俩个方法
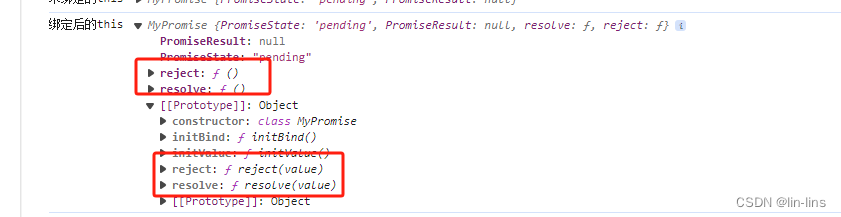
最后处理一下
3. Promise状态不可逆,第一次成功就永久为fulfilled,第一次失败就永远状态为rejected;只会执行resolve或reject其中一个
4. Promise中有throw的话,就相当于执行了reject;
在resolve、reject中添加判断,当状态不是pending时,说明被改变过,执行过resolve或reject
resolve(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='fulfilled'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window,
//所以需要将resolve的this指向指向PromiseState的同一个实例,构造函数里的属性会挂在new出来的实例,也就是,要指向p1
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
}
reject(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='rejected'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
}
Promise中有throw的话,就相当于执行了reject。这就要使用try catch了
try {
// 执行传进来的函数
executor(this.resolve, this.reject)
} catch (e) {
// 捕捉到错误直接执行reject
this.reject(e)
}
手写Promise(then)
then的使用
// 马上输出 ”success“
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('success')
}).then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err))
// 1秒后输出 ”fail“
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject('fail')
}, 1000)
}).then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err))
// 链式调用 输出 200
const p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(100)
}).then(res => 2 * res, err => console.log(err))
.then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err))
根据上述代码可以确定:
- then接收两个回调,一个是成功回调,一个是失败回调;
- 当Promise状态为fulfilled执行成功回调,为rejected执行失败回调;
- 如resolve或reject在定时器里,则定时器结束后再执行then;
- then支持链式调用,下一次then执行受上一次then返回值的影响;
实现1和2
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 接收两个回调 onFulfilled, onRejected
// 参数校验,确保一定是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : val => val
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason }
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
// 如果当前为成功状态,执行第一个回调
onFulfilled(this.PromiseResult)
} else if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
// 如果当前为失败状态,执行第二哥回调
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
}
完整代码为
class MyPromise {
// 构造方法
constructor(executor) {
// 初始化值
this.initValue()
// 初始化this指向
this.initBind()
try {
// 执行传进来的函数
executor(this.resolve, this.reject)
} catch (e) {
// 捕捉到错误直接执行reject
this.reject(e)
}
}
initBind() {
// 初始化this
this.resolve = this.resolve.bind(this)
this.reject = this.reject.bind(this)
}
initValue() {
// 初始化值
this.PromiseResult = null // 终值
this.PromiseState = 'pending' // 状态
}
resolve(value) {
// state是不可变的
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 如果执行resolve,状态变为fulfilled
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled'
// 终值为传进来的值
this.PromiseResult = value
}
reject(reason) {
// state是不可变的
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 如果执行reject,状态变为rejected
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 终值为传进来的reason
this.PromiseResult = reason
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 接收两个回调 onFulfilled, onRejected
// 参数校验,确保一定是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : val => val
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason }
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
// 如果当前为成功状态,执行第一个回调
onFulfilled(this.PromiseResult)
} else if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
// 如果当前为失败状态,执行第二哥回调
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
}
}
测试:
// 输出 ”success“
const test = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('success')
}).then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err))
实现第3点:如resolve或reject在定时器里,则定时器结束后再执行then;
这里先明白一个概念,
const test = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('success')
}).then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err))
resolve .then调用函数是同步的,即MyPromise创建,马上执行resolve改变状态,马上执行then里的判断状态,状态是成功,走成功分支,状态是失败走失败分支
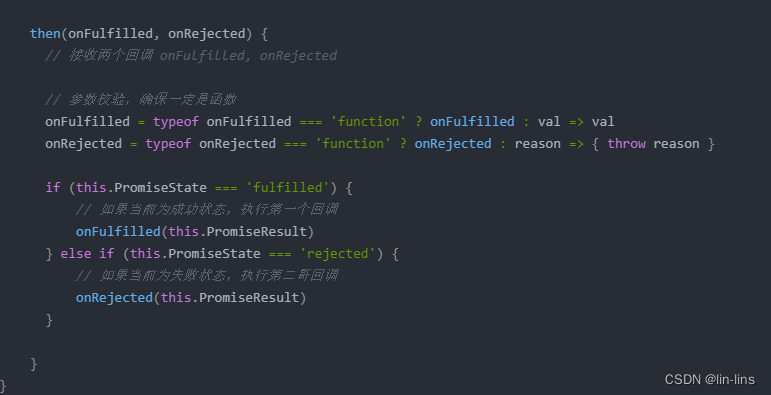
当resolve外层套一个定时器(resolve还未执行),同步进入then的时候,状态还没改变,是pending。then函数就没有反馈。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要在then里对状态为pending的时候处理,存储onFulfilled和onRejected
Promise A规范里 存在多次then调用情况
- 当 Promise 成功执⾏时,所有 onFulfilled 需按照其注册顺序依次回调。
- 当 Promise 被拒绝执⾏时,所有的onRejected需按照其注册顺序依次回调。
具体Promise/A+规范,可以看http://malcolmyu.github.io/malnote/2015/06/12/Promises-A-Plus/,或者我的3.2、理解Promise/A+规范意味着:我们可以多次调用,可以const p=promise,p.then(),p.then(),p.then()
因为同一个实例可能存在多次then调用,多个成功回调,多个失败回调,所以我们需要用队列存储。当resolve或者reject执行的时候,依次执行存储的成功队列或失败队列。一个实例只会promise只会执行resolve或reject里的一个,成功,则每个then都是执行成功,失败,则每个then都是执行失败。
另外:链式调用的时候promise.then().then().then(),每个then都返回的promise实例对象(下面详细讲)。对第三个then来说,他的调用者是p2=promise.then().then(),p2执行resolve或者reject之后,结果返回第三个then的onFulfilled或onRejected。也就是说单个链式调用里的then都是一个成功函数,一个失败函数。用回调队列来存储函数,不是因为链式调用的多个then。
实现:
class MyPromise{
constructor(executor){
this.initValue()
this.initBind()
try {
//执行传进来的执行函数
executor(this.resolve,this.reject)//resolve,reject
// let executor =(resolve,reject)=>{
// setTimeout(()=>{
// reject('error message')
// },1000)
// }
// executor()
} catch (e) {
// 捕捉到错误直接执行reject
this.reject(e)
}
}
// 先创建Promise初始化
initValue(){
this.PromiseState='pending'//Promise的状态
this.PromiseResult=null//Promise的输出结果
this.onFulfilledCallbacks=[]//成功回调
this.onRejectedCallbacks=[]//失败回调
}
//绑定this指向
initBind(){
//console.log('未绑定的this',this)//没有改变resolve和reject的this指向,此时resolve和reject函数是在class上,也就是实例的原型上
this.resolve = this.resolve.bind(this)//对class上的resolve函数,改变this指向,指向实例。this是实例,resolve不在实例上,实例上找不到,顺着在实例的原型上找
//等价于 this.resolve =this.__proto__.resolve.bind(this) ,在实例上创建一个函数,函数赋值原型上的函数resolve,此时函数内部的this指向是实例
this.reject = this.reject.bind(this)
// console.log('绑定后的this',this)
}
resolve(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='fulfilled'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window,
//所以需要将resolve的this指向指向PromiseState的同一个实例,构造函数里的属性会挂在new出来的实例,也就是,要指向p1
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
//执行resolve改变状态后,当成功回调里有值时,执行,注意先进先出
while(this.onFulfilledCallbacks.length){
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.shift()(this.PromiseResult)//shift()获取数组第一个元素,且改变原数组
//获取的第一个元素是一个函数,执行函数
}
}
reject(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='rejected'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
while(this.onRejectedCallbacks.length){
this.onRejectedCallbacks.shift()(this.PromiseResult)//shift()获取数组第一个元素,且改变原数组
//获取的第一个元素是一个函数,执行函数
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : val => val
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason }
if(this.PromiseState=='fulfilled'){
onFulfilled(this.PromiseResult)
}else if(this.PromiseState=='rejected'){
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}else{
//暂存函数
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push(onFulfilled.bind(this))//onFulfilled是箭头函数的话,不bind也没影响。bind可以将onFulfilled挂在实例上。
//onFulfilled一会儿会在resolve上执行,不改变this指向的话,onFulfilled也能执行,不过内部的this不是实例
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected.bind(this))
}
}
}
// 链式调用 输出 200
const p3 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(100)
},100)
})
p3.then(res => console.log('res',res), err => console.log('err',err))
p3.then(res => console.log('res2',res*2), err => console.log('err2',err))
p3.then(res => console.log('res3',res*3), err => console.log('err3',err))
//依次输出
// res 100
// res2 200
// res3 300
实现最后一点:then支持链式调用,下一次then执行受上一次then返回值的影响;
思路:链式调用,意味着调用then(),返回的结果也是个promise
1.如果回调函数返回的是Promise对象,根据返回的Promise的状态来决定then方法返回的Promise对象的状态,
const test1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(100)
})
//执行成功分支的Promise,该Promise返回reject,所以test2的返回结果与该Promise一致,走reject
const test2=test1.then(res => new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject(2 * res)), err => new Promise((resolve, reject) => resolve(3 * err)))
//
const test3= test2.then(res => console.log('success', res), err => console.log('fail', err))// 输出 状态:fail 值:200
- 如果回调函数返回的是非Promise对象,then方法放回的Promise对象状态为fulfilled
const test4 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(100)
}).then(res => 2 * res, err => 3 * err)//执行err分支,3 * err,执行成功
.then(res => console.log('success', res), err => console.log('fail', err))// 输出 success 300
- 如果回调的不是函数,需要进行包装,且值向下传递,即res=>res,err=>err(无视回调)
const promise1= new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(100)
})
const promise2 =promise1.then(200,'据因')
promise2.then(res => console.log('res',res), err => console.log('err',err)) //'res',100(返回promise1的value值100,不是200)
const promise3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(100)
}).then(200,'据因')
promise2.then(res => console.log('res',res), err => console.log('err',err)) //'err',据因
实现代码:
class MyPromise{
constructor(executor){
this.initValue()
this.initBind()
try {
//执行传进来的执行函数
executor(this.resolve,this.reject)//resolve,reject
// let executor =(resolve,reject)=>{
// setTimeout(()=>{
// reject('error message')
// },1000)
// }
// executor()
} catch (e) {
// 捕捉到错误直接执行reject
this.reject(e)
}
}
// 先创建Promise初始化
initValue(){
this.PromiseState='pending'//Promise的状态
this.PromiseResult=null//Promise的输出结果
this.onFulfilledCallbacks=[]//成功回调
this.onRejectedCallbacks=[]//失败回调
}
//绑定this指向
initBind(){
//console.log('未绑定的this',this)//没有改变resolve和reject的this指向,此时resolve和reject函数是在class上,也就是实例的原型上
this.resolve = this.resolve.bind(this)//对class上的resolve函数,改变this指向,指向实例。this是实例,resolve不在实例上,实例上找不到,顺着在实例的原型上找
//等价于 this.resolve =this.__proto__.resolve.bind(this) ,在实例上创建一个函数,函数赋值原型上的函数resolve,此时函数内部的this指向是实例
this.reject = this.reject.bind(this)
// console.log('绑定后的this',this)
}
resolve(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='fulfilled'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window,
//所以需要将resolve的this指向指向PromiseState的同一个实例,构造函数里的属性会挂在new出来的实例,也就是,要指向p1
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
//执行resolve改变状态后,当成功回调里有值时,执行,注意先进先出
while(this.onFulfilledCallbacks.length){
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.shift()(this.PromiseResult)//shift()获取数组第一个元素,且改变原数组
//获取的第一个元素是一个函数,执行函数
}
}
reject(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='rejected'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
while(this.onRejectedCallbacks.length){
this.onRejectedCallbacks.shift()(this.PromiseResult)//shift()获取数组第一个元素,且改变原数组
//获取的第一个元素是一个函数,执行函数
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : val => val
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason }
var thenPromise= new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if(this.PromiseState=='fulfilled'){
// 接收一下回调函数的结果 PromiseResult this.PromiseResult=value就是onFulfilled的参数
let result= onFulfilled(this.PromiseResult)
//如果回调函数是一个Promise,那么then的结果跟该Promise一致。如果回调函数不是Promise,那么把该值或表达式作为resolve的参数传递出去
if(result instanceof MyPromise){
thenPromise.then(v => {//该promise走成功,则resolve,走失败,则reject
// 如果返回的是resolve状态
resolve(v)
}, r => {
reject(r);
})
}else{
resolve(result)
}
}else if(this.PromiseState=='rejected'){
//失败分支同理
let result= onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
//如果回调函数是一个Promise,那么then的结果跟该Promise一致。如果回调函数不是Promise,那么把该值或表达式作为resolve的参数传递出去
if(result instanceof MyPromise){
thenPromise.then(v => {//该promise走成功,则resolve,走失败,则reject
// 如果返回的是resolve状态
resolve(v)
}, r => {
reject(r);
})
}else{
resolve(result)
}
}else if(this.PromiseState=='pending'){
//暂存函数
//要判断onFulfilled的执行结果。可以新建一个函数resultPromise,在函数内对函数结果判断。把新函数push进栈里,先不执行,等resolve上执行
//因为成功和失败的执行逻辑一样,只是调用的函数名onFulfilled、onRejected不同,所以传参区分
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push(onFulfilled.bind(this))//onFulfilled是箭头函数的话,不bind也没影响。bind可以将onFulfilled挂在实例上。
//onFulfilled一会儿会在resolve上执行,不改变this指向的话,onFulfilled也能执行,不过内部的this不是实例
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected.bind(this))
}
})
return thenPromise
}
}
验证之后,发现成功和失败回调都是正常的。现在来处理状态pending分支,这里我们的onFulfilled或onRejected函数还没执行,需要等会儿执行。
- 我们可以在外面包一层函数,新建函数resultPromise,在栈中push 这个resultPromise函数
- onFulfilled和onRejected处理逻辑一致,只是函数名不同,可以进行传参封装
- 同时可以替换fulfilled和rejected分支里的代码,改为resultPromise(onFulfilled)
最后:then方法是微任务(后续事件循环章节总结会讲),所以可以套一个setTimeout代替,模拟实现异步(setTimeout为宏任务,此处主要跟在全局上的console对比)
最终实现代码:
class MyPromise{
constructor(executor){
this.initValue()
this.initBind()
try {
//执行传进来的执行函数
executor(this.resolve,this.reject)//resolve,reject
} catch (e) {
// 捕捉到错误直接执行reject
this.reject(e)
}
}
// 先创建Promise初始化
initValue(){
this.PromiseState='pending'//Promise的状态
this.PromiseResult=null//Promise的输出结果
this.onFulfilledCallbacks=[]//成功回调
this.onRejectedCallbacks=[]//失败回调
}
//绑定this指向
initBind(){
//console.log('未绑定的this',this)//没有改变resolve和reject的this指向,此时resolve和reject函数是在class上,也就是实例的原型上
this.resolve = this.resolve.bind(this)//对class上的resolve函数,改变this指向,指向实例。this是实例,resolve不在实例上,实例上找不到,顺着在实例的原型上找
//等价于 this.resolve =this.__proto__.resolve.bind(this) ,在实例上创建一个函数,函数赋值原型上的函数resolve,此时函数内部的this指向是实例
this.reject = this.reject.bind(this)
// console.log('绑定后的this',this)
}
resolve(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='fulfilled'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window,
//所以需要将resolve的this指向指向PromiseState的同一个实例,构造函数里的属性会挂在new出来的实例,也就是,要指向p1
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
//执行resolve改变状态后,当成功回调里有值时,执行,注意先进先出
while(this.onFulfilledCallbacks.length){
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.shift()(this.PromiseResult)//shift()获取数组第一个元素,且改变原数组
//获取的第一个元素是一个函数,执行函数
}
}
reject(value){
if(this.PromiseState!='pending'){
return
}
this.PromiseState='rejected'//Promise的状态 //此时this是undefind,因为resolve的调用者指向的是window
this.PromiseResult=value//Promise的输出结果
while(this.onRejectedCallbacks.length){
this.onRejectedCallbacks.shift()(this.PromiseResult)//shift()获取数组第一个元素,且改变原数组
//获取的第一个元素是一个函数,执行函数
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : val => val //包装函数,相当于res=>res,即不对结果进行处理,向下传递
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason } //包装函数,相当于err=>err,即不对结果进行处理,向下传递,同时抛出异常
var thenPromise= new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const resultPromise=(FnName)=>{
setTimeout(() => { //模拟实现then异步任务
try{
// 接收一下回调函数的结果 PromiseResult this.PromiseResult=value就是onFulfilled的参数
let result= FnName(this.PromiseResult)
if (result === thenPromise) {
// 不能返回自身哦
throw new Error('不能返回自身。。。')
}
//如果回调函数是一个Promise,那么then的结果跟该Promise一致。如果回调函数不是Promise,那么把该值或表达式作为resolve的参数传递出去
if(result instanceof MyPromise){
thenPromise.then(v => {//该promise走成功,则resolve,走失败,则reject
// 如果返回的是resolve状态
resolve(v)
}, r => {
reject(r);
})
}else{
resolve(result)
}
} catch(err){
reject(err)
throw new Error(err)
}
})
}
if(this.PromiseState=='fulfilled'){
//调用函数
resultPromise(onFulfilled)
}else if(this.PromiseState=='rejected'){
//失败分支同理
resultPromise(onRejected)
}else{
//暂存函数
//要判断onFulfilled的执行结果。可以新建一个函数resultPromise,在函数内对函数结果判断。把新函数push进栈里,先不执行,等resolve上执行
//因为成功和失败的执行逻辑一样,只是调用的函数名onFulfilled、onRejected不同,所以传参区分
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push(resultPromise.bind(this,onFulfilled))//onFulfilled是箭头函数的话,不bind也没影响。bind可以将onFulfilled挂在实例上。
//onFulfilled一会儿会在resolve上执行,不改变this指向的话,onFulfilled也能执行,不过内部的this不是实例
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(resultPromise.bind(this,onRejected))
}
})
return thenPromise
}
}
Promise相关 API实现
all
- 接收一个Promise数组,数组中如有非Promise项,则此项当做成功;
- 如果所有Promise都成功,则返回成功结果数组;
- 如果有一个Promise失败,则返回这个失败结果;
实现思路:
定义一个数组和计数器,当Promise成功的时候数组添加成功回调值,计数器加1,同时判断此时的计数器与Promise数组长度是否相同,相同resolve(数组)
static all(promises) {
const result = []
let count = 0
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const addData = (index, value) => {
result[index] = value
count++
if (count === promises.length) resolve(result)
}
promises.forEach((promise, index) => {
if (promise instanceof MyPromise) {
promise.then(res => {
addData(index, res)
}, err => reject(err))
} else {
addData(index, promise)
}
})
})
}
race
- 接收一个Promise数组,数组中如有非Promise项,则此项当做成功;
- 哪个Promise最快得到结果,就返回那个结果,无论成功失败;
实现思路:
遍历循环Promise数组,都进行输出,哪个结果最快,就会输出,返回那个值,利用Promise的状态一旦改变,就不会更改,只执行第一个resolve或reject
static race(promises) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
promises.forEach(promise => {
if (promise instanceof MyPromise) {
promise.then(res => {
resolve(res)
}, err => {
reject(err)
})
} else {
resolve(promise)
}
})
})
}
allSettled
- 接收一个Promise数组,数组中如有非Promise项,则此项当做成功;
- 把每一个Promise的结果,集合成数组后返回;
实现思路:
定义一个数组和计数器,当Promise数组的每次Promise调用,数组添加回调值,计数器加1,当计数器与Promise数组长度相同时,返回esolve(数组)
static allSettled(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const res = []
let count = 0
const addData = (status, value, i) => {
res[i] = {
status,
value
}
count++
if (count === promises.length) {
resolve(res)
}
}
promises.forEach((promise, i) => {
if (promise instanceof MyPromise) {
promise.then(res => {
addData('fulfilled', res, i)
}, err => {
addData('rejected', err, i)
})
} else {
addData('fulfilled', promise, i)
}
})
})
}
any
与all相反
- 接收一个Promise数组,数组中如有非Promise项,则此项当做成功;
- 如果有一个Promise成功,则返回这个成功结果;返回第一个兑现的值
- 如果所有Promise都失败,则报错;
实现思路:
定义计数器,当Promise数组的每次Promise调用,当成功的时候,直接返回成功(第一个成功的返回,和race一样);失败的时候,计数器加1,当计数器与Promise数组长度相同时,返回报错信息
static any(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let count = 0
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(val => {
resolve(val)
}, err => {
count++
if (count === promises.length) {
reject(new AggregateError('All promises were rejected'))
}
})
})
})
}
}
思考题(下一章讲)
实现一个带并发限制的异步调度器 Scheduler,保证同时运行的任务最多有N个。完善下面代码中的 Scheduler 类,使得以下程序能正确输出:
class Scheduler {
add(promiseCreator) { ... }
// ...
}
const timeout = (time) => new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time)
})
const scheduler = new Scheduler(n)
const addTask = (time, order) => {
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time)).then(() => console.log(order))
}
addTask(1000, '1')
addTask(500, '2')
addTask(300, '3')
addTask(400, '4')
// 打印顺序是:2 3 1 4
async/await和Promise的关系
async/await和Promise的对应关系:async封装Promise,await相当then,try…catch相当于catch
1. 执行async函数,返回的是Promise对象
async function fn1(){
return 100 //相当于return Promise.resolve(100)
}
const res1=fn1()//执行async函数,返回的是一个Promise对象,比如上面的return 100封装成了一个Promise对象进行返回
console.log('res1',res1)//Promise对象
res1.then(data=>{
console.log('data',data)//100
})
//可以用const data= await fn1()接收data值 使用await,要和async配套
2. await相当于Promise的then
!( async function(){
const res2=Promise.resolve(100)//相当于上面例子的res1 也就是fn1()
const data= await res2 //await相当于Promise的then res1.then(data=>{})
console.log('data',data)//100
})()
!( async function(){
const res2=await 400 //await Promise.resolve(400) await后面不跟Promise,也会被封装成Promise
console.log('res2',res2)//400
})()
3. try…catch 可捕获异常,代替了Promise的catch
!( async function(){
const p4=Promise.reject('err')//rejected状态
try{
const res=await p4 //await相当于then,但是reject不会触发then
console.log(res) //不会输出,因为const res=await p4被报错,被catch捕获
} catch(ex){
console.error(ex)//try...catch 相当于Promise的catch
}
})()
async/await的使用
async/await的用处:用同步方式,执行异步操作
现在有一个新的要求:先请求完接口1,再拿接口1返回的数据,去当做接口2的请求参数,那我们可以这么做:
Promise做法
function request(num) { // 模拟接口请求
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
request(5).then(res1 => {
console.log(res1) // 1秒后 输出 10
request(res1).then(res2 => {
console.log(res2) // 2秒后 输出 20
})
})
async/await做法
function request(num) { // 模拟接口请求
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
async function fn () {
const res1 = await request(5)
const res2 = await request(res1)
console.log(res2) // 2秒后输出 20
}
fn()
在async函数中,await规定了异步操作只能一个一个排队执行,从而达到用同步方式,执行异步操作的效果。
注意:await只能在async函数中使用
刚刚上面的例子await后面都是跟着异步操作Promise,那如果不接Promise?
function request(num) { // 去掉Promise
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(num * 2)
}, 1000)
}
async function fn() {
await request(1) // 2
await request(2) // 4
// 1秒后执行完 同时输出
}
fn()
可以看出,如果await后面接的不是Promise的话,等同于async/await不生效,等价于
function request(num) { // 去掉Promise
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(num * 2)
}, 1000)
}
function fn() {
request(1) // 2
request(2) // 4
// 1秒后执行完 同时输出
}
fn()
Q:什么是async?
async是一个位于function之前的前缀,只有async函数中,才能使用await。
async执行完是返回一个 Promise ,状态为fulfilled,值是function的返回值
async function fn (num) {
return num //相当于return Promise.resolve(num)
}
console.log(fn) // [AsyncFunction: fn]
console.log(fn(10)) // Promise {<fulfilled>: 10}
fn(10).then(res => console.log(res)) // 10
总结
- await只能在async函数中使用,不然会报错;
- async函数返回的是一个Promise对象,有无值看有无return值;
- await后面最好是接Promise,虽然接其他值也能达到排队效(但是作用等于原来不使用await的时候);
- async/await作用是用同步方式,执行异步操作
- async/await是一种语法糖,用到的是ES6里的迭代函数——generator函数(可以自行了解)(ES6的class也是语法糖,用普通function也能实现同样效果)