1.举例1:子类继承父类以后,对父类方法进行了重写,那么在子类中,是否还可以对父类中被重写的方法进行调用?
可以!
举例2:子类继承父类以后,发现子类和父类中定义了同名的属性,是否可以在子类中区分两个同名的属性?(比如子类父类都有叫做id的属性,调用时如何正确区分?)
当然可以,用super(详见-代码举例1)。
2.super的理解: 父类的
- super可以调用的结构:属性,方法,构造器
具体的:
3.1 super调用属性,方法
子类继承父类之后,我们就可以在子类的方法或构造器中,调用父类中声明的属性或方法(满足封装性的前提下,因为没有权限调不成),调用时,需要使用"super."的结构,表示调用父类的属性或方法。
一般情况下,可以考虑省略super.结构,但是,如果出现了子类重写父类的方法或子父类中出现了同名的属性时,则必须使用super.声明,显示调用父类被重写的方法 或 父类中声明的同名属性。
3.2 super调用构造器
- 子类继承父类时,不会继承父类的构造器,只能通过super(形参列表)的方式调用父类指定的构造器。
- 规定super形参列表,必须声明在构造器的首行。
- 前面讲过,构造器的首行可以使用this(形参列表),调用本类中重载的构造器。 结合上面2得到结论,在构造器的首行,this和super只能二选一。
- 如果子类构造器的首行既没有使用this(形参列表)也没有调用super(形参列表),则此类构造器默认调用super(),即父类中空参的构造器。参考代码举例4.
- 由3&4得到:子类的任何一个构造器中,要么会调用本类中重载的构造器,要么会调用父类的构造器,只能是这两种情况之一。
换言之,- 1. 子类构造器的首行,程序员自己写了调用this()那就强制调用了this(),系统不会再默认调用super()了;- 2. 子类构造器的首行,程序员自己写了调用super()那就按命令调用super(),系统不会再默认首行插入super()调用命令了; - 3. 子类构造器的首行,程序员啥也没写。系统默认首行插入super()调用命令,系统会强制调用super();- 4. this(),super()这两个调用,写在子类构造器的首行,只能出现一个。参考代码举例5
- 由5得到:一个类中声明有n个构造器,最多有n-1个构造器中使用了this(形参列表),则剩下的那个一定使用super(形参列表)。(可以是程序员自己写的super()也可以是系统默认插入的super())子类构造器们必须有至少一个去调用父类super,不然子类构造器们全都是this(),那子类构造器就一起形成一个闭环导致死循环啦!
我们在通过子类的构造器创建对象时,一定在调用子类构造器的过程中,直接或间接的调用到父类的构造器,也正因为调用过父类的构造器,我们才会将父类中声明的属性或方法加载道内存中,供子类对象使用。
二、子类对象实例化全过程
代码举例1,当子类Student调用Student定义的方法show(),方法里又调用了父类super.eat()方法,那么将会输出父类eat()方法:“人吃饭”。
代码:父类Person类,它有一个子类叫做Student
package this_super.supertest;
public class Person{
String name;
int age; //属性为age
public Person() {
}
public Person(String n) {
this.name = n;
this.eat();
}
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人睡觉");
}
}
子类Student
package this_super.supertest;
public class Student extends Person{
String school;
public void study() {
System.out.println("学生学习");
}
//对Person中已有的eat方法重写
public void eat(){
System.out.println("学生餐");
}
//对Person中已有的sleep方法重写
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("学生睡觉9小时保证时长");
}
public void show(){
eat();//省略了this,和下面的this.eat()功能一样。
this.eat();
super.eat();
}
}
StudentTest测试代码
package this_super.supertest;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.eat();//调用Student定义的方法eat(),输出“学生餐”
s1.sleep();//调用Student定义的方法sleep(),输出“学生睡觉9小时保证时长”
System.out.println("---------->");
s1.show();//调用Student定义的方法show(),里面调用了super.eat()方法,将会输出父类eat()方法:"人吃饭"
}
}
运行结果:
学生餐
学生睡觉9小时保证时长
---------->
学生餐
学生餐
人吃饭
Process finished with exit code 0
代码举例2
父类Person类其中包含id为身份证号默认值10086,它有一个子类叫做Student包含id为学生号默认值1000,输出这两个id。
Person.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Person{
String name;
int age; //属性为age
int id=10086;//身份证号
public Person() {
}
public Person(String n) {
this.name = n;
this.eat();
}
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人睡觉");
}
}
Student.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Student extends Person{
String school;
int id=1000;//学号
public void study() {
System.out.println("学生学习");
}
//对Person中已有的eat方法重写
public void eat(){
System.out.println("学生餐");
}
//对Person中已有的sleep方法重写
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("学生睡觉9小时保证时长");
}
public void show1(){
eat();//省略了this,和下面的this.eat()功能一样。
this.eat();
super.eat();
}
public void show2(){
System.out.println("student id = "+this.id);//1000
System.out.println("Person id = "+super.id);//person_id=10086
}
}
StudentTest.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.eat();//调用Student定义的方法eat(),输出“学生餐”
s1.sleep();//调用Student定义的方法sleep(),输出“学生睡觉9小时保证时长”
System.out.println("---------->");
s1.show2();
}
}
输出结果:
学生餐
学生睡觉9小时保证时长
---------->
student id = 1000
Person id = 10086
代码举例3,当子类中并不存在这个对象,默认会向父类去寻找,找到即可输出。如果还是没有,会继续向上层搜索,最终所有文件都找不到,就会报错。
Person.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Person{
String name= "LISA";
int age; //属性为age
int id=10086;//身份证号
public Person() {
}
public Person(String n) {
this.name = n;
this.eat();
}
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人睡觉");
}
}
Student.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Student extends Person{
String school;
int id=1000;//学号
public void study() {
System.out.println("学生学习");
}
//对Person中已有的eat方法重写
public void eat(){
System.out.println("学生餐");
}
//对Person中已有的sleep方法重写
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("学生睡觉9小时保证时长");
}
public void show1(){
eat();//省略了this,和下面的this.eat()功能一样。
this.eat();
super.eat();
}
public void show2(){
System.out.println("student id = "+this.id);//1000
System.out.println("Person id = "+super.id);//person_id=10086
}
public void show3(){
System.out.println(name);//这里要求输出name其实要求输出的是this.name
System.out.println(this.name);//本例Student文件没有定义name,所以this.name并不存在。于是向上一级求索,找到Person文件里的name对象,最终找到可输出的对象Person.name。
// 如果Person文件里也没有name对象,那么会一层一层往上找,直到找到name对象为止。如果实在找不到,最后会报错。
System.out.println(super.name);//Person.name 对于本例而言,这三行输出是一模一样的,都是最终找到了super.name也就是Person.name进行输出的。
}
}
StudentTest.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println("---------->");
s1.show3();
}
}
输出结果:
---------->
LISA
LISA
LISA
Process finished with exit code 0
代码举例4
当Person父类拥有一个Student子类时,子类Student新建对象时会先去运行父类Person的空参constructor,然后再去运行子类Student的空参constructor。
//空参constructor表示Person()或者Student()的括号里面是空的,没有输入参数的。
Person.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Person{
String name= "LISA";
int age; //属性为age
int id=10086;//身份证号
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person() 父类空参处...");
}
public Person(String n) {
this.name = n;
this.eat();
}
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
}
}
Student.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Student extends Person{
String school;
int id=1000;//学号
//测试super调用父类的构造器
public Student() {
super();//this和super必须出现在首行,并且只能二选一
System.out.println("Student()...子类空参处");
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
System.out.println("Student()...子类有参处");
}
}
StudentTest.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("---------->");
Student s2 = new Student();
System.out.println("*****");
}
}
会输出
---------->
Person() 父类空参处...
Student()...子类空参处
*****
现在修改Student.java文件,将其中的 //super();删除或注释掉,文件空参构造器应变为
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student()...子类空参处");
}
Student.java文件应变为:
package this_super.supertest;
public class Student extends Person{
String school;
int id=1000;//学号
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student()...子类空参处");
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
System.out.println("Student()...子类有参处");
}
}
运行发现,结果输出并无变化
---------->
Person() 父类空参处...
Student()...子类空参处
*****
Process finished with exit code 0
以上程序运行可以看出,就算用户并不在子类构造器中明确写出,调用super(); 子类默认一定会去调用父类的空参构造器。
现在将StudentTest文件改写,再新增一新增一个Student对象s3,观察结果输出:
package this_super.supertest;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("---------->");
Student s2 = new Student();
System.out.println("*****");
Student s3 = new Student();
}
}
运行结果
---------->
Person() 父类空参处...
Student()...子类空参处
*****
Person() 父类空参处...
Student()...子类空参处
Process finished with exit code 0
以上运行可以发现,每新建一个Student object 就调用一次父类和子类的空参构造器,新建了两个Student object,实际调用父类和子类的空参构造器各两次。
系统默认在第一行添加的super()
代码举例5
当子类Student新建一个带参数的对象s3,新建这个对象时,系统会自动追溯到Student.java里面的有参构造器,(我们已经知道,在子类Student的无参构造器第一行,系统会隐藏着默认去调用父类Person的无参构造器,即在子类Student的无参构造器第一行,系统会在构造器第一行帮你偷偷写入super()😉,下面这个例子展示了类似的结论:在子类Student的有参构造器第一行,无论程序员写不写,系统会在第一行偷偷写入super(); 去默认调用父类Person无参构造器。
Person.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Person{
String name= "LISA";
int age; //属性为age
int id=10086;//身份证号
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person() 父类空参处...");
}
public Person(String n) {
this.name = n;
this.eat();
}
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("Person() 父类有参name email处...");
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
System.out.println("Person() 父类有参name age处...");
}
public Person(String name, int age, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
}
}
Student.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class Student extends Person{
String school;
int id=1000;//学号
public void study() {
System.out.println("学生学习");
}
//测试super调用父类的构造器
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student()...子类空参处");
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
//super();无论程序员写不写,系统默认这里会加这一句
System.out.println("Student()...子类有参处");
}
}
StudentTest.java
package this_super.supertest;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("---------->");
Student s3 = new Student("lisa",22);
}
}
运行结果
---------->
Person() 父类空参处...
Student()...子类有参处
Process finished with exit code 0
结论:可以观察到 尽管子类使用的是有参构造器,系统在有参构造器第一行默认添加的仍是空参super();
练习题目一:
修改下面Kids类中employeed()方法,当前运行时仅仅会输出一行星号;
目标:希望Kids中的该employeed()方法,先调用父类ManKInd的employeed()方法,然后再输出“but Kids should study and no job”
子类Kids.java
package this_super.Kids;
public class Kids extends Mankind {
private int yearsOld;
public Kids() {
}
public Kids(int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
}
public Kids(int sex, int salary, int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
setSex(sex);
setSalary(salary);
}
public int getYearsOld(){return yearsOld;}
public void setYearsOld(int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
}
public void printAge(){
System.out.println("I am"+ yearsOld + "years old.");
}
public void employeed(){
}
}
父类Mankind.java
package this_super.Kids;
public class Mankind {
private int sex; //性别
private int salary; //薪资
public void ManKind() {
}
public void ManKind(int sex, int salary) {
this.sex = sex;
this.salary = salary;
}
public void manOrWoman(){
if(sex==1){
System.out.println("man");
}else if(sex==0){
System.out.println("woman");
}
}
public void employeed(){
if(salary==0){
System.out.println("no job");
}else if(salary!=0){
System.out.println("job");
}
}
public int getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
KidsTest.java
package this_super.Kids;
public class KidsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Kids kid = new Kids();
System.out.println("*************");
kid.employeed();
}
}
当前KidsTest主程序运行后,系统会输出*************
按照题目要求,修改Kids.java文件,代码如下
package this_super.Kids;
public class Kids extends Mankind {
private int yearsOld;
public Kids() {
}
public Kids(int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
}
public Kids(int sex, int salary, int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
setSex(sex);
setSalary(salary);
}
public int getYearsOld(){return yearsOld;}
public void setYearsOld(int yearsOld) {
this.yearsOld = yearsOld;
}
public void printAge(){
System.out.println("I am"+ yearsOld + "years old.");
}
public void employeed(){
super.employeed();
System.out.println("but Kids should study and no job");
}
}
运行结果:
no job
but Kids should study and no job
Process finished with exit code 0
练习题目二:
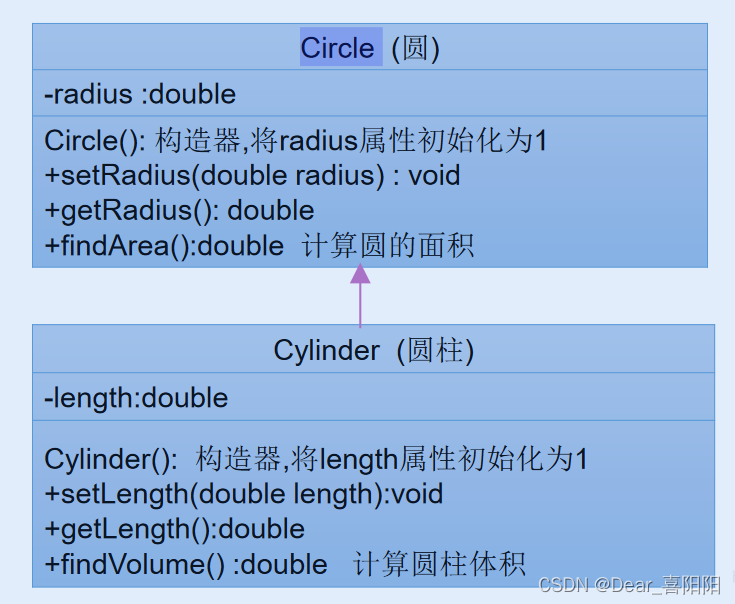
在CylinderTest中创建Cylinder圆柱类的对象,设置圆柱的底面半径和高,并输出圆柱的体积。
注意在Cylinder()类中设计求表面积的方法findArea()和求体积的方法findVolume(),使用上super.
圆柱类为Circle类的子类。
Circle.java
package this_super.Cylinder;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Circle {
double radius =1; //半径R
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double findArea(double radius) {
//计算圆的面积 PI*R^2
System.out.println("findArea is "+ Math.PI *radius*radius);
return Math.PI *radius*radius;
}
}
Cylinder.java
package this_super.Cylinder;
public class Cylinder extends Circle {
double length = 1;
double radius = 1;
public Cylinder() {
}
public Cylinder( double radius , double length) {
this.length = length;
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double findVolume() {
double radius = this.radius;
double length = this.length;
return super.findArea(radius)*length;
}
}
CylinderTest.java
package this_super.Cylinder;
public class CylinderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double radius=5;
double length=3;
//from calculator: 25×3.14×3 = 235.5
Cylinder cy1 = new Cylinder(radius, length);
System.out.println(cy1.findVolume());
}
}
运行结果
findArea is 78.53981633974483
235.61944901923448
Process finished with exit code 0
练习题目三:
写一个名为Account的类模拟账户。该类的属性和方法如下图所示。
该类包括的属性,账号id余额balance年利率annualInterestRate
包含的方法:访问器方法(getter和setter方法),返回月利率的方法getMonthlyInterest(),取款方法withdraw
写一个用户测试Account类,在用户程序中,创建一个账号为1122,余额为20000,年利率为4.5%的Account对象。
使用withdraw方法提款30000元,并打印余额。
再使用withdraw方法提款2500元,使用deposit方法存款3000元,然后打印余额和月利率
提示:在提款方法withdraw中,需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数字的要求,如果不能要给予提示。
Account.java
package this_super.Accounting;
public class Account {
private int id;
private double balance;
double annualInterestRate;
public Account() {
}
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return this.balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return this.annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public double getMonthlyInterest() {
return this.annualInterestRate/12;
}
public double withdraw(double req_amt) {
double temp = this.balance-req_amt;
if(temp >0){
System.out.println("取款成功");
setBalance(temp);
return temp;
}
else {
System.out.println("取款失败,余额不足");
return -1;
}
}
public double deposit(double req_amt) {
double balance=this.balance+req_amt;
setBalance(balance);
return balance;
}
}
AccountTest.java
package this_super.Accounting;
public class AccountTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account a1 = new Account();
a1.setId(1122);
a1.setBalance(20000);
a1.setAnnualInterestRate(0.045);
a1.getBalance();
a1.withdraw(30000);
System.out.println("当前账户余额: "+a1.getBalance());//
System.out.println("申请取款2500元: 最新balance为: "+a1.withdraw(2500));//17500
System.out.println("申请存储3000元,最新balance为: "+a1.deposit(3000));//20500
System.out.print("最新余额为:");
a1.getBalance();
System.out.println("月利率为"+a1.getMonthlyInterest());//0.00375
}
}
运行结果
取款失败,余额不足
当前账户余额: 20000.0
取款成功
申请取款2500元: 最新balance为: 17500.0
申请存储3000元,最新balance为: 20500.0
最新余额为:月利率为0.00375
Process finished with exit code 0
练习题目四:在练习题目三的基础上,创建Account类中的一个子类CheckAccount代表可透支的账户,该账户中定义一个属性overdraft代表可透支限额,在CheckAccount类中重写withdraw方法,其算法如下:
如果(取款金额<账户余额) 可直接取款
如果(取款金额>账户余额) 计算要透支的额度
判断可透支额度overdraft是否足够支付本次透支需要,如果可以将账户余额修改为0,冲减可透支金额
如果不可以,提示用户超过可透支的限额
测试:要求写一个用户程序测试CheckAccount类。
在用户程序中,创建一个账号为1122,余额为2000,年利率为4.5%,可透支限额为5000元的CheckAccount对象。
使用withdraw方法提款5000元,打印账户余额和可透支额。
再使用withdraw方法提款18000元,打印账户余额和可透支额。
再使用withdraw方法提款2000元,打印账户余额和可透支额。
提示:子类CheckAccount的构造方法需要将父类继承的3个属性和子类自己的属性全部初始化。
父类Account的属性balance被设置为private,但在子类CheckAccount的withdraw方法中需要修改它的值
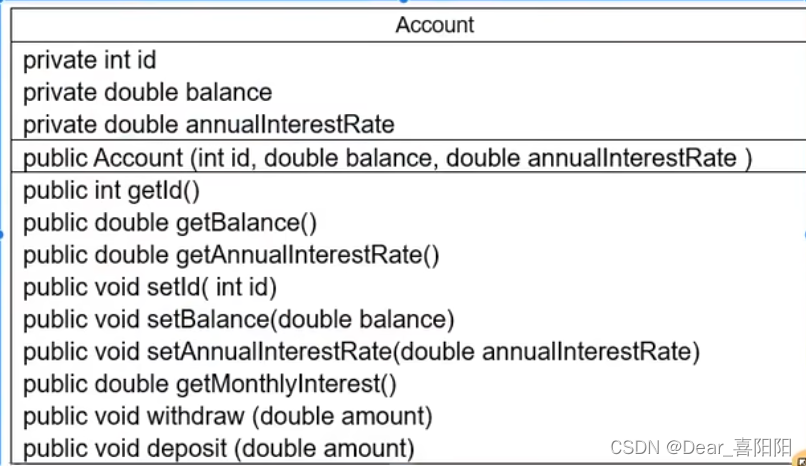
Account.java父类文件不变
package this_super.Accounting;
public class Account {
private int id;
private double balance;
private double annualInterestRate;
public Account() {
}
public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return this.balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return this.annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public double getMonthlyInterest() {
return this.annualInterestRate/12;
}
public double withdraw(double req_amt) {
double temp = this.balance-req_amt;
if(temp >0){
System.out.println("取款成功");
setBalance(temp);
return temp;
}
else {
System.out.println("取款失败,余额不足");
return -1;
}
}
public double deposit(double req_amt) {
double balance=this.balance+req_amt;
setBalance(balance);
return balance;
}
}
CheckAccount.java作为子类
package this_super.Accounting;
public class CheckAccount extends Account{
private int id=0;
private double balance=0;
private double annualInterestRate=0;
private double overdraft=0;
public CheckAccount() {
}
@Override
public void setId(int id) {
super.setId(id);
}
@Override
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
super.setAnnualInterestRate(annualInterestRate);
}
@Override
public int getId() {
return super.getId();
}
@Override
public double getBalance() {
return super.getBalance();
}
@Override
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return super.getAnnualInterestRate();
}
public double getOverdraft() {
return this.overdraft;
}
public void setOverdraft(double overdraft) {
this.overdraft = overdraft;
}
@Override
public void setBalance(double balance) {
super.setBalance(balance);
//update client's balance, no overdraft
}
@Override
public double withdraw(double req_amt) {
double org_balance=this.getBalance();
System.out.println("org_balance:"+org_balance);
if(req_amt<=org_balance){
System.out.println("余额可用,取款成功");
this.setBalance(org_balance - req_amt);
return org_balance - req_amt; //返回账户余额
}
else {
if(org_balance + overdraft >= req_amt){
System.out.println("余额不足,透支成功");
this.setOverdraft(org_balance + overdraft - req_amt);
this.setBalance(0);
return 0; //返回账户余额
}
else {
System.out.println("余额透支不足,取款失败");
this.setBalance(org_balance);
return org_balance; //返回账户余额
}
}
}
}
测试文件
package this_super.Accounting;
public class TestCheckAccount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在用户程序中,创建一个账号为1122,余额为2000,年利率为4.5%,可透支限额为5000元的CheckAccount对象。
CheckAccount ca1 = new CheckAccount();
ca1.setId(1122);
ca1.setBalance(2000);
ca1.setAnnualInterestRate(0.045);
ca1.setOverdraft(5000);
System.out.println("----提款5000元------->");
System.out.println("账户余额为: "+ca1.withdraw(5000));
System.out.println("可透支余额为: "+ca1.getOverdraft());
System.out.println("----提款18000元------->");
System.out.println("账户余额为: "+ca1.withdraw(18000));
System.out.println("可透支余额为: "+ca1.getOverdraft());
System.out.println("----提款2000元------->");
System.out.println("账户余额为: "+ca1.withdraw(2000));
System.out.println("可透支余额为: "+ca1.getOverdraft());
}
}
运行结果:
----提款5000元------->
org_balance:2000.0
余额不足,透支成功
账户余额为: 0.0
可透支余额为: 2000.0
----提款18000元------->
org_balance:0.0
余额透支不足,取款失败
账户余额为: 0.0
可透支余额为: 2000.0
----提款2000元------->
org_balance:0.0
余额不足,透支成功
账户余额为: 0.0
可透支余额为: 0.0
Process finished with exit code 0
课后练习:
请探讨下面程序的输出结果,并说明为什么
子类程序
package this_super.test01;
public class Son extends Father{
private String info = "上学啦";
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.getInfo());
System.out.println(super.getInfo());
}
}
父类程序
package this_super.test01;
public class Father {
private String info ="上班狗";
public void setInfo(String info){
this.info=info;
}
public String getInfo(){
return info;
}
}
主程序:
package this_super.test01;
public class question02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
System.out.println(f.getInfo());//上班狗
System.out.println(s.getInfo());//上班狗
s.test();//上班狗 上班狗
System.out.println("------->");
s.setInfo("逛吃逛吃");
System.out.println(f.getInfo());//上班狗
// 这里优点绕,注意根据s子类改变的father父类的info,实际只会影响s自己调用父类getInfo方法时候的结果,
// 本身father内部原来的info的数值并不会改变。
System.out.println(s.getInfo());//逛吃逛吃
}
}
运行结果
上班狗
上班狗
上班狗
上班狗
------->
上班狗
逛吃逛吃
Process finished with exit code 0