目录
一、模块的概念
二、模块的导入方式
三、案例演示
3.1 import模块名
3.2 from 模块名 import 功能名
3.3 from 模块名 import *
3.4 as定义别名
四、自定义模块
4.1 制作自定义模块
4.2 测试模块
4.3 注意事项
4.4 __all__
五、Python包
5.1 包的概念
5.2 快速入门
5.3 安装使用第三方包
安装第三方包 - pip
pip的网络优化
安装第三方包 - PyCharm
一、模块的概念
Python 模块(Module),是一个 Python 文件,以 .py 结尾。 模块能定义函数、类和变量,模块里也能包含可执行的代码。
模块的作用: python中有很多各种不同的模块,每一个模块都可以帮助我们快速的实现一些功能。比如实现和时间相关的功能就可以使用time模块,我们可以认为一个模块就是一个工具包, 每一个工具包中都有各种不同的工具,供我们使用进而实现各种不同的功能。
大白话:模块就是一个Python文件,里面有类、函数、变量等,我们可以拿过来用(导入模块去使用)。
二、模块的导入方式
模块在使用前需要先导入,导入的语法如下:

常用的组合形式如:
import 模块名
from 模块名 import 类、变量、方法等
from 模块名 import *
import 模块名 as 别名
from 模块名 import 功能名 as 别名
三、案例演示
3.1 import模块名
import 模块名
import 模块名1,模块名2
模块名.功能名()
import time
print("倒计时 开始")
time.sleep(1)
for i in range(5):
print(5 - i)
time.sleep(1)
print("时间到!")
time模块是python内置的,有兴趣可以点开看一下:
# encoding: utf-8
# module time
# from (built-in)
# by generator 1.147
"""
This module provides various functions to manipulate time values.
There are two standard representations of time. One is the number
of seconds since the Epoch, in UTC (a.k.a. GMT). It may be an integer
or a floating point number (to represent fractions of seconds).
The Epoch is system-defined; on Unix, it is generally January 1st, 1970.
The actual value can be retrieved by calling gmtime(0).
The other representation is a tuple of 9 integers giving local time.
The tuple items are:
year (including century, e.g. 1998)
month (1-12)
day (1-31)
hours (0-23)
minutes (0-59)
seconds (0-59)
weekday (0-6, Monday is 0)
Julian day (day in the year, 1-366)
DST (Daylight Savings Time) flag (-1, 0 or 1)
If the DST flag is 0, the time is given in the regular time zone;
if it is 1, the time is given in the DST time zone;
if it is -1, mktime() should guess based on the date and time.
"""
# no imports
# Variables with simple values
altzone = -3600
daylight = 0
timezone = 0
_STRUCT_TM_ITEMS = 11
# functions
def asctime(p_tuple=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
asctime([tuple]) -> string
Convert a time tuple to a string, e.g. 'Sat Jun 06 16:26:11 1998'.
When the time tuple is not present, current time as returned by localtime()
is used.
"""
return ""
def ctime(seconds=None): # known case of time.ctime
"""
ctime(seconds) -> string
Convert a time in seconds since the Epoch to a string in local time.
This is equivalent to asctime(localtime(seconds)). When the time tuple is
not present, current time as returned by localtime() is used.
"""
return ""
def get_clock_info(name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
get_clock_info(name: str) -> dict
Get information of the specified clock.
"""
return {}
def gmtime(seconds=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
gmtime([seconds]) -> (tm_year, tm_mon, tm_mday, tm_hour, tm_min,
tm_sec, tm_wday, tm_yday, tm_isdst)
Convert seconds since the Epoch to a time tuple expressing UTC (a.k.a.
GMT). When 'seconds' is not passed in, convert the current time instead.
If the platform supports the tm_gmtoff and tm_zone, they are available as
attributes only.
"""
pass
def localtime(seconds=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
localtime([seconds]) -> (tm_year,tm_mon,tm_mday,tm_hour,tm_min,
tm_sec,tm_wday,tm_yday,tm_isdst)
Convert seconds since the Epoch to a time tuple expressing local time.
When 'seconds' is not passed in, convert the current time instead.
"""
pass
def mktime(p_tuple): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
mktime(tuple) -> floating point number
Convert a time tuple in local time to seconds since the Epoch.
Note that mktime(gmtime(0)) will not generally return zero for most
time zones; instead the returned value will either be equal to that
of the timezone or altzone attributes on the time module.
"""
return 0.0
def monotonic(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
monotonic() -> float
Monotonic clock, cannot go backward.
"""
return 0.0
def monotonic_ns(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
monotonic_ns() -> int
Monotonic clock, cannot go backward, as nanoseconds.
"""
return 0
def perf_counter(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
perf_counter() -> float
Performance counter for benchmarking.
"""
return 0.0
def perf_counter_ns(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
perf_counter_ns() -> int
Performance counter for benchmarking as nanoseconds.
"""
return 0
def process_time(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
process_time() -> float
Process time for profiling: sum of the kernel and user-space CPU time.
"""
return 0.0
def process_time_ns(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
process_time() -> int
Process time for profiling as nanoseconds:
sum of the kernel and user-space CPU time.
"""
pass
def sleep(seconds): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
sleep(seconds)
Delay execution for a given number of seconds. The argument may be
a floating point number for subsecond precision.
"""
pass
def strftime(format, p_tuple=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
strftime(format[, tuple]) -> string
Convert a time tuple to a string according to a format specification.
See the library reference manual for formatting codes. When the time tuple
is not present, current time as returned by localtime() is used.
Commonly used format codes:
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61].
%z Time zone offset from UTC.
%a Locale's abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale's full weekday name.
%b Locale's abbreviated month name.
%B Locale's full month name.
%c Locale's appropriate date and time representation.
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM.
Other codes may be available on your platform. See documentation for
the C library strftime function.
"""
return ""
def strptime(string, format): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
strptime(string, format) -> struct_time
Parse a string to a time tuple according to a format specification.
See the library reference manual for formatting codes (same as
strftime()).
Commonly used format codes:
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61].
%z Time zone offset from UTC.
%a Locale's abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale's full weekday name.
%b Locale's abbreviated month name.
%B Locale's full month name.
%c Locale's appropriate date and time representation.
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM.
Other codes may be available on your platform. See documentation for
the C library strftime function.
"""
return struct_time
def thread_time(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
thread_time() -> float
Thread time for profiling: sum of the kernel and user-space CPU time.
"""
return 0.0
def thread_time_ns(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
thread_time() -> int
Thread time for profiling as nanoseconds:
sum of the kernel and user-space CPU time.
"""
pass
def time(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
time() -> floating point number
Return the current time in seconds since the Epoch.
Fractions of a second may be present if the system clock provides them.
"""
return 0.0
def time_ns(): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
time_ns() -> int
Return the current time in nanoseconds since the Epoch.
"""
return 0
# classes
class struct_time(tuple):
"""
The time value as returned by gmtime(), localtime(), and strptime(), and
accepted by asctime(), mktime() and strftime(). May be considered as a
sequence of 9 integers.
Note that several fields' values are not the same as those defined by
the C language standard for struct tm. For example, the value of the
field tm_year is the actual year, not year - 1900. See individual
fields' descriptions for details.
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass
tm_gmtoff = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""offset from UTC in seconds"""
tm_hour = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""hours, range [0, 23]"""
tm_isdst = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""1 if summer time is in effect, 0 if not, and -1 if unknown"""
tm_mday = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""day of month, range [1, 31]"""
tm_min = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""minutes, range [0, 59]"""
tm_mon = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""month of year, range [1, 12]"""
tm_sec = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""seconds, range [0, 61])"""
tm_wday = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""day of week, range [0, 6], Monday is 0"""
tm_yday = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""day of year, range [1, 366]"""
tm_year = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""year, for example, 1993"""
tm_zone = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""abbreviation of timezone name"""
n_fields = 11
n_sequence_fields = 9
n_unnamed_fields = 0
__match_args__ = (
'tm_year',
'tm_mon',
'tm_mday',
'tm_hour',
'tm_min',
'tm_sec',
'tm_wday',
'tm_yday',
'tm_isdst',
)
class __loader__(object):
"""
Meta path import for built-in modules.
All methods are either class or static methods to avoid the need to
instantiate the class.
"""
def create_module(spec): # reliably restored by inspect
""" Create a built-in module """
pass
def exec_module(module): # reliably restored by inspect
""" Exec a built-in module """
pass
@classmethod
def find_module(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Find the built-in module.
If 'path' is ever specified then the search is considered a failure.
This method is deprecated. Use find_spec() instead.
"""
pass
@classmethod
def find_spec(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
@classmethod
def get_code(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return None as built-in modules do not have code objects. """
pass
@classmethod
def get_source(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return None as built-in modules do not have source code. """
pass
@classmethod
def is_package(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return False as built-in modules are never packages. """
pass
@classmethod
def load_module(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Load the specified module into sys.modules and return it.
This method is deprecated. Use loader.exec_module() instead.
"""
pass
def module_repr(module): # reliably restored by inspect
"""
Return repr for the module.
The method is deprecated. The import machinery does the job itself.
"""
pass
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
__weakref__ = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""list of weak references to the object (if defined)"""
_ORIGIN = 'built-in'
__dict__ = None # (!) real value is "mappingproxy({'__module__': '_frozen_importlib', '__doc__': 'Meta path import for built-in modules.\\n\\n All methods are either class or static methods to avoid the need to\\n instantiate the class.\\n\\n ', '_ORIGIN': 'built-in', 'module_repr': <staticmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.module_repr at 0x0000023892692320>)>, 'find_spec': <classmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.find_spec at 0x00000238926923B0>)>, 'find_module': <classmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.find_module at 0x0000023892692440>)>, 'create_module': <staticmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.create_module at 0x00000238926924D0>)>, 'exec_module': <staticmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.exec_module at 0x0000023892692560>)>, 'get_code': <classmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.get_code at 0x0000023892692680>)>, 'get_source': <classmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.get_source at 0x00000238926927A0>)>, 'is_package': <classmethod(<function BuiltinImporter.is_package at 0x00000238926928C0>)>, 'load_module': <classmethod(<function _load_module_shim at 0x00000238926917E0>)>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'BuiltinImporter' objects>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'BuiltinImporter' objects>})"
# variables with complex values
tzname = (
'Coordinated Universal Time',
'Coordinated Universal Time',
)
__spec__ = None # (!) real value is "ModuleSpec(name='time', loader=<class '_frozen_importlib.BuiltinImporter'>, origin='built-in')"
3.2 from 模块名 import 功能名
例如刚才的时间模块,还可以这样写:
from time import sleep
print("倒计时 开始")
sleep(1)
for i in range(5):
print(5 - i)
sleep(1)
print("时间到!")效果是一样的,这里就不展示了。
3.3 from 模块名 import *
from 模块名 import *
功能名()
from time import *
print("倒计时 开始")
sleep(1)
for i in range(5):
print(5 - i)
sleep(1)
print("时间到!")这个写法和直接import time的区别是:后者需要time.类函数变量,而该方式可以直接写模块里面的内容,不需要time.。
3.4 as定义别名
# 模块定义别名
import 模块名 as 别名
# 功能定义别名
from 模块名 import 功能 as 别名
# 模块别名
import time as tt
tt.sleep(2)
print('hello')
# 功能别名
from time import sleep as sl
sl(2)
print('hello')
四、自定义模块
4.1 制作自定义模块
Python中已经帮我们实现了很多的模块,不过有时候我们需要一些个性化的模块,这里就可以通过自定义模块实现, 也就是自己制作一个模块。
案例:新建一个Python文件,命名为my_module1.py,并定义test函数。


注意:
每个Python文件都可以作为一个模块,模块的名字就是文件的名字。 也就是说自定义模块名必须要符合标识符命名规则。
4.2 测试模块
在实际开发中,当一个开发人员编写完一个模块后,为了让模块能够在项目中达到想要的效果,这个开发人员会自行在py文件中添加一些测试信息,例如:在my_module1.py文件中添加测试代码test(1,1)。

问题:
此时,无论是当前文件,还是其他已经导入了该模块的文件,在运行的时候都会自动执行`test`函数的调用。
换句话说,就是导入模块的时候,相当于执行了一遍模块里面的全部内容。
解决方案:

4.3 注意事项
注意事项:当导入多个模块的时候,且模块内有同名功能. 当调用这个同名功能的时候,调用到的是后面导入的模块的功能。
4.4 __all__
如果一个模块文件中有`__all__`变量,当使用`from xxx import *`导入时,只能导入这个列表中的元素。

![]()

五、Python包
5.1 包的概念
基于Python模块,我们可以在编写代码的时候,导入许多外部代码来丰富功能。但是,如果Python的模块太多了,就可能造成一定的混乱,那么如何管理呢?
通过Python包的功能来管理。
从物理上看,包就是一个文件夹,在该文件夹下包含了一个 __init__.py 文件,该文件夹可用于包含多个模块文件。
从逻辑上看,包的本质依然是模块
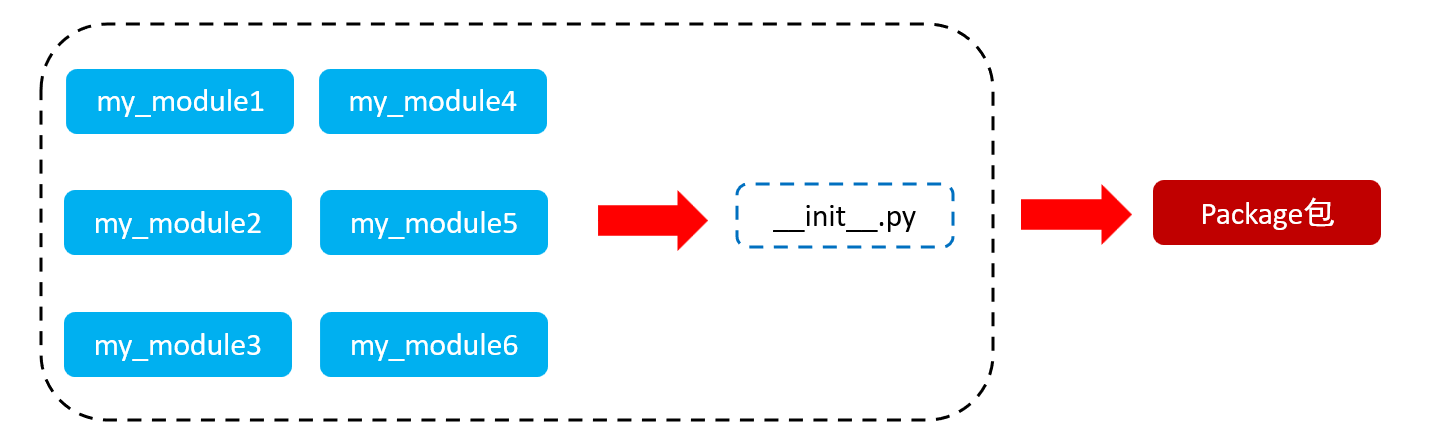
包的作用:
当我们的模块文件越来越多时,包可以帮助我们管理这些模块, 包的作用就是包含多个模块,但包的本质依然是模块。
5.2 快速入门
步骤如下:
① 新建包`my_package`
② 新建包内模块:`my_module1` 和 `my_module2`
③ 模块内代码如下



Pycharm中的基本步骤:
[New] → [Python Package] → 输入包名 → [OK] → 新建功能模块(有联系的模块)
注意:新建包后,包内部会自动创建`__init__.py`文件,这个文件控制着包的导入行为



导入包
方式一
import 包名.模块名
包名.模块名.目标

方式二:
注意:在`__init__.py`文件中添加`__all__ = []`,控制允许导入的模块列表
from 包名 import *
模块名.目标



5.3 安装使用第三方包
我们知道,包可以包含一堆的Python模块,而每个模块又内含许多的功能。
所以,我们可以认为:一个包,就是一堆同类型功能的集合体。
在Python程序的生态中,有许多非常多的第三方包(非Python官方),可以极大的帮助我们提高开发效率,如:
•科学计算中常用的:numpy包
•数据分析中常用的:pandas包
•大数据计算中常用的:pyspark、apache-flink包
•图形可视化常用的:matplotlib、pyecharts
•人工智能常用的:tensorflow
•等
这些第三方的包,极大的丰富了Python的生态,提高了开发效率。
但是由于是第三方,所以Python没有内置,所以我们需要安装它们才可以导入使用哦。
安装第三方包 - pip
第三方包的安装非常简单,我们只需要使用Python内置的pip程序即可。
打开我们许久未见的:命令提示符程序,在里面输入:
pip install 包名称即可通过网络快速安装第三方包

pip的网络优化
由于pip是连接的国外的网站进行包的下载,所以有的时候会速度很慢。
我们可以通过如下命令,让其连接国内的网站进行包的安装:
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple 包名称

https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple 是清华大学提供的一个网站,可供pip程序下载第三方包。
安装第三方包 - PyCharm
PyCharm也提供了安装第三方包的功能: