SpringMVC
- SpringMVC简介
1.1什么是MVC
MVC是一种软件架构的思想,将软件按照模型、视图、控制器来划分
M:Model,模型层,指工程中的JavaBean,作用是处理数据
JavaBean分为两类:
一类称为实体类Bean:专门存储业务数据的,比如:Emp、Dept、User
一类称为业务处理Bean:指Service或Dao对象,专门用于处理业务逻辑和数据访问
V:View,视图层,指工程中的Html或jsp页面,作用是与用户进行交互,展示数据
C:Controller,控制层,指工程中的servlet,作用是接收请求和响应浏览器
MVC的工作流程:用户通过V(视图层)发送请求到服务器,在服务器中由C(控制器)接收,C(控制器)调用相应的M(模型层)层处理请求,处理完毕将结果返回到C,C再根据请求处理的结果,找到相应的V,渲染数据后最终响应给浏览器。
1.2、什么是SpringMVC
SpringMVC是Spring家族的一个后续产品,是Spring的一个子项目
SpringMVC是为表述层开发提供的一整套完备的解决方案。
注:三层架构分为表述层(表示层)、业务逻辑层、数据访问层。表述层表示前台页面+后台servlet
1.3SpringMVC的特点
- Spring 家族原生产品,与 IOC 容器等基础设施无缝对接
- 基于原生的Servlet,通过了功能强大的前端控制器DispatcherServlet,对请求和响应进行统一处理
- 表述层各细分领域需要解决的问题全方位覆盖,提供全面解决方案
- 代码清新简洁,大幅度提升开发效率
- 内部组件化程度高,可插拔式组件即插即用,想要什么功能配置相应组件即可
- 性能卓著,尤其适合现代大型、超大型互联网项目要求
- 入门案例
2.1、开发环境
IDE:idea 2022.2.3
构建工具:maven 3.6.0
服务器:tomcat8.5
Spring版本:5.3.1
2.2、创建maven工程
导pom依赖时,由于Maven具有传递性的,所以不需要将需要的所有包全部配置依赖,只需要配置最顶端的依赖即可,其它靠maven的传递性导入
2.3配置web.xml
注:
<url-pattern>标签中使用/和/*的区别:
/所匹配的请求可以是/login或.html或.js或.css方式的请求路径,但是/不能匹配.jsp请求路径的请求因此就可以避免在访问jsp页面时,该请求被DispatcherServlet处理,从而找不到相应的页面/*则能够匹配所有请求,例如在使用过滤器时,若需要对所有请求进行过滤,就需要使用/*的写法
3、@RequestMapping注解
3.1、功能
就是将用户的请求和处理请求的控制器的方法关联起来,建立映射关系。
SpringMVC接收到指定的请求以后,就会找到在映射关系中对应的控制器的方法来处理这个请求
3.2、注解的位置
@RequestMapping注解标识到类或方法上
3.3、value属性
通过value的属性请求的请求地址匹配请求映射
value属性是必须设置的
value属性是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求
3.4、method属性
method属性通过请求的请求方式(get或post)匹配请求映射
它是一个RequestMethod[]类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求,当前浏览器所发送的请求方式匹配method属性中的任何一种请求方式,则当前请求就会被注解所标识的方法进行处理
如果当前请求的请求地址满足映射的value属性,但是请求方式不满足method属性,则浏览器报405错误:Request method 'xxx' not supported
在RequestMapping注解的基础上,结合请求方式派生出了一些注解
@PostMapping 就等同与@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method =RequestMethod.POST)
@GetMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
目前浏览器只支持get和post请求,如果在form表单提交时,为method设置了其他请求方式的字符串,比如put或delete,则按照默认的请求方式get处理
如果要发生put或delete的请求,则需要通过spring提供的过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter,在后续RESTful部分详细讲解
3.5、params属性 (了解)
通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params的属性设置
params可以使用四种表达式
“params”:表示当前所匹配的请求的请求参数中必须携带params参数
Parameter conditions "xxx" not met for actual request parameters:
“!params”表示当前所匹配的请求的请求参数中一定不能携带params参数
Parameter conditions "!xxx" not met for actual request parameters:
“params=value”:表示当前所匹配的请求的请求参数中必须携带params参数并且值必须为value
“params!=value”:表示当前所匹配的请求的请求参数中可以不携带params参数,如果携带值一定不能是value
3.6、headers
四种
"header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
"!header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
"header=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
"header!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到
3.7、支持ant风格的路径
?:表示任意的单个字符
*:表示任意的0个或者多个字符 不包括/
**:表示任意层数的任意目录,注意:使用**时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式
3.8、SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符
原始的方式:/deleteUserById?id=1
rest方式:/deleteUserById/1
占位符常用于restful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,再通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
只需要在控制器方法的形参位置,设置一个形参,形参的名字和请求参数的名字一致即可,但是必须加@PathVariable注解
4、springmvc获取请求参数
4.1、通过的ServletAPI获取
4.2、通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数
<form th:action="@{/param}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form> |
@RequestMapping("/param")
public String getParam(String username,String password){
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password);
return "success";
} |
* 只需要在控制器方法的形参位置,设置一个形参,形参的名字和请求参数的名字一致即可
4.3、@RequestParam
@RequestParam是将请求参数和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
| http://localhost:8080/springmvc_rest/param?password=123 |
@RequestMapping("/param")
public String getParam(@RequestParam(value = "username",required = true,
defaultValue = "hello")String username, String password){
/**
* @RequestParam注解的属性:
* value:设置和形参绑定的请求参数的名字
* required:设置是否必须传输value所对应的请求参数
* 默认值为true,表示value所对应的请求参数必须传输,否则页面报错
* Required String parameter 'xxx' is not present
* 若设置为false,则表示value所对应的请求参数不是必须传输,
* 如果此时获取该参数的值,则为null
*defaultValue:设置当没有传输value所对应的请求参数时,
* 为形参设置的默认值,此时和required属性值无关
*/
System.out.println("username:" + username + ",password:" + password);
return "success";
} |
4.4、@RequestHeaher
@RequestParam是将请求头信息和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@RequestMapping("/param")
public String getParam(@RequestParam(value = "username",required = true,
defaultValue = "hello")String username, String password,
@RequestHeader("referer") String referer){ |
4.5、@CookieValue
@CookieValue是将cookie数据和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@CookieValue("JSESSIONID")String jsessionId |
如果没有cookie数据JSESSIONID会报错:
Missing cookie 'JSESSIONID' for method parameter of type String
通过该超链接访问/param/servletAPI地址
<a th:href="@{/param/servletAPI}">测试@RequestMapping注解的value属性的占位符</a> |
跳转到该方法,通过 HttpSession session = request.getSession();生成JSESSIONID
@RequestMapping("/param/servletAPI")
public String getParamByServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password);
return "success";
} |
再通过
<form th:action="@{/param}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form> |
访问控制器方法
@RequestMapping("/param")
public String getParam(
@RequestParam(value = "username",required = true,
defaultValue = "hello")String username, String password,
@RequestHeader("referer") String referer,
@CookieValue("JSESSIONID")String jsessionId){
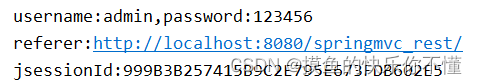
System.out.println("username:" + username + ",password:" + password);
System.out.println("referer:"+referer);
System.out.println("jsessionId:"+jsessionId);
return "success";
} |
输出:
4.6、通过pojo获取请求参数
可以在控制器方法的形参位置设置一个实体类类型的形参,此时如果浏览器传输的请求参数的参数名和实体类中的属性名一致,那么请求参数就会为此属性赋值
pojo
|
package com.qcby.pojo; |
Index.html
<form th:action="@{/param/pojo}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form> |
控制器
@RequestMapping("/param/pojo")
public String getParamByPojo(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "success";
} |
4.7解决获取请求参数的乱码问题
Springmvc提供的编码过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter
encoding->utf-8
forceEncoding->true
SpringMVC中处理编码的过滤器一定要配置到其他过滤器之前,否则无效
<!--配置springmvc的编码过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping> |
5、域对象共享数据
5.1、使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{testServletAPI}">测试通过ServletAPI向请求域共享数据</a> |
@RequestMapping("/testServletAPI")
public String testServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("testScope","hello,servletAPI");
return "success";
} |
<p th:text="${testScope}"></p> |
5.2、使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testmav}">测试通过ModelAndView向请求域共享数据</a> |
@RequestMapping("/testmav")
public ModelAndView testmav(){
/**
* ModelAndView包含Model和View的功能
* Model:向请求域中共享数据
* View:设置逻辑视图实现页面跳转
*/
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//向请求域中共享数据
modelAndView.addObject("testReqeustScope","hello,ModelAndView");
//设置逻辑视图
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
//使用View设置逻辑视图,但是控制器方法一定要将ModelAndView的对象作为方法的返回值
return modelAndView;
} |
<p th:text="${testReqeustScope}"></p> |
5.3、使用Model向request域对象共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testmodel}">测试通过Model向请求域共享数据</a><br> |
@RequestMapping("/testmodel")
public String testmodel(Model model){
//org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
System.out.println(model.getClass().getName());
model.addAttribute("testReqeustScope","hello,Model");
return "success";
} |
5.4、使用map向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testMap")
public String testMap(Map<String,Object> map){
//org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
System.out.println(map.getClass().getName());
map.put("testReqeustScope","hello,map");
return "success";
} |
5.5、使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testmodelmap")
public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){
//org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
System.out.println(modelMap.getClass().getName());
modelMap.addAttribute("testReqeustScope","hello,ModelMap");
return "success";
} |
5.6 Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
Model、ModelMap、Map类型的参数本质上其实都是BindingAwareModelMap类型的
org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
所以在底层中,这些类型的形参最终都是通过BindingAwareModelMap创建的
5.7、向session域共享数据
<a th:href="@{/testsession}">测试通过session向回话域共享数据</a><br> |
@RequestMapping("/testsession")
public String testSession(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("testSessionScope","hello,session");
return "success";
} |
<p th:text="${session.testSessionScope}"></p> |
5.8、向application域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testapplication")
public String testApplication(HttpSession session){
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("testApplicationScope","hello,Application");
return "success";
} |
<!--通过${application.属性名}获取的是application域对象数据-->
<p th:text="${application.testApplicationScope}"></p> |
6、springmvc的视图
SpringMVC中的视图是View接口,视图的作用渲染数据,将模型Model中的数据展示给用户,SpringMVC视图的种类很多,默认有转发视图和重定向视图
当工程引入jstl的依赖,转发视图会自动转换为JstlView ,若使用的视图技术为Thymeleaf,在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置了Thymeleaf的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是ThymeleafView
6.1、ThymeleafView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图后缀所得到的最终路径,会通过转发的方式实现跳转
6.2、转发视图
SpringMVC中默认的转发视图是InternalResourceView
SpringMVC中创建转发视图的情况:
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"forward:"为前缀时,创建InternalResourceView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"forward:"去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过转发的方式实现跳转
例如"forward:/","forward:/employee"
<a th:href="@{/test/view/forward}">测试SpringMVC的视图InternalResourceView </a> |
@RequestMapping("/testmodel")
public String testmodel(Model model){
//org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
System.out.println(model.getClass().getName());
model.addAttribute("testReqeustScope","hello,Model");
return "success";
} @RequestMapping("/test/view/forward")
public String testInternalResourceView(){
return "forward:/testmodel";
} |
<p th:text="${testReqeustScope}"></p> |
6.3、重定向视图
SpringMVC中默认的重定向视图是RedirectView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"redirect:"为前缀时,创建RedirectView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"redirect:"去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过重定向的方式实现跳转
例如"redirect:/","redirect:/employee"
注:
重定向视图在解析时,会先将redirect:前缀去掉,然后会判断剩余部分是否以/开头,若是则会自动拼接上下文路径
6.4、视图控制器view-contronller
当控制器方法中,仅仅用来实现页面跳转,即只需要设置视图名称时,可以将处理器方法使用view-controller标签进行表示
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index"></mvc:view-controller> |
注:
当springmvc中设置任何一个view-controller时,其它控制器中的请求映射将全部失效,
此时需要再SpringMVC的核心配置文件中开启mvc的注解驱动
<!--开启注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> |
- RESTFul
7.1、简介
REST:Representational State Transfer,表现层资源状态转移。
7.2、实现
具体说,就是 HTTP 协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。
它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源。
REST 风格提倡 URL 地址使用统一的风格设计,从前到后各个单词使用斜杠分开,不使用问号键值对方式携带请求参数,而是将要发送给服务器的数据作为 URL 地址的一部分,以保证整体风格的一致性。
| 操作 | 传统方式 | REST风格 |
| 查询操作 | getUserById?id=1 | user/1-->get请求方式 |
| 保存操作 | saveUser | user-->post请求方式 |
| 删除操作 | deleteUser?id=1 | user/1-->delete请求方式 |
| 更新操作 | updateUser | user-->put请求方式 |
7.3、HiddenHttpMethodFilter
由于浏览器只支持发送get和post方式的请求,那么该如何发送put和delete请求呢?
SpringMVC 提供了HiddenHttpMethodFilter,将 POST 请求转换为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求HiddenHttpMethodFilter 处理put和delete请求的条件:
a>当前请求的请求方式必须为post
b>当前请求必须传输请求参数_method
满足以上条件,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器就会将当前请求的请求方式转换为请求参数_method的值,因此请求参数_method的值才是最终的请求方式
在web.xml中注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter
<!--处理请求方式的过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping> |
8、RESTFul案例
8.1、准备工作
对员工表(模拟表数据)的员工信息进行增删改查
搭建环境
准备实体类
package com.qcby.pojo;
/**
* @Author che
* @Date 2024/6/9 19:16
* Description:TODO
* Version 1.0
*/
public class Employee {
private Integer id;//主键
private String lastName;//姓名
private String email;//邮箱
private Integer sex;//性别,1male,0female
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer sex) {
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.sex = sex;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(Integer sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
'}';
}
} |
准备dao模拟数据
package com.qcby.dao;
import com.qcby.pojo.Employee;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author che
* @Date 2024/6/9 19:19
* Description:TODO
* Version 1.0
*/
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
private static Map<Integer, Employee> employees = null;
static {
employees = new HashMap<Integer,Employee>();
employees.put(1001,new Employee(1001,"E-AA","aa@qq.com",1));
employees.put(1002,new Employee(1002,"E-AA","aa@qq.com",1));
employees.put(1003,new Employee(1003,"E-AA","aa@qq.com",0));
employees.put(1004,new Employee(1004,"E-AA","aa@qq.com",0));
employees.put(1005,new Employee(1005,"E-AA","aa@qq.com",1));
}
private static Integer initId = 1006;
/**
* 模拟添加操作
* @param employee
*/
public void save(Employee employee){
if(employee.getId() == null){
employee.setId(initId++);
}
employees.put(employee.getId(),employee);
}
/**
* 删除
* @param id
*/
public void delete(Integer id){
employees.remove(id);
}
/**
* 修改
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Employee get(Integer id){
return employees.get(id);
}
/**
* 查找
* @return
*/
public Collection<Employee> getAll(){
return employees.values();
}
} |
8.2功能清单
| 功能 | URL 地址 | 请求方式 |
| 访问首页√ | / | GET |
| 查询全部数据√ | /employee | GET |
| 删除√ | /employee/2 | DELETE |
| 跳转到添加数据页面√ | /toAdd | GET |
| 执行保存√ | /employee | POST |
| 跳转到更新数据页面√ | /employee/2 | GET |
| 执行更新√ | /employee | PUT |
index.html
8.3、访问首页
SpringMVC.xml
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index"></mvc:view-controller> |
创建index页面
<a th:href="@{/employee}">查询所有的员工信息</a><br> |
控制器
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
//@RequestMapping(value = "/employee",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/employee")
public String getAllEmployee(Model model) {
//获取所有的员工信息
Collection<Employee> allEmployee = employeeDao.getAll();
//将所有的员工信息在请求域中共享
model.addAttribute("allEmployee",allEmployee);
//返回到员工列表页面
return "employee_list";
} |
//@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/employee/{id}")
public String deleteEmploee(@PathVariable Integer id) {
//删除员工信息
employeeDao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/employee";
} |
⑴创建处理删除delete请求方式的表单
<!-- 作用:通过超链接控制表单的提交,将post请求转换为delete请求 -->
<form method="post">
<!-- HiddenHttpMethodFilter要求:必须传输_method请求参数,并且值为最终的请求方式 -->
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
</form> |
⑵删除超链接绑定点击事件
<a @click="deleteEmployee()" th:href="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}">delete</a> |
⑶
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/static/js/vue.js}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vue = new Vue({
el:"#app",
methods:{
deleteEmployee(){
//获取form表单
var form = document.getElementsByTagName("form")[0];
//将超链接的href属性赋值给form表单的action属性
//event.target表示当前触发事件的标签
form.action =event.target.href;
//表单提交
form.submit();
//阻止超链接的默认行为
event.preventDefault();
}
}
}); |