Misc
1. 被加密的生产流量
![]()
涉及到modbus协议
modbus && frame.len == 66过滤之后,每条流量最后两个字节是base32的密文
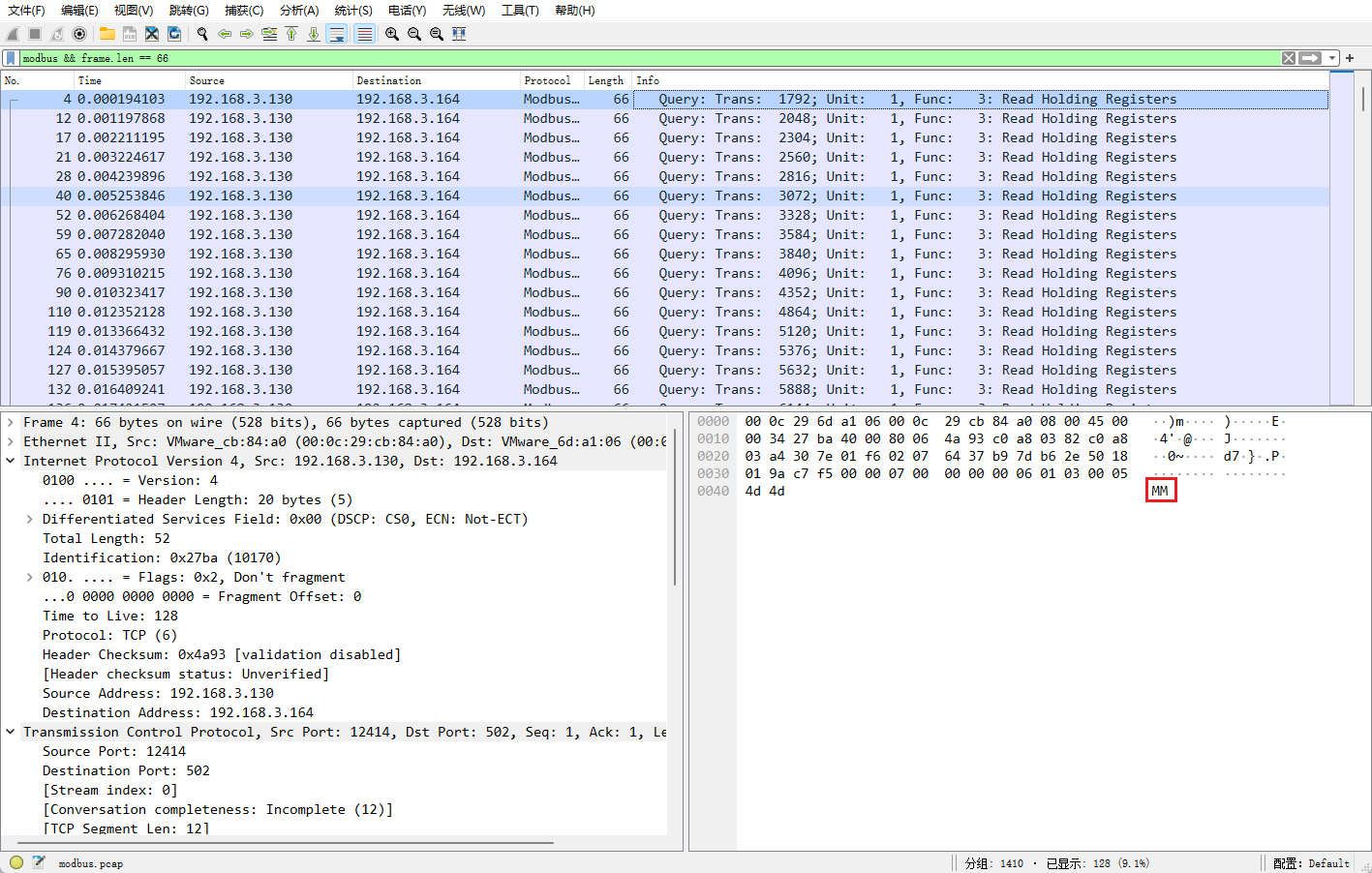
脚本一键提取
#modbus_exp
import pyshark
flag = ''
tmp = 0
cap = pyshark.FileCapture(input_file="D:/下载/CTF附件/ciscn2023/modbus.pcap",tshark_path='D:/Wireshark/',display_filter='modbus && frame.len == 66')
def hex2str(id:str) -> str:
return str(bytes.fromhex(id)).replace("b","").replace("\'","")
for p in cap:
try:
if len(p.modbus.word_cnt) == 5:
tmp = p.modbus.word_cnt
tmp = str(hex(int(p.modbus.word_cnt))).replace("0x","")
flag = flag + tmp
except:
pass
flag = hex2str(flag)
print(flag)
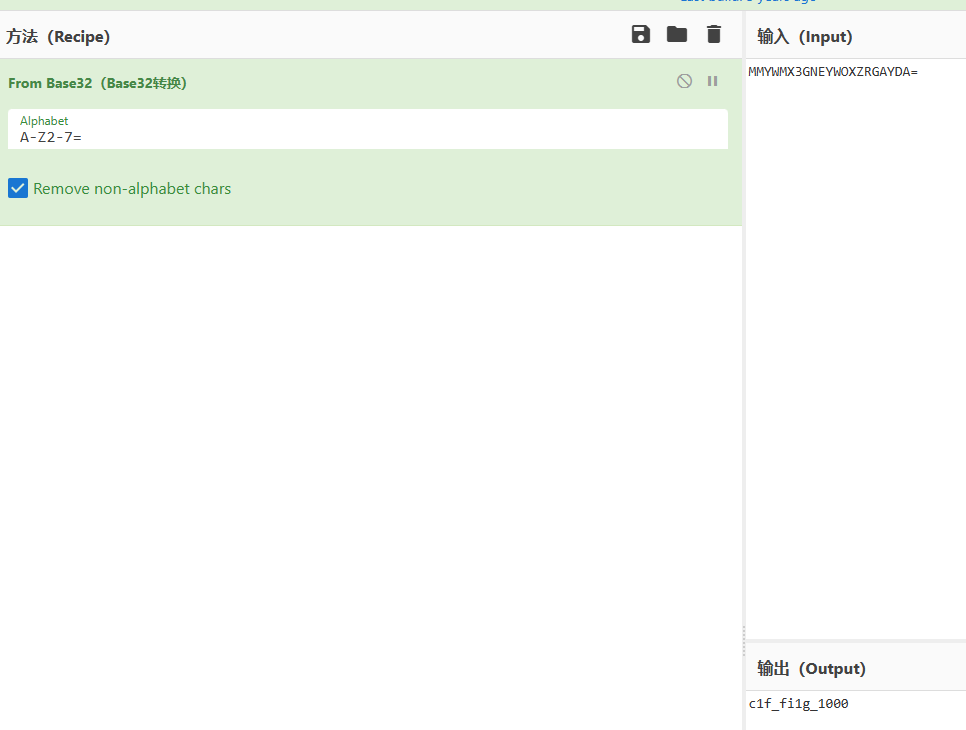
#MMYWMX3GNEYWOXZRGAYDA=结果是base32加密的内容
Crypto
1. Sign_in_passwd
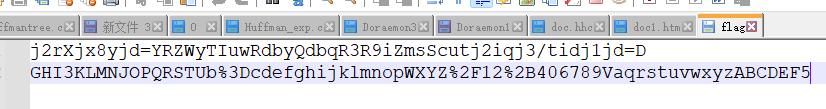
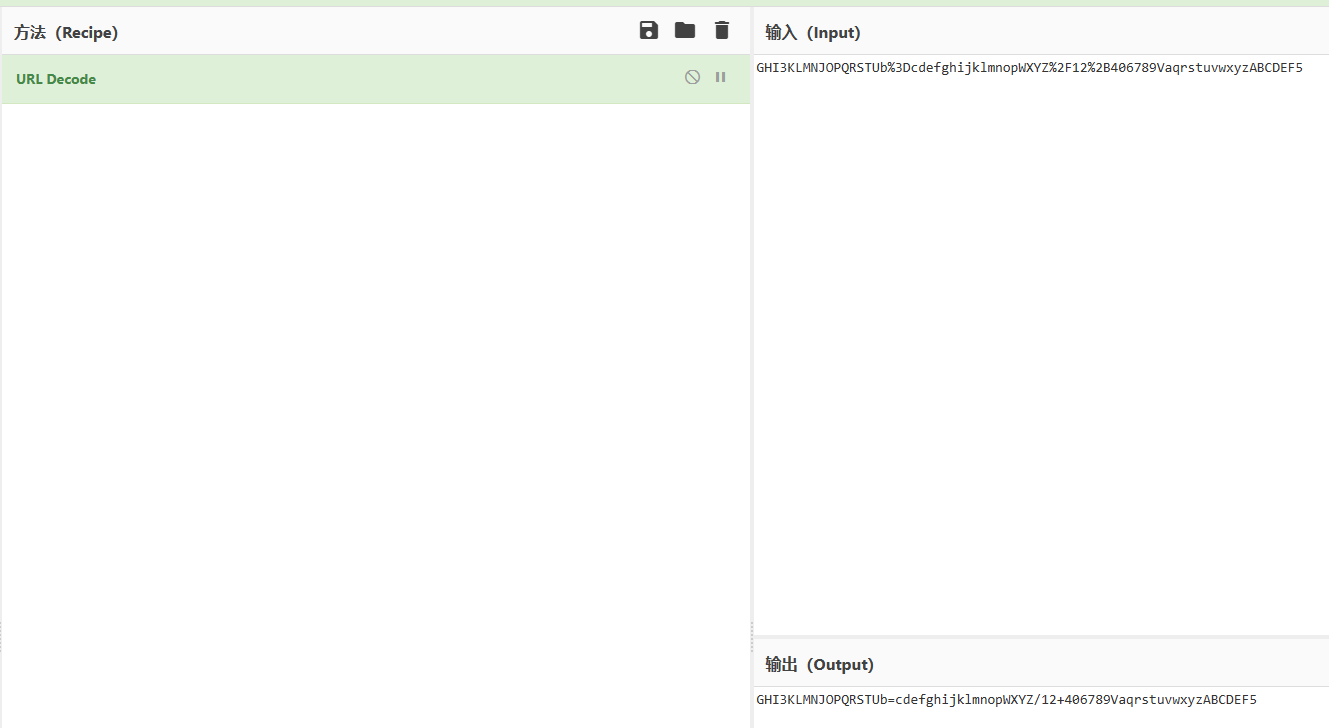
类似base64换表,第二行是URL编码

Re
1. babyRE
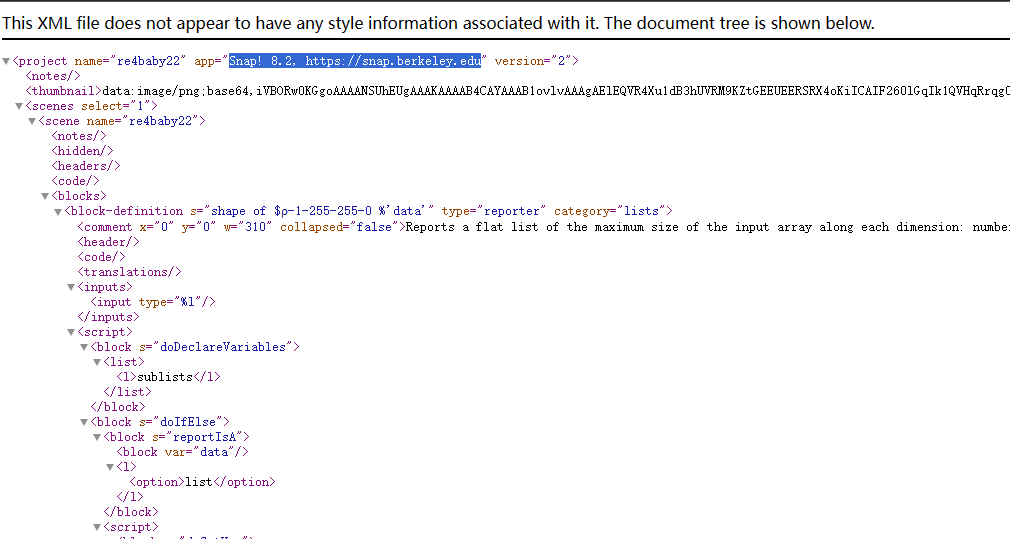
浏览器里可以打开这个xml文件,里面提到一个网站
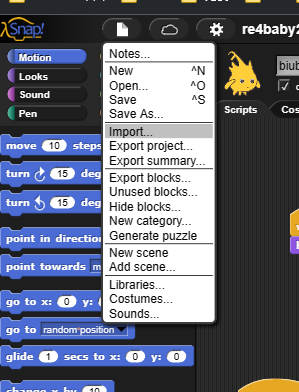
是个类似scratch的编程网站
把xml导进去
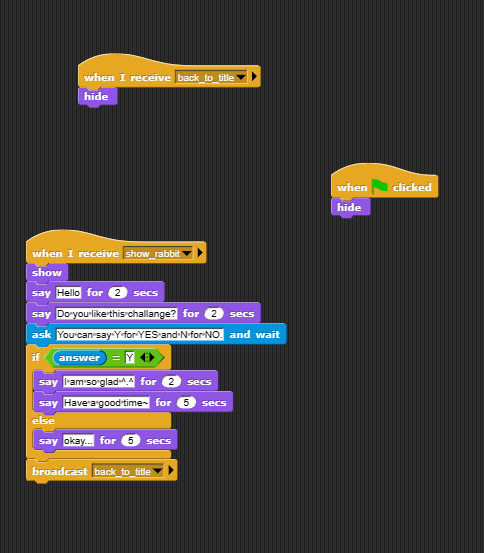
lock里面有主要的函数
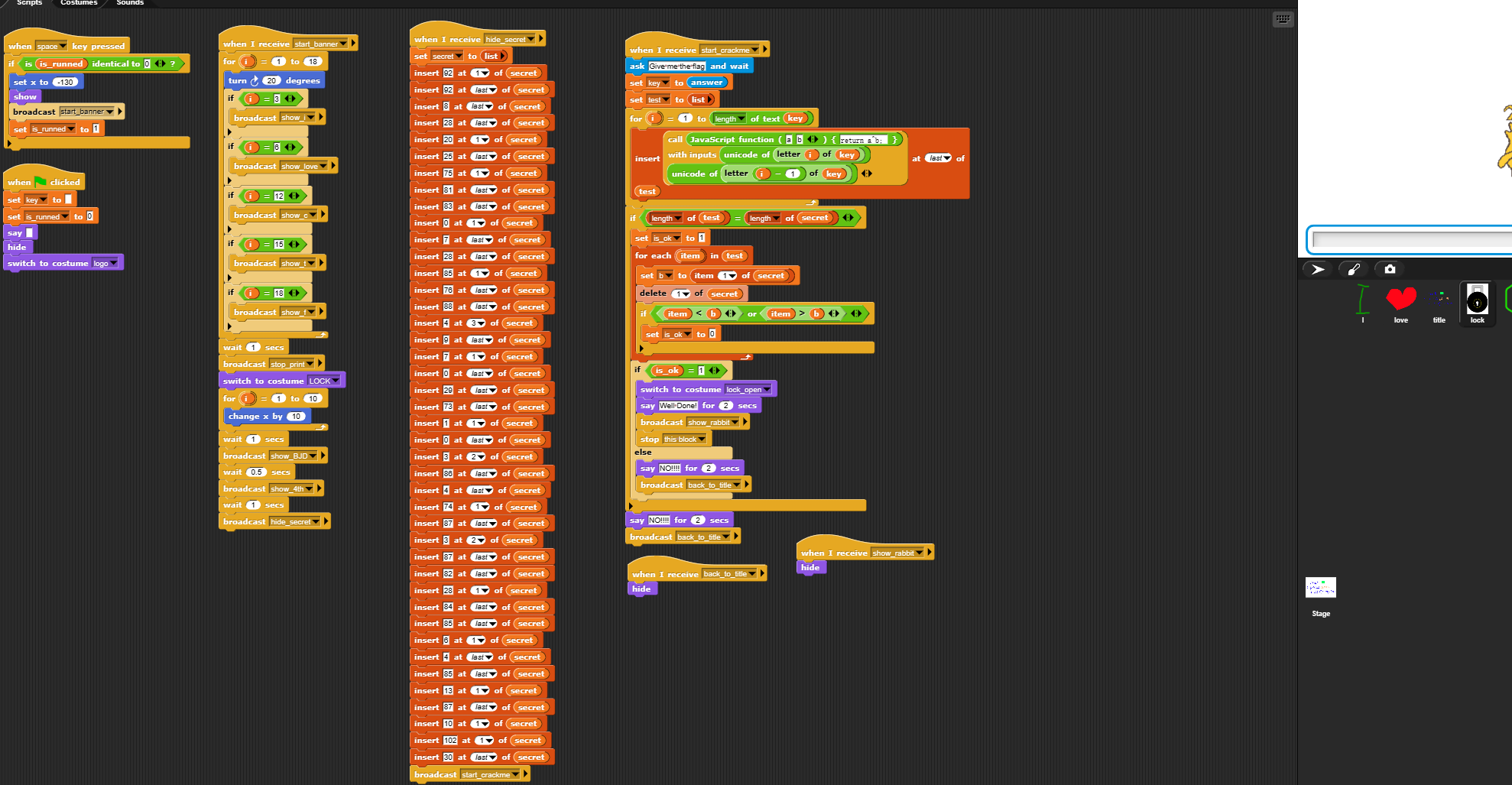
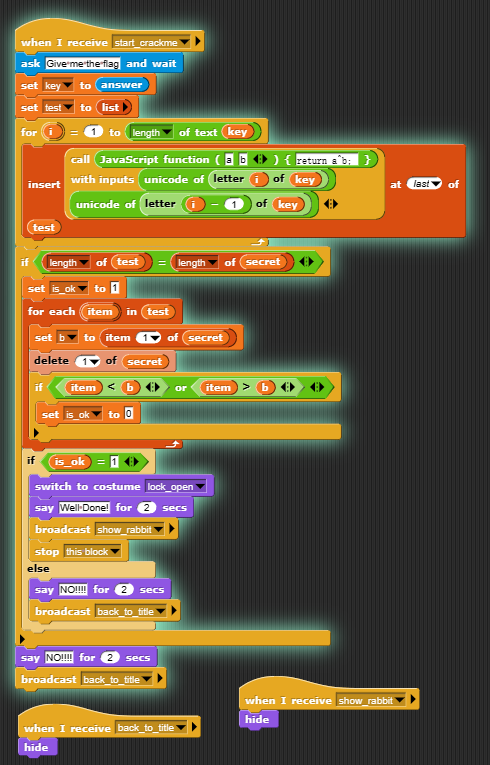
看一下主逻辑
把flag每一位和前一位异或,和密文对比
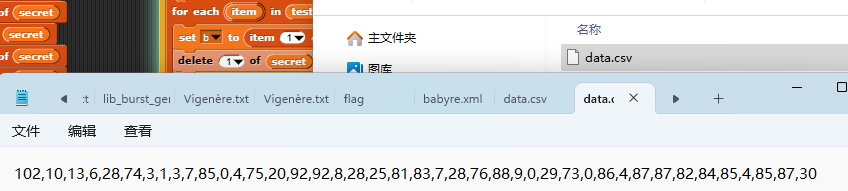
把密文导出来
复制一份
导出
#babyre wp
secret = [102,10,13,6,28,74,3,1,3,7,85,0,4,75,20,92,92,8,28,25,81,83,7,28,76,88,9,0,29,73,0,86,4,87,87,82,84,85,4,85,87,30]
decoded_flag = ['f']
# 假设我们从secret的第五个元素开始解码,并且异或的另一方是0(这只是一个示例)
for i in range(0, len(secret)-1):
secret[i+1] = secret[i] ^ secret[i+1]
decoded_flag.append(chr(secret[i+1]))
print(''.join(decoded_flag)) # 将列表转换为字符串并打印
#flag{12307bbf-9e91-4e61-a900-dd26a6d0ea4c}2. ez_byte
没符号表,找一下字符串
找到疑似主函数,但是也看不懂
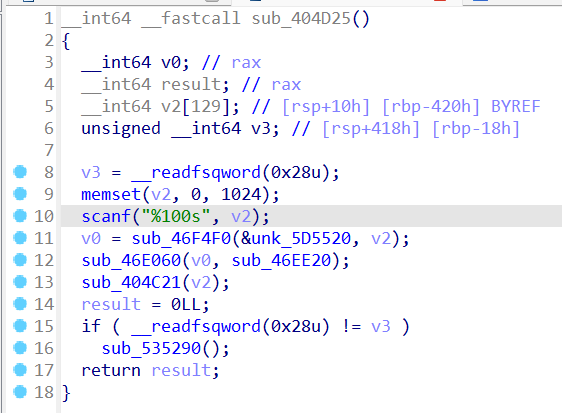
下面有个yes

引用在前面,但是伪代码没看到
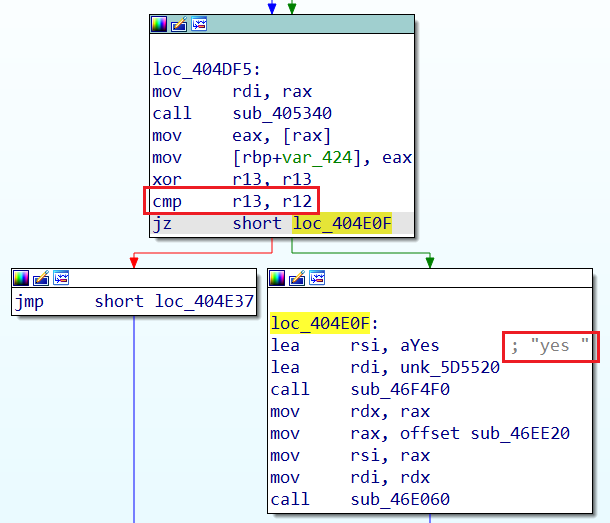
但这里的逻辑应该是正确跳到右边
调试一下发现这里断不下来,直接运行后面的scanf结束了
可以看到cmp上面r13和自己异或,也就是说结果为0
所以r12也要=0才可以跳转到yes
不过涉及r12计算的代码完全找不到,应该是被隐藏了
主函数里还有个函数

可以看到部分的flag验证
不知道怎么看出来的,这里使用了DWARF Expression将代码隐藏在栈展开过程中,在异常处理中恢复隐藏代码
通过以下指令获得隐藏的字节码
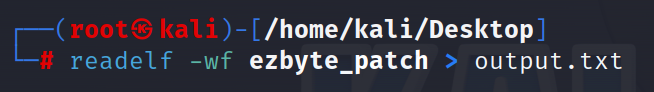
搜索一下r12,可以找到类似虚拟机保护的字节码
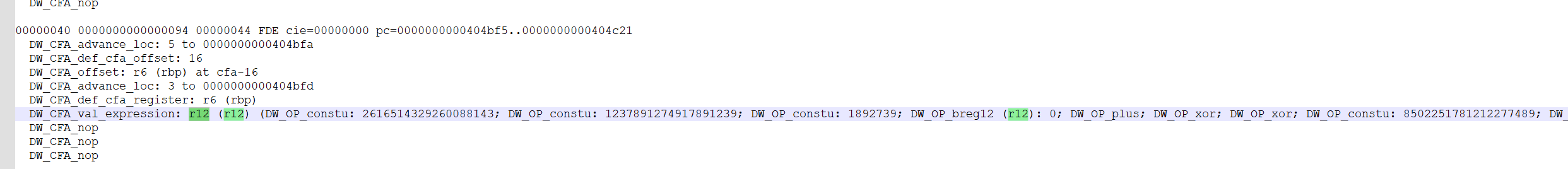

DW_OP_constu: 2616514329260088143;
DW_OP_constu: 1237891274917891239;
DW_OP_constu: 1892739;
DW_OP_breg12 (r12): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_constu: 8502251781212277489;
DW_OP_constu: 1209847170981118947;
DW_OP_constu: 8971237;
DW_OP_breg13 (r13): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_or;
DW_OP_constu: 2451795628338718684;
DW_OP_constu: 1098791727398412397;
DW_OP_constu: 1512312;
DW_OP_breg14 (r14): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_or;
DW_OP_constu: 8722213363631027234;
DW_OP_constu: 1890878197237214971;
DW_OP_constu: 9123704;
DW_OP_breg15 (r15): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_or然后有两种分析方法,一种就是根据DWARF的语法手撕字节码,另一种就是借助rust编写的解释器(来自https://richar.top/nothingchu-ti-si-lu-ji-wp/)转化为.o文件,用IDA反编译
法一:手撕

https://dwarfstd.org/doc/DWARF5.pdf
可通过官方文档细看,就是一种虚拟机对应各种指令

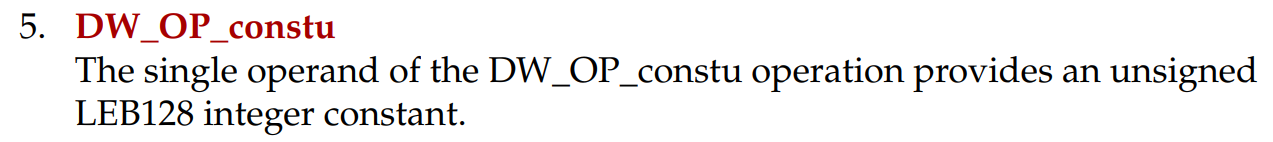

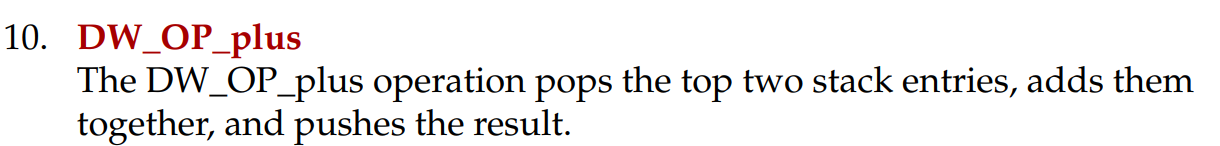
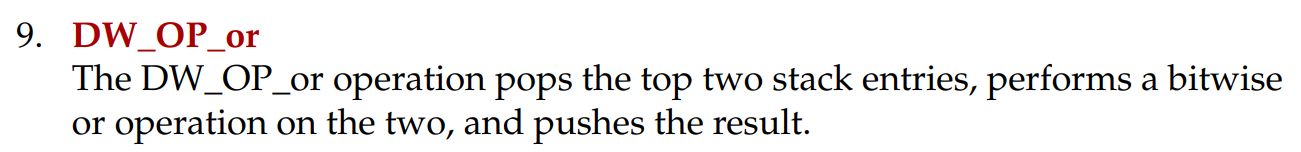

DW_OP_constu: 2616514329260088143; 将一个无符号整数压入堆栈
DW_OP_constu: 1237891274917891239;
DW_OP_constu: 1892739;
DW_OP_breg12 (r12): 0; r12寄存器中读取一个值,并将其加上偏移量 0
DW_OP_plus; 从堆栈中弹出两个值,相加后再将结果压入堆栈
DW_OP_xor; 堆栈中弹出两个值,进行异或运算后再将结果压入堆栈
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_constu: 8502251781212277489;
DW_OP_constu: 1209847170981118947;
DW_OP_constu: 8971237;
DW_OP_breg13 (r13): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_or;
DW_OP_constu: 2451795628338718684;
DW_OP_constu: 1098791727398412397;
DW_OP_constu: 1512312;
DW_OP_breg14 (r14): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_or;
DW_OP_constu: 8722213363631027234;
DW_OP_constu: 1890878197237214971;
DW_OP_constu: 9123704;
DW_OP_breg15 (r15): 0;
DW_OP_plus;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_xor;
DW_OP_or四个式子由or连接,结果需要=0,所以每个部分结果都为0
#ez_byte wp
r15 = (8722213363631027234 ^ 1890878197237214971) - 9123704
r14 = (2451795628338718684 ^ 1098791727398412397) - 1512312
r13 = (8502251781212277489 ^ 1209847170981118947) - 8971237
r12 = (2616514329260088143 ^ 1237891274917891239) - 1892739
def swap_endian(r):
r_str = hex(r12)[2::]
for i in range(len(r_str)-2, -1, -2):
print(r_str[i:i+2], end='')
swap_endian(r12)
swap_endian(r13)
swap_endian(r14)
swap_endian(r15)
print()
import binascii
hexstring = "65363039656662352d653730652d346539342d616336392d6163333164393663"
print("flag{" + binascii.unhexlify(hexstring).decode(encoding="utf-8") + "3861}")
#flag{e609efb5-e70e-4e94-ac69-ac31d96c3861}法二:反编译
https://juejin.cn/post/7238153003281154085
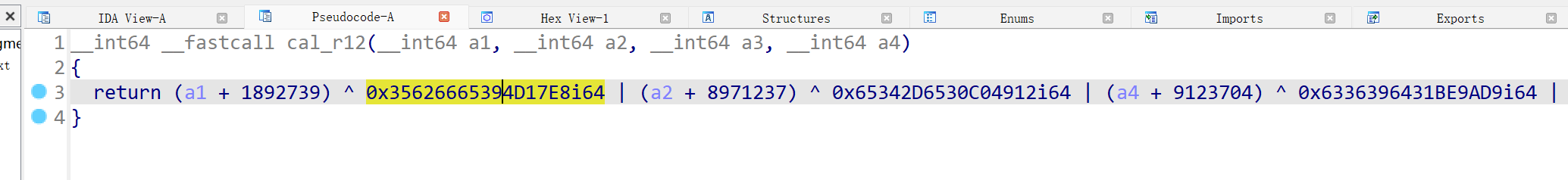
可以直接看见伪代码方程,可以z3爆,或者跟上面一样算,脚本都差不多
3. moveAside
movfuscator混淆,Demovfuscator是相关的去混淆工具,但是没啥用
GitHub - leetonidas/demovfuscator: A work-in-progress deobfuscator for movfuscated binaries
Demovfuscator的环境搭建 - 简书
装完了要修一下cpp和hpp的文件,里面少了个#include<stdint.h>头引用
然后编译就能跑了
但是没卵用,除了补充了一点控制流,其他啥也看不出来
ghindra也看不出来什么东西
跑起来似乎是利用sigaction注册两个异常处理循环判断
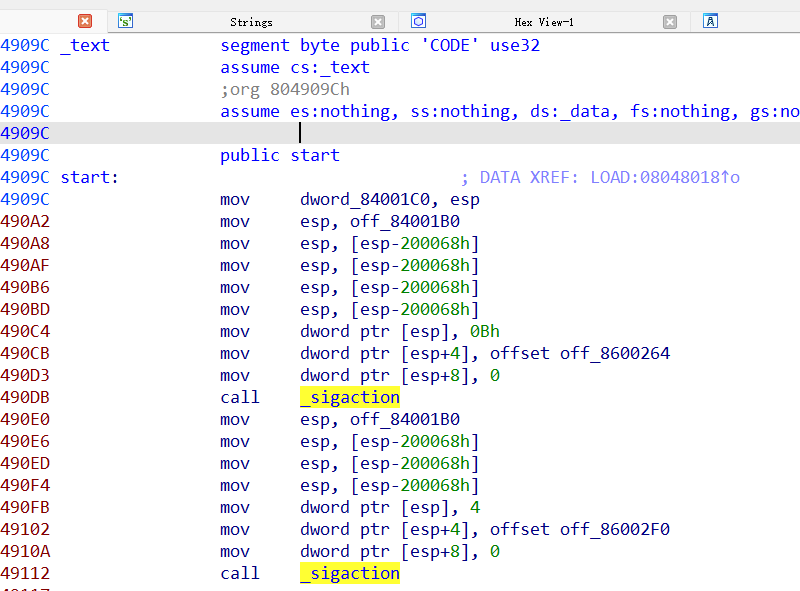
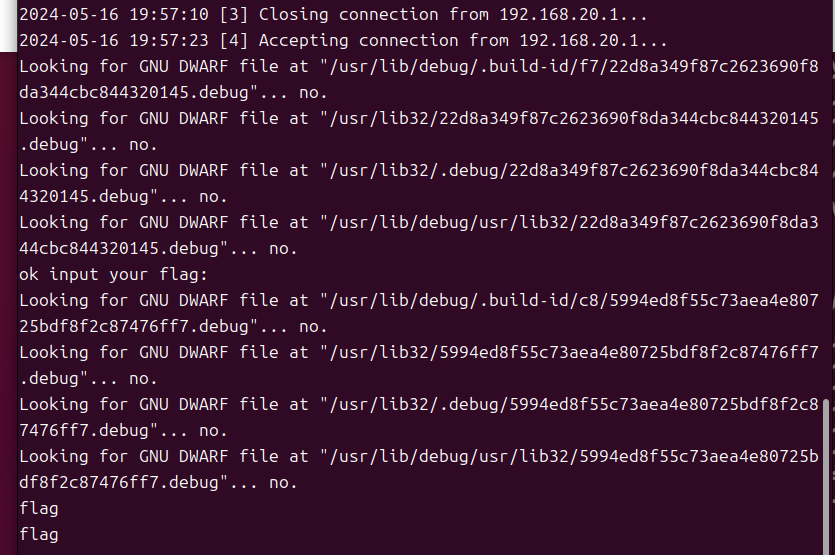
输入错误的flag就会返回相同的内容,然后卡在一个循环里等待输入,再次输错就退出了
strcmp也断不下来
法一:LD_PRELOAD hook
https://www.cnblogs.com/Carykd/p/17446160.html
参考的这一篇wp的方法,hook脚本很复杂,我也不太懂
先写这个.c文件
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dlfcn.h> // 用于LINUX动态链接库操作的头文件
#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x),0)
// #define likely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1)
// 使用likely(),执行 if 后面的语句的机会更大,使用 unlikely(),执行 else 后面的语句的机会更大。
// dlsym: 从一个动态链接库或者可执行文件中获取到符号地址。
// RTLD_NEXT: 找到该符号下一次出现的地方(也就是说可以劫持原本的函数,执行我们定义的函数)
// 实现:如果g_sys_##name,即系统本身的这个函数(在这里指strcmp)返回为0(即字符串相等)时,把系统的函数
#define TRY_LOAD_HOOK_FUNC(name) if(unlikely(!g_sys_##name)){ \
g_sys_##name=(sys_##name##_t)dlsym(RTLD_NEXT,#name); \
}
#define overwrite(name,return_type,...) \
typedef return_type (*sys_##name##_t)(__VA_ARGS__); \
static sys_##name##_t g_sys_##name = NULL; \
extern return_type name(__VA_ARGS__)
#define __log(format,...) fprintf(stderr,"\33[35m\033[1m[@]"format"\33[0m",##__VA_ARGS__)
overwrite(strcmp, int, char* a, char* b){
TRY_LOAD_HOOK_FUNC(strcmp);
printf("strcmp\n");
fflush(stdout);
return g_sys_strcmp(a,b);
}
// gcc -fPIC -shared -o strcmp_hook.so ./strcmp_hook.c -ldl -O3 -m32
/**
* 反编译代码如下
* 1. 首先检查是否已经初始化g_sys_strcmp,这是一个全局变量,用于保存真实函数指针,第一次调用hook时没有初始化
* 2. 未初始化,则初始化为真实函数地址;已初始化,则跳过这一步骤
* 3. 放出字符串
* 4. 清理输出缓冲区
* 5. 调用真正的strcmp
*
*/
// int __cdecl strcmp(int a1, int a2)
// {
// if ( !g_sys_strcmp )
// g_sys_strcmp = (int)dlsym((void *)4294967295, "strcmp");
// puts("strcmp");
// fflush(stdout);
// return ((int (__cdecl *)(int, int))g_sys_strcmp)(a1, a2);
// }
然后gcc -fPIC -shared -o strcmp_hook.so ./strcmp_hook.c -ldl -O3 -m32编译成so文件
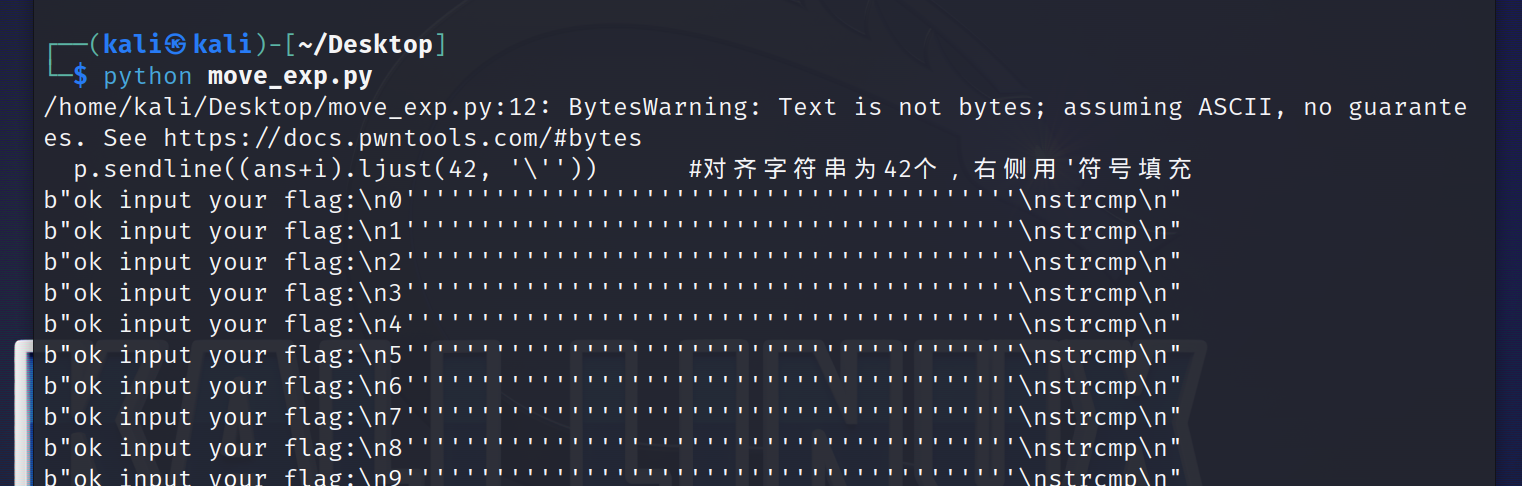
跑下面的脚本
#move_exp
from pwn import *
import string
context.log_level='error'
ans=''
# 操作内容
print(ans, end='')
for _ in range(42):
for i in string.printable: #只打印可见字符
p=process('/home/kali/Desktop/moveAside', env={"LD_PRELOAD":"/home/kali/Desktop/strcmp_hook.so"})
#LD_PRELOAD表示优先加载我们的so,从而让系统的so后加载,这样才能让strcmp调用时先找到hook函数
p.sendline((ans+i).ljust(42, '\'')) #对齐字符串为42个,右侧用'符号填充
recv=p.recvall(timeout=0.1)
print(recv)
if len(recv.splitlines())==len(ans)+4: #将返回的字符串分开,首先有一个提示输入,然后输入回显,然后是第一次strcmp字符串;如果正确则会打印第二次strcmp字符串。
print(i, end='') #打印出来给我们看
ans+=i
break
p.close()
# flag{781dda4e-d910-4f06-8f5b-5c3755182337}
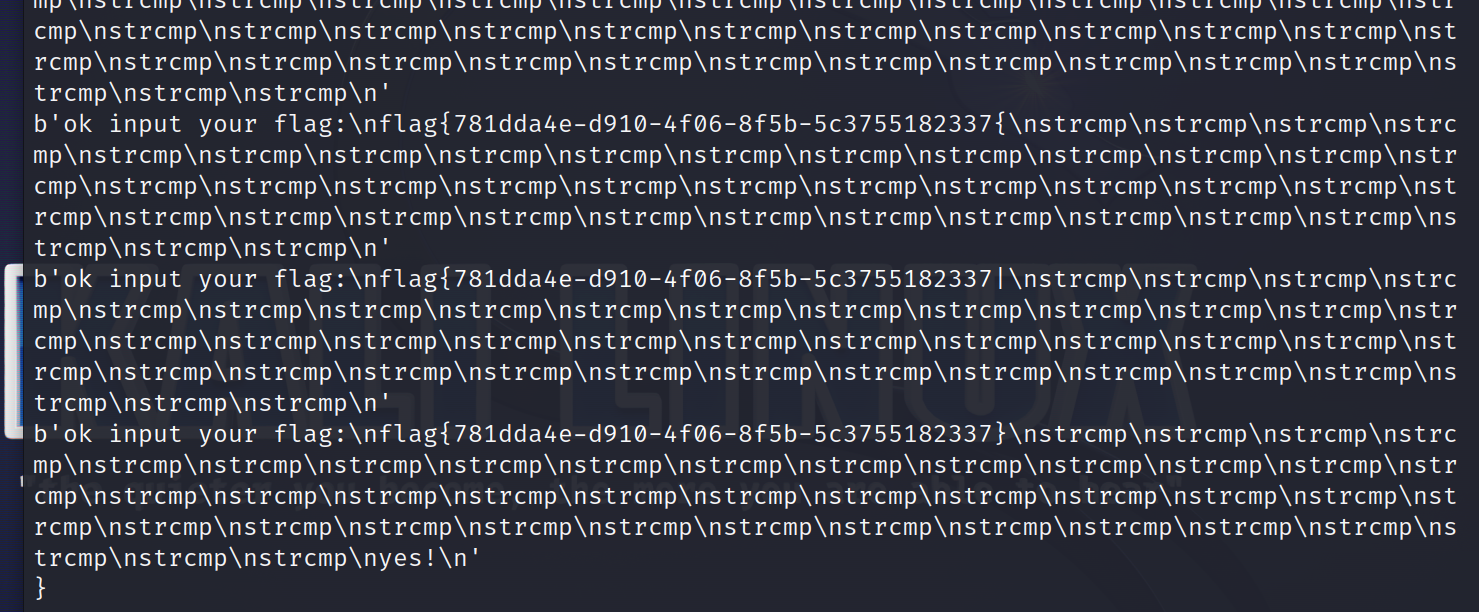
这篇博客讲的不够清晰,我根据以下视频再复现一个简洁一些的版本(这个讲的巨好)
External Player - 哔哩哔哩嵌入式外链播放器
具体原理:
LD_PRELOAD - CTF Wiki
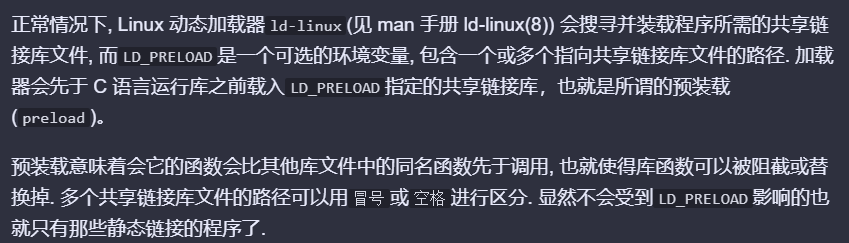
首先动调可以发现它是单字节加密,strcmp进行比对,可以单字节爆破的
先试着看能不能触发strcmp
#include<stdio.h>
int strcmp(const char*s1, const char*s2)
{
printf("strcmp clled!");
while(*s1 && (*s1 == *s2))
{
++s1;
++s2;
}
return *s1 - *s2;
}gcc -m32 -shared -O2 mystrcmp.c -o mystrcmp.so编译得到so文件
LD_PRELOAD=./mystrcmp.so ./moveAside运行一下
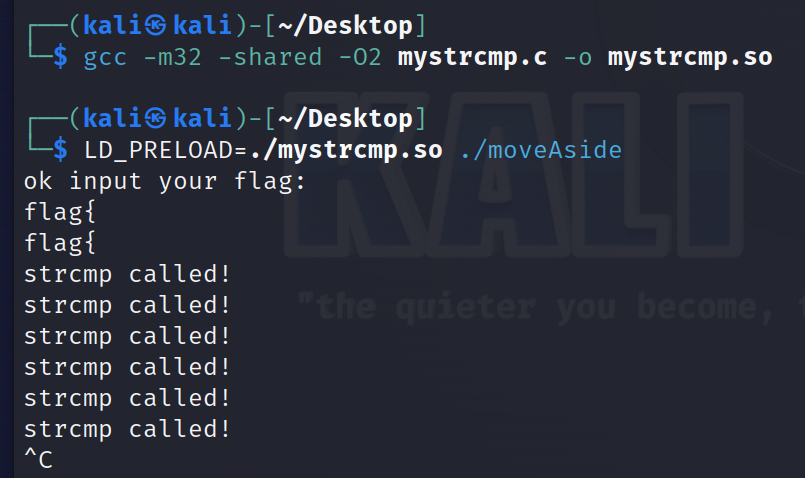
触发成功了
然后就是确定一下flag长度
#include<stdio.h>
int strcmp(const char*s1, const char*s2)
{
static int counter = 1;
printf("%02d strcmp called!\n", counter++);
while(*s1 && (*s1 == *s2))
{
++s1;
++s2;
}
return 0;
}
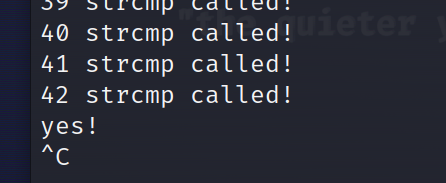
看到是42位
然后就可以写爆破脚本
from pwn import *
import string
context.log_level = 'error'
#设置pwntools的日志级别为'error',这意味着只有错误级别的消息才会被记录。这有助于减少输出中的噪声。
ans = ''
for i in range(42):
for ch in string.printable:
current_flag = ans + ch
print(current_flag)
p = process('./moveAside', env={'LD_PRELOAD':'./mystrcmp.so'})
p.recvline() #接收并忽略程序的第一行输出i
p.sendline(current_flag.encode()) #发送当前猜测的字符串到程序
recv = p.recvall(timeout=0.01) #尝试接收程序的输出,并设置一个非常短的超时(0.01秒),为了检测程序是否在接收到正确的输入后更快地响应
recvs = recv.splitlines() #将接收到的程序输出(recv)按照换行符(\n)进行分割
#print(recvs)
if len(recvs) > len(ans) + 2:
ans += ch
break
#如果接收到的行数比之前的猜测(加上两个额外的行,可能是提示和换行符)多,则认为该字符是输入字符串的一部分,将其添加到答案字符串中,并跳出内层循环以继续下一个字符的猜测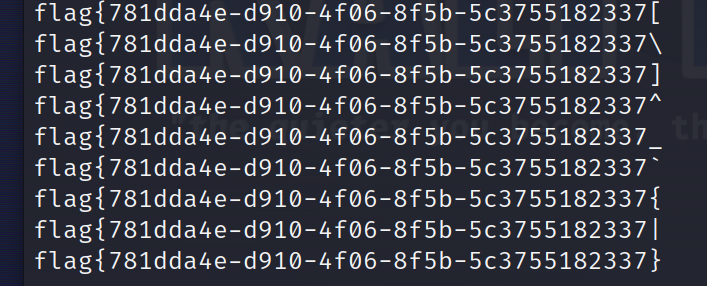
爆的真爽
法二:PinTools爆破
8.3 第八章_知识点3_程序插桩及Pintool_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
实验_第八章_PinTool用法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
工具原理和使用在这两个视频讲的很清楚了

找到准备插桩的函数地址
写一个cpp文件用于编译动态链接库
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "pin.H"
using std::cerr;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
static UINT64 icount = 0;
VOID docount(VOID* addr) {
if (( int )addr == 0x8049010) //每当strcmp被触发,就增加计数
{
icount++;
}
}
VOID Instruction(INS ins, VOID* v) //Pin工具每遇到一个新指令就会调用该函数
{
//每个指令前插入一个函数docount的调用
INS_InsertCall(ins, IPOINT_BEFORE, (AFUNPTR)docount, IARG_INST_PTR, IARG_END);
}
//指定输出文件
KNOB< string > KnobOutputFile(KNOB_MODE_WRITEONCE, "pintool", "o", "inscount.out", "specify output file name");
VOID Fini(INT32 code, VOID* v) //应用退出时调用此函数
{
std::cout << "Count " << icount << endl; //输出count值
}
INT32 Usage()
{
cerr << "This tool counts the number of dynamic instructions executed" << endl;
cerr << endl << KNOB_BASE::StringKnobSummary() << endl;
return -1;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (PIN_Init(argc, argv)) return Usage(); //调用PIN_Init初始化
INS_AddInstrumentFunction(Instruction, 0);
//注册一个名为Instruction的回调函数,该函数在每条指令执行前调用
PIN_AddFiniFunction(Fini, 0);
//应用退出时,注册函数Fini处理
PIN_StartProgram();
//启动程序
return 0;
}编译得到so文件
然后写个脚本进行爆破利用
#move_pin
import subprocess
import time
import copy
import os
STR_LEN = 30
start_time = time.time()
out_file_path = r"/home/kali/Desktop/pin_output.txt"
exe_path = r"/home/kali/Desktop/moveAside"
dll_path = r"/home/kali/Downloads/pin-3.30-98830-g1d7b601b3-gcc-linux/source/tools/MyPinTool/obj-ia32/exp.so"
record_ins_nums = {} # 指令计数器
except_str = "flag{"
except_inss = 0
find_str = ""
s_map = "0123456789qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm{}-"
# s_map = "0123456789"
def sub_intreaction(input_msg):
global start_time
sh = subprocess.Popen(['/home/kali/Downloads/pin-3.30-98830-g1d7b601b3-gcc-linux/pin','-t',dll_path,'-o',out_file_path,'--',exe_path],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
sh.stdin.write(str.encode(input_msg.ljust(42,"0"))) # 必须补齐,不然后面的sh.stdout 会出错 # 即将缓冲区中的数据立刻写入文件,同时清空缓冲区,不需要是被动的等待输出缓冲区写入
sh.stdin.flush()
sh.stdout.flush()
sh.stdin.write(str.encode(input_msg.ljust(42,"0")))
sh.stdin.flush()
sh.stdout.flush()
sh.stdin.write(str.encode(input_msg.ljust(42,"0")))
sh.stdin.flush()
sh.stdout.flush()
get_input = sh.stdout.readlines()
# print(get_input)
lenn = int(get_input[2][6:])
if record_ins_nums and lenn > max(record_ins_nums.values()):
record_ins_nums[input_msg] = lenn
sh.kill()
print(input_msg," : ",get_input)
return 1
record_ins_nums[input_msg] = lenn
sh.kill()
print(input_msg," : ",get_input)
if b"success" in get_input[1]:
print("Oh,my sir, you may got the flag:")
print(input_msg)
print(time.time() - start_time)
exit()
return 0
def intreaction():
for i in range(len(s_map)):
if sub_intreaction(except_str + s_map[i]) == 1:
return
def pintools():
global except_str,v,record_ins_nums,except_inss
intreaction()
for k,v in record_ins_nums.items():
if v >= except_inss: # 出错原因,之前用的 '>' 号,发现input_msg 填充的数据 0 也是input的数据,导致 0123456789 和 01234567890 指令数一样,从而导致无线循环
except_str = copy.deepcopy(k)
except_inss = v
print(except_str," ",except_inss)
record_ins_nums = {}
pintools()
if __name__ == '__main__':
pintools()
不知道是不是我的问题,这个爆破非常慢(比hook慢多了),不太推荐
脚本参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/lordtianqiyi/articles/17438974.html