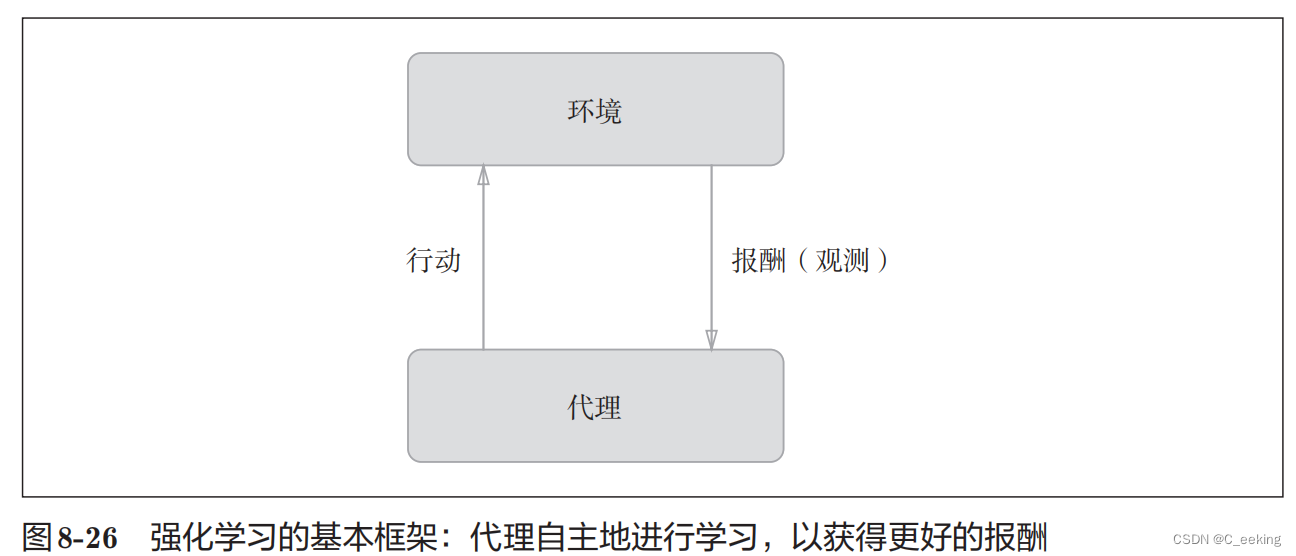
线程同步:
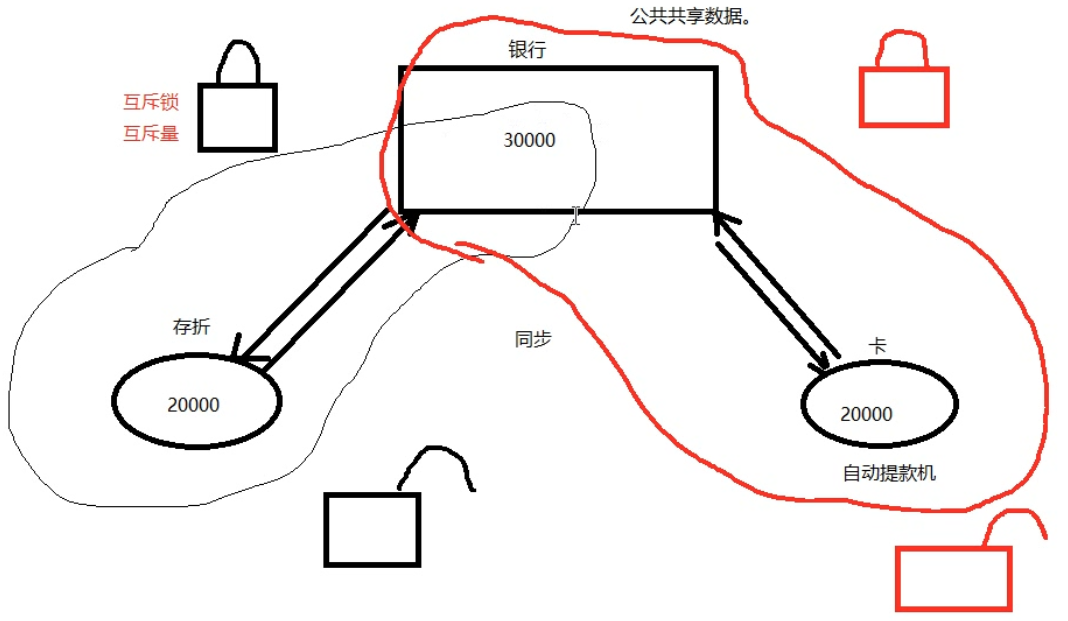
协同步调,对公共区域数据按序访问。防止数据混乱,产生与时间有关的错误。
数据混乱的原因

一、互斥锁/互斥量mutex
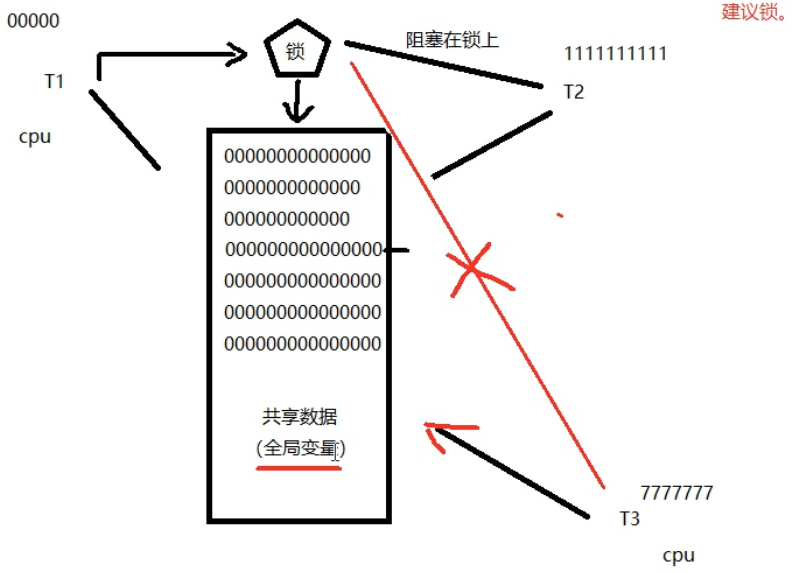
1. 建议锁(协同锁):
公共数据进行保护。所有线程【应该】在访问公共数据前先拿锁再访问。但,锁本身不具备强制性。
2. 互斥锁的使用步骤:
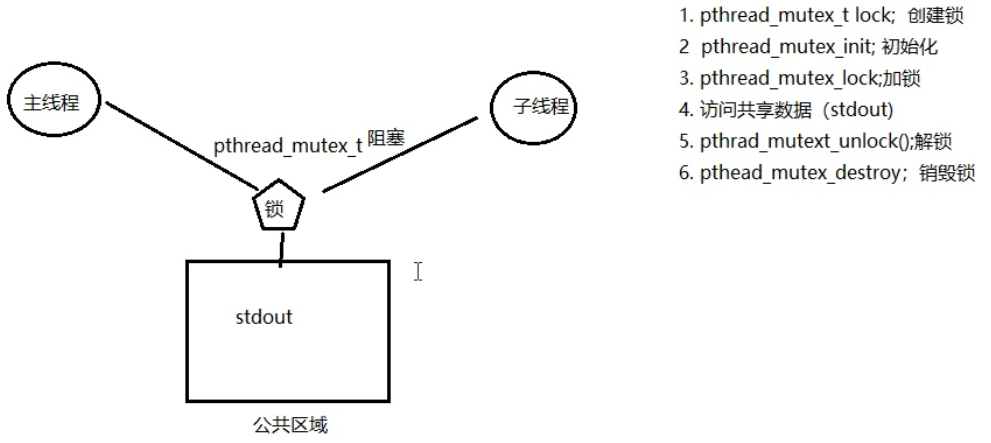
初始化互斥量:
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
1. pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 动态初始化。
2. pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; 静态初始化。
restrict关键字:
用来限定指针变量。被该关键字限定的指针变量所指向的内存操作,只能由本指针完成。
3. 使用锁的注意事项:
尽量保证锁的粒度, 越小越好。(访问共享数据前,加锁。访问结束【立即】解锁。)
互斥锁,本质是结构体。 可以看成整数。 初始化时值为 1。(pthread_mutex_init() 函数调用成功。)
lock加锁: --操作, 阻塞线程。
unlock解锁: ++操作, 换醒阻塞在锁上的线程。
try锁:尝试加锁,成功--。失败直接返回,同时设置错误号 EBUSY,不阻塞。
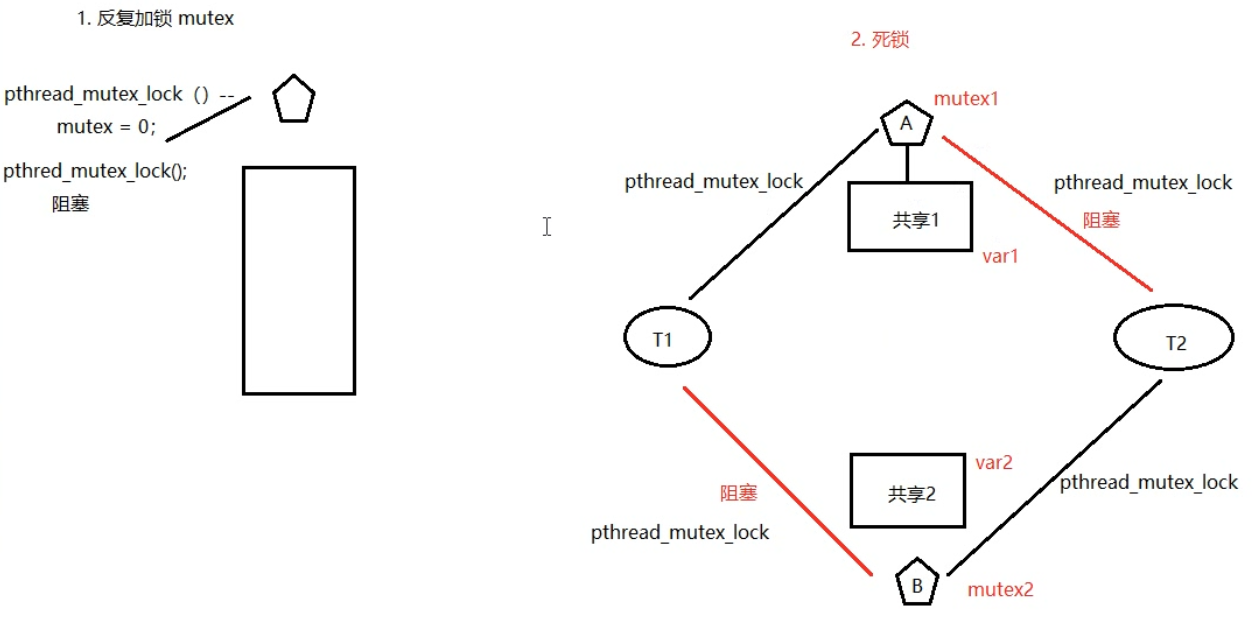
4. 死锁:
是使用锁不恰当导致的现象:
1. 线程视图对同一个互斥量A加锁两次。
2. 线程1拥有A锁,请求获得B锁;线程2拥有B锁,请求获得A锁。
示例:访问共享数据(stdout)
//pthrd_shared.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *tfn(void *arg)
{
srand(time(NULL));
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("hello ");
sleep(rand() % 3); /*模拟长时间操作共享资源,导致cpu易主,产生与时间有关的错误*/
printf("world\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand() % 3);//保证锁的粒度越小越好,(访问结束立即解锁)
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t tid;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, tfn, NULL);
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("HELLO ");
sleep(rand() % 3);
printf("WORLD\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
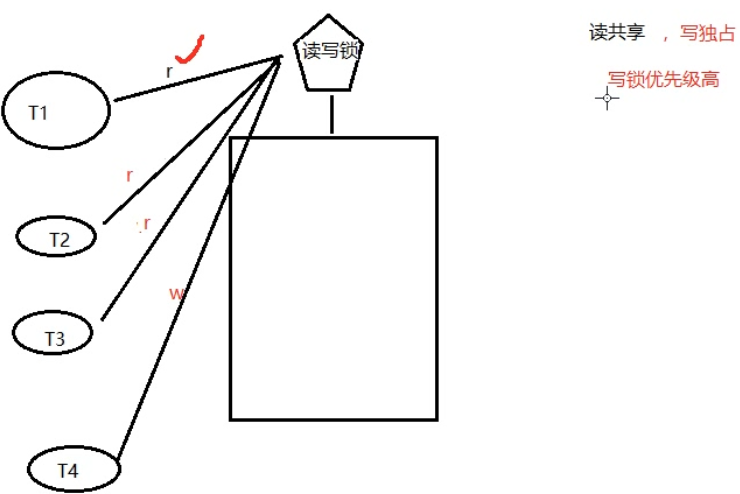
二、读写锁:
-
锁只有一把。以读方式给数据加锁——读锁。以写方式给数据加锁——写锁。
-
读共享,写独占。
-
写锁优先级高。
-
相较于互斥量而言,当读线程多的时候,提高访问效率

pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;类型
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(&rwlock);
pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(&rwlock);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);
示例:3个线程不定时 “写” 全局资源,5个线程不定时 “读” 同一全局资源
//rwlock.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int counter; //全局资源
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
void *th_write(void *arg)
{
int t;
int i = (int)arg;
while (1) {
t = counter; // 保存写之前的值
usleep(1000);
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
printf("=======write %d: %lu: counter=%d ++counter=%d\n", i, pthread_self(), t, ++counter);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
usleep(9000); // 给 r 锁提供机会
}
return NULL;
}
void *th_read(void *arg)
{
int i = (int)arg;
while (1) {
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
printf("----------------------------read %d: %lu: %d\n", i, pthread_self(), counter);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
usleep(2000); // 给写锁提供机会
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
pthread_t tid[8];
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, th_write, (void *)i);
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
pthread_create(&tid[i+3], NULL, th_read, (void *)i);
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock); //释放读写琐
return 0;
}
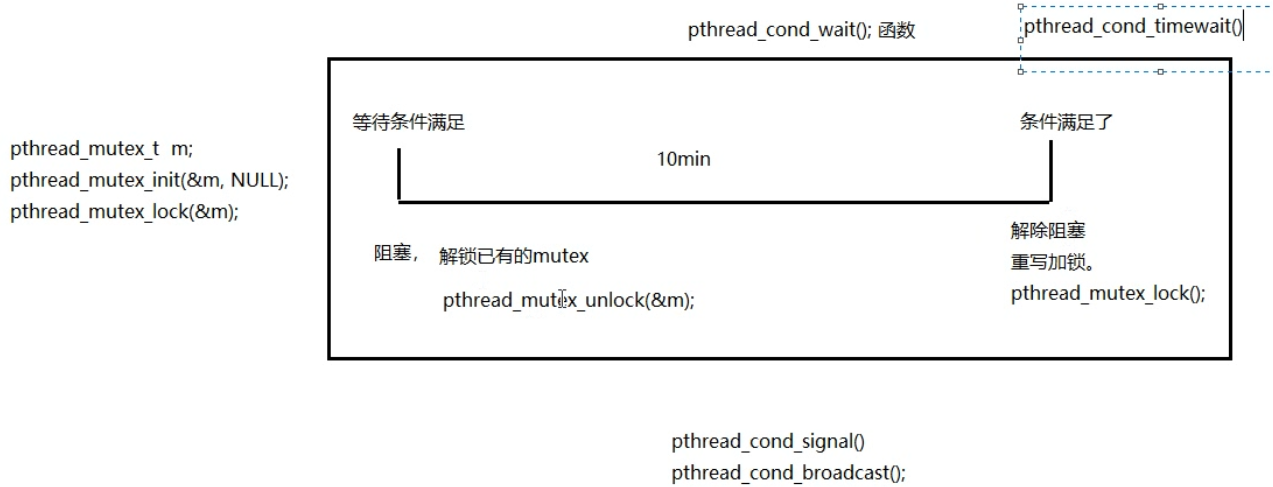
三、条件变量:
本身不是锁! 但是通常结合锁来使用。 mutex
pthread_cond_t cond;//类型
初始化条件变量:
1. pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); 动态初始化。
2. pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; 静态初始化。
阻塞等待条件:
3. pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
作用: 1) 阻塞等待条件变量满足
2) 解锁已经加锁成功的信号量 (相当于 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex))
注:1和2两步为一个原子操作
3) 当条件满足,函数返回时,重新加锁信号量 (相当于, pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);)
4. pthread_cond_timedwait():可设置超时
5. pthread_cond_signal(): 唤醒阻塞在条件变量上的 (至少)一个线程。
6. pthread_cond_broadcast(): 唤醒阻塞在条件变量上的 所有线程。
7. pthread_cond_destroy(&cond):销毁条件变量
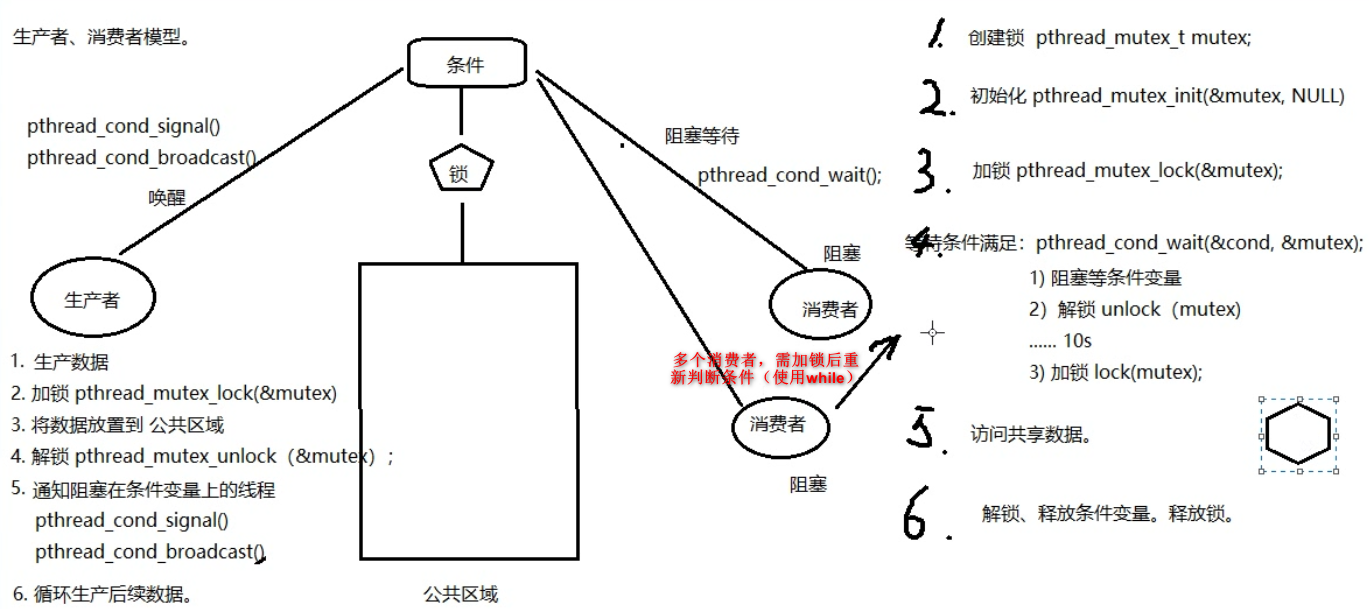
示例:使用条件变量完成生产者、多个消费者模型
//借助条件变量模拟 生产者-消费者问题
//pthread_cond_produce_consumer.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void err_thread(int ret, char *str)
{
if (ret != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%s\n", str, strerror(ret));
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
struct msg {
int num;
struct msg *next;
};
struct msg *head;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; // 定义/初始化一个互斥量
pthread_cond_t has_data = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; // 定义/初始化一个条件变量
void *produser(void *arg)
{
while (1) {
struct msg *mp = malloc(sizeof(struct msg));
mp->num = rand() % 1000 + 1; // 模拟生产一个数据`
printf("--produce %d\n", mp->num);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 加锁 互斥量
mp->next = head; // 写公共区域
head = mp;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 互斥量
pthread_cond_signal(&has_data); // 唤醒阻塞在条件变量 has_data上的线程.
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return NULL;
}
void *consumer(void *arg)
{
while (1) {
struct msg *mp;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 加锁 互斥量
while (head == NULL) { // 注:多个消费者,这里需要使用while,不能使用if
pthread_cond_wait(&has_data, &mutex); // 阻塞等待条件变量, 解锁
} // pthread_cond_wait 返回时, 重新加锁 mutex
mp = head; //读公共区域
head = mp->next;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 互斥量
printf("---------consumer id: %lu :%d\n", pthread_self(), mp->num);
free(mp);
sleep(rand()%3);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
pthread_t pid, cid;
srand(time(NULL));
ret = pthread_create(&pid, NULL, produser, NULL); // 生产者
if (ret != 0)
err_thread(ret, "pthread_create produser error");
ret = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); // 消费者
if (ret != 0)
err_thread(ret, "pthread_create consuer error");
ret = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); // 消费者
if (ret != 0)
err_thread(ret, "pthread_create consuer error");
ret = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); // 消费者
if (ret != 0)
err_thread(ret, "pthread_create consuer error");
pthread_join(pid, NULL);
pthread_join(cid, NULL);
return 0;
}
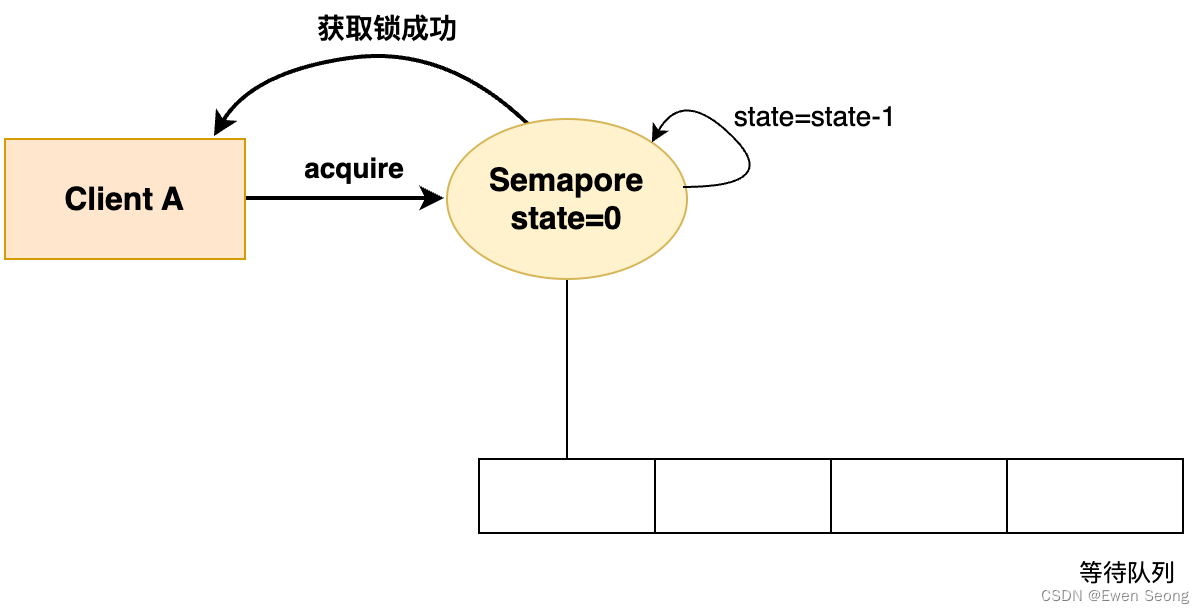
四、信号量:
-
应用于线程、进程间同步(既能保证同步,数据不混乱,又能提高线程并发)。
-
相当于 初始化值为 N 的互斥量。 N值,表示可以同时访问共享数据区的线程数。

sem_t sem; 定义类型。
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
参数:
sem: 信号量
pshared: 0: 用于线程间同步
1: 用于进程间同步
value:N值。(指定同时访问的线程数)
sem_destroy();
sem_wait(); 一次调用,做一次-- 操作, 当信号量的值为 0 时,再次 -- 就会阻塞。 (对比 pthread_mutex_lock)
sem_post(); 一次调用,做一次++ 操作. 当信号量的值为 N 时, 再次 ++ 就会阻塞。(对比 pthread_mutex_unlock)
sem_timewait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec* abs_timeout);
//abs_timeout 采用的是绝对时间。
定时1秒:
time_t cur = time(NULL);获取当前时间(相对时间)
struct timespec t;定义timespec结构体变量t
t.tv_sec = cur + 1;定时1秒
t.tv_nsec = t.tv_sec+100;
sem_timedwait(&sem, &t);传参
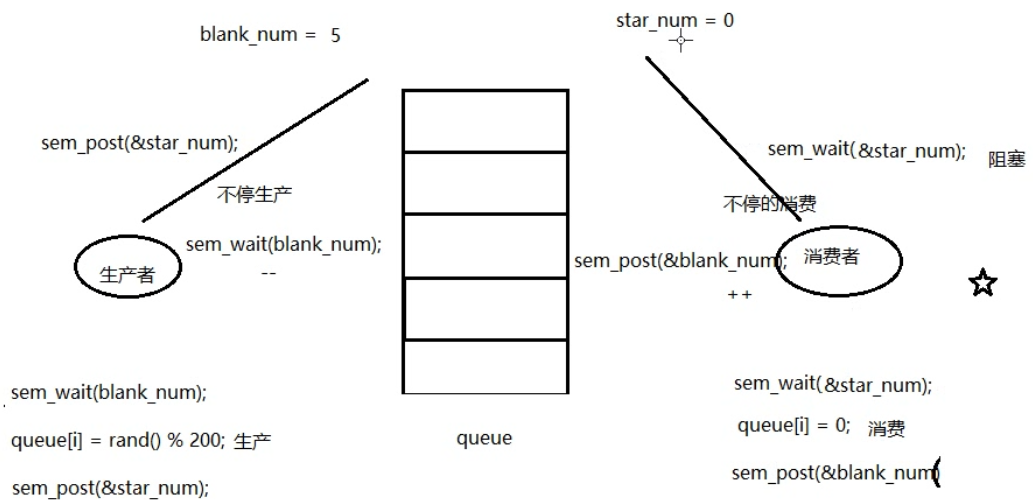
示例:使用信号量实现生产者、消费者模型
//sem_product_consumer.c
/*信号量实现 生产者 消费者问题*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM 5
int queue[NUM]; //全局数组实现环形队列
sem_t blank_number, product_number; //空格子信号量, 产品信号量
void *producer(void *arg)
{
int i = 0;
while (1) {
sem_wait(&blank_number); //生产者将空格子数--,为0则阻塞等待
queue[i] = rand() % 1000 + 1; //生产一个产品
printf("----Produce---%d\n", queue[i]);
sem_post(&product_number); //将产品数++
i = (i+1) % NUM; //借助下标实现环形
sleep(rand()%1);
}
}
void *consumer(void *arg)
{
int i = 0;
while (1) {
sem_wait(&product_number); //消费者将产品数--,为0则阻塞等待
printf("-Consume---%d\n", queue[i]);
queue[i] = 0; //消费一个产品
sem_post(&blank_number); //消费掉以后,将空格子数++
i = (i+1) % NUM;
sleep(rand()%3);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t pid, cid;
sem_init(&blank_number, 0, NUM); //初始化空格子信号量为5, 线程间共享 -- 0
sem_init(&product_number, 0, 0); //产品数为0
pthread_create(&pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join(pid, NULL);
pthread_join(cid, NULL);
sem_destroy(&blank_number);
sem_destroy(&product_number);
return 0;
}