一、论文简述
1. 第一作者:Keyang Luo
2. 发表年份:2020
3. 发表期刊:CVPR
4. 关键词:MVS、代价体、注意力机制、正则化
5. 探索动机:
- However, the feature matching results from different channels are usually not of the same importance since the captured scenes could be significantly different across channels.
- Another major problem faced by learning-based MVS methods is how to effectively aggregate and regularize the matching confidence volume into a latent depth probability volume (LPV), from which the depth/disparity map then can be inferred via some regression or multi-class classification techniques.
- The multi-view ground-truth depth maps introduced in MVSNet for training MVS networks have been widely used, but they still contain quite many wrongly labeled pixels, which could potentially cause some undesired effects on training and validation.
6. 工作目标:结合注意力机制的优势,解决上述问题。
7. 核心思想:
- We design an attention-enhanced matching confidence volume, which takes account of both perceptual information and contextual information of the local scene to improve the matching robustness.
- We propose a novel attention-guided regularization module for hierarchically aggregating and regularizing the matching confidence volume in the topdown/bottom-up manner.
- We develop a simple but effective filtering strategy to improve the quality of multi-view ground-truth depth maps for network training.
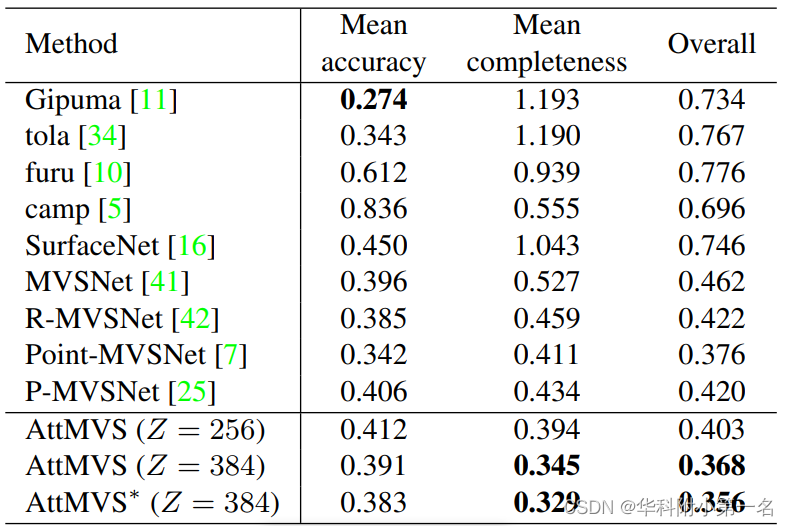
8. 实验结果:
Our method achieves the best overall performance on the DTU benchmark and the intermediate sequences of Tanks & Temples benchmark over many state-of-theart MVS approaches.
9.论文下载:
https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/papers/Luo_Attention-Aware_Multi-View_Stereo_CVPR_2020_paper.pdf
二、实现过程
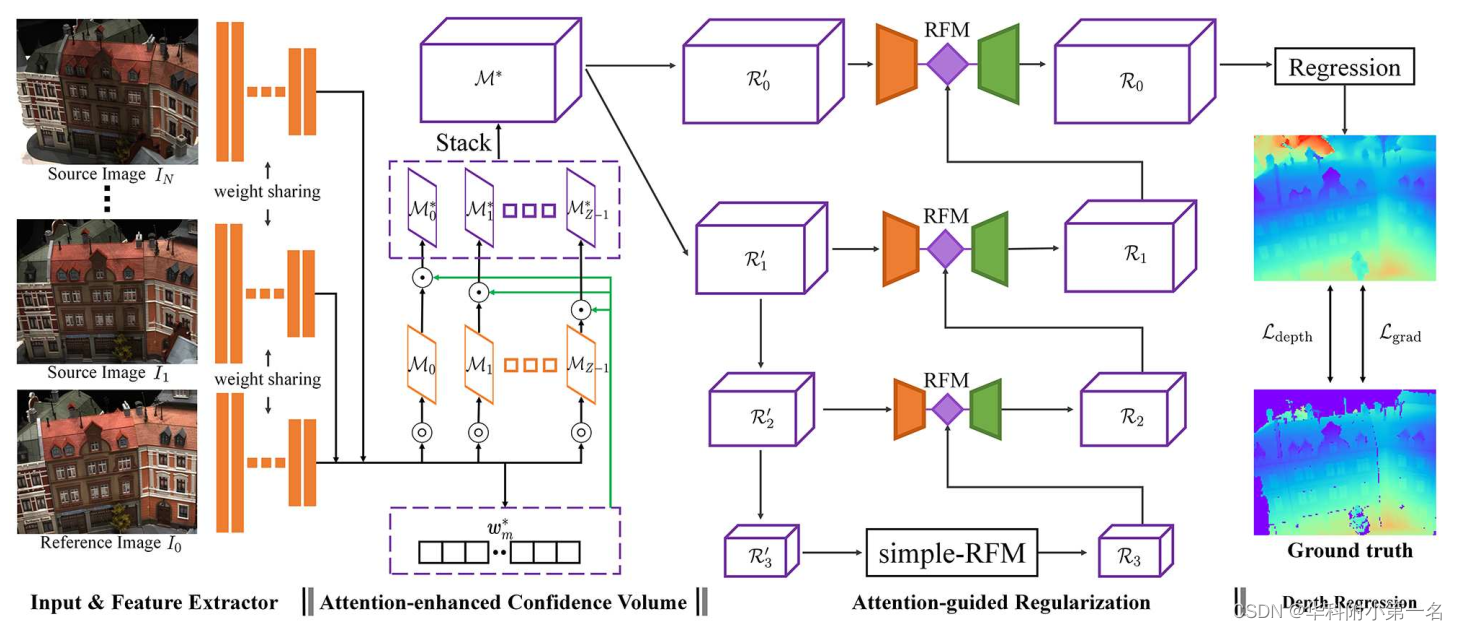
1. AttMVS结构
- 首先使用编码器网络从输入图像中提取感知特征;
- 使用特征构建注意力增强匹配置信体实现鲁棒和准确匹配;
- 通过注意力引导的分层正则化模块RFMs)对匹配置信度进行分层聚合和正则化;
- 使用3D卷积从正则化置信体估计深度图;
- “⊙”表示信道相乘,“⊚”表示单应性变化和原始像素置信度匹配,R’i和Ri分别为第i级上的非正则化和正则化匹配置信体。
2. 特征提取器
使用修改后的P-mvsnet的特征提取器提取参考图像I0和N张大小为H × W的源图像的感知特征,用于学习多视图光度一致性。特征提取网络必须具有足够的容量,对于获得精确和鲁棒的特征表示进行像素级匹配至关重要,因此增加了通道数和层数(10)。输出维度[1/4H, 1/4W, 16],使用Instance Normalization, LeakyReLU。
3. 注意力增强匹配置信度
目前基于学习的MVS方法中,仅使用像素的局部感知特征构建匹配置信体。因此,整体场景的上下文信息往往被忽略。而本文将光度一致性信息与来自参考图像和相应源图像特征图的上下文线索结合起来,构建了一个注意力增强匹配置信体。
通过全局average pooling把每个特征体压缩到单通道vi(individual channel,个人是这么理解的)
首先,通过全局平均池化将所有提取的图像特征映射压缩为各自的通道描述符{vi}N中,接着计算局部场景的上下文通道统计Wv,如下所示:
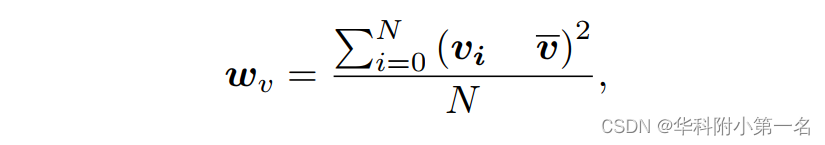
其中v是{vi}N的通道平均值。接下来Wv通过squeeze-and-excitation块计算注意力通道加权向量Wv∗为:
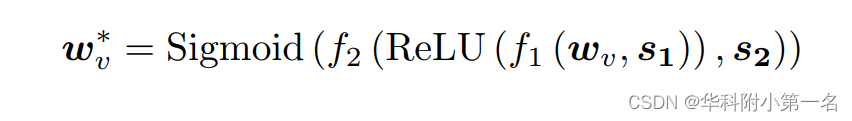
其中f1(·,·)和f2(·,·)是两个线性变换,s1和s2表示对应的变换参数。最后,得到第j个采样假设深度平面上的注意力增强匹配置信度图M*j为:
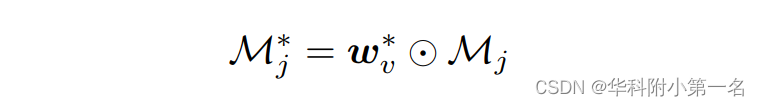
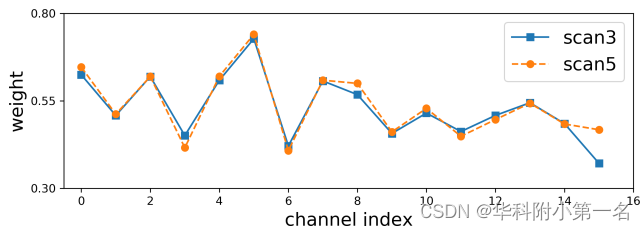
对于j = 0,1,····,Z-1,其中Z是采样假设深度平面的总数,⊙表示通道乘法,Mj表示基于单应性变化的特征图的中生成的原始像素置信度图。图中学习权重的例子可以看出:i)不同的场景在一些通道拥有不同的权重,而在另一些通道拥有相似的权重;(2)对于每个场景,不同的通道拥有不同的权重。
计算完所有的注意力增强匹配置信度图后,沿着深度方向堆叠,产生注意力增强匹配置信体M*,送入正则化模块。
特征图的维度16,核心要做的事情是给特征图16维度增加不同的权重,体现了每个维度不一样的重要性,因为代码没有开源,讲的不太清晰。
4. 注意力引导的层次正则化
首先,M*通过两个步幅分别为1和2的卷积块被编码为两个非正则匹配的置信体R'0和R'1,接着下采样生成R'2和R'3,因此得到四层非正则匹配置信体{R'i}。
接下来,使用简单的RFM处理3级的R'3,多射线融合模块RFMs用于0级、1级和2级。其结构如下,由前上下文理解模块、射线注意力模块(RAM)和后上下文理解模块组成。
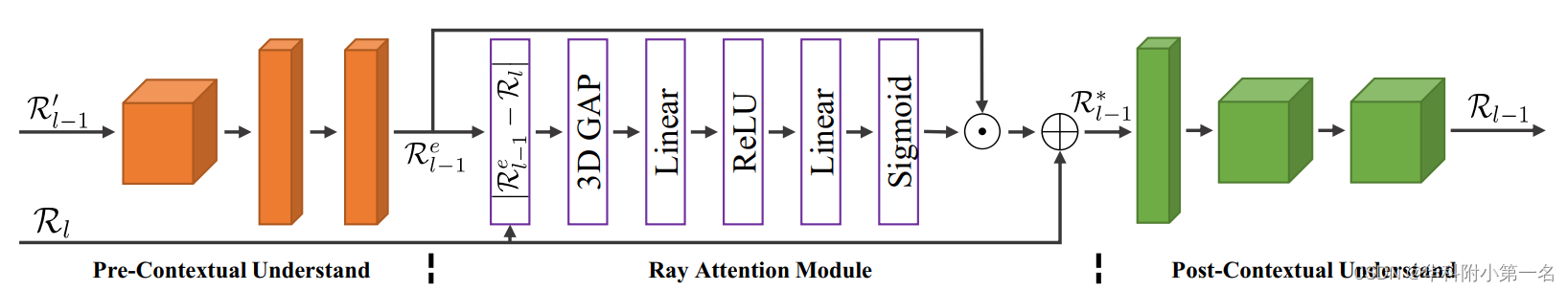
两个上下文理解模块都由三个3D卷积块组成,其中前上下文模块中的第二个块对匹配置信体进行下采样并增加通道,后上下文模块中的第二个块进行反向操作。 l -1层(l=1,2,3)的RAM可以表述为:
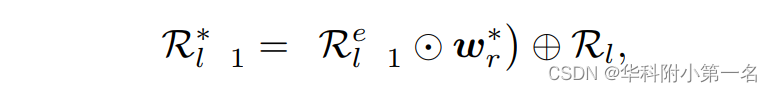
其中,Re l-1是由R'l-1提供的前上下文理解模块的输出,Rl是level l上正则化的匹配置信体,⊕表示逐元素相加,射线加权图wr*由wr =|Re-1-R|用与式(2)相同。然后,通过后上下文理解模块对R*l-1进行进一步处理,得到正则化匹配置信度Rl-1。
简单RFM是通过从RFM中删除RAM和上采样和下采样操作来创建的,但保持从第二层到第五层的c残差连接。注意,它只在第3级用于正则化R′3为R3,可以避免训练样本和评价样本的过度裁剪。
5. 深度回归和损失函数
得到正则化的R0后,首先应用三维卷积层将其编码为深度概率体V。然后使用[深度回归方法来推断深度图。每个采样深度d的概率由V通过Softmax运算σ(·)计算。每个标签的像素的预测深度d的计算为:
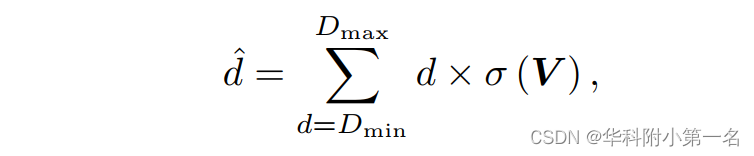
其中Dmin和Dmax分别表示估计的最小深度和最大深度。结合相对深度损失Ldepth和梯度间正则化损失Lgrad来共同优化:
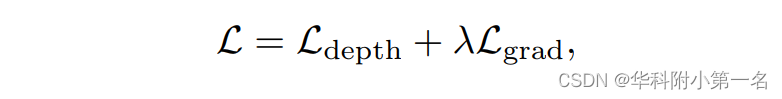
其中λ > 0为加权系数。相对深度损失函数定义为
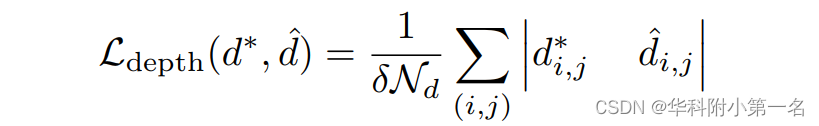
其中Nd表示真实像素的总数(i, j),δ = (Dmax-Dmin)/(Z-1)是假设深度平面之间采样间隔的长度,d∗是真实深度。为了保证预测深度图与真实深度图之间深度梯度的一致性,定义梯度间正则化损失为:
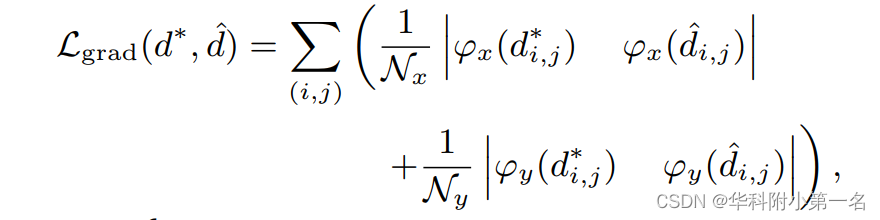
其中Nx表示真实像素的数量,这些像素在x方向上的相邻像素也被标记,ϕx为对应的在x方向上的深度导数,Ny和ϕy表示在y方向上类似的信息。
6. 点云重建
在获得所有深度图后,使用深度图滤波和融合方法来重建完整的三维点云。另一方面,对于深度范围较大的高分辨率场景,由于GPU内存的限制,可能无法采样足够多的假设平面,以获得令人满意的精度来估计深度图。为缓解这个问题,建议通过最大化像素级视图选择的多视图光度一致性来进一步改进生成的深度图。
7. 实验
7.1. 实现
论文对DTU数据集生成的深度图进行了改进。
先计算单应性变化。We also notice that all scanned scenes share the same set of camera parameters and the adjacent relationships between the cameras are also fixed. Therefore, we pre-calculate all possible homography transformations in advance and directly use them during training of the network, which reduces the training time of each minibatch from around 1.8s to 1.2s (saves about one-third of the training time).
7.2. 基准结果及泛化性
Tanks & Temples数据集重叠度很大,点云融合时采用了更严格的阈值,抑制异常值。在advanced中的效果没有intermediate好,是由于深度范围特别大,这也是深度方法普遍的限制。
The performance of our method on the advanced sequences is still competitive but is worse than that on the intermediate sequences when compared with some conventional MVS methods. We think the main reason is that for great majority part of images in the advanced sequences, the interested depth ranges are very large, but due to the GPU memory limitation, our method could not sample sufficient hypothesized depth planes to assure the
quality of predicted depth maps even though the depth map refinement has been used. Thus, our method suits better to reconstruct the scenes with the interested depth range of the captured images being concentrated, which is also the common restriction of current learning-based MVS algorithms.