✨个人主页: 熬夜学编程的小林
💗系列专栏: 【C语言详解】 【数据结构详解】【C++详解】
目录
1、函数补充
2、迭代器完善
3、const迭代器
总结
1、函数补充
拷贝构造
思路:
- 先构造一个头结点,然后将 lt 类中的元素依次尾插到新的结点上。
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();//构造一个头结点
for (auto& x : lt)
{
push_back(x);
}
}{}初始化构造
思路:
- 先构造一个头结点,然后将 il 类中的元素依次尾插到新的结点上。
list(initializer_list<T> il)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& x : il)
{
push_back(x);
}
}赋值操作符重载
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}大小相关函数
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()
{
return _size == 0;
}clear()
清空list的内容,保留头结点。
//清空数据
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);//更新迭代器
}
}~list()
析构函数,清空list的内容并释放头结点。
~list()
{
clear();//清空内容函数
delete _head;//释放头结点
_head = nullptr;//置空
}2、迭代器完善
前面我们处理的都是内置类型的情况,如果我们出现自定义类型,如何解决?
自定义类型举例:
struct A
{
int _a1;
int _a2;
A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0)
:_a1(a1)
, _a2(a2)
{}
};首先我们先看看几种自定义类型的尾插方式:
void test_list3()
{
list<A> lt;
A aa1(1, 1);//实例化对象
A aa2{ 2,2 };//多参数的隐式类型转换,C++11
lt.push_back(aa1);//有名对象实例化
lt.push_back(aa2);
lt.push_back(A(3, 3));//匿名对象
lt.push_back({ 4,4 });//多参数的隐式类型转换,C++11
}对自定义类型进行遍历:
list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";//自定义类型输出不了
it++;
}
cout << endl;
A是自定义类型,不支持留插入,我们解引用得到的_data是A的对象 。在结构体中我们获取到自定义类型的对象可以通过 . 进行访问内部成员,此处我们也可以使用 . 进行访问内部成员。
cout << (*it)._a1 << ":" << (*it)._a2 << " ";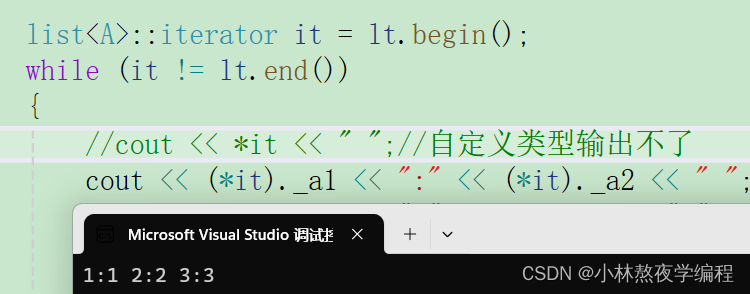
但是如果这么使用会有一点别捏,我们在自定义类型中,也可以通过自定义类型的地址来访问成员,即通过 ->访问,此处我们也可以通过 ->进行访问,因此我们需要重载一个operator->()函数 。
迭代器类中重载operator->
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;//取数据的地址
}使用->访问元素
cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << " ";使用重载函数版
cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << " ";测试结果:
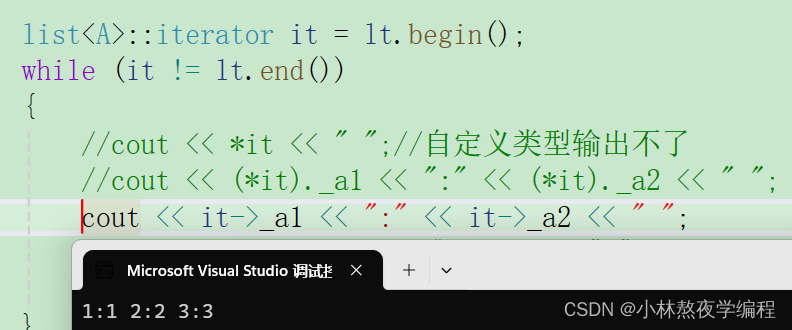
注意:
这里隐藏了一个箭头,一个是重载,一个是原生指针的访问操作。
当重载 operator->,不会直接返回成员的值,而是应该返回一个指针,这个指针指向的对象包含我们想要访问的成员。当使用
->运算符时,C++ 会自动和透明地调用重载的operator->并继续 “链式” 访问成员,而不需要程序员显示地添加多余的箭头。
3、const迭代器
我们上一弹写的普通迭代器对于const对象是无法编译成功的,const不能调用非const成员函数(权限放大)。
下面我们则实现一个const迭代器的类。
与普通迭代器类似,我们需要先在list类中重命名一个const迭代器
typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;//const迭代器类
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);//匿名对象
//return _head->_next;//单参数类型转换
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}注意:
const迭代器名字不能写成 const iterator,因为const迭代器的本质是迭代器指向的内容不能修改,而不是迭代器本身不能修改,const_iterator这样定义是迭代器不能修改,内容还是可以修改的
实现const_iterator类有两种方式,如下:
方式一(单独实现一个新的类,修改普通迭代器的部分地方):
template<class T>
struct ListConstIterator
{
typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;//对迭代器类重定义
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
Node* _node;
//构造
ListConstIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
const T& operator*()//只能访问,不能修改值
{
return _node->_data;
}
const T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;//返回指针
}
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
我们可以看到,const迭代器与普通迭代器的区间只在operator*与operator->的返回的类型上,那么我们是不是可以将两个类封装成一个模板类呢???
//普通迭代器和const迭代器只有两个返回值不同,因此我们使用模板封装
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>//reference引用 point指针
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//对迭代器类重定义
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
Node* _node;
//构造
ListIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//T& operator*()//遍历及修改
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//T* operator->()
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;//返回指针
}
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;//返回临时变量
}
//前置--
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;//返回临时变量
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};合并之后的三个类模板参数:
T:链表结点存储_data值的数据类型Ref:通过迭代器访问数据时的返回类型,可以是T&或者const T&。Ptr:通过迭代器访问数据的指针类型,可以是T*或者const T*。
链表实例化如下:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;//普通迭代器类
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//const迭代器类list实现全部代码
namespace lin
{
//链表基本结构
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _prev;
ListNode<T>* _next;
T _data;
ListNode(const T& val = T())//初始化值构造
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,_data(val)
{}
};
//原版普通迭代器
//迭代器操作类 方法都要被访问,使用struct
//template<class T>
//struct ListIterator
//{
// typedef ListIterator<T> Self;//对迭代器类重定义
// typedef ListNode<T> Node;
// Node* _node;
// //构造
// ListIterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {}
// T& operator*()//遍历及修改
// {
// return _node->_data;
// }
// T* operator->()
// {
// return &_node->_data;//返回指针
// }
// //前置++
// Self& operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// //后置++
// Self operator++(int)
// {
// Self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// bool operator!=(const Self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
// bool operator==(const Self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//};
//原版const迭代器
//template<class T>
//struct ListConstIterator
//{
// typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;//对迭代器类重定义
// typedef ListNode<T> Node;
// Node* _node;
// //构造
// ListConstIterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {}
// const T& operator*()//只能访问,不能修改值
// {
// return _node->_data;
// }
// const T* operator->()
// {
// return &_node->_data;//返回指针
// }
// //前置++
// Self& operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// //后置++
// Self operator++(int)
// {
// Self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// Self& operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return *this;
// }
// Self operator--(int)
// {
// Self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return tmp;
// }
// bool operator!=(const Self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
// bool operator==(const Self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//};
//普通迭代器和const迭代器只有两个返回值不同,因此我们使用模板封装
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>//reference引用 point指针
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListIterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;//对迭代器类重定义
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
Node* _node;
//构造
ListIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//T& operator*()//遍历及修改
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//T* operator->()
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;//返回指针
}
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;//返回临时变量
}
//前置--
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;//返回临时变量
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;//将链表结构重命名
public:
//普通版本
//typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;//需要被访问,放在public内
//typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;//const迭代器类
//类模板
typedef ListIterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;//需要被访问,放在public内
typedef ListIterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;//const迭代器类
//构造哨兵结点
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
list()//默认构造
{
empty_init();//创建哨兵头结点
}
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
void clear()//清空数据,不销毁哨兵头结点
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
~list()//析构函数
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
list(const list<T>& lt)//拷贝构造
{
empty_init();//创建头结点,然后进行尾插
for (auto& x : lt)
{
push_back(x);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);//匿名对象
//return _head->_next;//单参数类型转换
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
//解决打印修改值问题
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);//匿名对象
//return _head->_next;//单参数类型转换
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
//单独实现的尾插
//void push_back(const T& val)
//{
// //tail
// Node* newnode = new Node(val);
// Node* tail = _head->_prev;
// tail->_next = newnode;
// newnode->_prev = tail;
// newnode->_next = _head;
// _head->_prev = newnode;
//}
void insert(iterator pos, const T& val)//在pos位置前插入val
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
//prev newnode cur
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
_size++;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置,防止迭代器失效,返回迭代器后一个位置
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
//prev next
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
_size--;
return iterator(next);
}
//调用insert函数
void push_back(const T& val)
{
//insert(--begin(),val);//不能使用+n,在--begin前面插入
insert(end(), val);//end()前面
}
void push_front(const T& val)
{
insert(begin(), val);//begin()前面插入
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());//end()前面删除
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());//begin()位置删除
}
private:
Node* _head;//链表成员变量
size_t _size;//链表大小
};
}总结
本篇博客就结束啦,谢谢大家的观看,如果公主少年们有好的建议可以留言喔,谢谢大家啦!