话不多说,直接启动!👌🤣
目录
一、线性表😎
1、建立链表
2、插入元素
3、删除特定位置的元素
4、输出特定元素值的位置
5、输出特定位置的元素值
6、输出整个链表
实现
二、栈和队列😘
栈
顺序栈
1、建立顺序栈
2、入栈
3、出栈
4、取栈顶
5、遍历栈
6、判栈空
实现:
链栈
1、建立链栈
2、入栈
3、出栈
4、取栈顶
5、遍历栈
6、判栈空
实现:
队列
顺序队列
1、建立顺序队列
2、入队
3、出队
4、求队列长度
5、遍历队列
实现:
链式队列
1、建立链式队列
2、入队
3、出队
4、求队列长度
5、遍历队列
实现:
三、树和二叉树
实现:
四、图
实现:
五、查找和排序
折半查找实现:
快速排序实现:
一、线性表😎

1、建立链表
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//定义单链表结点结构体
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode* next;
};
//创建链表
ListNode* CreateList(){
ListNode* head = new ListNode();//创建头结点
head->next = nullptr;//初始化头结点的next指针为空
return head;
}
int main(){
ListNode* head = CreateList();
}2、插入元素
//在链表中插入元素
void Insert(ListNode* head, int i, int val) { // 需要链表,第i个位置,插入val值
ListNode* current = head; // 初始化当前结点为头结点
while (i-- > 0) { // 循环i次找插入位置
current = current->next;
}
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = current->next;
current->next = newNode;
}3、删除特定位置的元素
//删除特定位置的元素
void Delete(ListNode* head,int index){//需要链表,第i个位置
if(index<0)return;
ListNode* current = head;
for(int i=0;i<index&¤t!=nullptr;i++){
current=current->next;
}
if(current==nullptr)return;
ListNode* toDelete = current->next;
current->next = current->next->next;
delete toDelete;
}4、输出特定元素值的位置
//输出特定元素值的位置
void PrintValue(ListNode* head, int index) {
ListNode* current = head;
int position = 0;
while (current != nullptr) {
if (current->val == index) {
cout << "元素值:" << current->val << " 的位置是:" << position << endl;
break;
}
current = current->next;
position++;
}
if (current == nullptr) {
cout << "索引超出链表范围" << endl;
}
}5、输出特定位置的元素值
//输出特定位置的元素值
void PrintNodeAtPosition(ListNode* head, int index) {
ListNode* current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index && current != nullptr; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
if (current != nullptr) {
cout << "元素位置:" << index << ", 值:" << current->val << endl;
} else {
cout << "索引超出链表范围" << endl;
}
}6、输出整个链表
//输出整个链表
void PrintList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->val << " --> ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << "nullptr" << endl;
}实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//定义单链表结点结构体
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode* next;
};
//创建链表
ListNode* CreateList(){
ListNode* head = new ListNode();//创建头结点
head->next = nullptr;//初始化头结点的next指针为空
return head;
}
//在链表中插入元素
void Insert(ListNode* head, int i, int val) { // 需要链表,第i个位置,插入val值
ListNode* current = head; // 初始化当前结点为头结点
while (i-- > 0) { // 循环i次找插入位置
current = current->next;
}
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = current->next;
current->next = newNode;
}
//删除特定位置的元素
void Delete(ListNode* head,int index){//需要链表,第i个位置
if(index<0)return;
ListNode* current = head;
for(int i=0;i<index&¤t!=nullptr;i++){
current=current->next;
}
if(current==nullptr)return;
ListNode* toDelete = current->next;
current->next = current->next->next;
delete toDelete;
}
//从输入读取链表元素并插入
void ReadInputToList(ListNode* head) {
cout << "请输入你需要建立的初始链表(只允许实数):" << endl;
vector<double> LinkList;
double input;
while (cin >> input) {
LinkList.push_back(input);
if(cin.peek() == '\n'){
cin.ignore();
break;
}
}
int index = 0;
for (double value : LinkList) {
Insert(head, index++, static_cast<int>(value)); // 将读取的实数转换为整数后插入链表
}
}
//输出特定元素值的位置
void PrintValue(ListNode* head, int index) {
ListNode* current = head;
int position = 0;
while (current != nullptr) {
if (current->val == index) {
cout << "元素值:" << current->val << " 的位置是:" << position << endl;
break;
}
current = current->next;
position++;
}
if (current == nullptr) {
cout << "索引超出链表范围" << endl;
}
}
//输出特定位置的元素值
void PrintNodeAtPosition(ListNode* head, int index) {
ListNode* current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index && current != nullptr; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
if (current != nullptr) {
cout << "元素位置:" << index << ", 值:" << current->val << endl;
} else {
cout << "索引超出链表范围" << endl;
}
}
//输出整个链表
void PrintList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->val << " --> ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << "nullptr" << endl;
}
int main(){
ListNode* head = CreateList();
ReadInputToList(head);
cout<<"1.输出链表中的所有结点"<<endl;
PrintList(head);
cout<<"2.输出元素25的位置"<<endl;
PrintValue(head,25);
cout<<"3.输出第5个元素"<<endl;
PrintNodeAtPosition(head,5);
cout<<"4.在第 3 个元素前插入值为 98 的元素,然后输出链表"<<endl;
Insert(head,3,98);
PrintList(head);
cout<<"5.输出删除第 4 个元素后的链表"<<endl;
Delete(head,4);
PrintList(head);
return 0;
}二、栈和队列😘

栈
顺序栈
1、建立顺序栈
// 建立顺序栈
struct Stack {
int *elem; // 指向动态分配的数组
int top; // 栈顶指针
int MaxSize; // 栈的最大容量
};
// 创建栈
Stack* CreateStack(int MaxSize) {
Stack* stack = new Stack();
stack->elem = new int[MaxSize];
stack->top = -1;
stack->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return stack;
}2、入栈
// 入栈
void Push(Stack* stack, int val) {
if (stack->top < stack->MaxSize - 1) { // 如果栈未满
stack->elem[++stack->top] = val; // 栈顶指针后移并赋值
} else {
cout << "栈已满,无法入栈" << endl;
}
}3、出栈
// 出栈
int Pop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top >= 0) { // 如果栈非空
return stack->elem[stack->top--]; // 返回栈顶元素并移动栈顶指针
} else {
cout << "栈为空,无法出栈" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
}4、取栈顶
// 取栈顶
int GetTop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top >= 0) { // 如果栈非空
return stack->elem[stack->top]; // 返回栈顶元素
} else {
cout << "栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
}5、遍历栈
// 遍历栈
void TraverseStack(Stack* stack) {
for (int i = 0; i <= stack->top; i++) {
cout << stack->elem[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}6、判栈空
// 判断栈是否为空
bool IsEmpty(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top < 0; // 如果栈顶指针小于0,则栈为空
}实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 建立顺序栈
struct Stack {
int *elem; // 指向动态分配的数组
int top; // 栈顶指针
int MaxSize; // 栈的最大容量
};
// 创建栈
Stack* CreateStack(int MaxSize) {
Stack* stack = new Stack();
stack->elem = new int[MaxSize];
stack->top = -1;
stack->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return stack;
}
// 入栈
void Push(Stack* stack, int val) {
if (stack->top < stack->MaxSize - 1) { // 如果栈未满
stack->elem[++stack->top] = val; // 栈顶指针后移并赋值
} else {
cout << "栈已满,无法入栈" << endl;
}
}
// 出栈
int Pop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top >= 0) { // 如果栈非空
return stack->elem[stack->top--]; // 返回栈顶元素并移动栈顶指针
} else {
cout << "栈为空,无法出栈" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
}
// 取栈顶
int GetTop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top >= 0) { // 如果栈非空
return stack->elem[stack->top]; // 返回栈顶元素
} else {
cout << "栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
}
// 遍历栈
void TraverseStack(Stack* stack) {
for (int i = 0; i <= stack->top; i++) {
cout << stack->elem[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// 判断栈是否为空
bool IsEmpty(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top < 0; // 如果栈顶指针小于0,则栈为空
}
// 从输入读取元素并添加
void ReadInputToStack(Stack* stack) {
cout << "请输入你需要建立的初始顺序栈(只允许实数):" << endl;
vector<double> Arr;
double input;
while (cin >> input) {
Arr.push_back(input);
if (cin.peek() == '\n') {
cin.ignore();
break;
}
}
int index = 0;
for (double value : Arr) { // 遍历Arr而不是stack
Push(stack, static_cast<int>(value));
}
}
int main() {
int max = 0;
cout << "请输入栈的最大容量:" << endl;
cin >> max;
Stack* stack = CreateStack(max);
ReadInputToStack(stack);
TraverseStack(stack);
return 0;
}链栈
1、建立链栈
// 定义链栈节点结构体
struct StackNode {
int val;
StackNode* next;
};
// 创建链栈
StackNode* CreateStack() {
StackNode* head = new StackNode(); // 创建头节点
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}2、入栈
// 入栈操作
void Push(StackNode* head, int val) {
StackNode* newNode = new StackNode{val, nullptr}; // 创建新节点
newNode->next = head->next; // 将新节点链接到链表
head->next = newNode; // 头节点指向新节点
}3、出栈
// 出栈操作
int Pop(StackNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "栈为空,无法出栈。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
StackNode* temp = head->next; // 临时节点
int val = temp->val; // 保存要返回的值
head->next = temp->next; // 头节点指向下一个节点
delete temp; // 释放临时节点
return val; // 返回栈顶元素
}4、取栈顶
// 获取栈顶元素
int GetTop(StackNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
return head->next->val; // 返回栈顶元素
}5、遍历栈
// 遍历链栈
void TraverseStack(StackNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "栈为空。" << endl;
return;
}
StackNode* current = head->next; // 从栈顶开始遍历
cout << "链栈元素: ";
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next; // 移动到下一个节点
}
cout << endl;
}
6、判栈空
// 判断栈是否为空
bool IsEmpty(StackNode* head) {
return head->next == nullptr; // 如果头节点的next指针为空,则栈为空
}实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 定义链栈节点结构体
struct StackNode {
int val;
StackNode* next;
};
// 创建链栈
StackNode* CreateStack() {
StackNode* head = new StackNode(); // 创建头节点
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
// 入栈操作
void Push(StackNode* head, int val) {
StackNode* newNode = new StackNode{val, nullptr}; // 创建新节点
newNode->next = head->next; // 将新节点链接到链表
head->next = newNode; // 头节点指向新节点
}
// 出栈操作
int Pop(StackNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "栈为空,无法出栈。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
StackNode* temp = head->next; // 临时节点
int val = temp->val; // 保存要返回的值
head->next = temp->next; // 头节点指向下一个节点
delete temp; // 释放临时节点
return val; // 返回栈顶元素
}
// 遍历链栈
void TraverseStack(StackNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "栈为空。" << endl;
return;
}
StackNode* current = head->next; // 从栈顶开始遍历
cout << "链栈元素: ";
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next; // 移动到下一个节点
}
cout << endl;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
int GetTop(StackNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示栈空
}
return head->next->val; // 返回栈顶元素
}
// 判断栈是否为空
bool IsEmpty(StackNode* head) {
return head->next == nullptr; // 如果头节点的next指针为空,则栈为空
}
int main() {
StackNode* stack = CreateStack(); // 创建链栈
cout << "入栈元素: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50" << endl;
Push(stack, 10);
Push(stack, 20);
Push(stack, 30);
Push(stack, 40);
Push(stack, 50);
cout << "栈顶元素: " << GetTop(stack) << endl;
cout << "出栈元素: " << Pop(stack) << endl;
cout << "栈顶元素: " << GetTop(stack) << endl;
TraverseStack(stack); // 调用遍历链栈的方法
cout << "栈是否为空: " << (IsEmpty(stack) ? "是" : "否") << endl;
return 0;
}
队列
顺序队列
1、建立顺序队列
// 定义队列结构体
struct Queue {
vector<int> elements; // 使用vector来存储队列元素
};
// 创建队列
Queue* CreateQueue() {
return new Queue(); // 创建队列对象
}2、入队
// 入队操作
void Enqueue(Queue* queue, int val) {
queue->elements.push_back(val); // 将元素添加到队列末尾
}3、出队
// 出队操作
int Dequeue(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->elements.empty()) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空,无法出队。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示队空
}
int val = queue->elements.front(); // 获取队首元素
queue->elements.erase(queue->elements.begin()); // 删除队首元素
return val; // 返回队首元素
}4、求队列长度
int GetQueueLength(Queue* queue) {
return queue->elements.size(); // 返回队列中元素的数量
}5、遍历队列
// 遍历队列
void TraverseQueue(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->elements.empty()) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空。" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "队列元素: ";
for (int val : queue->elements) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// 定义队列结构体
struct Queue {
vector<int> elements; // 使用vector来存储队列元素
};
// 创建队列
Queue* CreateQueue() {
return new Queue(); // 创建队列对象
}
// 入队操作
void Enqueue(Queue* queue, int val) {
queue->elements.push_back(val); // 将元素添加到队列末尾
}
// 出队操作
int Dequeue(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->elements.empty()) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空,无法出队。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示队空
}
int val = queue->elements.front(); // 获取队首元素
queue->elements.erase(queue->elements.begin()); // 删除队首元素
return val; // 返回队首元素
}
// 获取队列长度
int GetQueueLength(Queue* queue) {
return queue->elements.size(); // 返回队列中元素的数量
}
// 遍历队列
void TraverseQueue(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->elements.empty()) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空。" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "队列元素: ";
for (int val : queue->elements) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// 获取队首元素
int GetFront(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->elements.empty()) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空,无法获取队首元素。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示队空
}
return queue->elements.front(); // 返回队首元素
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool IsEmpty(Queue* queue) {
return queue->elements.empty(); // 如果队列大小为0,则队列为空
}
int main() {
Queue* queue = CreateQueue(); // 创建队列
cout << "入队元素: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50" << endl;
Enqueue(queue, 10);
Enqueue(queue, 20);
Enqueue(queue, 30);
Enqueue(queue, 40);
Enqueue(queue, 50);
TraverseQueue(queue); // 遍历队列
cout << "队列长度: " << GetQueueLength(queue) << endl;
cout << "队首元素: " << GetFront(queue) << endl;
cout << "出队元素: " << Dequeue(queue) << endl;
cout << "队首元素: " << GetFront(queue) << endl;
cout << "队列是否为空: " << (IsEmpty(queue) ? "是" : "否") << endl;
return 0;
}
链式队列
1、建立链式队列
// 定义链队列节点结构体
struct QueueNode {
int val;
QueueNode* next;
};
// 创建链队列
QueueNode* CreateQueue() {
QueueNode* head = new QueueNode(); // 创建头节点
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}2、入队
// 入队操作
void Enqueue(QueueNode* head, int val) {
QueueNode* newNode = new QueueNode{val, nullptr}; // 创建新节点
newNode->next = head->next; // 将新节点链接到链表
head->next = newNode; // 头节点指向新节点
}3、出队
// 出队操作
int Dequeue(QueueNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "队列为空,无法出队。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示队空
}
QueueNode* temp = head->next; // 临时节点
int val = temp->val; // 保存要返回的值
head->next = temp->next; // 头节点指向下一个节点
delete temp; // 释放临时节点
return val; // 返回队首元素
}4、求队列长度
// 获取队列长度
int GetQueueLength(QueueNode* head) {
int length = 0;
QueueNode* current = head->next;
while (current != nullptr) {
length++; // 计算队列中元素的数量
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}5、遍历队列
// 遍历队列
void TraverseQueue(QueueNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空。" << endl;
return;
}
QueueNode* current = head->next;
cout << "队列元素: ";
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next; // 移动到下一个节点
}
cout << endl;
}实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 定义链队列节点结构体
struct QueueNode {
int val;
QueueNode* next;
};
// 创建链队列
QueueNode* CreateQueue() {
QueueNode* head = new QueueNode(); // 创建头节点
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
// 入队操作
void Enqueue(QueueNode* head, int val) {
QueueNode* newNode = new QueueNode{val, nullptr}; // 创建新节点
QueueNode* current = head;
while (current->next != nullptr) {
current = current->next; // 移动到链表末尾
}
current->next = newNode; // 将新节点链接到链表末尾
}
// 出队操作
int Dequeue(QueueNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "队列为空,无法出队。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示队空
}
QueueNode* temp = head->next; // 临时节点
int val = temp->val; // 保存要返回的值
head->next = temp->next; // 头节点指向下一个节点
delete temp; // 释放临时节点
return val; // 返回队首元素
}
// 获取队列长度
int GetQueueLength(QueueNode* head) {
int length = 0;
QueueNode* current = head->next;
while (current != nullptr) {
length++; // 计算队列中元素的数量
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}
// 遍历队列
void TraverseQueue(QueueNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) { // 如果队列为空
cout << "队列为空。" << endl;
return;
}
QueueNode* current = head->next;
cout << "队列元素: ";
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next; // 移动到下一个节点
}
cout << endl;
}
// 获取队首元素
int GetFront(QueueNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "队列为空,无法获取队首元素。" << endl;
return -1; // 返回-1表示队空
}
return head->next->val; // 返回队首元素
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool IsEmpty(QueueNode* head) {
return head->next == nullptr; // 如果头节点的next指针为空,则队列空
}
int main() {
QueueNode* queue = CreateQueue(); // 创建链队列
cout << "入队元素: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50" << endl;
Enqueue(queue, 10);
Enqueue(queue, 20);
Enqueue(queue, 30);
Enqueue(queue, 40);
Enqueue(queue, 50);
TraverseQueue(queue); // 遍历队列
cout << "队列长度: " << GetQueueLength(queue) << endl;
cout << "队首元素: " << GetFront(queue) << endl;
cout << "出队元素: " << Dequeue(queue) << endl;
cout << "队首元素: " << GetFront(queue) << endl;
cout << "队列是否为空: " << (IsEmpty(queue) ? "是" : "否") << endl;
return 0;
}
三、树和二叉树

实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 结构体
struct Bittree {
char data;
Bittree *lchild;
Bittree *rchild;
};
// 先序构建二叉树
Bittree* Creat() {
char n;
scanf(" %c", &n); // 注意在%c前加空格,以跳过任何前导空白
if (n == '#') {
return NULL;
} else {
Bittree* T = new Bittree();
T->data = n;
T->lchild = Creat();
T->rchild = Creat();
return T;
}
}
// 先序遍历
void PreOrder(Bittree *T) {
if (T) {
printf("%2c", T->data);
PreOrder(T->lchild);
PreOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
// 中序遍历
void InOrder(Bittree *T) {
if (T) {
InOrder(T->lchild);
printf("%2c", T->data);
InOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
// 后序遍历
void PostOrder(Bittree *T) {
if (T) {
PostOrder(T->lchild);
PostOrder(T->rchild);
printf("%2c", T->data);
}
}
// 统计叶子结点的个数
int Leaf(Bittree *T) {
int LeafCount;
if (T == NULL)
LeafCount = 0;
else if (T->lchild == NULL && T->rchild == NULL)
LeafCount = 1;
else
LeafCount = Leaf(T->lchild) + Leaf(T->rchild);
return LeafCount;
}
// 计算二叉树的深度
int TreeDepth(Bittree *T) {
if (T == NULL)
return 0;
else {
int depthleft = TreeDepth(T->lchild) + 1;
int depthright = TreeDepth(T->rchild) + 1;
return depthleft > depthright ? depthleft : depthright;
}
}
int main() {
printf("先序构造一颗二叉树(左/右孩子为空用'#'表示):");
Bittree *T = Creat();
printf("此二叉树的先序遍历序列是:");
PreOrder(T);
printf("\n");
printf("此二叉树的中序遍历序列是:");
InOrder(T);
printf("\n");
printf("此二叉树的后序遍历序列是:");
PostOrder(T);
printf("\n");
printf("这棵树叶子结点有%d个\n", Leaf(T));
printf("这棵树的深度为:%d\n", TreeDepth(T));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
四、图

实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack> // 引入栈头文件
using namespace std;
#define MAX_NUM 100
// 定义邻接矩阵
struct Graph{
int MaxArr[MAX_NUM][MAX_NUM];
int num;
};
// 初始化图
Graph* create(int n){
Graph* graph=new Graph();
graph->num=n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
graph->MaxArr[i][j]=0;
}
}
return graph;
}
// 添加单向边
void addEdge(Graph* graph,int src,int dest){
graph->MaxArr[src][dest]=1;
}
// 广度优先搜索
bool bfs(Graph* graph,int start,int end,int* parent){
int visited[MAX_NUM];
bool inQueue[MAX_NUM];
int queue[MAX_NUM];
int front=0,rear=0;
for(int i=0;i<graph->num;i++){
visited[i]=false;
inQueue[i]=false;
parent[i]=-1;
}
queue[rear++]=start;
inQueue[start]=true;
visited[start]=true;
while(front<rear){
int current=queue[front++];
for(int i=0;i<graph->num;i++){
if(!visited[i]&&graph->MaxArr[current][i]==1){
queue[rear++]=i;
inQueue[i]=true;
visited[i]=true;
parent[i]=current;
}
}
}
return visited[end];
}
// 输出路径
void printPath(int* parent,int end){
printf("Path from start to %d: ", end);
if(parent[end]==-1){
printf("There is no path\n");
return;
}
stack<int> path; // 使用栈来存储路径
int current = end;
while(current != -1) {
path.push(current); // 将节点压入栈中
current = parent[current];
}
// 逐个弹出栈中的元素以实现倒序输出
while(!path.empty()) {
printf("%d ", path.top());
path.pop();
if(!path.empty()) {
printf("-> ");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int Num,start,end;
printf("输入结点个数:");
scanf("%d",&Num);
Graph* graph=create(Num);
printf("输入边(以'src dest'形式,输入0 0结束):");
int src,dest;
while(true){
cin >> src >> dest;
if(src == 0 && dest == 0) break; // 如果输入是0 0,则结束循环
addEdge(graph,src,dest);
}
printf("输入起点:");
scanf("%d",&start);
printf("输入终点:");
scanf("%d",&end);
int* parent=(int*)malloc(Num*sizeof(int));
if(bfs(graph,start,end,parent)){
printPath(parent,end);
}else{
printf("There is no path\n");
}
free(parent);
delete graph;
return 0;
}


五、查找和排序
折半查找实现:
#include <stdio.h>
// 折半查找函数
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x) {
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// 如果中间元素正好是要找的值,返回索引
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// 如果中间元素比要找的值小,在右半部分继续查找
if (arr[mid] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
// 如果中间元素比要找的值大,在左半部分继续查找
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
}
// 如果数组中没有找到值,返回-1
return -1;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {12, 23, 28, 35, 37, 39, 50, 60, 78, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x;
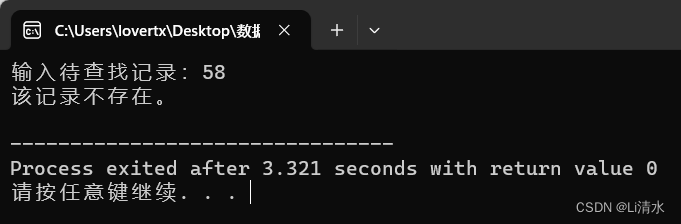
printf("输入待查找记录:");
scanf("%d", &x);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
printf("该记录不存在。\n");
else
printf("该记录在表中位置 %d。\n", result);
return 0;
}


快速排序实现:

#include <stdio.h>
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high);
void swap(int *xp, int *yp);
// 快速排序函数
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// 递归排序左半部分
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
// 递归排序右半部分
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// 用于快速排序的辅助函数,用于分区
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high]; // 选择最后一个元素作为基准
int i = (low - 1); // 初始化指向比基准小的元素的指针
for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) {
// 如果当前元素小于或等于基准,则交换元素
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]); // 将基准元素放在正确的位置
return (i + 1);
}
// 交换两个元素
void swap(int *xp, int *yp) {
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {12, 23, 28, 35, 37, 39, 50, 60, 78, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("排序后的数组:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}