文章目录
- 一、模拟list类的框架
- 二、函数接口实现
- 1、迭代器接口
- 2、常用删除、插入接口
- 3、常用其他的一些函数接口
- 4、默认成员函数
一、模拟list类的框架
1、使用带哨兵的双向链表实现。
2、链表结点:
// List的结点类
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _pPre; //后继指针
ListNode<T>* _pNext; //前驱指针
T _val; //数据
//构造结点
ListNode(const T& val = T()) :_val(val), _pPre(nullptr), _pNext(nullptr)
{}
};
3、list类的成员变量和构造双向链表的哨兵位结点函数。
//让哨兵位结点指向自己
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
void CreateHead()
{
_pHead = new Node;
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
}
PNode _pHead; //哨兵位结点
二、函数接口实现
1、迭代器接口
list的迭代器是双向迭代器,支持++、–,但是它们在内存上储存是不连续的,无法简单通过指针去进行++、–操作,所以我们要对list的迭代器进行封装。
(1)list正向迭代器类
成员变量:两个结点指针。
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
PNode _pNode; //结点指针
PNode _P;//保存哨兵位结点指针,用于判断解引用是否访问哨兵位结点
构造函数:
//构造函数 ,获取一个结点指针
ListIterator(const PNode & pNode = nullptr, const PNode& const P = nullptr) :_pNode(pNode),_P(P)
{}
拷贝构造、赋值、析构函数:
因为_pNode的指针指向的内存是有list类释放的,所以该类无需进行资源清理,使用浅拷贝即可,所以拷贝、赋值、析构都使用编译器生成的即可。
重载操作符:
//Ref为T& Ptr为T*
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
//解引用
Ref operator*()
{
assert(_P != _pNode);
return _pNode->_val;
}
//该运算符重载的意义为T为自定义类型时使用,迭代器可以通过该运算符直接访问自定义类型成员
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_pNode->_val);
}
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return tmp;
}
//比较
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode != _pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode == _pNode;
}
获取成员变量函数:
//获取该迭代器成员变量
PNode get()
{
return _pNode;
}
ListIterator类一览:
//Ref为T& Ptr为T*
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
public:
//构造函数 ,获取一个结点指针
ListIterator(const PNode & pNode = nullptr, const PNode& const P = nullptr) :_pNode(pNode),_P(P)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
assert(_P != _pNode);
return _pNode->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode != _pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode == _pNode;
}
PNode get()
{
return _pNode;
}
private:
PNode _pNode;
PNode _P;
};
};
(2)反向迭代器类
与正向迭代器不一样的有 * 操作符,_pNode保存的是有效元素的下一个位置,如:想要的是_pNode->_pPre指向的元素,但是该迭代器保存的是_pNode的指针,还有++,–与正向迭代器相反。
其他操作与正向迭代器一致。
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class Reverse_ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef Reverse_ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
public:
Reverse_ListIterator(const PNode& pNode = nullptr, const PNode& const P = nullptr) :_pNode(pNode), _P(P)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
assert(_P != _pNode ->_pPre);
return _pNode->_pPre->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode != _pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode == _pNode;
}
PNode get()
{
return _pNode;
}
private:
PNode _pNode;
PNode _P;
};
(3)list迭代器接口
//一些类型的重命名
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef Reverse_ListIterator<T, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef Reverse_ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> reverse_const_iterator;
// List Iterator
//第一个有效元素位置的迭代器
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_pHead->_pNext,_pHead);
}
//最后一个有效元素位置的下一个位置的迭代器
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_pHead,_pHead);
}
//加了const 修饰
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_pHead->_pNext,_pHead);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(_pHead,_pHead);
}
//反向迭代器
//哨兵位的位置
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(_pHead,_pHead);
}
//第一个有效元素位置
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(_pHead ->_pNext,_pHead);
}
//加了const修饰
reverse_const_iterator rbegin() const
{
return reverse_const_iterator(_pHead,_pHead);
}
reverse_const_iterator rend()const
{
return reverse_const_iterator(_pHead->_pNext,_pHead);
}
2、常用删除、插入接口
(1)insert
在迭代器位置前插入一个结点。
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T & val)
{
//创造一个结点
PNode tmp = new Node(val);
//获取迭代器中的指针
PNode _pos = pos.get();
//进行插入
PNode prv = _pos->_pPre;
prv->_pNext = tmp;
tmp->_pPre = prv;
tmp->_pNext = _pos;
_pos->_pPre = tmp;
//返回新迭代器
return iterator(tmp);
}
迭代器是否失效:
因为插入新的结点,不会影响到原来的结点,所以该迭代器不会失效。
(2)erase
删除迭代器位置结点。
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
//判断是否为哨兵位结点
iterator it = end();
assert(pos != it);
//获取迭代器结点指针
PNode tmp = pos.get();
//进行删除
PNode next = tmp->_pNext;
PNode prv = tmp->_pPre;
prv->_pNext = next;
next->_pPre = prv;
delete tmp;
tmp = nullptr;
//返回被删除结点的下一个位置的结点迭代器
return iterator(next);
}
迭代器是否失效:
因为将结点删除了,所以原本的迭代器是不能使用的,所以迭代器失效了。
(3)push_back、pop_back、push_front、pop_front
这里的头插、尾插、头删、尾删均复用上面两个函数接口。
void push_back(const T & val) { insert(end(), val); }
void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }
void push_front(const T & val) { insert(begin(), val); }
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
3、常用其他的一些函数接口
(1)size
返回大小,通过遍历链表即可找到。
size_t size()const
{
//保存哨兵位的下一个位置
PNode tmp = _pHead->_pNext;
//开始遍历
size_t count = 0;
while (tmp != _pHead)
{
tmp = tmp->_pNext;
++count;
}
return count;
}
(2)empty
是否为空,判断哨兵位结点是否指向自己即可。
bool empty()const
{
return _pHead == _pHead->_pNext;
}
(3)clear
清空链表,遍历链表逐个清空,保留哨兵位结点,再让哨兵位结点自己连接自己。
void clear()
{
//保存有效结点位置
PNode tmp = _pHead->_pNext;
//遍历删除
while (tmp != _pHead)
{
PNode p = tmp->_pNext;
delete tmp;
tmp = p;
}
//重新指向
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
(4)swap
交换,只需要交换指向哨兵位结点的指针即可。
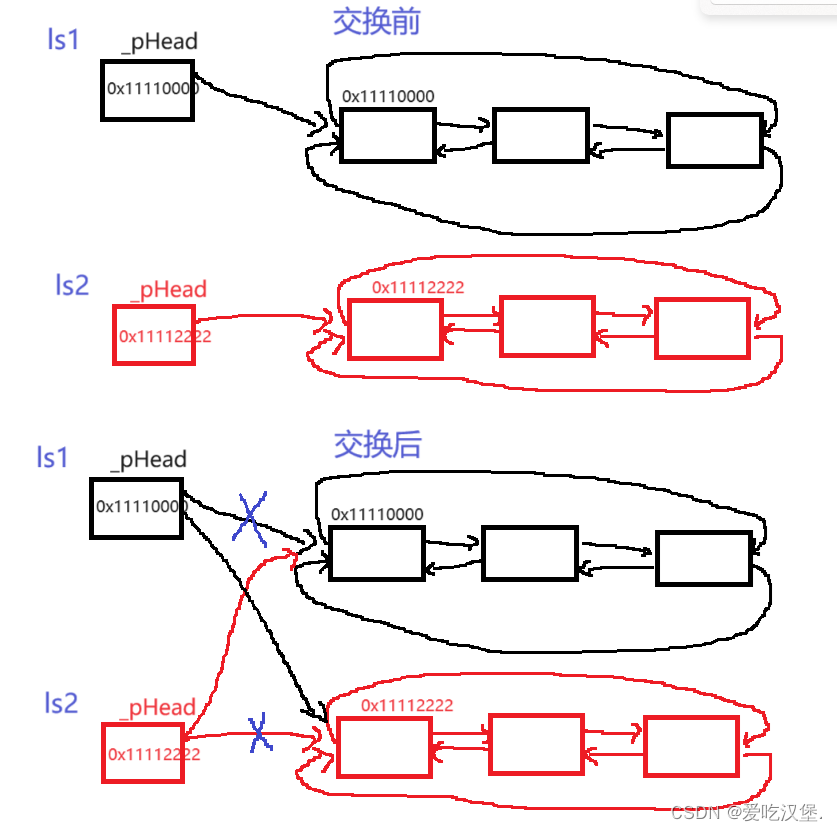
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);
}
(4)front
获取第一个位置的元素。
T& front()
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pNext->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pNext->_val;
}
(5)back
获取最后一个位置元素。
T& back()
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pPre->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pPre->_val;
}
4、默认成员函数
(1)构造函数
构造函数都会先进行构造哨兵位结点,再进行下面的操作,除了无参构造,其他都复用了尾插,将元素尾插到链表结尾。
//无参构造
list()
{ //构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
}
//利用n个val值进行构造
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
//构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
//将元素尾插入
while (n != 0)
{
push_back(value);
--n;
}
}
//这里用迭代器区间构造,重写一个模板,使其可以使用其他容器的迭代器
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
//构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
//将元素尾插入
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
//拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& l)
{
//构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
//遍历+将元素尾插入
PNode tmp = l._pHead->_pNext;
while (tmp != l._pHead)
{
push_back(tmp->_val);
tmp = tmp->_pNext;
}
}
(2)重载赋值运算符
通过传值传参构造一个临时容器 l ,再将其与原来的容器交换,当出了函数作用域之后临时容器就会调用析构函数,对临时容器的资源进行清理(就是原来容器的资源)。
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l)
{
//与临时变量进行交换
swap(l);
return *this;
}
(3)析构函数
对链表清理。
~list()
{
//清空链表
clear();
//删除哨兵位结点
delete _pHead;
_pHead = nullptr;
}
三、总代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
namespace xu
{
// List的结点类
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _pPre; //后继指针
ListNode<T>* _pNext; //前驱指针
T _val; //数据
//构造结点
ListNode(const T& val = T()) :_val(val), _pPre(nullptr), _pNext(nullptr)
{}
};
//List的正向迭代器类
//Ref为T& Ptr为T*
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
public:
//构造函数 ,获取一个结点指针
ListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr) :_pNode(pNode)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode != _pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode == _pNode;
}
PNode get()
{
return _pNode;
}
private:
PNode _pNode;
};
//List的反向迭代器类
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class Reverse_ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef Reverse_ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
public:
Reverse_ListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr) :_pNode(pNode)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->_pPre->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(_pNode);
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode != _pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return l._pNode == _pNode;
}
PNode get()
{
return _pNode;
}
private:
PNode _pNode;
};
//list类
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
public:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef Reverse_ListIterator<T, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef Reverse_ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> reverse_const_iterator;
public:
//默认构造
list()
{ //构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
}
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
//构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
//将元素尾插入
while (n != 0)
{
push_back(value);
--n;
}
}
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
//构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
//将元素尾插入
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{
//构造一个哨兵位结点
CreateHead();
//遍历+将元素尾插入
PNode tmp = l._pHead->_pNext;
while (tmp != l._pHead)
{
push_back(tmp->_val);
tmp = tmp->_pNext;
}
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l)
{
//与临时变量进行交换
swap(l);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
//清空链表
clear();
//删除哨兵位结点
delete _pHead;
_pHead = nullptr;
}
///
// List Iterator
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_pHead->_pNext);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_pHead);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_pHead->_pNext);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(_pHead);
}
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(_pHead);
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(_pHead ->_pNext);
}
reverse_const_iterator rbegin() const
{
return reverse_const_iterator(_pHead);
}
reverse_const_iterator rend()const
{
return reverse_const_iterator(_pHead->_pNext);
}
///
// List Capacity
size_t size()const
{
PNode tmp = _pHead->_pNext;
size_t count = 0;
while (tmp != _pHead)
{
tmp = tmp->_pNext;
++count;
}
return count;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _pHead == _pHead->_pNext;
}
// List Access
T& front()
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pNext->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pNext->_val;
}
T& back()
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pPre->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{
assert(!empty());
return _pHead->_pPre->_val;
}
// List Modify
void push_back(const T & val) { insert(end(), val); }
void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }
void push_front(const T & val) { insert(begin(), val); }
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T & val)
{
//创造一个结点
PNode tmp = new Node(val);
//获取迭代器中的指针
PNode _pos = pos.get();
//进行插入
PNode prv = _pos->_pPre;
prv->_pNext = tmp;
tmp->_pPre = prv;
tmp->_pNext = _pos;
_pos->_pPre = tmp;
//返回新迭代器
return iterator(tmp);
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
//判断是否为哨兵位结点
iterator it = end();
assert(pos != it);
//获取迭代器结点指针
PNode tmp = pos.get();
//进行删除
PNode next = tmp->_pNext;
PNode prv = tmp->_pPre;
prv->_pNext = next;
next->_pPre = prv;
delete tmp;
tmp = nullptr;
//返回被删除结点的下一个位置的结点迭代器
return iterator(next);
}
void clear()
{
//保存有效结点位置
PNode tmp = _pHead->_pNext;
//遍历删除
while (tmp != _pHead)
{
PNode p = tmp->_pNext;
delete tmp;
tmp = p;
}
//重新指向
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
}
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);
}
private:
//让哨兵位结点指向自己
void CreateHead()
{
_pHead = new Node;
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
}
PNode _pHead; //哨兵位结点
};
};






![[数据集][目标检测]叶子计数检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式240张1类别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fa8b709df1d244a4b03111351d73f050.png)






