目录
0、项目介绍
1、效果展示
2、项目搭建
3、项目代码展示
HandTrackingModule.py
VirtualMouse.py
4、项目资源
5、项目总结
0、项目介绍
在Opencv项目实战:15 手势缩放图片中,我们搭建了HandTrackingModule模块,但在这里你还得用本节的HandTrackingModule,因为有些功能并不需要,且也是分散了一些函数的功能。
在这一节中,我的想法是通过点单个食指控制move,双指合并控制click,这样就能够实现手势控制鼠标。
1、效果展示
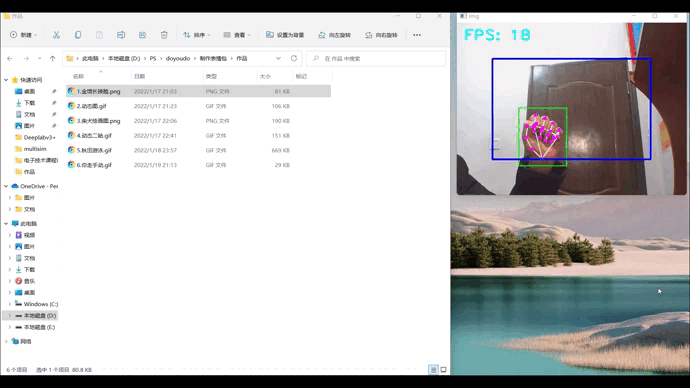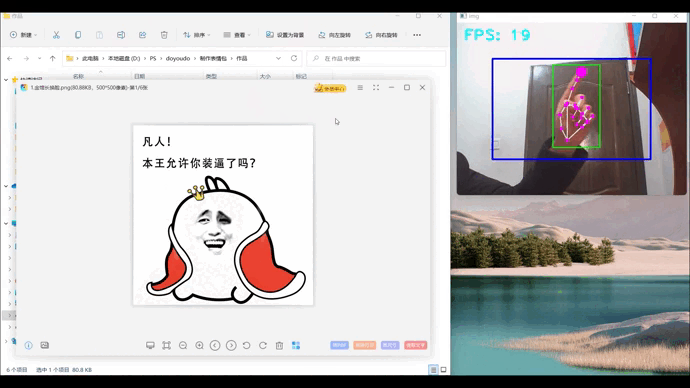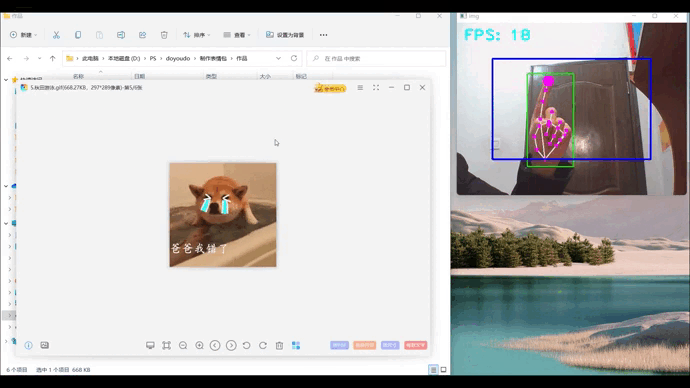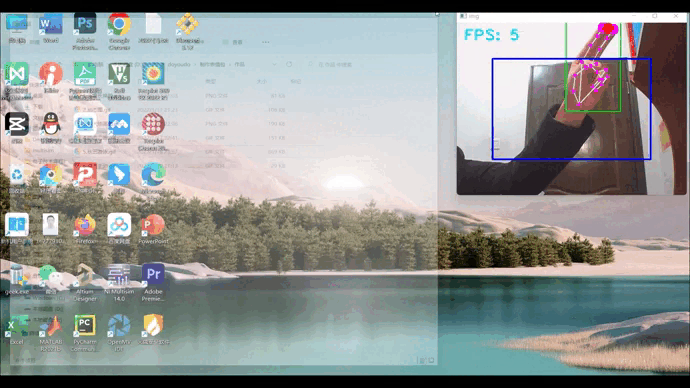
2、项目搭建
简单来说,并没有上面需要添加的,只是在此之前你需要下载autopy:
pip install autopy
3、项目代码展示
HandTrackingModule.py
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import math
import time
class handDetector:
def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5):
self.mode = mode
self.maxHands = maxHands
self.detectionCon = detectionCon
self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon
self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(static_image_mode=self.mode, max_num_hands=self.maxHands,
min_detection_confidence=self.detectionCon,
min_tracking_confidence=self.minTrackCon)
self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20]
self.fingers = []
self.lmList = []
def findHands(self, img, draw=True):
imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB)
# print(results.multi_hand_landmarks)
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if draw:
self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms,
self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return img
def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True):
self.lmList=[]
bbox = 0
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo]
xList = []
yList = []
for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark):
# print(id, lm)
h, w, c = img.shape
cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
xList.append(cx)
yList.append(cy)
# print(id, cx, cy)
self.lmList.append([id, cx, cy])
if draw:
cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList)
ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList)
bbox = xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
if draw:
cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin - 20, ymin - 20), (xmax + 20, ymax + 20),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
return self.lmList, bbox
def fingersUp(self):
fingers = []
# Thumb
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][1] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][1]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
# Fingers
for id in range(1, 5):
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][2] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][2]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
# totalFingers = fingers.count(1)
return fingers
def findDistance(self, p1, p2, img=None):
x1, y1 = self.lmList[p1][1:]
x2, y2 = self.lmList[p2][1:]
cx, cy = (x1 + x2) // 2, (y1 + y2) // 2
length = math.hypot(x2 - x1, y2 - y1)
info = (x1, y1, x2, y2, cx, cy)
if img is not None:
cv2.circle(img, (x1, y1), 15, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
cv2.circle(img, (x2, y2), 15, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 15, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
return length, info, img
else:
return length, info
def main():
pTime = 0
cTime = 0
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
detector = handDetector()
while True:
success, img = cap.read()
img = detector.findHands(img)
lmList, bbox = detector.findPosition(img)
if len(lmList) != 0:
print(lmList[4])
cTime = time.time()
fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime)
pTime = cTime
cv2.putText(img, str(int(fps)), (10, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(255, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
k=cv2.waitKey(1)
if k==27:
break
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
VirtualMouse.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
import autopy
import HandTrackingModule as htm
class fpsReader():
def __init__(self):
self.pTime = time.time()
def FPS(self,img=None,pos=(20, 50), color=(255, 255, 0), scale=3, thickness=3):
cTime = time.time()
try:
fps = 1 / (cTime - self.pTime)
self.pTime = cTime
if img is None:
return fps
else:
cv2.putText(img, f'FPS: {int(fps)}', pos, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,
scale, color, thickness)
return fps, img
except:
return 0
fpsReader = fpsReader()
cap=cv2.VideoCapture(0)
smooth=6
clocx,plocx=0,0
clocy,plocy=0,0
Boundary=100
Wcam, Hcam=640,480
Wscr, Hscr=autopy.screen.size()
# print(Wscr,Hscr)
#1536.0 864.0
cap.set(3,Wcam)
cap.set(4,Hcam)
detector=htm.handDetector(maxHands=1, detectionCon=0.65)
while True:
_, img=cap.read()
img=detector.findHands(img, draw=True)
lmList,bbox=detector.findPosition(img)
if len(lmList)!=0:
x1,y1=lmList[8][1:]
x2,y2=lmList[12][1:]
fingersUp=detector.fingersUp()
# print(fingersUp)
cv2.rectangle(img,(Boundary,Boundary),(Wcam-Boundary,Hcam-Boundary),(255,0,0),thickness=3)
if fingersUp[1]==1 and fingersUp[2]==0:
x3 = np.interp(x1, (0, Wcam), (0, Wscr))
y3 = np.interp(y1, (0, Hcam), (0, Hscr))
clocx=plocx+(x3-plocx)/smooth
clocy = plocy + (y3 - plocy) / smooth
autopy.mouse.move(Wscr-clocx,clocy)
cv2.circle(img,(x1,y1),15,(255,0,255),cv2.FILLED)
plocx,plocy=clocx,clocy
if fingersUp[1] == 1 and fingersUp[2] == 1:
length, info, img=detector.findDistance(8,12,img)
# print(length) 30可能是一个不错的范围
if length<30:
cv2.circle(img,(info[-2],info[-1]),15,(0,0,255),cv2.FILLED)
autopy.mouse.click()
new_window = cv2.flip(img, 1)
fps, img = fpsReader.FPS(new_window)
cv2.imshow("img",img)
k=cv2.waitKey(1)
if k==27:
break
几个重要的参数讲解:
- fpsReader()类,以后就不用再重新打印帧率,可以直接调用;
- Wscr, Hscr=autopy.screen.size(),用于查看自己屏幕的尺寸,设备各有不同;
- smooth,用于设置手势与鼠标之间的平滑程度;
- new_window,完成镜像翻转,使手势移动方向与鼠标移动方向一致;
- info = (x1, y1, x2, y2, cx, cy),取得-1,-2就是指中心值;
- length,为findDistance()返回的参数,需要打印出来,观察一个合适的值。
4、项目资源
GitHub:Opencv项目实战:19 Virtual Mouse
5、项目总结
本次项目通过autopy,HandTrackingModule制作了本次项目虚拟鼠标,在最后的展示当中也能看到窗口的帧率适合,手指控制鼠标比较的平滑,基本的功能很好的实现了。
![[Linux]进程地址空间](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/980719c3338f4eea8c90e2219186019e.png)



![[Ext JS] Grid Summary(汇总行)特性](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/84b3bd4a876044b38e9bb7295068504d.png)