目录
一、模板
1.1类型模板
1.2非类型模板
二、STL
2.1链表实现
2.2迭代器
2.3STL容器
2.4STL算法
三、模板特化的匹配规则
(1) 类模板的匹配规则
(2) 函数模板的匹配规则
一、模板
1.1类型模板

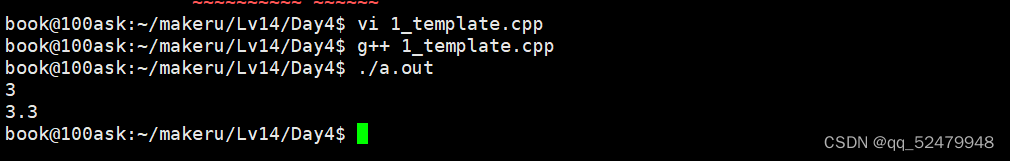
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#if 1
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
double add(double a, double b)
{
return a+b;
}
#else
template<typename XXX>
XXX add(XXX a, XXX b)
{
return a+b;
}
#endif
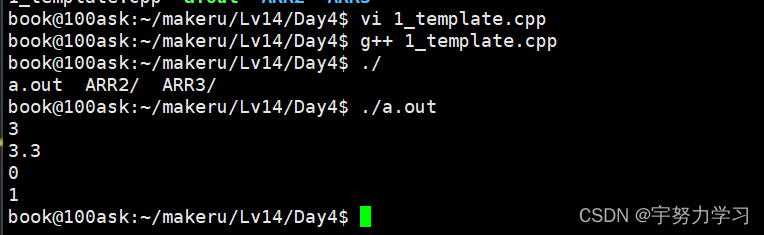
int main()
{
cout << add(1,2) << endl;
cout << add(1.1,2.2) << endl;
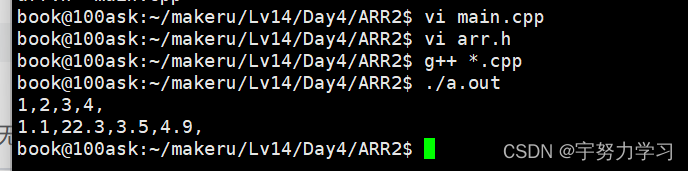
}arr.c >> arr.h :将前面的文件追加到后面的文件的尾巴上
#ifndef _ARR_
#define _ARR_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename XXX>
class ARR{
public:
ARR():tail(0){
}
void addtail(XXX data);
void show(void);
private:
XXX data[100];
int tail;
};
template <typename XXX>
void ARR<XXX>::addtail(XXX data)
{
this->data[tail++] = data;
}
template <typename XXX>
void ARR<XXX>::show(void)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<tail; i++)
cout<< data[i] <<',';
cout<<endl;
}
#endif
template <typename XXX>每次使用都要写一次
#include "arr.h"
int main()
{
ARR<int> arr;
arr.addtail(1);
arr.addtail(2);
arr.addtail(3);
arr.addtail(4);
arr.show();
ARR<double> arr1;
arr1.addtail(1.1);
arr1.addtail(22.3);
arr1.addtail(3.5);
arr1.addtail(4.9);
arr1.show();
}
1.2非类型模板

#define _ARR_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename XXX, int SIZE>
class ARR{
public:
ARR():tail(0){
}
void addtail(XXX data);
void show(void);
private:
XXX data[SIZE];
int tail;
};
template <typename XXX, int SIZE>
void ARR<XXX, SIZE>::addtail(XXX data)
{
this->data[tail++] = data;
}
template <typename XXX, int SIZE>
void ARR<XXX, SIZE>::show(void)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<tail; i++)
cout<< data[i] <<',';
cout<<endl;
}
#endif
#include "arr.h"
int main()
{
ARR<int, 100> arr;
arr.addtail(1);
arr.addtail(2);
arr.addtail(3);
arr.addtail(4);
arr.show();
ARR<double, 1000> arr1;
arr1.addtail(1.1);
arr1.addtail(22.3);
arr1.addtail(3.5);
arr1.addtail(4.9);
arr1.show();
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#if 0
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
double add(double a, double b)
{
return a+b;
}
#else
template<typename XXX>
XXX add(XXX a, XXX b)
{
return a+b;
}
#endif
template<>
bool add(bool a, bool b)
{
if (a == true && b == true)
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
cout << add(1,2) << endl;
cout << add(1.1,2.2) << endl;
cout << add(true, false) <<endl;
cout << add(true, true) <<endl;
}
二、STL
2.1链表实现
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
class myList{
struct Node{
Node(int x, Node *ptr=NULL):data(x), next(ptr) { }
int data;
Node *next;
};
public:
myList():head(NULL) { }
~myList() {
while(head)
{
Node *tem = head;
head = head->next;
delete tem;
}
}
void insert_head(int data)
{
Node *node = new Node(data);
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const myList &list);
private:
Node *head;
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const myList &list)
{
myList::Node *tem = list.head;
while(tem)
{
out<< tem->data <<',';
tem = tem->next;
}
out << endl;
return out;
}
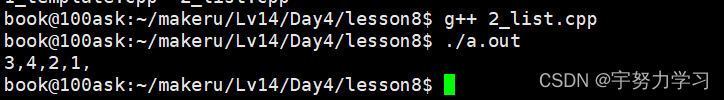
int main()
{
myList list;
list.insert_head(1);
list.insert_head(2);
list.insert_head(4);
list.insert_head(3);
cout << list;
}
2.2迭代器
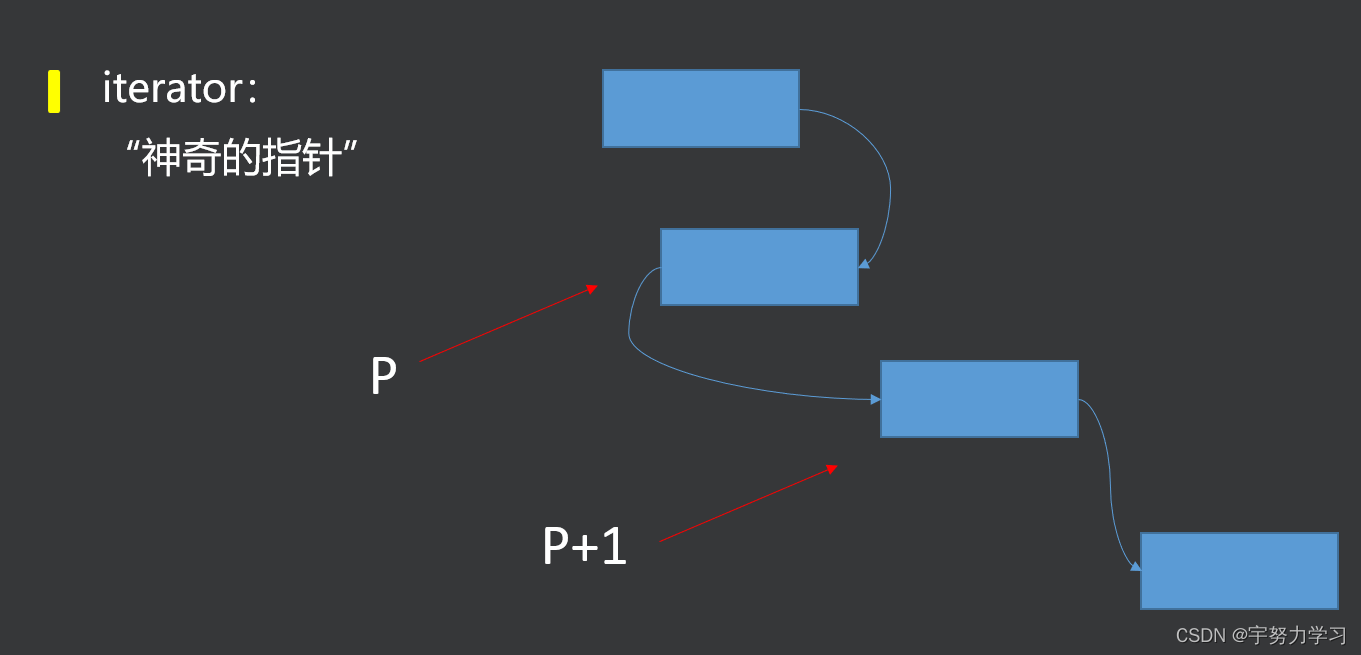
C++迭代器(STL迭代器)iterator详解
百度百科-验证
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
class myList{
struct Node{
Node(int x, Node *ptr=NULL):data(x), next(ptr) { }
int data;
Node *next;
};
public:
class iterator{
public:
iterator(Node *ptr=NULL):pos(ptr) { }
iterator &operator++(int)
{
if(NULL != pos)
pos = pos->next;
return *this;
}
int &operator*()
{
return pos->data;
}
bool operator!=(iterator x)
{
return pos != x.pos;
}
private:
Node *pos;
};
public:
myList():head(NULL) { }
~myList() {
while(head)
{
Node *tem = head;
head = head->next;
delete tem;
}
}
void insert_head(int data)
{
Node *node = new Node(data);
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(head);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(NULL);
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const myList &list);
private:
Node *head;
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const myList &list)
{
myList::Node *tem = list.head;
while(tem)
{
out<< tem->data <<',';
tem = tem->next;
}
out << endl;
return out;
}
int main()
{
myList list;
list.insert_head(1);
list.insert_head(2);
list.insert_head(4);
list.insert_head(3);
cout << list;
myList::iterator i = list.begin();
while(i != list.end() )
{
cout << *i <<endl;
i++;
}
}
2.3STL容器

我们把前面迭代器链表模板化一下:
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class myList{
struct Node{
Node(T x, Node *ptr=NULL):data(x), next(ptr) { }
T data;
Node *next;
};
public:
class iterator{
public:
iterator(Node *ptr=NULL):pos(ptr) { }
iterator &operator++(int)
{
if(NULL != pos)
pos = pos->next;
return *this;
}
int &operator*()
{
return pos->data;
}
bool operator!=(iterator x)
{
return pos != x.pos;
}
private:
Node *pos;
};
public:
myList():head(NULL) { }
~myList() {
while(head)
{
Node *tem = head;
head = head->next;
delete tem;
}
}
void insert_head(T data)
{
Node *node = new Node(data);
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(head);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(NULL);
}
template <typename X>
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const myList<X> &list);
private:
Node *head;
};
template <typename X>
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const myList<X> &list)
{
typename myList<X>::Node *tem = list.head;
while(tem)
{
out<< tem->data <<',';
tem = tem->next;
}
out << endl;
return out;
}
int main()
{
myList<int> list;
list.insert_head(1);
list.insert_head(2);
list.insert_head(4);
list.insert_head(3);
cout << list;
myList<int>::iterator i = list.begin();
while(i != list.end() )
{
cout << *i <<endl;
i++;
}
} 






举个例子vector
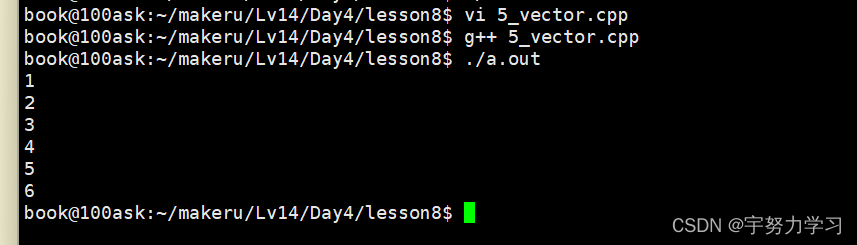
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
#if 1
vector<int> arr;
arr.push_back(1);
arr.push_back(2);
arr.push_back(3);
arr.push_back(4);
arr.push_back(5);
arr.push_back(6);
#endif
vector<int>::iterator i = arr.begin();
while(i != arr.end() )
{
cout << *i << endl;
i++;
}
}
如果是个double类型
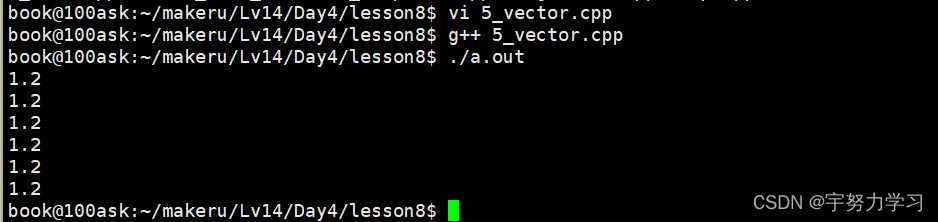
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
#if 0
vector<int> arr;
arr.push_back(1);
arr.push_back(2);
arr.push_back(3);
arr.push_back(4);
arr.push_back(5);
arr.push_back(6);
#else
vector<double> arr;
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
#endif
// vector<int>::iterator i = arr.begin();
vector<double>::iterator i = arr.begin();
while(i != arr.end() )
{
cout << *i << endl;
i++;
}
}
把vector和list结合
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
#if 0
vector<int> arr;
arr.push_back(1);
arr.push_back(2);
arr.push_back(3);
arr.push_back(4);
arr.push_back(5);
#endif
// vector<double> arr;
list<double> arr;
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
arr.push_back(1.2);
// vector<int>::iterator i = arr.begin();
// vector<double>::iterator i = arr.begin();
list<double>::iterator i = arr.begin();
while(i != arr.end() )
{
cout<< *i <<endl;
i++;
}
}map:
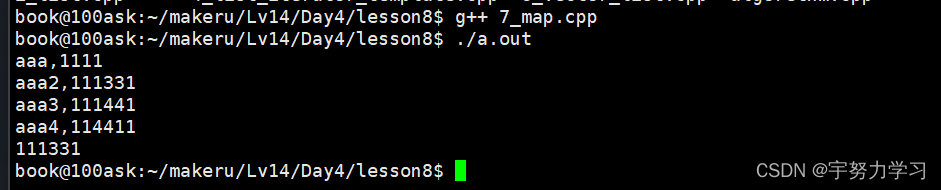
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> user_passwd;
user_passwd.insert(user_passwd.begin(), pair<string, string>("aaa", "1111") );
user_passwd.insert(user_passwd.begin(), pair<string, string>("aaa4", "114411") );
user_passwd.insert(user_passwd.begin(), pair<string, string>("aaa2", "111331") );
user_passwd.insert(user_passwd.begin(), pair<string, string>("aaa3", "111441") );
map<string, string>::iterator i = user_passwd.begin();
while(i != user_passwd.end())
{
cout<< (*i).first<< ',' <<(*i).second <<endl;
i++;
}
cout<< user_passwd["aaa2"] << endl;
}
2.4STL算法

#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a>b;
}
void show(int data)
{
cout<< data<< endl;
}
bool fcmp(int data)
{
return data == 34;
}
int main()
{
//vector<int> arr;
int arr[] = {1,1234,23,4,23,42,34,23,42,34,2,2,2,444,22};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
int *p = find_if(arr, arr+n, fcmp);
if(p != arr+n)
cout<<"got it !\n";
cout <<"num of 34: "<< count_if(arr, arr+n, fcmp) << endl;
/*
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout <<arr[i]<<',';
cout<<endl;
*/
for_each(arr, arr+n, show);
sort(arr, arr+n);
// sort(arr, arr+n, cmp);
cout<<"xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n";
unique(arr, arr+n);
for_each(arr, arr+n, show);
/*
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout <<arr[i]<<',';
cout<<endl;
*/
}
三、模板特化的匹配规则
(1) 类模板的匹配规则
最优化的优于次特化的,即模板参数最精确匹配的具有最高的优先权
例子:
template <class T> class vector{//…//}; // (a) 普通型
template <class T> class vector<T*>{//…//}; // (b) 对指针类型特化
template <> class vector <void*>{//…//}; // (c) 对void*进行特化
每个类型都可以用作普通型(a)的参数,但只有指针类型才能用作(b)的参数,而只有void*才能作为(c)的参数
(2) 函数模板的匹配规则
非模板函数具有最高的优先权。如果不存在匹配的非模板函数的话,那么最匹配的和最特化的函数具有高优先权
例子:
template <class T> void f(T); // (d)
template <class T> void f(int, T, double); // (e)
template <class T> void f(T*); // (f)
template <> void f<int> (int) ; // (g)
void f(double); // (h)
bool b;
int i;
double d;
f(b); // 以 T = bool 调用 (d)
f(i,42,d) // 以 T = int 调用(e)
f(&i) ; // 以 T = int* 调用(f)
f(d); // 调用(g)
参考文献
[1] Bjarne Stroustrup, The C++ Programming Language (Special Edition), Addison Wesley,2000
[2] Nicolai M.Josuttis, The C++ Standard Library – A Tutorial and Reference ,Addison Wesley,1999
[3] Stanley Lippman and Josée Lajoie ,C++ Primier, 3rd Edition ,Addison Wesley Longman ,1998
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
最近有点沉迷看书有几句话感觉很有道理记录一下:
想要保持人格独立,就必须经济独立,哪怕只是独立一部分,也能过的很从容,下班以后可以干干兼职,可以做做小生意,可以考考证,我觉得这都是非常积极的状态,不要嫌少,积少成多,机会是留给有准备的人的~~
“人是很复杂的东西,不管遇见谁,都是一场修炼,只有保持自我,才能享受人生!”
感情就是合适的时间遇上了合适的人,这其中,关键还是合适的时间,这个真没什么遗憾的,因为人生很长,合适的人会有很多,总有一个人在合适的节点等着跟你相遇~~”
制度这种东西,尤其是专业性很强的制度,搞的人字斟句酌费时费力,懂的人视若珍宝,不懂的人,就当是一堆废纸,感觉通篇都是毫无意义的空话套话。这就是人和人的差别,有些人总能保持热忱,不管周围的人怎么叽叽喳喳,一直知道自己想要的是什么,秉承艺不压身的理念,既来之则安之,既安之则多学点东西,就算学不到什么,长长见识也是好的。有些人总是在抱怨,很少真正静下来心来权衡利弊,很多时候其实就是在随大流,别人抱怨我也抱怨,别人有可能只是嘴花花,只有你自己当了真,各种自以为是,各种抨击别人傻乎乎,看着身边人一个个高升,最终也没意识到,其实小丑只是自己。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------