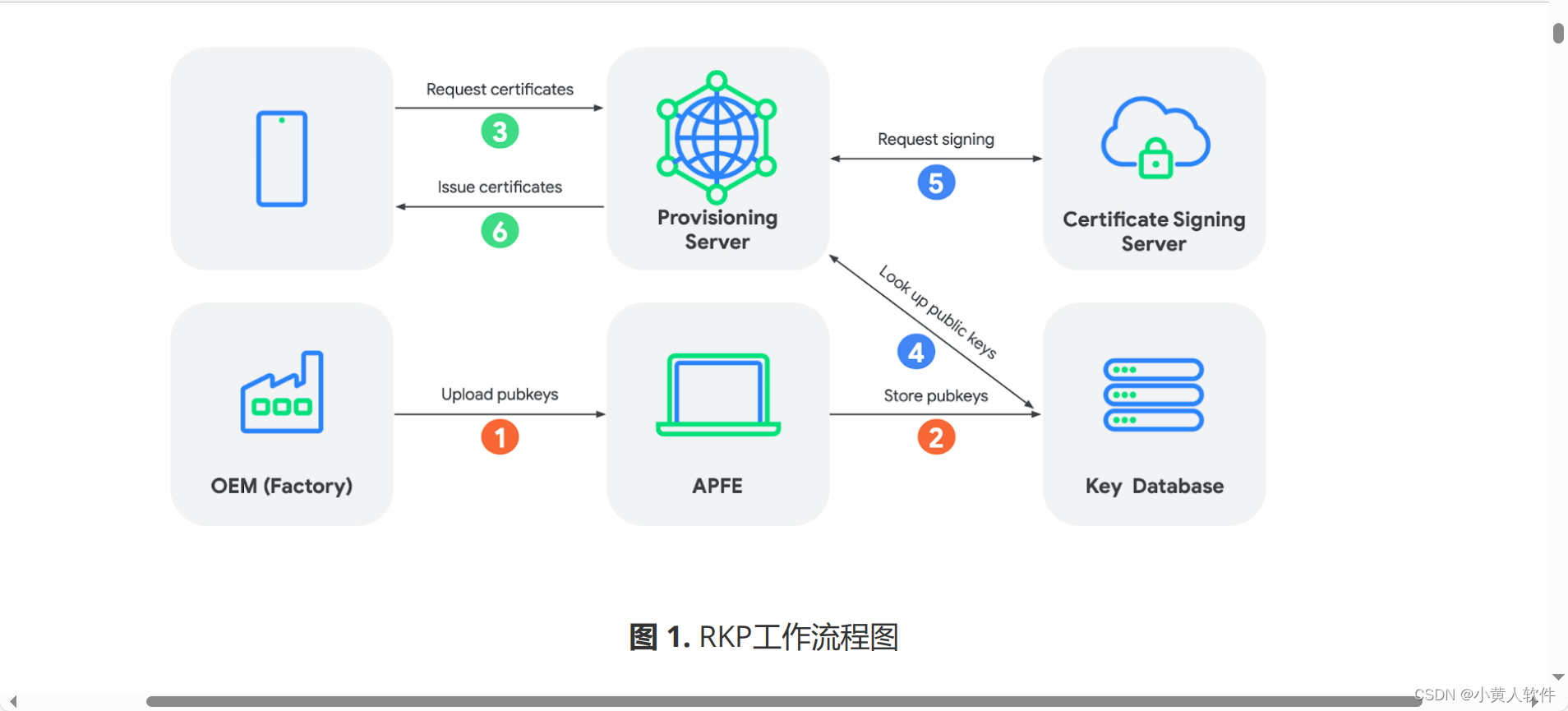
任务描述
本周任务,将模型进行封装,实现模型推理的基本API,从而可以根据输入数据输出蒙版数据。
模型输入数据处理
首先进行模型输入数据的预处理。首先支持点击和框选两种模式,所以这里需要对这两种模式进行适配。
modelData函数接收一个关于用户点击或者框选操作的输入,以及一个此前的推理结果(sam模型要求提供一个上次的推理结果)。
然后我们首先判断框选类型。
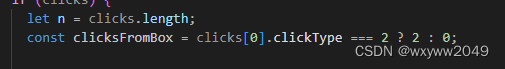
这里如果clickType为2那么说明是框选,否则是点击。
如果是框选的话,我们需要计算出模型的左上角和右下角坐标。
if (clicksFromBox) {
// For box model need to include the box clicks in the point
pointCoords = new Float32Array(2 * (n + clicksFromBox));
pointLabels = new Float32Array(n + clicksFromBox);
const {
upperLeft,
bottomRight,
}: {
upperLeft: { x: number; y: number };
bottomRight: { x: number; y: number };
} = getPointsFromBox(clicks[0])!;
pointCoords = new Float32Array(2 * (n + clicksFromBox));
pointLabels = new Float32Array(n + clicksFromBox);
pointCoords[0] = upperLeft.x / modelScale.onnxScale;
pointCoords[1] = upperLeft.y / modelScale.onnxScale;
pointLabels[0] = 2.0; // UPPER_LEFT
pointCoords[2] = bottomRight.x / modelScale.onnxScale;
pointCoords[3] = bottomRight.y / modelScale.onnxScale;
pointLabels[1] = 3.0; // BOTTOM_RIGHT
last_pred_mask = null;
}
如果是点击的话,我们需要知道所有的点击点,这里我们用一个clicks数组来保存每个点击操作的坐标。然后将所有的点击添加到最终输入给模型的pointCoords数组。
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pointCoords[2 * (i + clicksFromBox)] = clicks[i].x / modelScale.onnxScale;
pointCoords[2 * (i + clicksFromBox) + 1] =
clicks[i].y / modelScale.onnxScale;
pointLabels[i + clicksFromBox] = clicks[i].clickType;
}
if (!clicksFromBox) {
pointCoords[2 * n] = 0.0;
pointCoords[2 * n + 1] = 0.0;
pointLabels[n] = -1.0;
// update n for creating the tensor
n = n + 1;
}
这里pointlabels直接根据click的type来判断就行,-1就是反点(不选的点),1就是被选择的点。
然后根据需要将数据转换成Tensor,最后得到了模型需要的输入。
pointCoordsTensor = new Tensor("float32", pointCoords, [
1,
n + clicksFromBox,
2,
]);
pointLabelsTensor = new Tensor("float32", pointLabels, [
1,
n + clicksFromBox,
]);
}
const imageSizeTensor = new Tensor("float32", [
modelScale.maskHeight,
modelScale.maskWidth,
]);
if (pointCoordsTensor === undefined || pointLabelsTensor === undefined)
return;
const lastPredMaskTensor =
last_pred_mask && clicks && !isFirstClick(clicks)
? last_pred_mask
: new Tensor("float32", new Float32Array(256 * 256), [1, 1, 256, 256]);
const hasLastPredTensor = new Tensor("float32", [
+!!(last_pred_mask && clicks && !isFirstClick(clicks)),
]);
模型运行与蒙版生成
const feeds = modelData({
clicks,
tensor,
modelScale,
last_pred_mask: predMask,
});
if (feeds === undefined) return;
const results = await model.run(feeds);
const output = results[model.outputNames[0]];
if (hasClicked) {
const pred_mask = results[model.outputNames[1]];
setPredMask(pred_mask);
if (!predMasksHistory) {
setPredMasks([...(predMasks || []), pred_mask]);
}
const svgStr = traceOnnxMaskToSVG(
output.data,
output.dims[1],
output.dims[0]
);
setSVG(svgStr);
setMask(output.data);
}
使用刚才编写modelData来生成一个模型输入需要的数据feeds之后,使用model.run方法来执行推理,最终的推理结果将转换成svg蒙在原图之上,形成一种被选中的“错觉”。