文章目录
- 队列
- 双端队列 deque
- 底层存储
- deque接口
- 1. `__init__(self, iterable: Iterable[_T], maxlen: int | None = None) -> None`
- 2. `append(self, __x: _T) -> None`
- 3. `appendleft(self, __x: _T) -> None`
- 4. `copy(self) -> Self`
- 5. `count(self, __x: _T) -> int`
- 6. `extend(self, __iterable: Iterable[_T]) -> None`
- 7. `extendleft(self, __iterable: Iterable[_T]) -> None`
- 8. `insert(self, __i: int, __x: _T) -> None`
- 9. `index(self, __x: _T, __start: int = 0, __stop: int = ...) -> int`
- 10. `pop(self) -> _T`
- 11. `popleft(self) -> _T`
- 12. `remove(self, __value: _T) -> None`
- 13. `rotate(self, __n: int = 1) -> None`
- 线程安全队列Queue
- 属性
- 方法
- `__init__(self, maxsize: int = 0) -> None`
- `_init(self, maxsize: int) -> None`
- `empty(self) -> bool`
- `full(self) -> bool`
- `get(self, block: bool = True, timeout: float | None = None) -> _T`
- `get_nowait(self) -> _T`
- `_get(self) -> _T`
- `put(self, item: _T, block: bool = True, timeout: float | None = None) -> None`
- `put_nowait(self, item: _T) -> None`
- `_put(self, item: _T) -> None`
- `join(self) -> None`
- `qsize(self) -> int`
- `_qsize(self) -> int`
- `task_done(self) -> None`
- 线程安全优先级队列
- 线程安全——栈
- 线程安全的简单的队列——SimpleQueue
队列
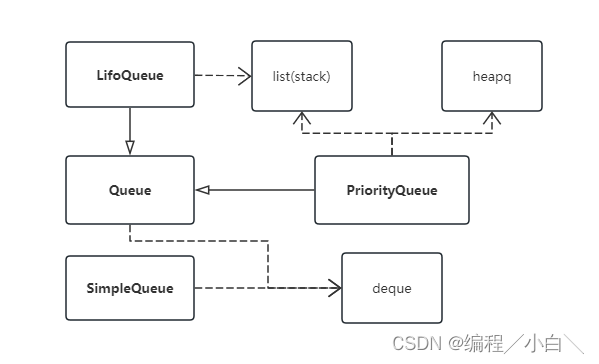
在python有以下几种队列
- deque 双端队列
- Queue 队列 FIFO
- LifoQueue 栈 LIFO
- PriorityQueue 优先队列
- SimpleQueue 简单队列 FIFO
除了deque,其他都有一个共同的特点——线程安全
双端队列 deque
由于python中的队列是基于双端队列来实现的,所以我们先查看deque的实现,如果你通过pycharm去追溯deque的源代码,你会发现里面只有类的定义并没有具体的实现,其代码如下:
class deque(MutableSequence[_T], Generic[_T]):
@property
def maxlen(self) -> int | None: ...
@overload
def __init__(self, *, maxlen: int | None = None) -> None: ...
@overload
def __init__(self, iterable: Iterable[_T], maxlen: int | None = None) -> None: ...
def append(self, __x: _T) -> None: ...
def appendleft(self, __x: _T) -> None: ...
def copy(self) -> Self: ...
def count(self, __x: _T) -> int: ...
def extend(self, __iterable: Iterable[_T]) -> None: ...
def extendleft(self, __iterable: Iterable[_T]) -> None: ...
def insert(self, __i: int, __x: _T) -> None: ...
def index(self, __x: _T, __start: int = 0, __stop: int = ...) -> int: ...
def pop(self) -> _T: ... # type: ignore[override]
def popleft(self) -> _T: ...
def remove(self, __value: _T) -> None: ...
def rotate(self, __n: int = 1) -> None: ...
def __copy__(self) -> Self: ...
def __len__(self) -> int: ...
# These methods of deque don't take slices, unlike MutableSequence, hence the type: ignores
def __getitem__(self, __key: SupportsIndex) -> _T: ... # type: ignore[override]
def __setitem__(self, __key: SupportsIndex, __value: _T) -> None: ... # type: ignore[override]
def __delitem__(self, __key: SupportsIndex) -> None: ... # type: ignore[override]
def __contains__(self, __key: object) -> bool: ...
def __reduce__(self) -> tuple[type[Self], tuple[()], None, Iterator[_T]]: ...
def __iadd__(self, __value: Iterable[_T]) -> Self: ...
def __add__(self, __value: Self) -> Self: ...
def __mul__(self, __value: int) -> Self: ...
def __imul__(self, __value: int) -> Self: ...
def __lt__(self, __value: deque[_T]) -> bool: ...
def __le__(self, __value: deque[_T]) -> bool: ...
def __gt__(self, __value: deque[_T]) -> bool: ...
def __ge__(self, __value: deque[_T]) -> bool: ...
def __eq__(self, __value: object) -> bool: ...
if sys.version_info >= (3, 9):
def __class_getitem__(cls, __item: Any) -> GenericAlias: ...
底层存储
这说明其底层并不是由python写的,而是由效率更高的c语言的结构体实现,让我们大致浏览一下python的deque的底层实现:
在python的gihub仓库中,我门可以从cpython(cpython/Modules/_collectionsmodule.c)中找到deque的踪迹
#define BLOCKLEN 64
#define CENTER ((BLOCKLEN - 1) / 2)
#define MAXFREEBLOCKS 16
typedef struct BLOCK {
struct BLOCK *leftlink;
PyObject *data[BLOCKLEN];
struct BLOCK *rightlink;
} block;
typedef struct {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
block *leftblock;
block *rightblock;
Py_ssize_t leftindex; /* 0 <= leftindex < BLOCKLEN */
Py_ssize_t rightindex; /* 0 <= rightindex < BLOCKLEN */
size_t state; /* incremented whenever the indices move */
Py_ssize_t maxlen; /* maxlen is -1 for unbounded deques */
Py_ssize_t numfreeblocks;
block *freeblocks[MAXFREEBLOCKS];
PyObject *weakreflist;
} dequeobject;
如果学过数据结构的都知道,双端队列可以由动态数组或双向列表实现
- 如果使用数组实现双端队列,那么当从头结点删除数据时那么需要将后面的数据都要向前移动一格,在大批量数据的情况,从头结点删除的效率就很低,复杂度为
O(n) - 如果使用双向链表实现双端队列,尽管能够解决动态数组从头结点效率低下的问题,但是算向链表会占用额外的空间、且随机访问的复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),此外它具有链表的通病:缓存性能差(非连续存储空间,无法将整个存储块加载到内存,在内存中访问是跳跃式访问,不是连续访问,性能会差很多)
所以python底层选择了折中的方式,即使用链表保证在队头插入元素的高效性,也使用数组提高连续访问的高效能力,从上面的代码看,python的双端队列是一个双向链表块dequeobject,每个块block(BLOCK)是一个64大小的数组data,这样将其性能进行了折中。当然其插入删除的操作也变的更复杂。
deque接口
这些方法和构造函数都是Python标准库中collections.deque类的接口,用于操作双端队列。以下是对每个方法的详细介绍和用法示例:
1. __init__(self, iterable: Iterable[_T], maxlen: int | None = None) -> None
构造函数,用于初始化一个双端队列对象。
参数:
iterable: 可选,初始化队列的可迭代对象。如果提供,该对象的元素会被按顺序添加到队列中。maxlen: 可选,队列的最大长度。如果设置了最大长度,当队列满时,添加新元素会导致旧元素被丢弃。
示例:
>>> from collections import deque
>>> deque()
deque([])
>>> deque([1,2,3])
deque([1, 2, 3])
>>> deque([1,2,3], maxlen=5)
deque([1, 2, 3], maxlen=5)
2. append(self, __x: _T) -> None
在队列的右端添加一个元素。
参数:
__x: 要添加的元素。
示例:
>>> dq = deque([1, 2, 3])
>>> dq.append(4)
>>> dq
deque([1, 2, 3, 4])
3. appendleft(self, __x: _T) -> None
在队列的左端添加一个元素。
参数:
__x: 要添加的元素。
示例:
>>> dq
deque([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> dq.appendleft(0)
>>> dq
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
4. copy(self) -> Self
返回一个双端队列的浅拷贝。
示例:
>>> dq.copy()
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> dq.copy() == dq #判断相等的方法是元素相同
True
>>> dq_copy = dq.copy()
>>> dq_copy.append(5)
>>> dq_copy
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> dq
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
5. count(self, __x: _T) -> int
返回队列中指定元素的出现次数。
参数:
__x: 要计数的元素。
示例:
>>> dq
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> dq.count(1)
1
6. extend(self, __iterable: Iterable[_T]) -> None
在队列的右端扩展一个可迭代对象的所有元素。
参数:
__iterable: 包含要添加元素的可迭代对象。
示例:
>>> dq.extend([3,4,5]) #接收可迭代类型
>>> dq
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5])
7. extendleft(self, __iterable: Iterable[_T]) -> None
在队列的左端扩展一个可迭代对象的所有元素。注意,元素会按相反的顺序添加。
参数:
__iterable: 包含要添加元素的可迭代对象。
示例:
>>> dq
deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5])
>>> dq.extendleft((0,1,2)) # 并不是直接拼接在left,而是反向后拼接的
>>> dq
deque([2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5])
8. insert(self, __i: int, __x: _T) -> None
在指定位置插入一个元素。
参数:
__i: 要插入的位置索引。如果索引超出范围,元素会被插入到队列的两端。__x: 要插入的元素。
示例:
>>> dq
deque([2, 1, 100, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5])
>>> dq.insert(20,100) # 超过的索引直接插在末尾
>>> dq
deque([2, 1, 100, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 100])
>>> dq.insert(-1,200) #支持负数索引
>>> dq
deque([2, 1, 100, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 200, 100])
>>> dq.insert(-20,50)
>>> dq
deque([50, 2, 1, 100, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 200, 100])
9. index(self, __x: _T, __start: int = 0, __stop: int = ...) -> int
返回指定值首次出现的索引。如果没有找到该值,将引发ValueError。
参数:
__x: 要查找的元素。__start: 可选,搜索的起始位置。__stop: 可选,搜索的结束位置。
示例:
>>> dq.index(100)
3
>>> dq.index(100,start=5) # 非关键字参数
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: index() takes no keyword arguments
>>> dq.index(100,5)
14
10. pop(self) -> _T
移除并返回队列右端的元素。如果队列为空,将引发IndexError。
示例:
>>> dq = deque([1, 2, 3])
>>> dq.pop()
3
>>> dq.pop()
2
>>> dq.pop()
1
>>> dq.pop()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: pop from an empty deque
>>>
11. popleft(self) -> _T
移除并返回队列左端的元素。如果队列为空,将引发IndexError。
示例:
>>> dq = deque([1, 2, 3])
>>> dq.popleft()
1
>>> dq.popleft()
2
>>> dq.popleft()
3
>>> dq.popleft()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: pop from an empty deque
>>>
12. remove(self, __value: _T) -> None
移除队列中第一个匹配的元素。如果没有找到该值,将引发ValueError。
参数:
__value: 要移除的元素。
示例:
>>> dq = deque([1, 2, 3,4,3])
>>> dq.remove(3)
>>> dq
deque([1, 2, 4, 3])
>>> dq.remove(0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: deque.remove(x): x not in deque
13. rotate(self, __n: int = 1) -> None
将队列旋转 n 步。如果 n 为正数,元素将从右端移到左端。如果 n 为负数,元素将从左端移到右端。
参数:
__n: 旋转的步数。
示例:
>>> dq = deque([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> dq.rotate(2) #向右旋转
>>> dq
deque([3, 4, 1, 2])
>>> dq.rotate(-1) #向左旋转
>>> dq
deque([4, 1, 2, 3])
这些方法和接口提供了丰富的操作来管理和操作双端队列,适用于需要在两端进行频繁插入和删除操作的数据结构。
线程安全队列Queue
Queue的底层是基于deque实现的,因为Queue的功能是deque中的部分,只要对其进行限制其双端性遵循FIFO就可以使用。下面是Queue的官方代码
class Queue:
'''Create a queue object with a given maximum size.
If maxsize is <= 0, the queue size is infinite.
'''
def __init__(self, maxsize=0):
self.maxsize = maxsize
self._init(maxsize)
# mutex must be held whenever the queue is mutating. All methods
# that acquire mutex must release it before returning. mutex
# is shared between the three conditions, so acquiring and
# releasing the conditions also acquires and releases mutex.
self.mutex = threading.Lock()
# Notify not_empty whenever an item is added to the queue; a
# thread waiting to get is notified then.
self.not_empty = threading.Condition(self.mutex)
# Notify not_full whenever an item is removed from the queue;
# a thread waiting to put is notified then.
self.not_full = threading.Condition(self.mutex)
# Notify all_tasks_done whenever the number of unfinished tasks
# drops to zero; thread waiting to join() is notified to resume
self.all_tasks_done = threading.Condition(self.mutex)
self.unfinished_tasks = 0
def task_done(self):
'''Indicate that a formerly enqueued task is complete.
Used by Queue consumer threads. For each get() used to fetch a task,
a subsequent call to task_done() tells the queue that the processing
on the task is complete.
If a join() is currently blocking, it will resume when all items
have been processed (meaning that a task_done() call was received
for every item that had been put() into the queue).
Raises a ValueError if called more times than there were items
placed in the queue.
'''
with self.all_tasks_done:
unfinished = self.unfinished_tasks - 1
if unfinished <= 0:
if unfinished < 0:
raise ValueError('task_done() called too many times')
self.all_tasks_done.notify_all()
self.unfinished_tasks = unfinished
def join(self):
'''Blocks until all items in the Queue have been gotten and processed.
The count of unfinished tasks goes up whenever an item is added to the
queue. The count goes down whenever a consumer thread calls task_done()
to indicate the item was retrieved and all work on it is complete.
When the count of unfinished tasks drops to zero, join() unblocks.
'''
with self.all_tasks_done:
while self.unfinished_tasks:
self.all_tasks_done.wait()
def qsize(self):
'''Return the approximate size of the queue (not reliable!).'''
with self.mutex:
return self._qsize()
def empty(self):
'''Return True if the queue is empty, False otherwise (not reliable!).
This method is likely to be removed at some point. Use qsize() == 0
as a direct substitute, but be aware that either approach risks a race
condition where a queue can grow before the result of empty() or
qsize() can be used.
To create code that needs to wait for all queued tasks to be
completed, the preferred technique is to use the join() method.
'''
with self.mutex:
return not self._qsize()
def full(self):
'''Return True if the queue is full, False otherwise (not reliable!).
This method is likely to be removed at some point. Use qsize() >= n
as a direct substitute, but be aware that either approach risks a race
condition where a queue can shrink before the result of full() or
qsize() can be used.
'''
with self.mutex:
return 0 < self.maxsize <= self._qsize()
def put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None):
'''Put an item into the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until a free slot is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Full exception if no free slot was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), put an item on the queue if a free slot
is immediately available, else raise the Full exception ('timeout'
is ignored in that case).
'''
with self.not_full:
if self.maxsize > 0:
if not block:
if self._qsize() >= self.maxsize:
raise Full
elif timeout is None:
while self._qsize() >= self.maxsize:
self.not_full.wait()
elif timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
else:
endtime = time() + timeout
while self._qsize() >= self.maxsize:
remaining = endtime - time()
if remaining <= 0.0:
raise Full
self.not_full.wait(remaining)
self._put(item)
self.unfinished_tasks += 1
self.not_empty.notify()
def get(self, block=True, timeout=None):
'''Remove and return an item from the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until an item is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Empty exception if no item was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), return an item if one is immediately
available, else raise the Empty exception ('timeout' is ignored
in that case).
'''
with self.not_empty:
if not block:
if not self._qsize():
raise Empty
elif timeout is None:
while not self._qsize():
self.not_empty.wait()
elif timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
else:
endtime = time() + timeout
while not self._qsize():
remaining = endtime - time()
if remaining <= 0.0:
raise Empty
self.not_empty.wait(remaining)
item = self._get()
self.not_full.notify()
return item
def put_nowait(self, item):
'''Put an item into the queue without blocking.
Only enqueue the item if a free slot is immediately available.
Otherwise raise the Full exception.
'''
return self.put(item, block=False)
def get_nowait(self):
'''Remove and return an item from the queue without blocking.
Only get an item if one is immediately available. Otherwise
raise the Empty exception.
'''
return self.get(block=False)
# Override these methods to implement other queue organizations
# (e.g. stack or priority queue).
# These will only be called with appropriate locks held
# Initialize the queue representation
def _init(self, maxsize):
self.queue = deque()
def _qsize(self):
return len(self.queue)
# Put a new item in the queue
def _put(self, item):
self.queue.append(item)
# Get an item from the queue
def _get(self):
return self.queue.popleft()
__class_getitem__ = classmethod(types.GenericAlias)
其重要体现队列的代码很少,大多数代码都在保证线程安全,如下:
def _init(self, maxsize):
self.queue = deque()
def _qsize(self):
return len(self.queue)
# Put a new item in the queue
def _put(self, item):
self.queue.append(item)
# Get an item from the queue
def _get(self):
return self.queue.popleft()
从上面可以看出,Queue的核心操作get、put都是基于deque实现的
其Queue类的定义如下:
class Queue(Generic[_T]):
maxsize: int
mutex: Lock # undocumented
not_empty: Condition # undocumented
not_full: Condition # undocumented
all_tasks_done: Condition # undocumented
unfinished_tasks: int # undocumented
# Despite the fact that `queue` has `deque` type,
# we treat it as `Any` to allow different implementations in subtypes.
queue: Any # undocumented
def __init__(self, maxsize: int = 0) -> None: ...
def _init(self, maxsize: int) -> None: ...
def empty(self) -> bool: ...
def full(self) -> bool: ...
def get(self, block: bool = True, timeout: float | None = None) -> _T: ...
def get_nowait(self) -> _T: ...
def _get(self) -> _T: ...
def put(self, item: _T, block: bool = True, timeout: float | None = None) -> None: ...
def put_nowait(self, item: _T) -> None: ...
def _put(self, item: _T) -> None: ...
def join(self) -> None: ...
def qsize(self) -> int: ...
def _qsize(self) -> int: ...
def task_done(self) -> None: ...
if sys.version_info >= (3, 9):
def __class_getitem__(cls, item: Any) -> GenericAlias: ...
这些函数和属性是Python标准库中的queue.Queue类的接口。queue.Queue提供了一个线程安全的FIFO(First In, First Out)队列,常用于多线程环境下的任务管理。以下是每个函数和属性的详细介绍及其用法:
属性
-
maxsize: int
队列的最大大小。如果maxsize为 0 或负数,则队列大小没有限制。 -
mutex: Lock
一个锁对象,用于同步队列的访问,确保线程安全。 -
not_empty: Condition
一个条件变量,用于在队列非空时进行通知。 -
not_full: Condition
一个条件变量,用于在队列未满时进行通知。 -
all_tasks_done: Condition
一个条件变量,用于在所有任务完成时进行通知。 -
unfinished_tasks: int
未完成任务的计数。 -
queue: Any
实际存储队列元素的容器,类型可以是任意的。该属性未公开文档。在_init中将其初始化。
方法
__init__(self, maxsize: int = 0) -> None
构造函数,用于初始化一个队列对象。
参数:
maxsize: 队列的最大大小。如果为 0 或负数,则队列大小没有限制。
示例:
from queue import Queue
q = Queue(maxsize=10)
_init(self, maxsize: int) -> None
初始化队列的内部方法。通常由构造函数调用,不直接使用。
参数:
maxsize: 队列的最大大小。
empty(self) -> bool
如果队列为空,返回 True。
示例:
>>> from queue import Queue
>>> q = Queue()
>>> q.empty()
True
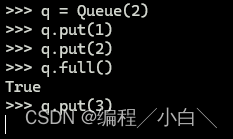
full(self) -> bool
如果队列已满,返回 True。
示例:
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.put(2)
>>> q.full()
True
>>> q.put(3) # 满了之后添加元素会一直等待
get(self, block: bool = True, timeout: float | None = None) -> _T
从队列中移除并返回一个元素。
参数:
block: 如果为True,在队列为空时会阻塞,直到有元素可用。timeout: 阻塞的最大时间(以秒为单位)。如果为None,将一直阻塞直到有元素可用。
示例:
>>> from queue import Queue
>>> q = Queue()
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.put(2)
>>> q
<queue.Queue object at 0x0000020DD481AD30>
>>> list(q) # Queue是不可迭代类型
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'Queue' object is not iterable
>>> print(q)
<queue.Queue object at 0x0000020DD481AD30>
>>> q.get() # FIFO
1
>>> q.get() # LILO
2
get_nowait(self) -> _T
非阻塞地从队列中移除并返回一个元素。如果队列为空,抛出 queue.Empty 异常。
示例:
>>> q = Queue()
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.get_nowait()
1
>>> q.get_nowait() # 不等待会报错 如果使用q.get()会一直等待,直到右元素入队
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "D:\Python\Python36\lib\queue.py", line 192, in get_nowait
return self.get(block=False)
File "D:\Python\Python36\lib\queue.py", line 161, in get
raise Empty
queue.Empty
_get(self) -> _T
内部方法,用于从队列中获取一个元素。通常由 get 方法调用,不直接使用。
put(self, item: _T, block: bool = True, timeout: float | None = None) -> None
将一个元素放入队列。
参数:
item: 要放入队列的元素。block: 如果为True,在队列已满时会阻塞,直到有空间可用。timeout: 阻塞的最大时间(以秒为单位)。如果为None,将一直阻塞直到有空间可用。
示例:
>>> q = Queue(2)
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.put(2)
>>> q.put(3,True,3) # 3秒之后报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "D:\Python\Python36\lib\queue.py", line 141, in put
raise Full
queue.Full
put_nowait(self, item: _T) -> None
非阻塞地将一个元素放入队列。如果队列已满,抛出 queue.Full 异常。
示例:
>>> q = Queue(2)
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.put(2)
>>> q.put_nowait(3) # 立即报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "D:\Python\Python36\lib\queue.py", line 184, in put_nowait
return self.put(item, block=False)
File "D:\Python\Python36\lib\queue.py", line 130, in put
raise Full
queue.Full
_put(self, item: _T) -> None
内部方法,用于将一个元素放入队列。通常由 put 方法调用,不直接使用。
join(self) -> None
阻塞主线程,直到所有的队列项被处理。每次从 get 中获取一个项目后,需要调用 task_done 来表明该项目已经完成处理。
示例:
import threading
import time
from queue import Queue
def worker(q):
while True:
item = q.get()
if item is None:
break
print(f'Processing {item}')
time.sleep(1)
q.task_done()
q = Queue()
thread = threading.Thread(target=worker, args=(q,))
thread.start()
for item in range(5):
q.put(item)
q.join() # 阻塞,直到所有任务完成
q.put(None) # 停止工作线程
thread.join()
qsize(self) -> int
返回队列中的元素数量。
示例:
>>> q = Queue()
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.put(2)
>>> q.qsize()
2
>>> len(q) #并没有实现__len__
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: object of type 'Queue' has no len()
_qsize(self) -> int
内部方法,用于返回队列中的元素数量。通常由 qsize 方法调用,不直接使用。
task_done(self) -> None
表明一个队列中的任务已经完成。在每次从 get 中获取一个项目后调用。
示例:
>>> q = Queue()
>>> q.put(1)
>>> q.get()
1
>>> q.task_done()
线程安全优先级队列
优先级队列继承了Queue对象,其主要是继承了它的线程安全性,其底层存储于deque没有任何关系了,就是数组,插入和弹出都换成了堆的上虑和下虑操作,如果你不知道堆是什么,请看我的另一篇博文图解堆队列算法,这里就不介绍了
class PriorityQueue(Queue):
'''Variant of Queue that retrieves open entries in priority order (lowest first).
Entries are typically tuples of the form: (priority number, data).
'''
def _init(self, maxsize):
self.queue = []
def _qsize(self):
return len(self.queue)
def _put(self, item):
heappush(self.queue, item)
def _get(self):
return heappop(self.queue)
那么PriorityQueue的调用方法是继承了Queue,方法使用时一模一样的。
线程安全——栈
LifoQueue的线程安全也是套壳Queue的,只是将初始化换成数组,get和put换成我们使用的普通的栈的形式,就是直接拿数组作为栈append为入栈,pop为出栈。
class LifoQueue(Queue):
'''Variant of Queue that retrieves most recently added entries first.'''
def _init(self, maxsize):
self.queue = []
def _qsize(self):
return len(self.queue)
def _put(self, item):
self.queue.append(item)
def _get(self):
return self.queue.pop()
那么LifoQueue的调用方法是继承了Queue,方法使用时一模一样的。
线程安全的简单的队列——SimpleQueue
SimpleQueue 是Queue的简化版,他没有了大小限制,但是也是线程安全的,剩余的put、get、put_nowait、get_nowait、empty、qsize操作都相同。
class _PySimpleQueue:
'''Simple, unbounded FIFO queue.
This pure Python implementation is not reentrant.
'''
# Note: while this pure Python version provides fairness
# (by using a threading.Semaphore which is itself fair, being based
# on threading.Condition), fairness is not part of the API contract.
# This allows the C version to use a different implementation.
def __init__(self):
self._queue = deque()
self._count = threading.Semaphore(0)
def put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None):
'''Put the item on the queue.
The optional 'block' and 'timeout' arguments are ignored, as this method
never blocks. They are provided for compatibility with the Queue class.
'''
self._queue.append(item)
self._count.release()
def get(self, block=True, timeout=None):
'''Remove and return an item from the queue.
If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default),
block if necessary until an item is available. If 'timeout' is
a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises
the Empty exception if no item was available within that time.
Otherwise ('block' is false), return an item if one is immediately
available, else raise the Empty exception ('timeout' is ignored
in that case).
'''
if timeout is not None and timeout < 0:
raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number")
if not self._count.acquire(block, timeout):
raise Empty
return self._queue.popleft()
def put_nowait(self, item):
'''Put an item into the queue without blocking.
This is exactly equivalent to `put(item, block=False)` and is only provided
for compatibility with the Queue class.
'''
return self.put(item, block=False)
def get_nowait(self):
'''Remove and return an item from the queue without blocking.
Only get an item if one is immediately available. Otherwise
raise the Empty exception.
'''
return self.get(block=False)
def empty(self):
'''Return True if the queue is empty, False otherwise (not reliable!).'''
return len(self._queue) == 0
def qsize(self):
'''Return the approximate size of the queue (not reliable!).'''
return len(self._queue)
__class_getitem__ = classmethod(types.GenericAlias)
if SimpleQueue is None:
SimpleQueue = _PySimpleQueue