更好的阅读体验
CF249D - Donkey and Stars
Description
给定 n n n 个点 ( x i , y i ) (x_i,y_i) (xi,yi) 和 a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d,求出最多有多少个点依次连接而成的折线上线段的斜率在 ( a b , c d ) (\frac{a}{b},\frac{c}{d}) (ba,dc),其中第 1 1 1 条折线的起点必须在坐标原点且坐标原点不计入答案。
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 , 0 ≤ a , b , c , d ≤ 1 0 5 , 1 ≤ x i , y i ≤ 1 0 5 1\le n\le 10^5,0\le a,b,c,d\le 10^5,1\le x_i,y_i\le 10^5 1≤n≤105,0≤a,b,c,d≤105,1≤xi,yi≤105
Solution
不难想到通过 DP 来求解,暴力 DP 时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2),必然是过不去的。所以,考虑对于点 i i i,能够与 i i i 连线的点 j j j 应满足哪些性质?
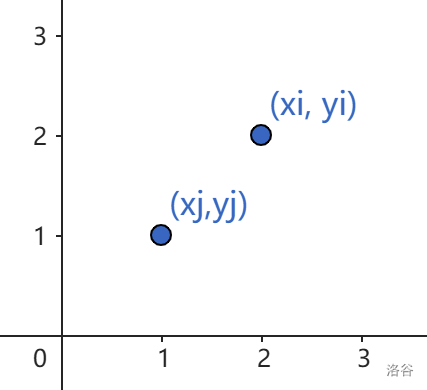
令 i i i 点位于 j j j 点的右上方,则有 a b < y i − y j x i − x j < c d \frac{a}{b}< \frac{y_i-y_j}{x_i-x_j}<\frac{c}{d} ba<xi−xjyi−yj<dc,通过简单的解不等式可以得到 b y j − a x j < b y i − a x i by_j-ax_j<by_i-ax_i byj−axj<byi−axi 以及 d y i − c x i < d y j − c x j dy_i-cx_i<dy_j-cx_j dyi−cxi<dyj−cxj,满足该条件的即可转移。注意到,这其实就是二维偏序,所以只需要令数组按 b y i − a x i by_i-ax_i byi−axi 排序,求最长下降子序列。不过,该题要求必须从原点开始,考虑从后往前枚举,这样相当于求最长上升子序列,最后输出在原点结束的最长长度即可(不要忘记 − 1 -1 −1)。
综上所述,可以做到 O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O(nlogn)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, a, b, c, d;
PII pnt[N];
int f[N];
std::vector<int> dct;
struct fenwick {
int tr[N];
void add(int x, int d) { for (int i = x; i < N; i += (i & -i)) tr[i] = max(tr[i], d); }
int sum(int x) {
int res = 0;
if (!x) return res;
for (int i = x; i; i -= (i & -i)) res = max(res, tr[i]);
return res;
}
}cnt;
int find(int x) {
return lower_bound(dct.begin(), dct.end(), x) - dct.begin() + 1;
}
signed main() {
scanf("%lld\n%lld/%lld %lld/%lld", &n, &a, &b, &c, &d);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
scanf("%lld%lld", &pnt[i].fi, &pnt[i].se), dct.push_back(d * pnt[i].se - c * pnt[i].fi);
pnt[0] = {0, 0};
sort(dct.begin(), dct.end());
dct.erase(unique(dct.begin(), dct.end()), dct.end());
sort(pnt, pnt + 1 + n, [&](PII tmp1, PII tmp2) {
return tmp1.se * b - tmp1.fi * a < tmp2.se * b - tmp2.fi * a;
});
for (int i = n, j = n; i >= 0; i --) {
while (j > i && pnt[j].se * b - pnt[j].fi * a != pnt[i].se * b - pnt[i].fi * a)
cnt.add(find(pnt[j].se * d - pnt[j].fi * c), f[j]), j --;
f[i] = cnt.sum(find(pnt[i].se * d - pnt[i].fi * c) - 1) + 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++)
if (pnt[i] == make_pair(0ll, 0ll)) {
cout << f[i] - 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
return 0;
}