目录
一、进程程序替换原理
二、进程替换函数
三、函数实现子进程进程替换
3.1 测试函数
3.2 写时拷贝保证替换后的进程独立性
四、自我实现一个简单的 shell
五、内置命令
5.1 pwd查询路径本质
5.2 内置命令概念
5.3 自我实现shell Pro
先见见进程替换:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("the process is running...\n");
execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","--color=auto",NULL);//进程替换
}
一、进程程序替换原理
用fork创建子进程后执行的是和父进程相同的程序(但有可能执行不同的代码分支),子进程往往要调用一种exec函数以执行另一个程序。当进程调用一种exec函数时,该进程的用户空间代码和数据完全被新程序替换,从新程序的启动例程开始执行。调用exec并不创建新进程,所以调用exec前后该进程的id并未改变!

二、进程替换函数
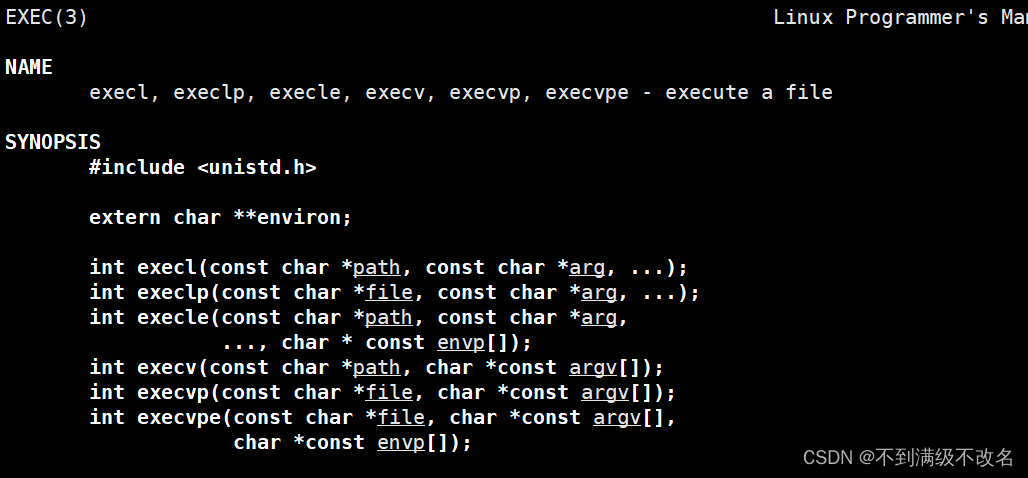

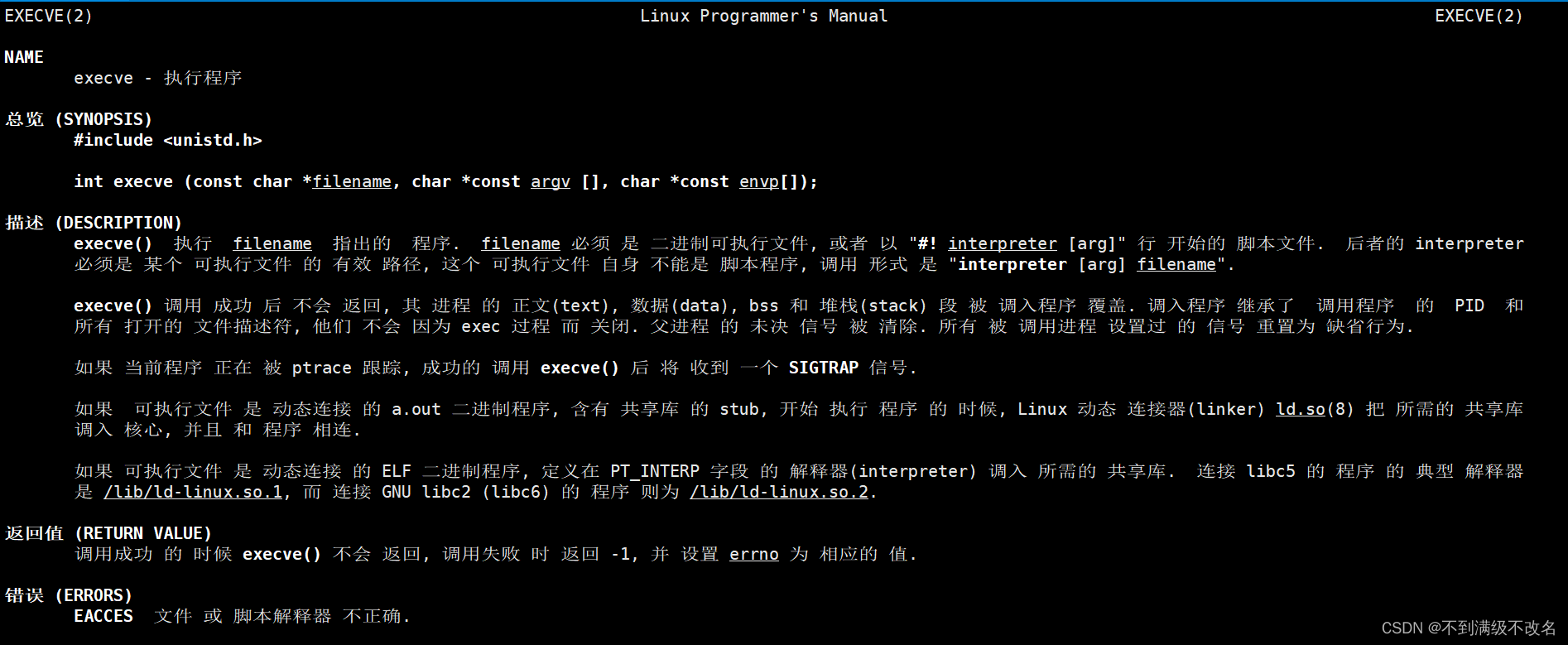
系统调用接口:
函数封装接口:
#include <unistd.h>`
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ...,char *const envp[]);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
l(list) : 表示参数采用列表
v(vector) : 参数用数组
p(path) : 有p自动搜索环境变量PATH
e(env) : 表示自己维护环境变量
可变参数:
我们发现每个函数参数表中都有...,这代表着我们的参数列表是可变参数列表!
可变参数列表允许参数个数是动态的,想传多少就传多少,最后以NULL结尾!我们原来用的printf函数也是典型的可变参数!
三、函数实现子进程进程替换
3.1 测试函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
pid_t id=fork();
if(id==0)
{
printf("the child process is running...\n");
printf("我是子进程,id=%d\n",getpid());
sleep(1);
//法一:execl 列表传命令
//execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","--color=auto",NULL);//系统命令
//execl("./mybin","mybin",NULL);//自己编写的程序
//法二:execlp 环境变量PATH
//execlp("ls","ls","--color=auto",NULL);
//法三:execv 数组传命令
// char* const _argv[]={
// "ls",
// "-a",
// "-l",
// "--color=auto",
// NULL
// };
//execv("/usr/bin/ls",_argv);
//法四:execvp 二和三的组合
// char* const _argv[]={
// "ls",
// "-a",
// "-l",
// "--color=auto",
// NULL
// };
// execvp("ls",_argv);
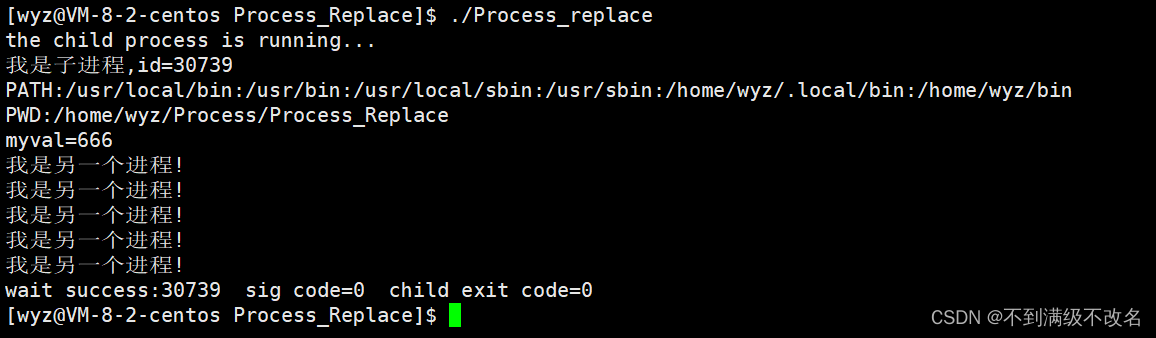
//法五:execle 获取环境变量
extern char**environ;
char* const _envp[]={
"myval=666",
NULL
};
putenv("myval=666");//自己设置环境变量
execle("./mybin","mybin",NULL,environ);
exit(-1);//进程替换失败
}
else if(id>0)
{
int status=0;
pid_t ret=waitpid(id,&status,0);
sleep(3);
if(ret>0)
printf("wait success:%d sig code=%d child exit code=%d\n",ret,status&0X7F,(status>>8)&0XFFFF);
}
else
{
printf("creat child process error!\n");
}
return 0;
}法四结果:
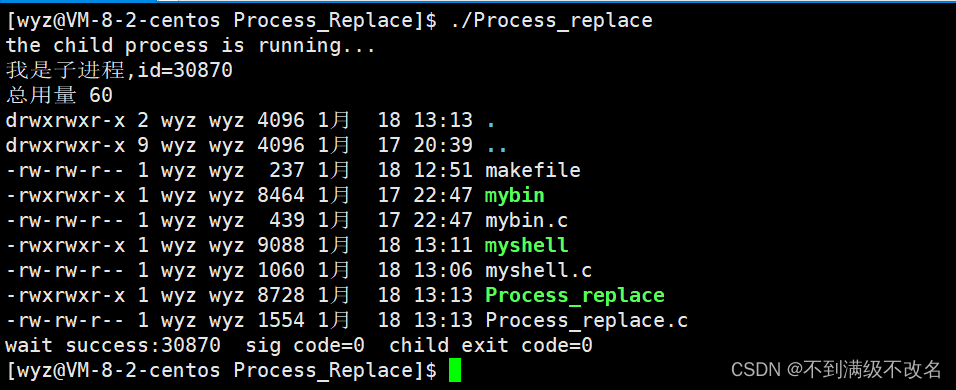
法五结果:
3.2 写时拷贝保证替换后的进程独立性
💡💡
子进程程序替换前共享父进程代码!程序替换会将磁盘代码替换原代码!进程具有独立性,子进程不能直接替换共享代码而影响父进程!所以操作系统会对子进程代码进行写时拷贝!
四、自我实现一个简单的 shell
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
#define NUM_SIEZ 1024
char Command_Line[NUM_SIEZ];
#define OPT_NUM 64
char* myargv[OPT_NUM];
#define DEBUG
int main()
{
while(1)
{
printf("[用户名@主机名 当前路径]$ ");
fflush(stdout);//刷新缓冲区
char* str=fgets(Command_Line,sizeof(Command_Line)-1,stdin);//从标准输入获取字符串
assert(str!=NULL);
//"abcde\n" 让最后一个字符为NULL(0)!为后面命令数组结尾获取0!
Command_Line[strlen(Command_Line)-1]=0;
#ifdef DEBUG
//以空格为分隔单位,获取命令与命令选项!
myargv[0]=strtok(Command_Line," ");
int i=1;
while(myargv[i++]=strtok(NULL," "));
#endif
//创建子进程
pid_t id=fork();
if(id==0)//子进程程序替换
{
execvp(myargv[0],myargv);
exit(1);//进程替换失败
}
else if(id>0)//父进程等待
{
waitpid(id,NULL,0);
}
else
{
printf("creat child process error!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
五、内置命令
问题引入:下面我们来看一看自我实现的shell 实现下面的命令:
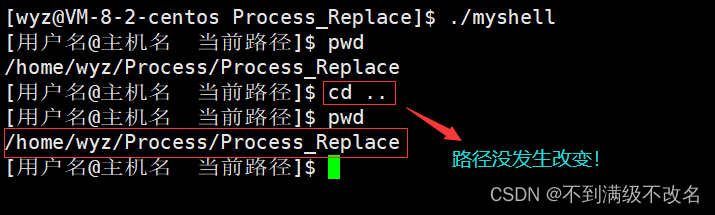
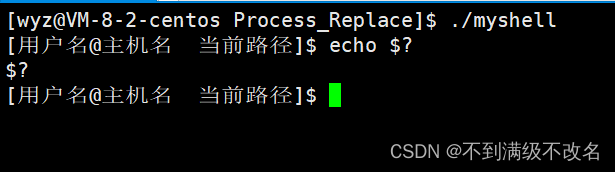
5.1 pwd查询路径本质
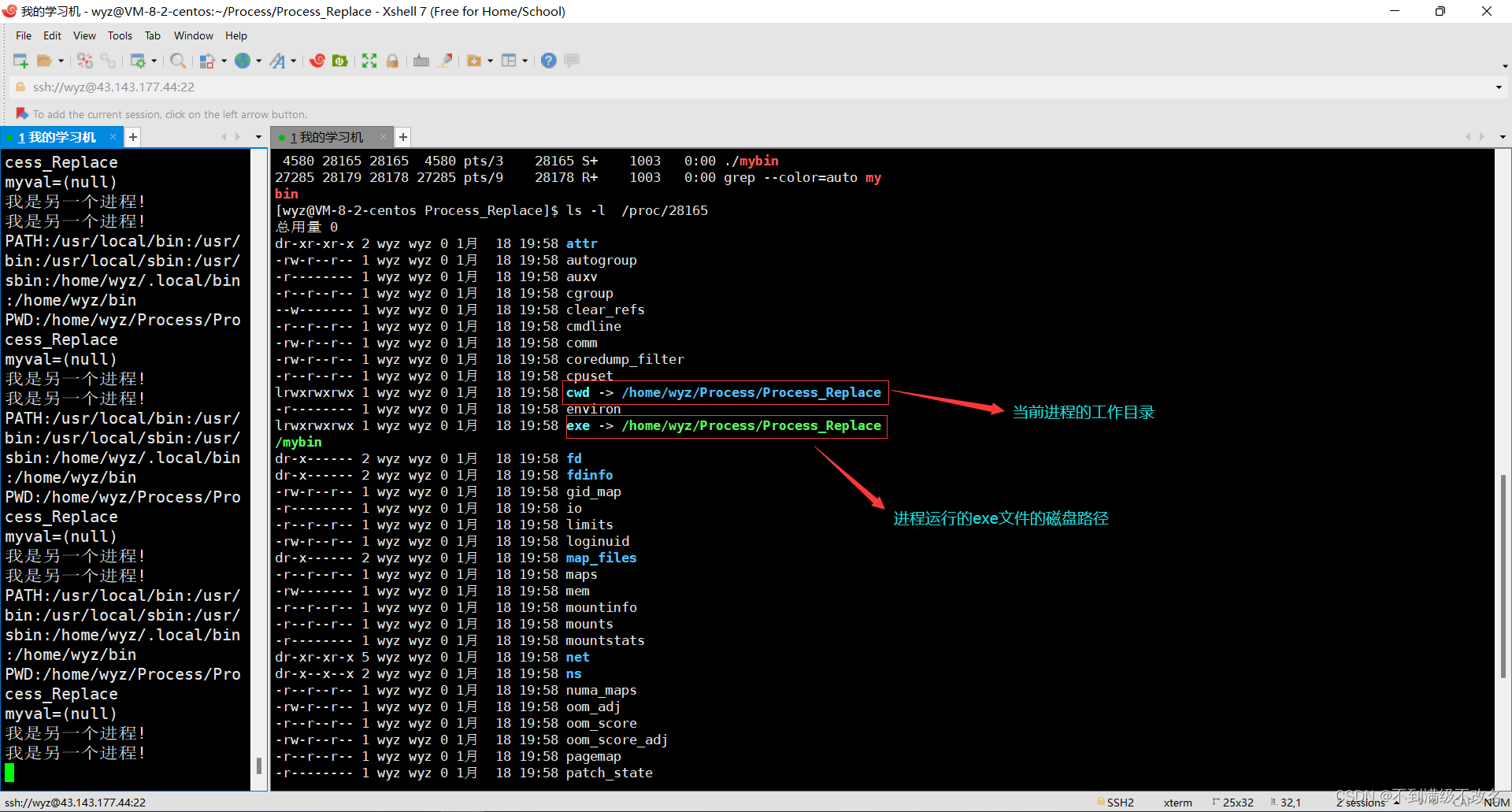
进程路径是可以被修改的,磁盘路径是亘古不变的!,pwd的本质是查询当前进程的工作目录!我们可以通过chdir修改工作路径!
5.2 内置命令概念
内置命令指的是命令由父进程本身执行,不靠子进程程序替换的命令!例如 echo pwd 命令!
5.3 自我实现shell Pro
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
#define NUM_SIEZ 1024
char Command_Line[NUM_SIEZ];
#define OPT_NUM 64
char* myargv[OPT_NUM];
//子进程返回结果
int last_sigcode=0;
int last_exit_code=0;
int main()
{
while(1)
{
printf("[用户名@主机名 当前路径]$ ");
fflush(stdout);
char* str=fgets(Command_Line,sizeof(Command_Line)-1,stdin);//从标准输入获取字符串
assert(str!=NULL);
//"abcde\n" 让最后一个字符为NULL(0)!为后面命令数组结尾获取0!
Command_Line[strlen(Command_Line)-1]=0;
//以空格为分隔单位,获取命令与命令选项!
myargv[0]=strtok(Command_Line," ");
int i=1;
//文件带上标识颜色
if(strcmp(myargv[0],"ls")==0)
{
myargv[i++]="--color=auto";
}
while(myargv[i++]=strtok(NULL," "));
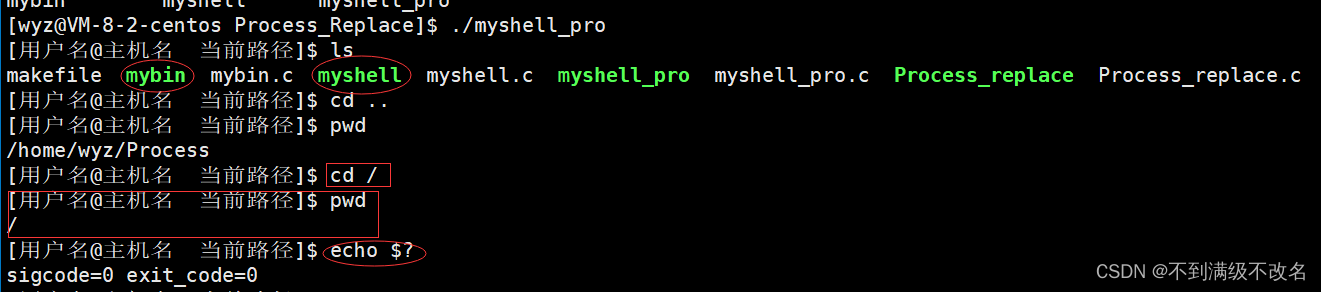
if(myargv[0]!=NULL && myargv[1]!=NULL && strcmp(myargv[0],"cd")==0)
{
chdir(myargv[1]);//改变父进程程序路径
continue;//内置命令,直接结束
}
if(myargv[0]!=NULL && myargv[1]!=NULL && strcmp(myargv[0],"echo")==0)
{
if(strcmp(myargv[1],"$?")==0)//获取上一次进程结果
{
printf("sigcode=%d exit_code=%d\n",last_sigcode,last_exit_code);
continue;
}
else
{
printf("%s\n",myargv[1]);
last_exit_code=0;
last_sigcode=0;
continue;
}
}
//创建子进程
pid_t id=fork();
if(id==0)
{
execvp(myargv[0],myargv);
exit(1);//进程替换失败
}
else if(id>0)
{
int status=0;
int ret=waitpid(id,&status,0);
assert(ret>0);
last_sigcode=status&0X7F;
last_exit_code=(status>>8)&0XFF;
}
else
{
printf("creat child process error!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}