0、各项回归指标简介
- Relative Root Mean Squared Error(RRMSE):The RRMSE normalizes the Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) by the mean of observations. It goes from 0 to infinity. The lower the better the prediction performance.
- The NRMSE(Normalized Root Mean Square Error) is calculated as the RMSE divided by the range of the observed values, expressed as a percentage. The range of the observed values is the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the observed data.
Best possible score is 0.0, smaller value is better. Range = [0, +inf) - MAE (Mean absolute error) represents the difference between the original and predicted values extracted by averaged the absolute difference over the data set.
- MSE (Mean Squared Error) represents the difference between the
original and predicted values extracted by squared the average
difference over the data set. - RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) is the error rate by the square root
of MSE. - R-squared (Coefficient of determination) represents the coefficient
of how well the values fit compared to the original values. The value
from 0 to 1 interpreted as percentages. The higher the value is, the
better the model is.
1、Python计算回归拟合各项指标:包括RMSE # RRMSE # RSE # NSE # MAE # R # R2 # MAPE # ρ
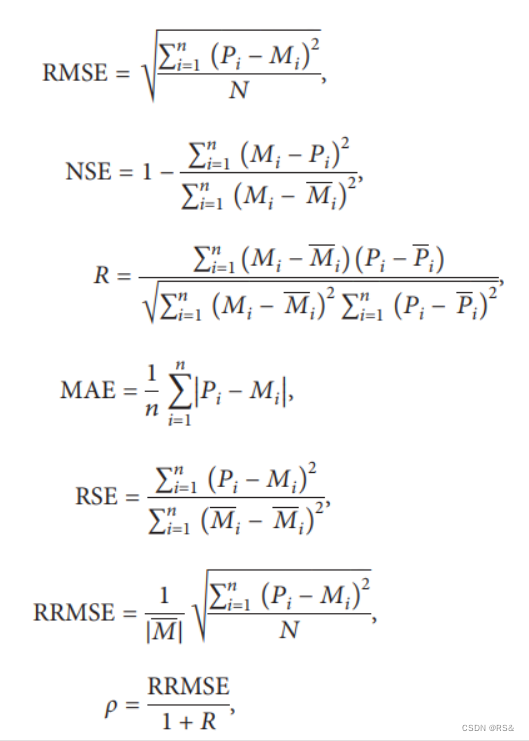
图片来源:https://github.com/alifrmf/Evaluation-Metrics-for-Linear-Regression/blob/main/README.md
代码:
# RMSE
def rmse(y_true, y_pred):
squared_diff = (y_true - y_pred) ** 2
mean_squared_diff = np.mean(squared_diff)
rmse_value = np.sqrt(mean_squared_diff)
return rmse_value
RRMSE计算方式一:RMSE除以真实值的均值
# RRMSE(Relative Root Mean Squared Error )
def rrmse(y_true, y_pred):
# Calculate the squared errors between the predicted and true values
squared_errors = (y_true - y_pred) ** 2
# Calculate the mean of the squared errors
mean_squared_error = np.mean(squared_errors)
# Take the square root of the mean squared error
root_mean_squared_error = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error)
# Calculate the relative error by dividing the root mean squared error by the mean of the true values
relative_error = root_mean_squared_error / np.mean(y_true)
# Return the RRMSE value
return relative_error
RRMSE计算方式二:除以真实值最大值-真实值最小值
def rrmse(s, o):
"""
Relative Root Mean Squared Error
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
relative root mean squared error
"""
return 100*np.sqrt(np.mean((s-o)**2))/(o.max()-o.min())
# RSE
def root_squared_error(y_true, y_pred):
"""
Calculate the Root Squared Error between two arrays (y_true and y_pred).
Args:
y_true (numpy.ndarray): Actual values.
y_pred (numpy.ndarray): Predicted values.
Returns:
float: The Root Squared Error.
"""
error = y_true - y_pred
squared_error = np.square(error)
mean_squared_error = np.mean(squared_error)
root_squared_error = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error)
return root_squared_error
# NSE
def nash_sutcliffe_efficiency(y_true, y_pred):
"""
Calculate the Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) between two arrays (y_true and y_pred).
Args:
y_true (numpy.ndarray): Actual values.
y_pred (numpy.ndarray): Predicted values.
Returns:
float: The Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency.
"""
numerator = np.sum(np.square(y_true - y_pred))
denominator = np.sum(np.square(y_true - np.mean(y_true)))
nse = 1 - (numerator / denominator)
return nse
# MAE
def mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred):
"""
Calculate the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) between two arrays (y_true and y_pred).
Args:
y_true (numpy.ndarray): Actual values.
y_pred (numpy.ndarray): Predicted values.
Returns:
float: The Mean Absolute Error.
"""
absolute_error = np.abs(y_true - y_pred)
mae = np.mean(absolute_error)
return mae
# R
def pearson_correlation_coefficient(y_true, y_pred):
"""
Calculate the Pearson Correlation Coefficient (R) between two arrays (y_true and y_pred).
Args:
y_true (numpy.ndarray): Actual values.
y_pred (numpy.ndarray): Predicted values.
Returns:
float: The Pearson Correlation Coefficient.
"""
correlation_matrix = np.corrcoef(y_true, y_pred)
r = correlation_matrix[0, 1]
return r
# R2
def r_squared(y_true, y_pred):
"""
Calculate the R squared value between two arrays (y_true and y_pred).
Args:
y_true (numpy.ndarray): Actual values.
y_pred (numpy.ndarray): Predicted values.
Returns:
float: The R squared value.
"""
correlation_matrix = np.corrcoef(y_true, y_pred)
correlation_xy = correlation_matrix[0,1]
r_squared = correlation_xy**2
return r_squared
# ρ (RRMSE / (1 + R))
def relative_rmse(y_true, y_pred):
rmse = np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred))
return rmse / (np.max(y_true) - np.min(y_true))
def pearson_correlation_coefficient(y_true, y_pred):
correlation_matrix = np.corrcoef(y_true, y_pred)
r = correlation_matrix[0, 1]
return r
代码来源:https://github.com/alifrmf/Evaluation-Metrics-for-Linear-Regression/blob/main/Regression%20Metrics%20for%20Machine%20Learning.py
2、Python计算bias、rbias、mae、rmse等指标
代码来源:https://github.com/dsi-llc/scripts/blob/d4445ef02a971754fdaef901250b42b8394539fa/EEstatslib.py#L80
import numpy as np
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# statistic functions
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def drop_nan(df):
"""
this function reads in dataframe after using
dffromdatfile function in dataFrameFromdatfiles.py
then returns a dataframe without nan
"""
df_dropped = df.dropna()
return df_dropped
def data_paired(df):
"""
this function return the number of data paired
after dropping nan values
"""
return df.shape[0]
def bias(s, o):
"""
Bias
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
bias
"""
return np.mean(s-o)
def rbias(s, o):
"""
Relative Bias
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
relative bias
"""
return 100*(np.sum(s-o))/np.sum(o)
def mae(s, o):
"""
Mean(Average) Absolute Error
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
mean absolute error
"""
return np.mean(np.abs(s-o))
def rmse(s, o):
"""
Root Mean Squared Error
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
root mean squared error
"""
return np.sqrt(np.mean((s-o)**2))
def rrmse(s, o):
"""
Relative Root Mean Squared Error
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
relative root mean squared error
"""
return 100*np.sqrt(np.mean((s-o)**2))/(o.max()-o.min())
def correlation(s, o):
"""
Correlation Coefficient
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
correlation coefficient
"""
return np.corrcoef(o, s)[0, 1]
def r_sqr(s, o):
"""
R Squared (Square of Correlation Coefficient)
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
R Squared
"""
return correlation(s, o)**2
def nsi(s, o):
"""
Nash-Sutcliffe Index of Efficiency
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
nash-sutcliffe index of efficiency
"""
return 1-np.sum((s-o)**2)/np.sum((o-np.mean(o))**2)
def coe(s, o):
"""
Coefficient of Efficiency
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
coefficient of efficiency
"""
return 1 - np.sum(np.abs(s-o))/np.sum(np.abs(o-np.mean(o)))
def ioa(s, o):
"""
Index of Agreement
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
index of agreement
"""
return 1 - (np.sum((o-s)**2))/\
(np.sum((np.abs(s-np.mean(o))+np.abs(o-np.mean(o)))**2))
def kge(s, o):
"""
Kling-Gupta Efficiency
input:
s: simulated
o: observed
output:
kgef: kling-gupta efficiency
cc: correlation
alpha: ratio of the standard deviation
beta: ratio of the mean
"""
cc = correlation(s, o)
alpha = np.std(s)/np.std(o)
beta = np.sum(s)/np.sum(o)
kgef = 1 - np.sqrt((cc-1)**2 + (alpha-1)**2 + (beta-1)**2)
return kgef, cc, alpha, beta
def stats_summary(df, sim_column_idx=0, obs_column_idx=1, decimals=3):
"""
Statistics Summary, output all statistics number in dictionary
input:
df: dataframe from EE.dat file
(default just two columns, model and data)
sim_column_idx: column index for simulated values (default 0)
obs_column_idx: column index for observed values (default 1)
decimals: round all statistics to the given number of decimals (default 3)
output:
statsummary: dictionary with all statistics number
"""
df_drop = drop_nan(df)
simulated = df_drop.iloc[:, sim_column_idx]
observed = df_drop.iloc[:, obs_column_idx]
statsummary = {'Data Paired': data_paired(df_drop),
'Bias': np.round(bias(simulated, observed), decimals),
'Percent Bias': np.round(rbias(simulated, observed), decimals),
'Mean Absolute Error': np.round(mae(simulated, observed), decimals),
'RMSE': np.round(rmse(simulated, observed), decimals),
'RRMSE': np.round(rrmse(simulated, observed), decimals),
'R': np.round(correlation(simulated, observed), decimals),
'R-Sqr': np.round(r_sqr(simulated, observed), decimals),
'Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency': np.round(nsi(simulated, observed), decimals),
'Coefficient of Efficiency': np.round(coe(simulated, observed),decimals),
'Index of Agreement': np.round(ioa(simulated, observed), decimals),
'Kling-Gupta Efficiency': np.round(list(kge(simulated, observed))[0], decimals)}
return statsummary













![[Windows] GIF动画、动图制作神器 ScreenToGif(免费)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d87330c7962a474bae1afe65393afe7e.png)