链表
表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包活两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
更用链表结构可以克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。
链表的特点
1.插入、删除数据效率高(1)级别(只需更改指针指向即可),随机访问效率低O(n)级别(需要从链头至链尾遍历)。
2.和数组相比,内存空间消耗更大,因为每个存储数据的节点都需要额外的空间存储后继指针a
单链表封装
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
append(val) {
let node = new Node(val);
if (this.head) {
let p = this.head;
while (p.next) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = node;
// val.next = this.hand;
} else {
this.head = node;
}
this.length++;
}
removeAt(index){
if(index > 0 && index < this.length){
let pre;
let current = this.head
if(index === 0){
this.head = this.head.next
}
for(let i=0 ;i < index;i++){
pre = current
current = current.next
}
pre.next = current.next
this.length--
return current.val
}
}
getNodeAt(index){
if(index >= 0 && index <this.length){
let node = this.head
for (let i= 0; i< index; i++) {
node = node.next
}
return node.val
}
return
}
remove(element){
let current;
for (let i= 0; i< this.length; i++) {
if(element === this.getNodeAt(index)){
return i
}
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
insert(element,index){
if(index >=0 && index< this.length){
let node = new Node(element)
if(index === 0){
let cur = this.head
this.head = node
node.next = cur
}else{
for(let i = 0 ;i < this.length; i++){
let pre = getNodeAt(index -1)
let cur = pre.next
node.next = cur
pre.next = node
}
}
this.length--
return true
}
return false
}
isEmpty(){
return this.length === 0
}
size(){
return this.length
}
getHead(){
return this.head
}
print() {
let p = this.head;
let str = "";
if (p) {
do {
str += p.val + " -> ";
p = p.next;
} while (p.next);
{
str += p.val;
console.log(str);
}
} else {
console.log("空链表");
}
}
}
双向链表
节点除了存储数据外,还有两个指针分别指向前一个节点地址(前驱指针prev)和下一个节点地址(后继指next)。
class Node {
constructor(val){
this.val = val
this.next = null
this.prev = null
}
}
class NodeList{
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail =null;
this.length = 0;
}
push(val){
let node = new Node(val)
if(this.head === null){
this.head = node
this.tail = node
}else{
this.tail.next = node
node.prev = this.tail
this.tail = node
}
this.length++
}
insert(val,index){
if(index >= 0 && index <= this.length){
let node = new Node(val)
let current= this.head
if(index === 0){
if(this.head === null){
this.head = node
this.tail = node
}else{
node.next = this.head
this.head.prev = node
this.head = node
}
}else if(index === this.length){
current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
}else{
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index -1)
current = previous.next
node.next = current
current.prev = node
previous.next= node
node.prev= prev
}
this.length++
return true
}
}
removeAt(index){
if(index >= 0 && index <= this.length){
let current = this.head
if(index === 0){
this.head = current.next
if(this.length === 1){
this.tail = null
}else{
this.head.prev = null
}
}else if(index ===this.length - 1){
current = this.tail
this.tail =current.prev
this.tail.next = null
}else{
let previous = this.getNodeAt(index -1)
current = previous.next
previous.next = current.next
current.next.prev = previous
}
this.length--;
return current.element
}
}
}
循环链表封装
环链表和链表之间准一的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下 元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用undefined,而是指向第一个元素(head)
class Node {
constructor(val){
this.val = val
this.next = null
}
}
class circleLinklist {
constructor(){
this.head = null
this.length = 0;
}
push(val){
let node= new Node(val)
if(this.length === 0){
this.head = node
}else{
let current = getNodeAt(this.size()-1)
current.next = node
}
node.next = this.head
this.length++
}
insert(val,index){
if(index>=0&& index<=this.count){
const node = new Node(val)
let current = this.head
if(index === 0){
if(this.head === null){
this.hand = node
node.next = this.head
}else{
node.next = current
//获取最后一个元素
current = this.getNodeAt(this.size() - 1)
this.head = node
current.next = this.head
}
}else{
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index -1)
node.next = previous.next
previous.next = node
}
this.length++
return true
}
return false
}
removeAt(index){
if(index >= 0 && index< this.length){
let current = this.head
if(index === 0){
if(this.size() === 1){
this.head = undefined
}else{
let last = this.getNodeat(this.size() -1)
this.head = this.head.next
last.next = this.head
}
}else{
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index -1)
current = previous.next
previous.next = current.next
}
this.count--
return current.val
}
}
size(){
return this.length
}
}
相交链表
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交**:**

题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
intersectVal- 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为0listA- 第一个链表listB- 第二个链表skipA- 在listA中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数skipB- 在listB中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
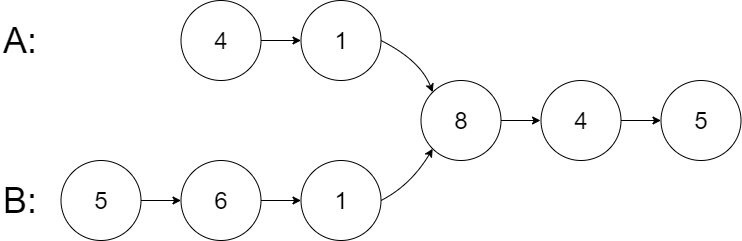
**输入:**intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
**输出:**Intersected at ‘8’
**解释:**相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
— 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
示例 2:
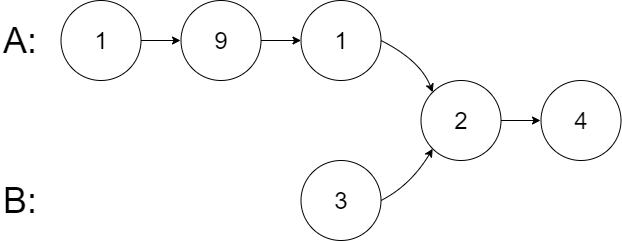
**输入:**intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
**输出:**Intersected at ‘2’
**解释:**相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
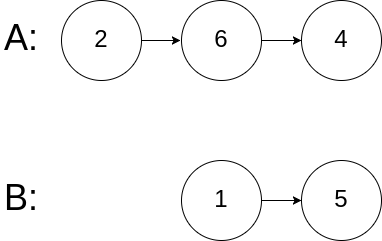
**输入:**intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
**输出:**null
**解释:**从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
思路:遍历两个链表,遇到相同值则返回
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
const visited = new Set();
let temp = headA;
while (temp !== null) {
visited.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp !== null) {
if (visited.has(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
};
反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

**输入:**head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:

**输入:**head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
**输入:**head = []
输出:[]
思路:将当前节点的 next\textit{next}next 指针改为指向前一个节点。由于节点没有引用其前一个节点,因此必须事先存储其前一个节点。在更改引用之前,还需要存储后一个节点。最后返回新的头引用。
思路:改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head;
while(cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
};
回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为
回文链表
。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:

**输入:**head = [1,2,2,1]
**输出:**true
示例 2:

**输入:**head = [1,2]
**输出:**false
思路:遍历然后对比
var isPalindrome = function(head) {
let arr = []
while (head) {
arr.push(head.val)
head = head.next
}
for (let i = 0, j = arr.length -1 ;i < j; i++, j--) {
if (arr[i] !== arr[j]) {
return false
}
}
return true
};
环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:

**输入:**head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
**输出:**true
**解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:

**输入:**head = [1,2], pos = 0
**输出:**true
**解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

**输入:**head = [1], pos = -1
**输出:**false
**解释:**链表中没有环。
思路:用set存储 碰见相同值则返回
var hasCycle = function(head) {
const set = new Set();
while(head) {
if(set.has(head)) return true;
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return false;
};
合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:

**输入:**l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
**输入:**l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
**输入:**l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
思路:代码比较l1和l2头节点的值。如果l1的值小于l2的值,那么将l1的next指针指向递归调用mergeTwoLists函数的结果,其中l1.next作为新的l1传入,而l2保持不变。然后返回l1。
如果l1的值大于等于l2的值,那么将l2的next指针指向递归调用mergeTwoLists函数的结果,其中l2.next作为新的l2传入,而l1保持不变。然后返回l2。
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
if(l1 === null){
return l2;
}
if(l2 === null){
return l1;
}
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
};