论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04670
github地址:GitHub - guochengqian/PointNeXt: [NeurIPS'22] PointNeXt: Revisiting PointNet++ with Improved Training and Scaling Strategies
本文主要提出优化PointNet++的两大关键点.
1) 好的训练策略
2)有效的模型尺度变换策略.
训练调整
数据增强
1. 随机去除点云颜色.
2. 增加噪声
3. 增加颜色对比度
4. 点云高度调整
优化调整
1. CrossEntropy with label smoothing
2. AdamW
3.Cosine Decay
架构现代化
感知域尺度调整(Receptive Field Scaling)
目前调整感知域范围主要有两种思路,一种是更大的感知半径去获取邻近点,另一种是采取结构化的架构(hierarchical architecture), 因为结构化的架构已经在PointNet++中被研究,因此我们主要关注前者,即尺度半径调整.
我们有如下发现:
1.最优半径是根据数据集不同,有不同大小.
2. 相对坐标被最近邻搜索半径除, 寻找效果更好.因为被除后,数值更小.
模型尺度调整(Model Scaling)
作者的观察:
- PointNet++ 参数2M(百万), 小于现在常规的深度学习网络大小(10M).
- 增加更多的SA层可以提高Accuracy, 但是降低Throughput.
Inverted Residual MLP(InvResMLP)
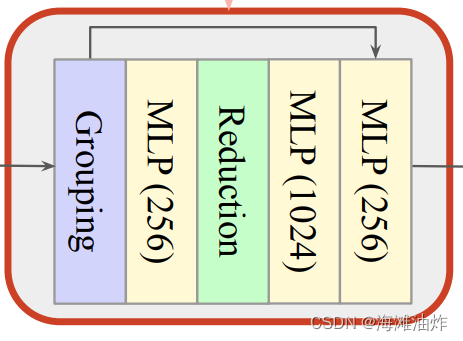
相比于PointNet++的SA结构,它有如下特征
1. 使用输入输出的残差链接去解决vanishing gradient问题.
2. 利用separable MLPs去减少计算和增强点的领域提取
其他结构改动
1. 使用4个SA层而不是2个,用于Encoder
2. 使用对称的decoder,编码器的channel大小可以匹配解码器
3. 一个MLP被添加到网络开始的位置.
实验内容
损失函数:CrossEntropy loss with label smoothing
优化器: Adam optimizer
学习率: 0.001,weight decay 10−4 , with Cosine Decay
Batch size:32
设备:32G V100 GPU
值得注意的是,针对不同的数据集,作者采用了不同的学习率,并且使用了降采样。
这篇论文的实验非常细致,因为把PointNext和各类模型基于各种任务,都做了对比。。。
所以下周再说。
相关问题:
作者是如何发现vanishing gradient问题的?
The VGP occurs when the elements of the gradient (the partial derivatives with respect to the parameters of the NN) become exponentially small so that the update of the parameters with the gradient becomes almost insignificant
什么是throughput?
Throughput is the number of images processed in one second. If more images are processed in one second, the server can process more images in a given time and hence, gives the server more power.

![[BJDCTF2020]Easy MD5(浅谈PHP弱类型hash比较缺陷)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/44a98362352b4eaa8996fc10d4c26504.png)