0 前言
在使用Linux的过程中,有时我们需要在obj文件或二进制文件中查找可打印的字符串,那么可以strings命令。
1. strings命令 的功能、格式和选项说明
我们可以使用命令 strings --help 来查看strings命令的帮助信息。
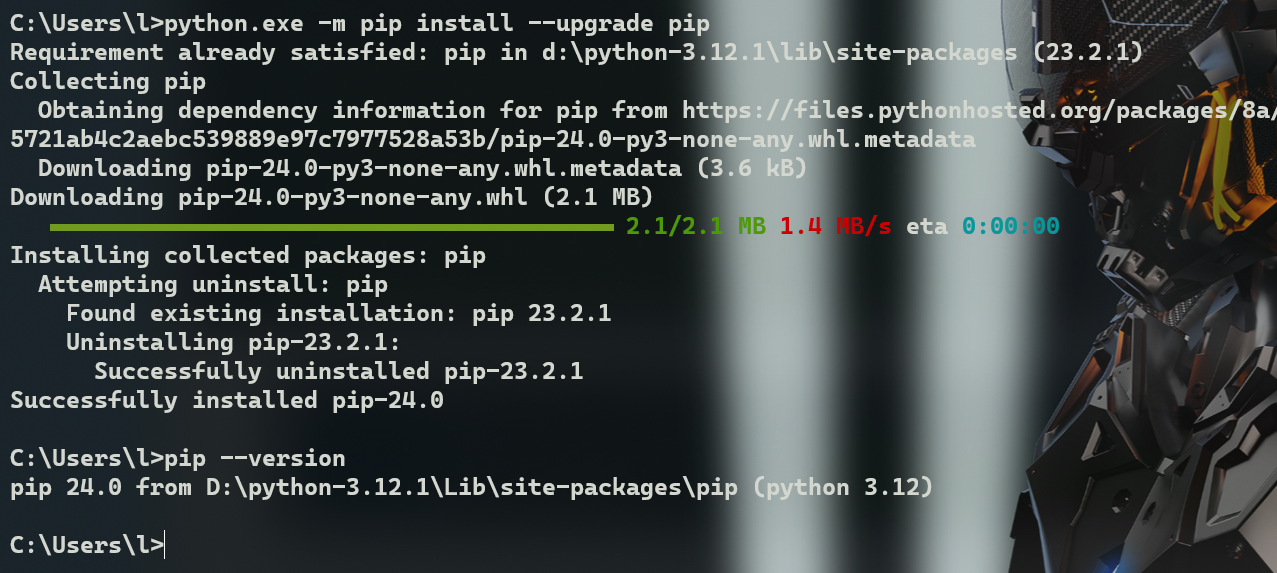
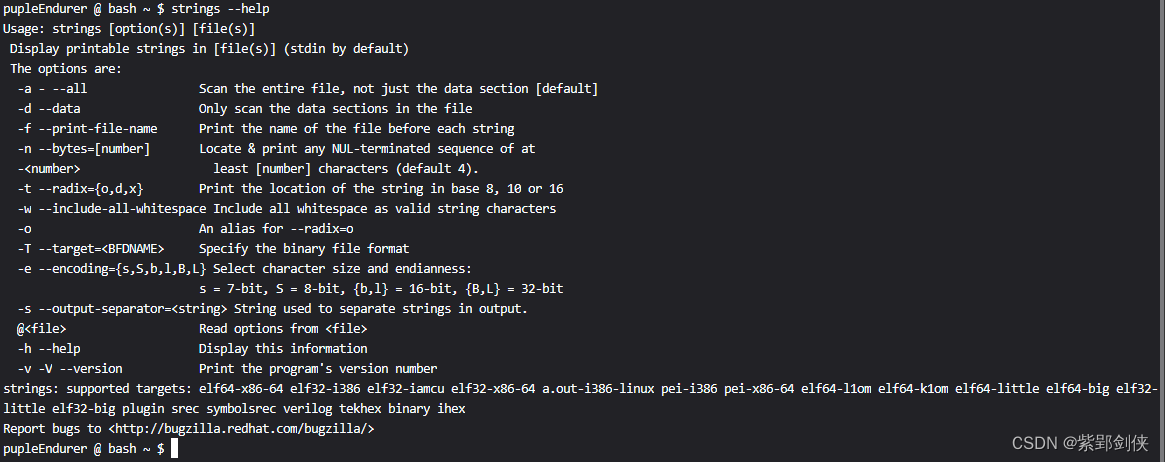
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings --help
Usage: strings [option(s)] [file(s)]
Display printable strings in [file(s)] (stdin by default)
The options are:
-a - --all Scan the entire file, not just the data section [default]
-d --data Only scan the data sections in the file
-f --print-file-name Print the name of the file before each string
-n --bytes=[number] Locate & print any NUL-terminated sequence of at
-<number> least [number] characters (default 4).
-t --radix={o,d,x} Print the location of the string in base 8, 10 or 16
-w --include-all-whitespace Include all whitespace as valid string characters
-o An alias for --radix=o
-T --target=<BFDNAME> Specify the binary file format
-e --encoding={s,S,b,l,B,L} Select character size and endianness:
s = 7-bit, S = 8-bit, {b,l} = 16-bit, {B,L} = 32-bit
-s --output-separator=<string> String used to separate strings in output.
@<file> Read options from <file>
-h --help Display this information
-v -V --version Print the program's version number
strings: supported targets: elf64-x86-64 elf32-i386 elf32-iamcu elf32-x86-64 a.out-i386-linux pei-i386 pei-x86-64 elf64-l1om elf64-k1om elf64-little elf64-big elf32-little elf32-big plugin srec symbolsrec verilog tekhex binary ihex
Report bugs to <http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla/>
1.1 strings命令的功能
显示文件中可打印的字符串。
1.2 strings命令的格式
strings [选项(s)] [文件(s)]
1.3 strings命令的选项说明
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -a --all - | 扫描整个文件而不是只扫描目标文件初始化和装载段 |
| -d --data | 仅打印文件中已初始化、加载的数据段中的字符串,这可能会减少输出中的垃圾量 |
| -e <encoding> --encoding=<s,S,b,l,B,L> | 选择字符编码与字节序。可取值: s=7bits的ASCII, S=8bits的Latin1, {b,l}=16bits宽字符大小端编码, {B,L}=32bits宽字符大小端编码。其中b,B代表bigendian,l,L代表littleendian |
| -f –-print-file-name | 在显示字符串前先显示文件名 |
| --help | 显示帮助信息 |
| -<min-len> -n <min-len> --bytes=<min-len> | 指定可打印字符序列的最小长度,不指定则默认是4个字符 |
| -o | 类似 --radix=o |
| -t <radix> --radix=<radix> | 输出字符串在文件中的偏移位置,radix可取值o(octal,八进制)、d(decimal,十进制)或者x(hexadecimal,十六进制) |
| -T <bfdname> --target=<bfdname> | 指定二进制文件格式 |
| -v -V --version | 显示版本信息 |
| -w --include-all-whitespace | 默认情况下,Tab和空格字符包含在字符串中,但其他空白字符除外,比如换行符和回车符等字符不是。-w使所有的空白字符被认为是字符串的一部分 |
| @<file> | 从指定的文件file总读取命令行选项 |
字符串: 支持的目标: elf64-x86-64 elf32-i386 elf32-iamcu elf32-x86-64 a.out-i386-linux pei-i386 pei-x86-64 elf64-l1om elf64-k1om elf64-little elf64-big elf32-little elf32-big plugin srec symbolsrec verilog tekhex binary ihex
2 strings命令使用实例
我们先用echo命令创建一个用来演示命令用法的文件a.txt
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo -e "Hello \t world. \n\r I am PurpleEnduer :-P \a\b ..." > a.txt
然后我们使用cat命令查看文件a.txt的内容
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat a.txt
Hello world.
I am PurpleEnduer :-P ...

2.1 strings 文件名:查看文件中的可打印字符
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings a.txt
Hello world.
I am PurpleEnduer :-P
...
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $

2.2 strings -f 文件名:在显示字符串前先显示文件名
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings -f a.txt
a.txt: Hello world.
a.txt: I am PurpleEnduer :-P
a.txt: ...
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $

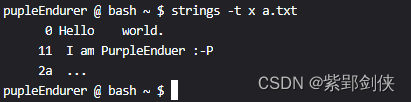
2.3 strings -t x 文件名:以16进制输出字符串在文件中的偏移位置
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings -t x a.txt
0 Hello world.
11 I am PurpleEnduer :-P
2a ...
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $
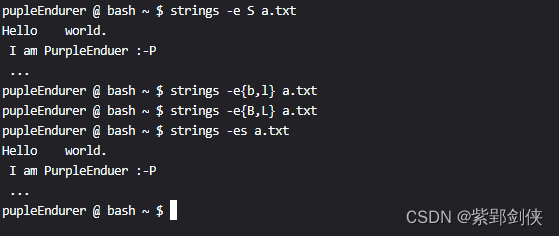
2.4 strings -e 字符编码与字节序 文件名:输出符合指定字符编码与字节序的可打印字符串
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings -e S a.txt
Hello world.
I am PurpleEnduer :-P
...
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings -e{b,l} a.txt
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings -e{B,L} a.txt
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ strings -es a.txt
Hello world.
I am PurpleEnduer :-P
...
pupleEndurer @ bash ~ $