实验环境:anaconda、jupyter notebook
实验用到的包:opencv、matplotlib、numpy
注:opencv在3.4.2之后sift就不是免费的了
我用的是3.4.1.15版本
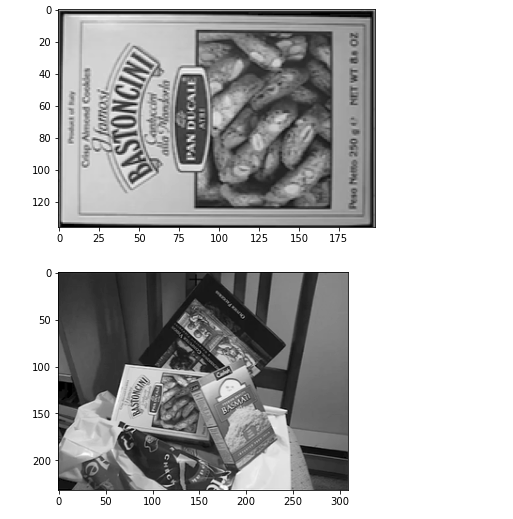
实验使用到的图片




一、sift函数获取特征值
读入图片
book = cv2.imread('book.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
pile = cv2.imread('pile.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
plt.imshow(book,'gray')
plt.show()
plt.imshow(pile,'gray')
plt.show()
获取特征点和特征向量
# 计算特征点和特征向量
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp1,des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(book, None)
kp2,des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(pile, None)
一对一匹配
# 一对一
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(crossCheck=True)
matches = bf.match(des1,des2)
matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda x : x.distance)
res = cv2.drawMatches(book, kp1, pile, kp2, matches[:10],None, flags=2)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.imshow(res,'gray')
plt.show()
显示前十个匹配
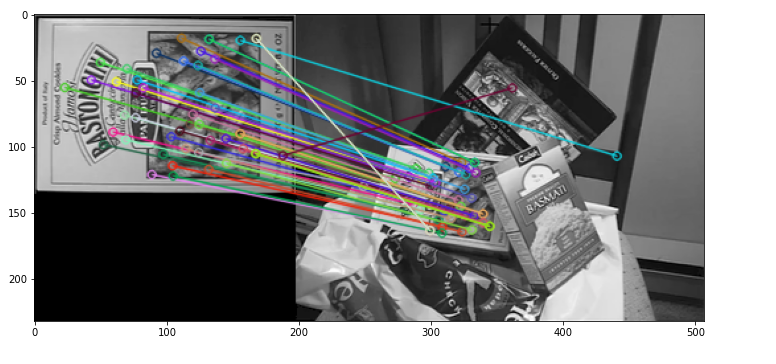
k对最佳匹配
# k对最佳匹配
bf = cv2.BFMatcher()
matches = bf.knnMatch(des1,des2, k=2)
# 把距离小于阈值的记录下来
good = []
for m,n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.75 * n.distance:
good.append([m])
res = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(book, kp1, pile, kp2,good,None, flags=2)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.imshow(res,'gray')
plt.show()
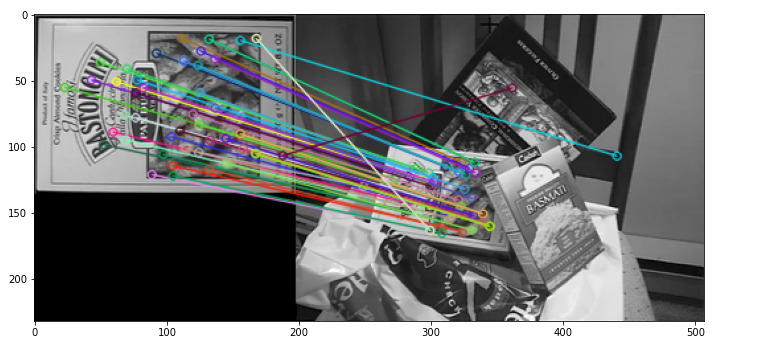
二、图像拼接实验
读入图片
ml = cv2.imread('ml.png')
ml_gray = cv2.cvtColor(ml, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
mr = cv2.imread('mr.png')
mr_gray = cv2.cvtColor(mr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.imshow(ml_gray, 'gray')
plt.show()
plt.imshow(mr_gray, 'gray')
plt.show()
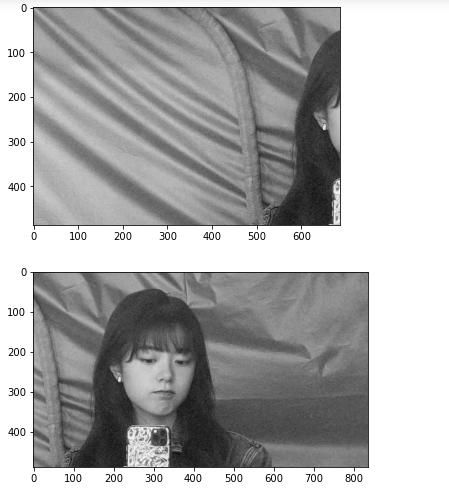
获取特征点和特征向量
# 获取特征点和特征向量
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kpl,desl = sift.detectAndCompute(ml_gray, None)
kpl_f = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kpl])
kpr,desr = sift.detectAndCompute(mr_gray, None)
kpr_f = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kpr])
# 匹配并显示
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(crossCheck=True)
matches = bf.match(desl,desr)
matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda x : x.distance)
res = cv2.drawMatches(ml_gray, kpl, mr_gray, kpr, matches[:100],None, flags=2)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.imshow(res,'gray')
plt.show()
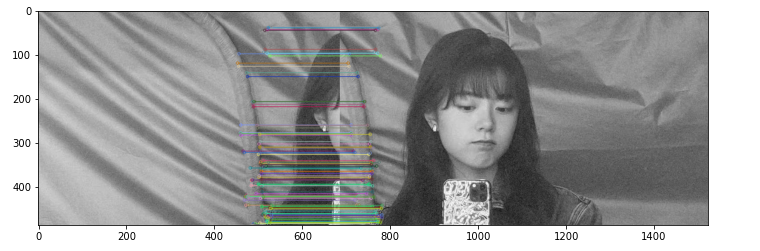
拼接图片
拼接图片实质上就是把一张图片的一部分变化到匹配另一张图片后,把另一张图片覆盖到变化的部分上
matcher = cv2.BFMatcher()
raw_matches = matcher.knnMatch(desr, desl, 2)
H = None
matches = []
for m in raw_matches:
# 保留合适的特征值
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * 0.75 :
matches.append([m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx])
# 配对大于4时,计算时间变换矩阵
if len(matches) > 4:
# 获取配对的点坐标
ptsl = np.float32([kpl_f[i] for (i,_) in matches])
ptsr = np.float32([kpr_f[i] for (_,i) in matches])
# 计算视角变换矩阵
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsr, ptsl, cv2.RANSAC, 4)
#对右图进行变换
result = cv2.warpPerspective(mr,H,(mr.shape[1] + ml.shape[1],mr.shape[0]))
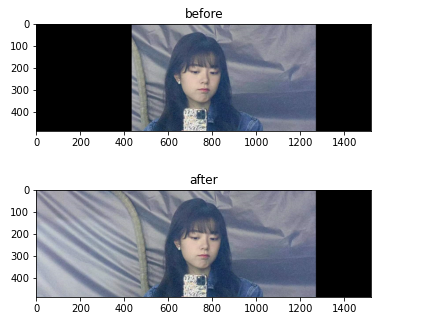
plt.title('before')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.show()
# 左图覆盖
result[0:ml.shape[0], 0:ml.shape[1]] = ml
plt.title('after')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.show()