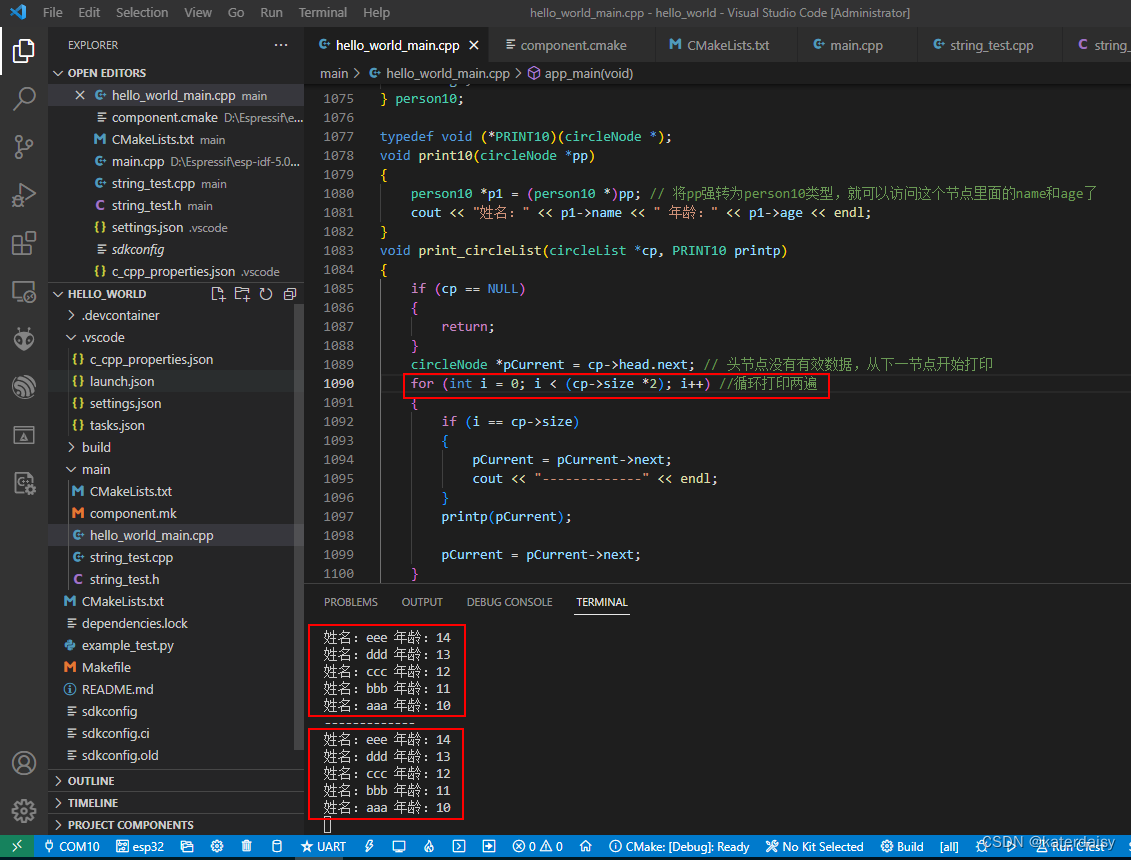
例程:
/* circle链表基于企业链表*/
// 链表节点
typedef struct CIRCLENODE
{
CIRCLENODE *next;
} circleNode;
typedef struct CIRCLELIST
{
circleNode head;
int size;
} circleList;
circleList *Inital_CircleList()
{
circleList *cp = (circleList *)malloc(sizeof(circleList));
cp->head.next = &(cp->head); // 循环链表,首节点指向它自己
cp->size = 0;
return cp;
}
void freeSpace_CircleList(circleList *cp)
{
if (cp == NULL)
{
return;
}
cp->head.next = NULL; // 其它节点都在用户空间分配和释放,这里只释放头节点即可
free(cp);
}
void insert_circleList(circleList *cp, circleNode *np, int pos)
{
if (cp == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (np == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (pos < 0 || pos > cp->size)
{
pos = 0; // 友好判断,如果超出pos超出范围,把数插入到第一个节点前
}
circleNode *pCurrent = &(cp->head);
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
{
pCurrent = pCurrent->next;
}
np->next = pCurrent->next; // 把pCurrent的下一个节点的地址赋值给新节点
pCurrent->next = np; // pCurrent指向新节点
cp->size++;
}
typedef struct PERSON10
{
circleNode *next;
string name;
int age;
} person10;
typedef void (*PRINT10)(circleNode *);
void print10(circleNode *pp)
{
person10 *p1 = (person10 *)pp; // 将pp强转为person10类型,就可以访问这个节点里面的name和age了
cout << “姓名:” << p1->name << " 年龄:" << p1->age << endl;
}
void print_circleList(circleList *cp, PRINT10 printp)
{
if (cp == NULL)
{
return;
}
circleNode *pCurrent = cp->head.next; // 头节点没有有效数据,从下一节点开始打印
for (int i = 0; i < (cp->size *2); i++) //循环打印两遍
{
if (i == cp->size)
{
pCurrent = pCurrent->next;
cout << “-------------” << endl;
}
printp(pCurrent);
pCurrent = pCurrent->next;
}
}
void test10()
{
person10 p1, p2, p3, p4, p5;
p1.name = “aaa”;
p2.name = “bbb”;
p3.name = “ccc”;
p4.name = “ddd”;
p5.name = “eee”;
p1.age = 10;
p2.age = 11;
p3.age = 12;
p4.age = 13;
p5.age = 14;
circleList *list10 = Inital_CircleList();
insert_circleList(list10,(circleNode *)&p1,0);
insert_circleList(list10,(circleNode *)&p2,0);
insert_circleList(list10,(circleNode *)&p3,0);
insert_circleList(list10,(circleNode *)&p4,0);
insert_circleList(list10,(circleNode *)&p5,0);
print_circleList(list10,print10);
}
extern “C” void app_main(void)
{
test10();
}
结果:



![[oeasy]python0051_ 转义_escape_字符_character_单引号_双引号_反引号_ 退格键](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/5df40d17e1c9c8b4286963afc6cb5e06.png)